How Does Food Stamps Verify Income? sets the stage for this exploration, examining the intricate process of determining eligibility for the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps. Understanding how income is verified is crucial for individuals seeking assistance, as it ensures that resources are allocated appropriately and program integrity is maintained.
The SNAP program plays a vital role in combating food insecurity, providing financial assistance to low-income households for food purchases. To ensure fair distribution, the program has established strict income eligibility criteria and verification procedures. These procedures involve a multi-faceted approach, encompassing documentation review, income reporting, and verification methods, all aimed at accurately assessing an applicant’s financial situation.
Eligibility for Food Stamps

The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps, is a federal program designed to help low-income individuals and families purchase food. Eligibility for SNAP is determined based on a complex set of criteria, primarily focused on income and household size.
Income Eligibility
To qualify for SNAP benefits, an individual or household must meet specific income requirements. The maximum gross income allowed for SNAP eligibility varies depending on household size and state. This income limit is adjusted annually based on inflation and cost of living.
- Gross Income:This refers to total income before taxes and deductions. It includes all sources of income, such as wages, salaries, self-employment earnings, unemployment benefits, and pensions.
- Net Income:This is the income remaining after certain deductions, such as taxes, medical expenses, and child support payments. For SNAP eligibility, the net income is calculated using a specific formula that accounts for these deductions.
Income Sources Considered for Eligibility
The following income sources are typically considered when determining SNAP eligibility:
- Earned Income:Wages, salaries, tips, commissions, and self-employment earnings.
- Unearned Income:Income from sources other than employment, such as unemployment benefits, Social Security benefits, pensions, and retirement income.
- Government Benefits:Income from government programs, such as TANF (Temporary Assistance for Needy Families), SSI (Supplemental Security Income), and VA benefits.
- Child Support:Payments received for child support.
- Alimony:Payments received for alimony.
- Interest and Dividends:Income earned from investments.
- Rental Income:Income received from renting out property.
Income Calculation for Eligibility
The income calculation for SNAP eligibility involves a complex formula that considers both gross and net income. The formula takes into account:
Household size
The number of people in the household.
State-specific deductions
Deductions allowed for expenses such as housing, medical, and child care costs.
Standard deduction
A fixed amount deducted from gross income for expenses not specifically documented.
Net income limit
The maximum net income allowed for SNAP eligibility, which varies by household size and state.
For example, a household of two in a specific state may have a gross income limit of $3,000 per month. However, after applying state-specific deductions and the standard deduction, their net income may be lower, allowing them to qualify for SNAP benefits.
Documentation Requirements

The SNAP program requires applicants to provide documentation to verify their income and household size. This documentation is crucial for ensuring that only eligible individuals receive benefits and that the program remains fiscally responsible.
Documentation Requirements for Income Verification
This section Artikels the types of documentation required for income verification.
| Document Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Pay stubs | To verify wages and salaries | A recent pay stub from an employer showing the applicant’s gross earnings, deductions, and net pay |
| Tax returns | To verify self-employment income or other income not reported on pay stubs | Form 1040, Form 1040-A, or Form 1040-EZ |
| Social Security benefit statements | To verify Social Security benefits | A statement from the Social Security Administration showing the amount of benefits received |
| Unemployment benefit statements | To verify unemployment benefits | A statement from the state unemployment agency showing the amount of benefits received |
| Pension or retirement benefit statements | To verify pension or retirement benefits | A statement from the pension or retirement plan administrator showing the amount of benefits received |
| Child support statements | To verify child support payments received | A statement from the child support agency showing the amount of payments received |
| Alimony statements | To verify alimony payments received | A statement from the payer showing the amount of alimony payments received |
| Other income documentation | To verify any other sources of income, such as interest, dividends, or rental income | Bank statements, investment statements, or lease agreements |
Process of Submitting Documentation
This section describes the process of submitting documentation for income verification.
