What is income reporting threshold for food stamps – What is the income reporting threshold for food stamps? This question is crucial for understanding eligibility for the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), a lifeline for millions of Americans struggling with food insecurity. The SNAP program, formerly known as food stamps, aims to ensure that low-income individuals and families have access to nutritious food.
However, navigating the intricacies of income reporting thresholds can be a daunting task, often leading to confusion and uncertainty. This article delves into the complexities of SNAP eligibility, exploring the various income categories considered, the factors influencing thresholds, and the methods used to calculate income for SNAP benefits.
To qualify for SNAP, individuals and households must meet specific income and asset requirements. These requirements are determined by a complex set of federal and state regulations, which vary based on factors such as household size, location, and other circumstances.
The income reporting threshold for SNAP is the maximum income level that a household can earn and still be eligible for benefits. This threshold is not a fixed number but rather a dynamic figure that changes depending on a multitude of factors.
What are Food Stamps?
Food stamps, officially known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), are a vital government assistance program designed to combat hunger and food insecurity in the United States. The program provides financial assistance to eligible low-income individuals and families to purchase food at authorized grocery stores and retailers.
History and Purpose
The SNAP program, formerly known as the Food Stamp Program, was established in 1964 as part of President Lyndon B. Johnson’s War on Poverty. The program has evolved significantly over the years, expanding its reach and adapting to changing needs.
The core purpose of SNAP remains the same: to ensure that all Americans have access to a nutritious and adequate food supply.
Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for SNAP benefits, individuals and households must meet specific income and asset requirements. The eligibility criteria are based on factors such as:
- Gross monthly income:This is the total income earned before taxes and deductions. The income limit varies depending on household size and state.
- Net monthly income:This is the income remaining after deducting certain expenses, such as housing costs and medical expenses.
- Household size:The number of people living in the household influences the eligibility threshold.
- Asset limits:SNAP recipients are subject to asset limits, which restrict the amount of money and property they can own.
- Citizenship status:Most legal residents, including non-citizens, are eligible for SNAP. However, there are specific requirements for non-citizens.
- Work requirements:Some SNAP recipients, such as able-bodied adults without dependents, are required to work or participate in work-related activities to remain eligible.
Benefits of the SNAP Program, What is income reporting threshold for food stamps
The SNAP program offers a range of benefits to eligible participants, including:
- Improved food security:SNAP benefits provide a consistent source of income for purchasing food, helping to alleviate hunger and food insecurity.
- Enhanced nutrition:SNAP benefits allow recipients to purchase a wider variety of nutritious foods, contributing to improved health and well-being.
- Economic stability:SNAP benefits can help families stretch their budgets and make ends meet, contributing to overall economic stability.
- Reduced healthcare costs:Improved nutrition through SNAP benefits can lead to fewer health problems, potentially reducing healthcare costs.
Limitations of the SNAP Program
While the SNAP program provides significant benefits, it also has certain limitations:
- Limited purchasing power:SNAP benefits can only be used to purchase food items, not other essential needs such as housing, utilities, or transportation.
- Stigma and shame:Some recipients may experience stigma and shame associated with receiving government assistance, which can impact their well-being.
- Administrative complexity:The application process and eligibility requirements can be complex and time-consuming for some individuals.
- Varying benefit levels:SNAP benefit levels vary depending on state and household size, leading to potential disparities in access to food assistance.
Income Reporting Thresholds for SNAP: What Is Income Reporting Threshold For Food Stamps
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps, has income eligibility requirements to ensure that benefits are provided to those who need them most. These income reporting thresholds are crucial in determining who qualifies for SNAP benefits and how much assistance they can receive.
Income Categories for SNAP Eligibility
To determine SNAP eligibility, two primary income categories are considered: gross income and net income.
- Gross Income: This refers to the total income earned before any deductions, such as taxes or contributions to retirement plans. It encompasses various sources, including wages, salaries, self-employment income, unemployment benefits, and pensions.
