Can you get food stamps and WIC? This question is often asked by individuals and families facing financial hardship. The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps, and the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) are government-funded programs designed to provide food assistance to low-income individuals and families.
These programs play a crucial role in ensuring food security and improving the nutritional health of vulnerable populations.
Eligibility for SNAP and WIC is determined based on income, assets, household size, and other factors. The application process for both programs involves submitting documentation and meeting with a caseworker. Once approved, recipients receive benefits that can be used to purchase eligible food items.
Both programs have limitations and restrictions, but they offer valuable assistance to those in need.
Applying for SNAP and WIC

Applying for SNAP (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program) and WIC (Women, Infants, and Children) can provide essential food assistance to eligible individuals and families. Both programs offer valuable support to ensure access to nutritious food. This guide provides a step-by-step overview of the application process for SNAP and WIC, outlining the required documentation and different submission methods.
Required Documentation for SNAP and WIC
To apply for SNAP and WIC, you will need to provide certain documentation to verify your eligibility.
- Proof of Identity: This can include a driver’s license, passport, birth certificate, or other government-issued identification.
- Proof of Residency: Documents such as a utility bill, lease agreement, or bank statement with your name and address can be used to prove your residency.
- Proof of Income: This may include pay stubs, tax returns, unemployment benefits, or Social Security statements.
- Proof of Household Size: Provide documents such as birth certificates, adoption papers, or court orders to confirm the number of individuals living in your household.
- Social Security Numbers: You will need to provide Social Security numbers for all members of your household.
- WIC Specific Documentation: If applying for WIC, you will also need to provide documentation related to pregnancy, breastfeeding, or the age and health of your child(ren).
Submitting Your Application
There are several ways to submit your SNAP and WIC application:
- Online: Many states offer online application portals for both SNAP and WIC. You can typically find links to these portals on the state’s human services website.
- In Person: You can apply for SNAP and WIC in person at your local SNAP or WIC office. You can find the location of your local office on the state’s human services website or by contacting your local social services agency.
- By Mail: You can also download an application form from the state’s website and submit it by mail. Be sure to follow the instructions provided on the application form.
SNAP and WIC Application Process Comparison
The application process for SNAP and WIC shares some similarities, but there are also key differences. Here’s a table comparing the two programs:
| Feature | SNAP | WIC |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Based on income, household size, and other factors | For pregnant women, breastfeeding women, postpartum women, infants, and children up to age 5 |
| Benefits | Cash assistance to purchase food | Vouchers or coupons for specific nutritious foods |
| Application Process | Typically requires online, in-person, or mail submission | May require a health assessment and nutrition counseling |
| Frequency of Re-certification | Annually or more frequently depending on your situation | Every six months |
Benefits and Restrictions
SNAP and WIC are essential programs that provide food assistance to low-income families and individuals. While they share the goal of ensuring food security, they differ in their eligibility criteria, benefit types, and restrictions.
Food Items Covered Under SNAP and WIC
Both SNAP and WIC offer benefits for specific food items, but their coverage varies. SNAP provides a monthly benefit for purchasing eligible foods from authorized retailers. This includes a wide range of food items, such as:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Meat, poultry, and fish
- Dairy products
- Bread and cereals
- Legumes and beans
- Snacks and non-alcoholic beverages
However, SNAP does not cover items like:
- Alcoholic beverages
- Tobacco products
- Vitamins and supplements
- Prepared meals
- Pet food
WIC, on the other hand, is a nutrition program that provides vouchers for specific food items deemed essential for pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, infants, and young children. These include:
- Milk (whole, low-fat, or skim)
- Fruits and vegetables
- Cereal (iron-fortified)
- Eggs
- Cheese
- Juices (100% juice)
- Infant formula (for eligible infants)
- Baby food (for eligible infants)
WIC also provides nutrition education and counseling services to help participants make healthy food choices.
Limitations and Restrictions
Both SNAP and WIC have limitations and restrictions in place to ensure the programs’ sustainability and prevent misuse.
SNAP Restrictions
- Income Limits:SNAP benefits are based on household size and income. Households must meet specific income requirements to be eligible.
- Asset Limits:SNAP also has asset limits, meaning households cannot exceed a certain amount of savings and other assets to qualify.
- Work Requirements:Able-bodied adults without dependents (ABAWDs) are typically required to work or participate in work-related activities for at least 20 hours per week to receive SNAP benefits.
- Time Limits:SNAP benefits are typically limited to a certain period, although extensions may be available in some cases.
- Food Purchase Restrictions:SNAP benefits cannot be used to purchase non-food items, such as toiletries, cleaning supplies, or pet food.
WIC Restrictions
- Eligibility Criteria:WIC is only available to pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, infants, and young children who meet specific nutritional risk criteria.