Flow Chart
- Applicant applies for SNAP benefits
- Applicant is required to provide documentation to verify income
- Applicant submits documentation to the SNAP office
- SNAP office reviews the documentation
- SNAP office approves or denies the application based on the documentation provided
Verification Methods: How Does Food Stamps Verify Income
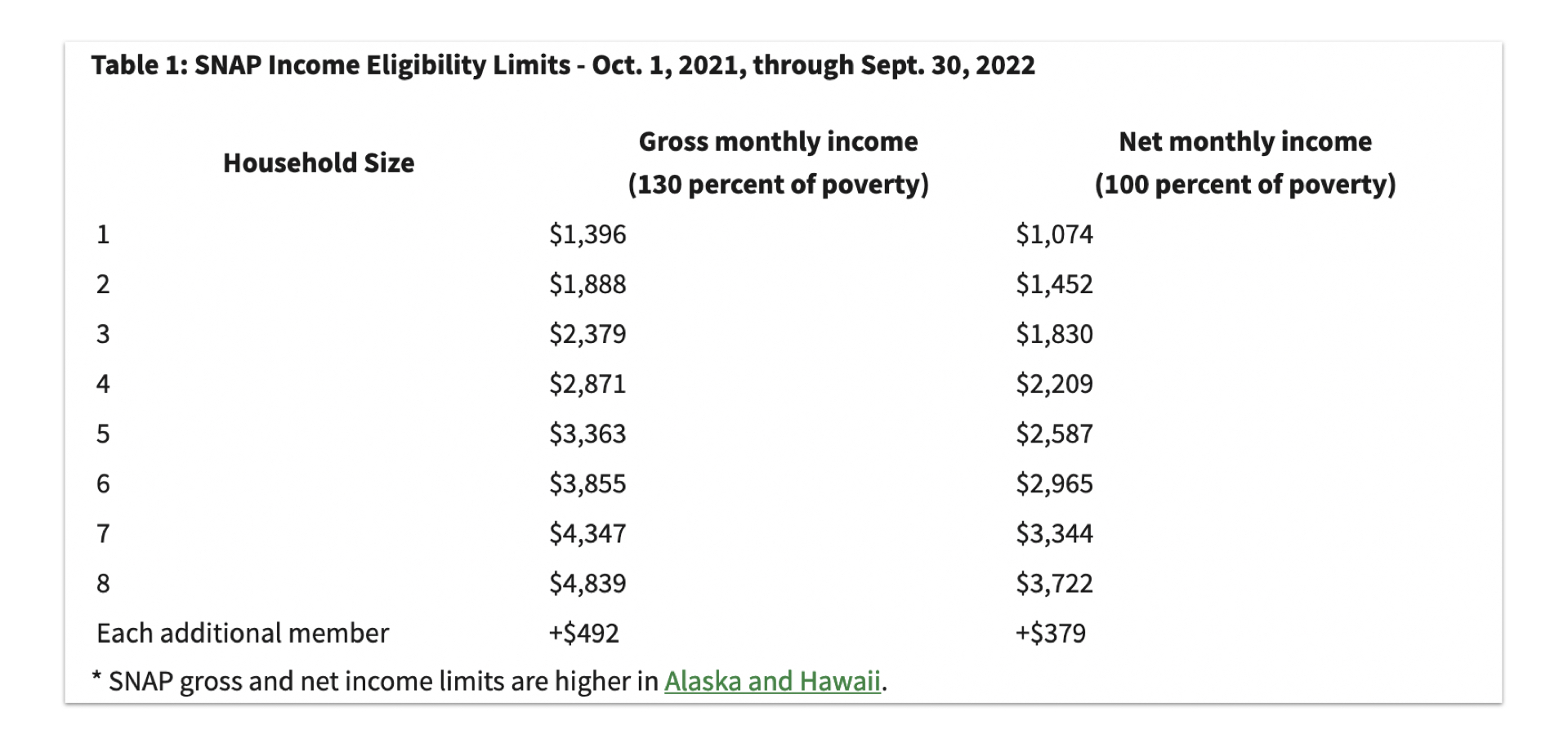
The process of verifying income for food stamps is crucial for ensuring that benefits are distributed fairly and efficiently. Various methods are employed to gather and assess income information from applicants. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, influencing the accuracy and effectiveness of the verification process.