- Net Income: This represents the income remaining after deducting certain allowable expenses from gross income. These deductions may include work-related expenses, child care costs, and medical expenses.
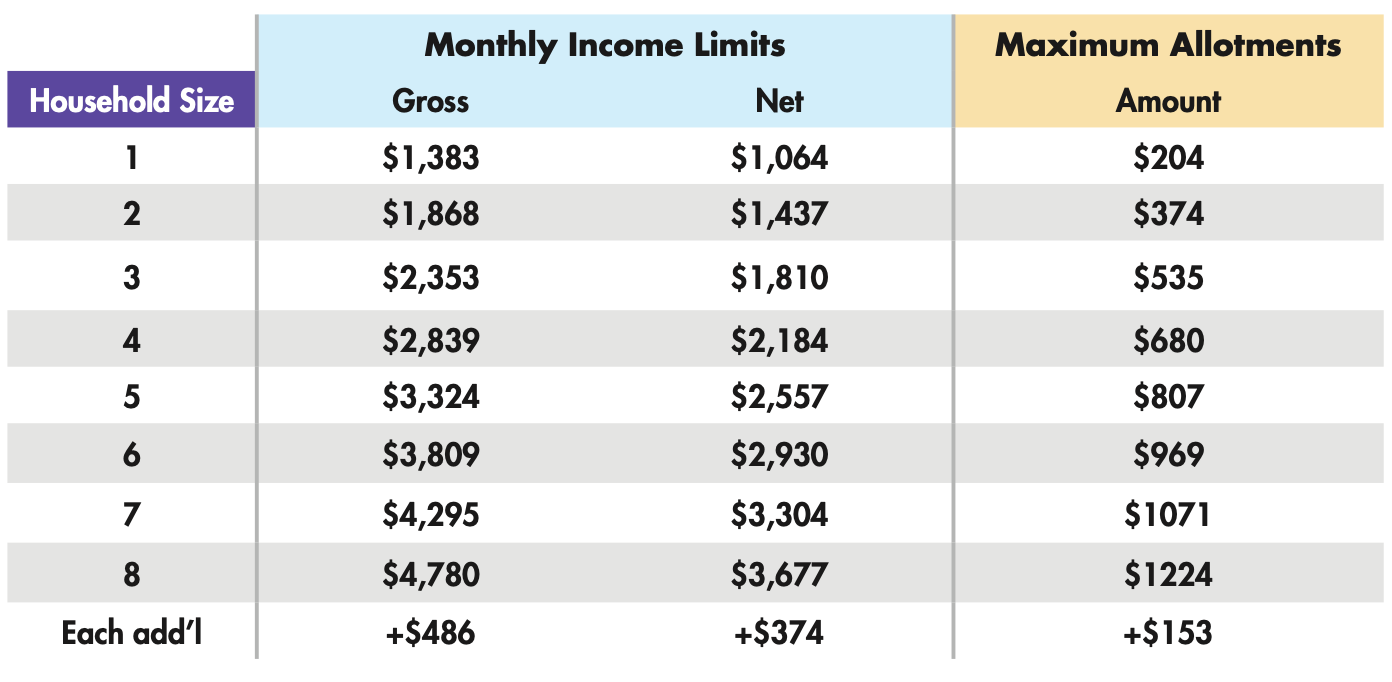
Income Reporting Thresholds for Different Household Sizes
The income reporting thresholds for SNAP eligibility vary based on household size and composition. These thresholds are adjusted annually to reflect changes in the cost of living.
The SNAP income reporting thresholds are based on the federal poverty guidelines, which are updated annually.
The following table illustrates the monthly gross income reporting thresholds for SNAP eligibility, as of October 2023:
| Household Size | Gross Income Threshold (Monthly) |
|---|---|
| 1 | $1,750 |
| 2 | $2,370 |
| 3 | $2,990 |
| 4 | $3,610 |
| 5 | $4,230 |
| 6 | $4,850 |
| 7 | $5,470 |
| 8 | $6,090 |
For each additional household member, the gross income threshold increases by $620 per month. It’s important to note that these are just examples, and the actual thresholds may vary slightly depending on the state and local regulations.
