What size wheel 14×8 4/4 bolt pattern? You’re probably wondering if those wheels will fit your ride, and you’re not alone! This size is popular for a reason, but it’s important to make sure it’s the right fit for your vehicle. We’ll break down the details, explore compatibility, and help you avoid any potential headaches when it comes to wheel fitment.
Understanding the 14×8 dimension, the 4/4 bolt pattern, and the crucial role of offset and backspacing will ensure your wheels are not only compatible but also enhance your vehicle’s performance and style. We’ll even give you a list of common vehicle makes and models that are known to be compatible with this popular wheel size. So, buckle up and let’s dive into the world of wheels!
Understanding the Wheel Size and Bolt Pattern
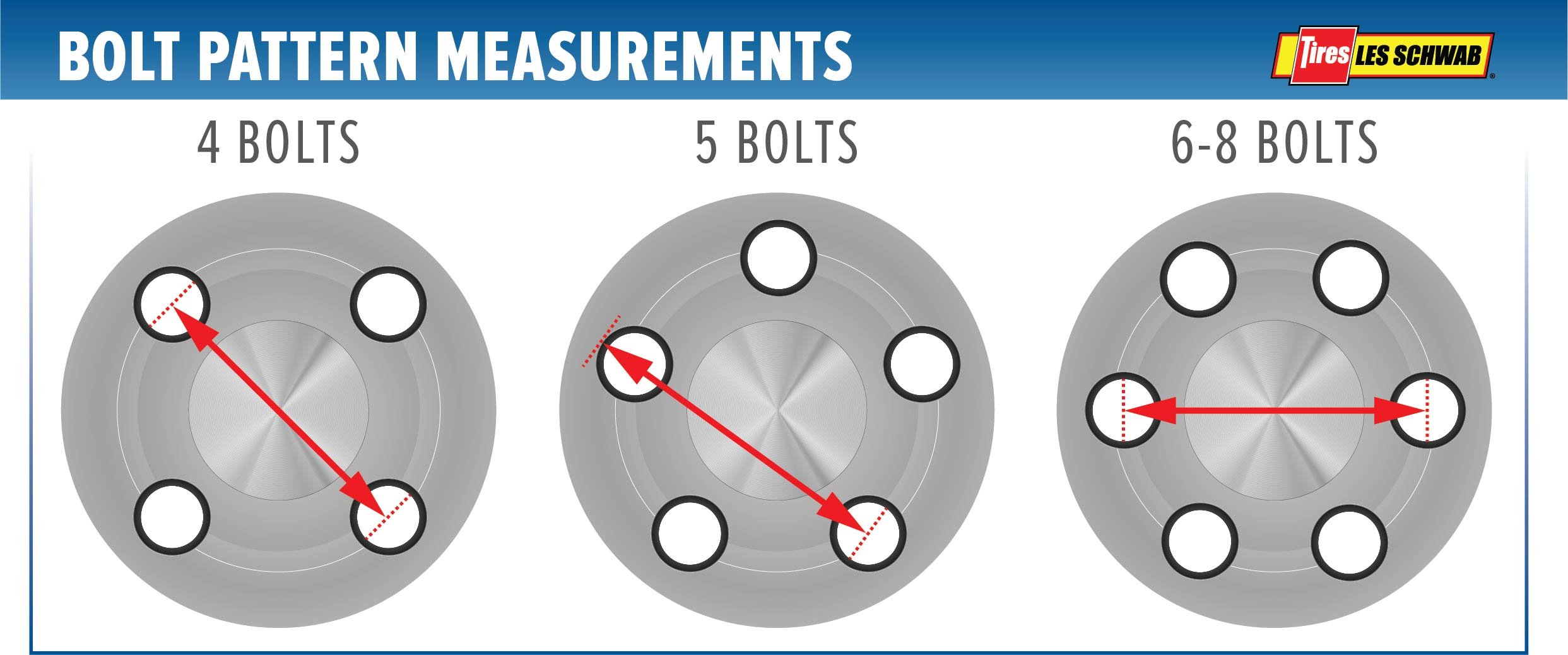
When choosing wheels for your vehicle, understanding the wheel size and bolt pattern is crucial for a safe and proper fit. These specifications ensure that the wheels are compatible with your vehicle’s hub and suspension system. Let’s break down the meaning of 14×8 and 4/4 bolt pattern.