Income Verification Methods
Several methods are used to verify income for food stamps. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Wage and Salary Verification: This method involves contacting the applicant’s employer to confirm their earnings. It is considered a reliable source of income verification as it directly confirms the applicant’s employment status and salary.
- Self-Reported Income: This method relies on the applicant’s own declaration of their income.
While convenient and less intrusive, it can be susceptible to inaccuracies or underreporting, especially when applicants have multiple income sources or are self-employed.
- Tax Records: Accessing tax records, including Form 1040, can provide a comprehensive view of the applicant’s income. It helps verify self-reported income and identify any inconsistencies.
However, accessing tax records can be time-consuming and requires proper authorization.
- Bank Statements: Reviewing bank statements can provide insights into the applicant’s income, particularly for self-employed individuals or those receiving income from multiple sources. It can help verify the flow of funds and identify potential discrepancies.
However, bank statements may not always reflect all income sources.
- Social Security Administration (SSA) Records: The SSA maintains records of benefits received by individuals, including Social Security retirement benefits, disability benefits, and survivor benefits. These records can be used to verify the applicant’s income from these sources.
- Unemployment Benefits: The state unemployment office can provide verification of unemployment benefits received by the applicant.
- Child Support: Child support payments can be verified through the state child support enforcement agency.
- Other Government Benefits: Other government benefits, such as TANF (Temporary Assistance for Needy Families) and SSI (Supplemental Security Income), can be verified through the respective agencies.
Face-to-Face Interview
A face-to-face interview is a crucial part of the income verification process. It provides an opportunity for caseworkers to directly interact with applicants, gather additional information, and address any discrepancies.
- Gathering Additional Information: During the interview, caseworkers can clarify any inconsistencies in the applicant’s self-reported income, gather additional documentation, and explore potential income sources that may not have been initially reported.
- Addressing Discrepancies: Caseworkers can use the interview to address any discrepancies between the applicant’s self-reported income and the information obtained through other verification methods.
They can investigate the reasons for these discrepancies and ensure that the applicant’s income is accurately assessed.
- Assessing Eligibility: The interview helps caseworkers determine the applicant’s eligibility for food stamps by verifying income, household size, and other relevant factors.
- Providing Guidance: Caseworkers can provide guidance to applicants on the income verification process, documentation requirements, and any potential appeals or re-evaluations.
Income Reporting and Changes
The food stamp program, officially known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), is designed to provide food assistance to low-income individuals and families. To ensure that benefits are distributed fairly, the program requires recipients to report any changes in their income or household circumstances.
This includes both increases and decreases in income. Failure to report changes in income can have serious consequences, including benefit reductions, overpayments, and even criminal charges. The process for reporting income changes can be complex and confusing, but it is essential to understand the requirements and potential repercussions.
Reporting Income Changes
Reporting income changes to the SNAP program is crucial for maintaining eligibility and receiving the correct amount of benefits. The process for reporting income changes varies depending on the state and local SNAP office. However, generally, recipients can report changes in income by:
- Calling their local SNAP office
- Visiting the SNAP office in person
- Using an online portal or mobile app
- Sending a written notification by mail
It is important to note that income changes must be reported promptly. Most states require recipients to report changes within 10 days of the change occurring.
Common Income Changes Requiring Reporting
A wide range of income changes may require reporting to the SNAP program. These include:
- Changes in employment status, such as starting a new job, losing a job, or changing hours
- Changes in wages or salary
- Changes in self-employment income
- Changes in unemployment benefits
- Changes in child support payments
- Changes in alimony payments
- Changes in Social Security benefits
- Changes in retirement income
- Changes in income from investments
- Changes in government benefits, such as TANF or SSI
- Changes in income from a spouse or other household member
Consequences of Failing to Report Income Changes, How does food stamps verify income
Failing to report income changes can lead to a number of serious consequences, including:
- Benefit Reduction or Termination:If a recipient’s income increases and they fail to report it, their SNAP benefits may be reduced or terminated. This is because the recipient may no longer meet the program’s income eligibility requirements.