Income Reporting Thresholds for Different Household Compositions
The income reporting thresholds for SNAP eligibility are also affected by the household composition. For example, households with elderly individuals or individuals with disabilities may have different income reporting thresholds than households without these members.
SNAP eligibility is determined by a complex set of rules and regulations. It’s essential to consult with your local SNAP office for the most up-to-date information.
Factors Affecting Income Reporting Thresholds
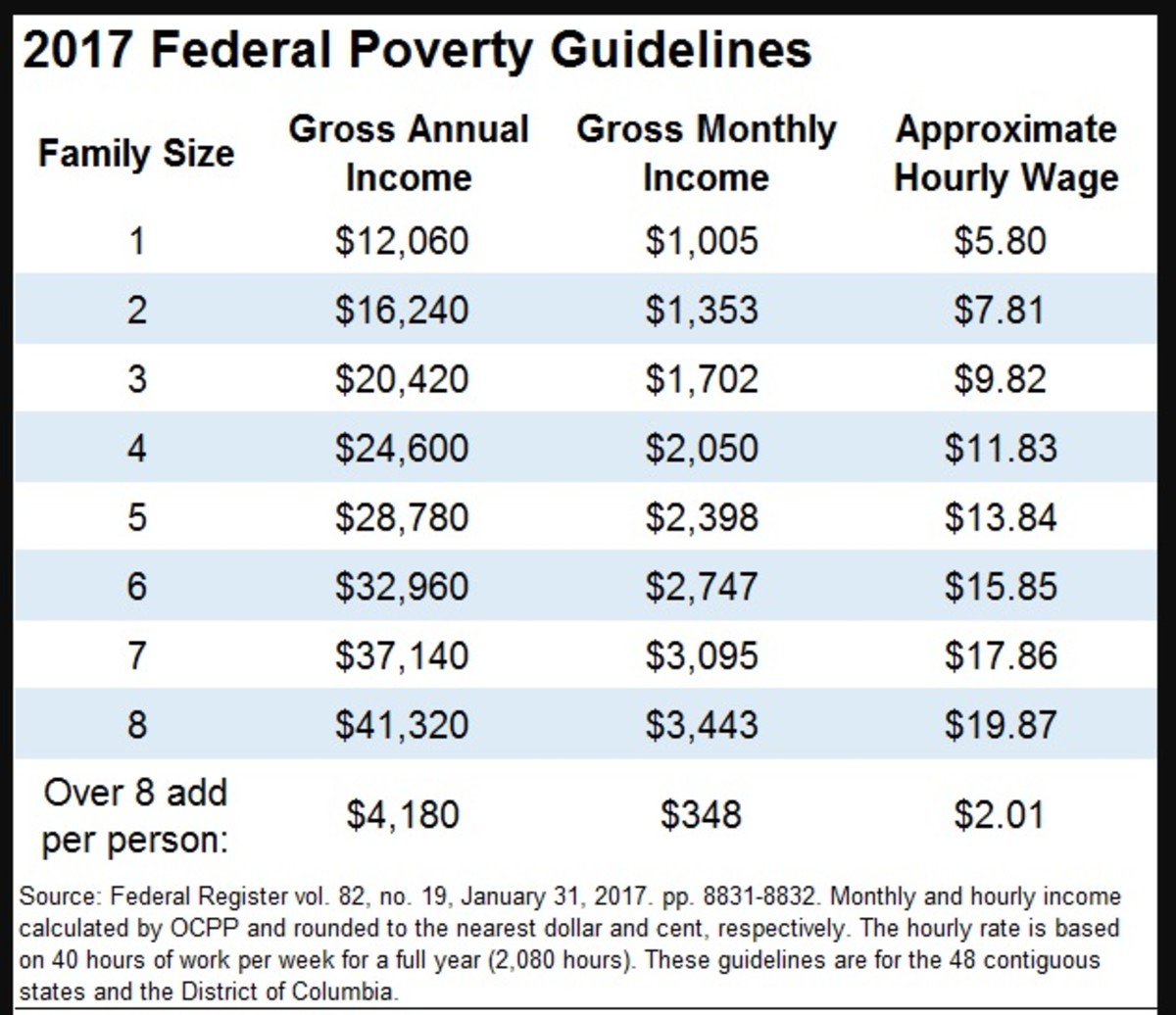
The income reporting thresholds for SNAP, also known as food stamps, are not static. They are subject to adjustments based on various factors, including federal and state regulations, cost of living changes, and economic conditions.