- Food Item Restrictions:WIC benefits are restricted to specific food items, such as milk, fruits, vegetables, and infant formula. Participants cannot purchase other food items with their WIC vouchers.
- Frequency of Benefits:WIC benefits are typically issued on a monthly basis, and participants must visit a WIC clinic regularly to receive their benefits.
Comparing SNAP and WIC, Can you get food stamps and wic
While both programs aim to provide food assistance, they differ in their eligibility criteria, benefit types, and restrictions.
SNAP
- Eligibility:Based on income and household size.
- Benefits:Monthly cash benefit for purchasing eligible food items.
- Restrictions:Income and asset limits, work requirements, time limits, and food purchase restrictions.
WIC
- Eligibility:Based on nutritional risk and specific demographics (pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, infants, and young children).
- Benefits:Vouchers for specific food items, nutrition education, and counseling services.
- Restrictions:Eligibility based on nutritional risk, food item restrictions, and frequency of benefits.
Benefit Amounts
The amount of SNAP and WIC benefits varies depending on factors such as household size, income, and state regulations. The following table illustrates an example of benefit amounts for different household sizes in a specific state:
| Household Size | SNAP Benefit Amount | WIC Benefit Amount |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $200 | $40 |
| 2 | $350 | $60 |
| 3 | $500 | $80 |
| 4 | $650 | $100 |
It’s important to note that these are just examples, and actual benefit amounts may vary.
Program Administration: Can You Get Food Stamps And Wic
The SNAP and WIC programs are administered at both the state and local levels, with each level playing a crucial role in ensuring the efficient delivery of benefits to eligible individuals and families.
State and Local Agency Roles
State and local agencies are responsible for implementing and administering SNAP and WIC programs within their jurisdictions. This includes determining eligibility, issuing benefits, and monitoring program compliance.
- State Agencies:State agencies are responsible for setting eligibility standards, developing program guidelines, and overseeing the distribution of federal funds to local agencies. They also conduct program reviews and audits to ensure compliance with federal regulations.
- Local Agencies:Local agencies, typically county or city-level offices, handle the day-to-day operations of the programs. This includes processing applications, conducting interviews, issuing benefits, and providing program information to participants. They also work closely with community organizations to promote program awareness and outreach.
Receiving Benefits and Managing Accounts
The process for receiving SNAP and WIC benefits varies slightly between states, but generally involves the following steps:
- Application:Individuals or families interested in receiving SNAP or WIC benefits must first submit an application to their local agency. This application typically includes information about income, household size, and other factors that determine eligibility.
- Interview:Once the application is submitted, a caseworker will usually schedule an interview to verify the information provided and assess eligibility. This interview may involve providing documentation such as income statements, rent receipts, or medical records.
- Approval and Benefit Issuance:If approved, participants will receive an Electronic Benefit Transfer (EBT) card for SNAP benefits, which can be used like a debit card at authorized retailers. WIC benefits are typically provided in the form of vouchers that can be redeemed for specific food items at authorized stores.
- Benefit Management:Participants are responsible for managing their benefits and ensuring they are used for eligible food purchases. They can check their balance online, by phone, or at an EBT terminal.
Funding and Regulation
Both SNAP and WIC programs are funded primarily by the federal government, with states contributing a small percentage of the overall costs.
- SNAP Funding:The federal government provides funding to states through block grants, which are then distributed to local agencies. States are required to match a portion of these funds, but the federal government covers the majority of the program’s costs.
- WIC Funding:The federal government provides funding to states through formula grants, which are based on the number of eligible participants in each state. States are required to match a portion of these funds, but the federal government covers the majority of the program’s costs.
The USDA’s Food and Nutrition Service (FNS) is responsible for overseeing the SNAP and WIC programs nationwide. The FNS sets program guidelines, monitors compliance, and provides technical assistance to states. State agencies are also responsible for ensuring compliance with federal regulations and reporting program data to the FNS.
State Agencies Responsible for Administering SNAP and WIC
The following table Artikels the state agencies responsible for administering SNAP and WIC in various states:
| State | SNAP Agency | WIC Agency |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | Alabama Department of Human Resources | Alabama Department of Public Health |
| Alaska | Alaska Department of Health and Social Services | Alaska Department of Health and Social Services |
| Arizona | Arizona Department of Economic Security | Arizona Department of Health Services |
| Arkansas | Arkansas Department of Human Services | Arkansas Department of Health |
| California | California Department of Social Services | California Department of Public Health |
Impact and Importance

SNAP and WIC programs play a crucial role in enhancing food security and nutrition, particularly for low-income individuals and families. These programs not only provide essential food assistance but also contribute to reducing poverty and hunger, fostering healthier communities, and promoting economic stability.