- Overpayment:If a recipient’s income decreases and they fail to report it, they may receive more SNAP benefits than they are entitled to. This is considered an overpayment, and the recipient will be required to repay it. Overpayments can be substantial and can lead to debt and financial hardship.
- Criminal Charges:In some cases, failing to report income changes can result in criminal charges. This is particularly true if the recipient intentionally withholds information or engages in fraud.
Income Verification and Fraud
The SNAP program, designed to combat food insecurity, is vulnerable to abuse. While many genuinely need assistance, a segment exploits the system, leading to significant financial losses for taxpayers. Understanding the types of fraud, prevention measures, and consequences is crucial for ensuring program integrity and protecting taxpayer dollars.
Types of Income Fraud
Income fraud in SNAP involves misrepresenting or concealing income to obtain benefits. This can take various forms, including:
- Undeclared Income:Individuals may fail to report all sources of income, such as wages, self-employment earnings, or income from investments. This can include unreported tips, cash payments, or income from informal work arrangements.
- Falsified Income Information:Individuals may provide false information about their income, such as inflating expenses or claiming dependents who do not exist. This can involve altering pay stubs, creating fake documents, or making false statements to caseworkers.
- Misrepresenting Employment Status:Individuals may claim to be unemployed or underemployed when they are actually working but not reporting their income. This can include working “off the books” or receiving payments in cash to avoid taxes and reporting requirements.
- Household Size Manipulation:Individuals may inflate their household size by claiming additional dependents who are not actually residing with them. This can involve adding fictional dependents or claiming unrelated individuals as household members.
Measures to Prevent and Detect Income Fraud
To combat income fraud, SNAP programs implement a multi-pronged approach:
- Data Matching:SNAP agencies routinely match recipient data with other databases, such as tax records, unemployment benefits, and wage information. This helps identify inconsistencies and potential fraud.
- Income Verification:SNAP agencies verify income information provided by applicants and recipients. This can involve contacting employers, reviewing bank statements, and requesting additional documentation.
- Fraud Investigations:Dedicated units investigate suspected cases of income fraud. These units use various techniques, such as surveillance, interviews, and document analysis, to gather evidence and build cases.
- Public Awareness Campaigns:SNAP agencies conduct public awareness campaigns to educate individuals about the program’s rules and the consequences of fraud. This aims to deter individuals from engaging in fraudulent activities.
Consequences of Income Fraud
Engaging in SNAP income fraud has serious consequences:
- Benefit Recoupment:Individuals who commit fraud are required to repay the benefits they received illegally. This can include both the value of the benefits and penalties.
- Criminal Charges:In severe cases, individuals may face criminal charges, including fines and imprisonment. The severity of the charges depends on the nature and extent of the fraud.
- Program Disqualification:Individuals convicted of SNAP fraud may be permanently disqualified from receiving benefits. This can have a significant impact on their ability to access food assistance.
- Damage to Program Integrity:Fraud erodes public trust in SNAP and undermines the program’s ability to effectively address food insecurity. This can lead to stricter eligibility requirements and reduced funding for the program.
Last Word
The verification process for food stamps is a complex system designed to ensure program integrity and prevent fraud. It involves a thorough review of income documentation, adherence to reporting requirements, and the utilization of various verification methods. While the process can be intricate, it ultimately serves the purpose of ensuring that SNAP benefits reach those who are truly in need, promoting food security and well-being for vulnerable populations.
Query Resolution
What happens if my income changes?
It is essential to report any changes in income to the SNAP program promptly. Failure to do so can result in overpayment of benefits and potential penalties.
What are some examples of income fraud?
Income fraud can include misrepresenting income, failing to report income, or using false documentation to obtain benefits.
How can I appeal a decision regarding my eligibility?
If you disagree with a decision regarding your eligibility, you have the right to appeal the decision through the established appeals process.