Federal and State Regulations
Federal and state regulations play a significant role in setting the income reporting thresholds for SNAP. The federal government sets the overall guidelines, while states have some flexibility in adjusting these thresholds within certain parameters.
- Federal Poverty Guidelines:The federal government establishes poverty guidelines, which are used to determine eligibility for various programs, including SNAP. These guidelines are based on family size and are adjusted annually for inflation.
- State Variations:While the federal government sets the overall framework, states have some discretion in setting their own income reporting thresholds. This allows states to consider the specific economic conditions and cost of living within their jurisdictions.
Cost of Living Adjustments
The cost of living can significantly impact the affordability of food and other essential items. To account for these fluctuations, income reporting thresholds are adjusted periodically.
The federal government adjusts the SNAP income thresholds annually to reflect changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
These adjustments ensure that the program remains effective in providing food assistance to those in need.
Calculating Income for SNAP Eligibility
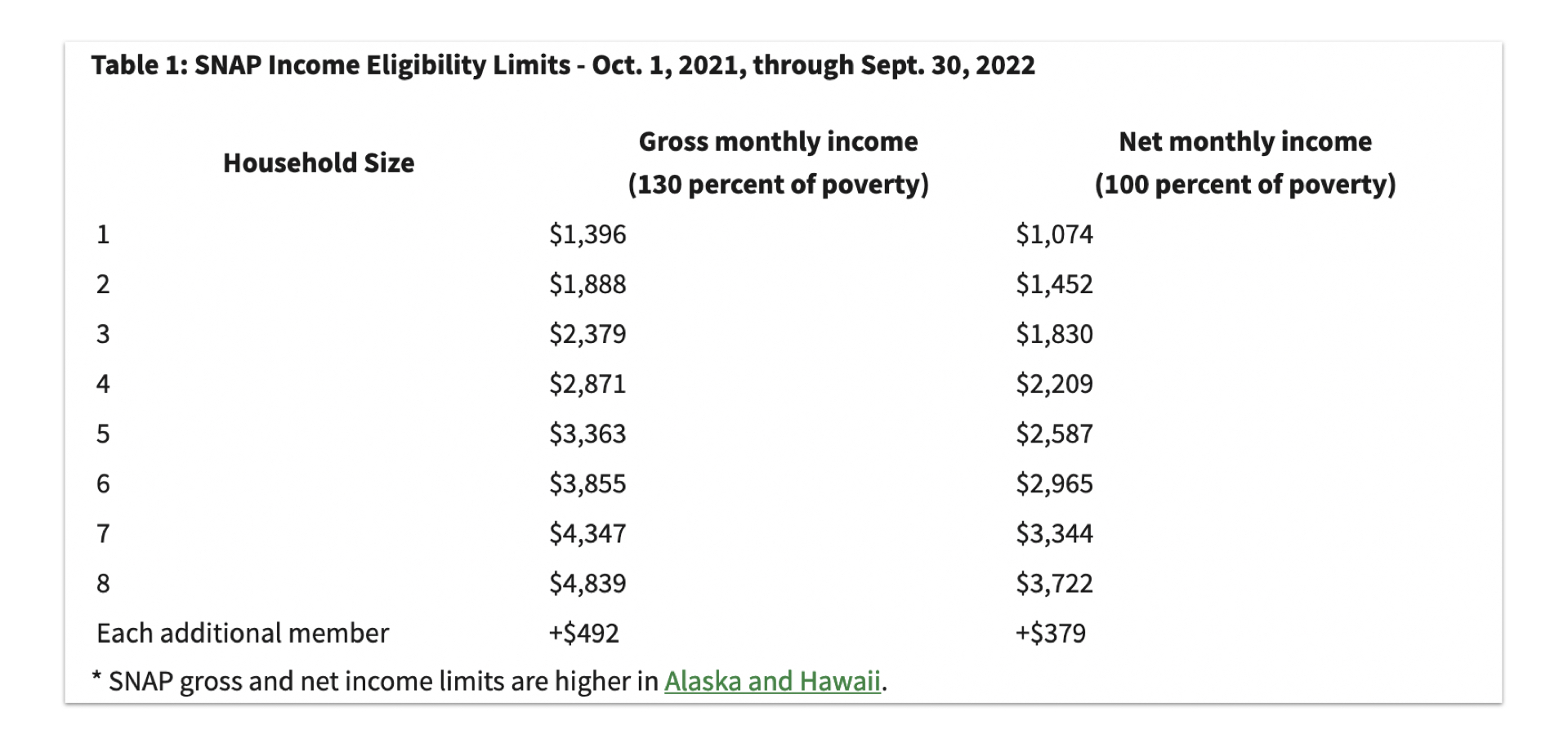
Determining SNAP eligibility involves calculating a household’s income. This calculation is crucial because it ensures that SNAP benefits are allocated to those who genuinely need them.
Income Calculation Methods
The SNAP program considers various income sources to determine eligibility. These sources are categorized into gross and net income, each playing a significant role in the final calculation.
- Gross Income:This refers to the total income received before deductions. It encompasses all income sources, such as wages, salaries, self-employment income, unemployment benefits, and Social Security payments.
- Net Income:This represents the income remaining after deductions are applied. It is calculated by subtracting certain allowable deductions from the gross income.
Deductions and Exemptions
Deductions and exemptions are essential components of the SNAP income calculation. They help reduce the household’s income, potentially making them eligible for benefits.
- Deductions:These are specific expenses that are subtracted from gross income. Common deductions include:
- Standard Deduction:This is a fixed amount deducted from the gross income of each household, regardless of size. The standard deduction varies by state and household size.
- Child Care Costs:This deduction covers expenses related to childcare for children under 13 years old. The deduction is limited to actual costs incurred, with specific requirements for documentation.
- Medical Expenses:This deduction covers certain medical expenses that exceed a specific threshold. The deduction is capped at a certain percentage of the household’s income.
- Shelter Costs:This deduction covers housing expenses, including rent, mortgage payments, and utilities. The deduction is limited to a specific percentage of the household’s income.
- Elderly or Disabled Deduction:This deduction is available for households with individuals who are 60 years or older or have a disability. It reduces the household’s income by a specific amount.
- Exemptions:These are specific income sources that are not considered when calculating SNAP eligibility. Some common exemptions include:
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC):This federal tax credit is not considered income for SNAP eligibility. It is designed to help low-income working families.
- Child Support Payments:Payments received for child support are not considered income for SNAP eligibility. These payments are intended to support the child’s well-being.
- Veterans’ Benefits:Certain veterans’ benefits, such as disability payments, are not considered income for SNAP eligibility. These benefits are intended to support veterans who have served their country.
- Public Assistance Payments:Payments received from public assistance programs, such as TANF or SSI, are not considered income for SNAP eligibility. These programs provide essential support to low-income families and individuals.
Income Source Treatment
Different income sources are treated differently for SNAP eligibility purposes. This section provides examples of how specific income sources are handled:
- Wages and Salaries:These are considered gross income and are subject to deductions. For example, a household with a monthly gross income of $3,000 from wages and salaries will have this amount included in the income calculation.
- Self-Employment Income:This income is calculated as the difference between business receipts and expenses. It is considered gross income and subject to deductions. For example, a household with a self-employment income of $2,000 after deducting business expenses will have this amount included in the income calculation.