Impact on Food Security and Nutrition
The impact of SNAP and WIC on food security and nutrition is significant. These programs ensure access to nutritious food for vulnerable populations, improving their overall health and well-being. By providing financial assistance for food purchases, SNAP empowers recipients to make healthier food choices, reducing the risk of diet-related health problems.
WIC, specifically targeted at women, infants, and children, provides supplemental foods, nutrition education, and breastfeeding support, promoting healthy growth and development.
Role in Reducing Poverty and Hunger
SNAP and WIC programs play a vital role in reducing poverty and hunger in the United States. By supplementing household incomes, SNAP helps families meet their basic needs, reducing food insecurity and alleviating financial strain. WIC, by providing essential nutrients and promoting healthy eating habits, contributes to reducing malnutrition and improving the health of vulnerable populations.
Number of Individuals and Families Benefitting
The reach of SNAP and WIC programs is substantial. According to the USDA, in 2022, SNAP served an average of 41.6 million people per month, providing crucial food assistance to millions of individuals and families across the country. WIC, in the same year, served an average of 8.9 million participants per month, offering essential nutrition support to women, infants, and children.
These numbers demonstrate the significant impact of these programs on the lives of millions of Americans.
Economic Benefits
The economic benefits of SNAP and WIC extend beyond individual households. These programs contribute to economic growth and stability by boosting local economies and creating jobs. SNAP spending directly stimulates local businesses, supporting farmers, food retailers, and other businesses in the food supply chain.
WIC, by promoting healthy growth and development, reduces healthcare costs associated with malnutrition and improves overall productivity in the workforce.
Ending Remarks
SNAP and WIC are essential programs that provide vital food assistance to millions of Americans. By understanding the eligibility requirements, application process, and benefits of these programs, individuals and families can access the resources they need to improve their food security and well-being.
The programs serve as a lifeline for many, offering a path to better nutrition and a brighter future.
Essential FAQs
How often can I receive benefits?
SNAP benefits are typically issued monthly, while WIC benefits are issued on a more frequent basis, often monthly or even bi-weekly. The specific frequency may vary by state.
What are the penalties for SNAP fraud?
Penalties for SNAP fraud can be severe and include fines, imprisonment, and disqualification from the program.
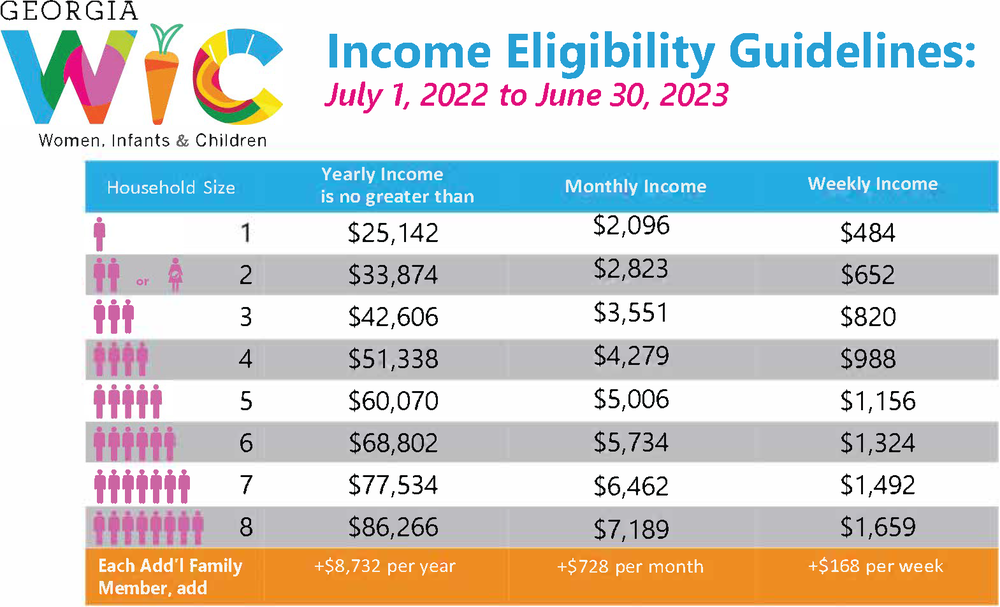
What are the income limits for SNAP and WIC?
The income limits for SNAP and WIC vary by state and household size. You can find the specific income limits for your state on the USDA website for SNAP and the WIC website.
Can I get SNAP and WIC at the same time?
Yes, you can receive both SNAP and WIC benefits simultaneously if you meet the eligibility requirements for both programs.
How do I know if I qualify for SNAP and WIC?
The best way to determine your eligibility is to contact your local SNAP or WIC office or visit the respective program websites. You can also use online eligibility calculators provided by the USDA and the WIC program.