- Unemployment Benefits:These are considered gross income and are subject to deductions. For example, a household receiving $500 per month in unemployment benefits will have this amount included in the income calculation.
- Social Security Payments:These are considered gross income and are subject to deductions. For example, a household receiving $1,000 per month in Social Security payments will have this amount included in the income calculation.
- Alimony and Child Support:These payments are considered gross income and are subject to deductions. For example, a household receiving $500 per month in alimony payments will have this amount included in the income calculation.
Resources for Determining Income Reporting Thresholds
Determining your eligibility for SNAP benefits requires understanding the income reporting thresholds. This section provides resources to help you navigate the process and find the information you need.
Official Websites for SNAP Income Reporting Thresholds
Official websites provide the most up-to-date information on SNAP income reporting thresholds. You can access detailed guidelines, eligibility criteria, and program updates directly from these sources.
- USDA Food and Nutrition Service (FNS):The USDA FNS website is the primary source for national SNAP information. It provides comprehensive resources, including program guidelines, state-specific information, and contact details for state agencies. https://www.fns.usda.gov/snap/eligibility
- Your State’s SNAP Website:Each state has a dedicated website that provides information about its SNAP program, including income reporting thresholds and eligibility requirements. You can find your state’s website by searching online for “SNAP [Your State Name].”
Contact Information for Local SNAP Offices and State Agencies
If you need assistance understanding the income reporting thresholds or have questions about your SNAP eligibility, you can contact your local SNAP office or state agency.
- Local SNAP Offices:To find the contact information for your local SNAP office, visit the USDA FNS website or your state’s SNAP website. You can usually locate this information under a “Contact Us” or “Find Your Local Office” section.
- State SNAP Agencies:You can also reach out to your state’s SNAP agency directly. The USDA FNS website provides a list of state agency contacts. You can also search online for “SNAP [Your State Name] Agency.”
Guide for Seeking Information on SNAP Income Reporting Thresholds
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you find the information you need:
- Identify your state:Determine the state where you reside, as income reporting thresholds vary by location.
- Visit the USDA FNS website:Begin your search by visiting the USDA FNS website. You can find general information about SNAP eligibility, income reporting thresholds, and other program details.
- Locate your state’s SNAP website:Once you’ve accessed the USDA FNS website, look for a section that lists state-specific SNAP websites. Alternatively, search online for “SNAP [Your State Name].”
- Review eligibility criteria:On your state’s SNAP website, carefully review the eligibility criteria, including income reporting thresholds. Look for specific guidelines and requirements for your situation.
- Contact your local SNAP office:If you have questions or need further clarification, contact your local SNAP office or state agency. They can provide personalized guidance and assistance.
Ultimate Conclusion
Understanding the income reporting threshold for food stamps is crucial for individuals and families seeking to access this essential program. While the complexities of eligibility requirements can be challenging to navigate, awareness of the various factors that influence income thresholds, coupled with the resources available for guidance, can empower individuals to make informed decisions and access the support they need.
This article has provided a comprehensive overview of the income reporting threshold for SNAP, shedding light on the key considerations and resources available for individuals seeking to determine their eligibility.
Quick FAQs
What are the different income categories considered for SNAP eligibility?
SNAP eligibility is based on both gross income and net income. Gross income refers to all income before taxes and deductions, while net income represents income after taxes and deductions. Both gross and net income are considered when determining SNAP eligibility.
How are deductions and exemptions treated in income calculations for SNAP?
SNAP regulations allow for specific deductions and exemptions to be applied to income calculations. These deductions can include expenses for work-related expenses, child care, and medical expenses. Exemptions may apply for certain income sources, such as earned income from a disability or unemployment benefits.
What are the resources available for determining income reporting thresholds for SNAP?
The USDA Food and Nutrition Service website provides comprehensive information on SNAP eligibility, including income reporting thresholds. State SNAP offices also offer assistance with eligibility inquiries and can provide specific information on state-level requirements.