Wheel Size
The 14×8 dimension represents the wheel’s diameter and width. The first number, 14, indicates the wheel’s diameter in inches. This means the wheel is 14 inches in diameter, measured from one edge of the rim to the opposite edge. The second number, 8, represents the wheel’s width in inches. This measurement refers to the distance across the wheel’s rim, excluding the tire.
Bolt Pattern
The 4/4 bolt pattern refers to the number of lug bolts and their arrangement on the wheel. The first number, 4, indicates the number of lug bolts that attach the wheel to the hub. The second number, 4, represents the bolt circle diameter (BCD) in inches. The BCD is the diameter of the circle that passes through the center of each lug bolt hole.
A 4/4 bolt pattern signifies that there are four lug bolts arranged in a circle with a diameter of 4 inches.
Common Wheel Sizes and Bolt Patterns
Understanding the differences between common wheel sizes and bolt patterns is essential for compatibility. Here’s a table showcasing some common wheel sizes and bolt patterns:
| Wheel Size | Bolt Pattern | Vehicle Compatibility |
|---|---|---|
| 14×6 | 4/4 | Small sedans, compact cars |
| 15×7 | 5/4.5 | Mid-size sedans, SUVs, trucks |
| 16×8 | 5/5 | Large SUVs, trucks, performance vehicles |
| 17×9 | 5/114.3 | Sports cars, performance vehicles |
| 18×10 | 5/120 | High-performance vehicles, luxury cars |
It’s important to note that this table is not exhaustive and only represents a few common examples. The specific wheel size and bolt pattern required for your vehicle will depend on the make, model, and year. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or consult a qualified mechanic for accurate information.
Compatibility with Vehicles
Determining the compatibility of a 14×8 wheel with a 4/4 bolt pattern is crucial for safe and proper vehicle operation. While this wheel size and bolt pattern may be common in certain vehicle types, compatibility is not guaranteed across all makes and models.
Compatibility Issues, What size wheel 14×8 4/4 bolt pattern
A mismatch in wheel size or bolt pattern can lead to several issues, including:
Wheel Wobble
An incorrect bolt pattern can result in uneven wheel mounting, leading to vibrations and instability.
Wheel Separation
If the wheel’s bolt holes do not align perfectly with the hub’s studs, the wheel could detach from the vehicle during driving.
Tire Damage
Improper wheel mounting can put undue stress on the tires, causing premature wear and tear or even blowouts.
Suspension Damage
Mismatched wheel size or bolt pattern can strain the suspension components, potentially causing damage.
Vehicles Compatible with 14×8 Wheels and 4/4 Bolt Pattern
- Classic American Muscle Cars: Vehicles like the Ford Mustang, Chevrolet Camaro, and Dodge Challenger, particularly those from the 1960s and 1970s, often used 14×8 wheels with a 4/4 bolt pattern. These vehicles were designed for performance and handling, making this wheel size a popular choice for enthusiasts.
- Vintage Trucks and SUVs: Older trucks and SUVs from brands like Chevrolet, Ford, and Dodge, particularly those from the 1970s and 1980s, also frequently featured 14×8 wheels with a 4/4 bolt pattern. These vehicles were built for durability and off-road capability, making this wheel size suitable for various terrains.
- Classic European Sports Cars: Certain classic European sports cars, such as the Porsche 911 and the Alfa Romeo Spider, also utilized 14×8 wheels with a 4/4 bolt pattern. These cars were known for their performance and handling, making this wheel size a suitable choice for enthusiasts.
Offset and Backspacing Considerations
Understanding the concepts of offset and backspacing is crucial for ensuring proper wheel fitment and optimal vehicle performance. These parameters directly influence how a wheel sits within the wheel well, affecting tire clearance, handling, and overall vehicle stability.
Offset and Backspacing Explained
Offset refers to the distance between the wheel’s mounting surface (where the wheel bolts to the hub) and the center of the wheel’s width. Backspacing, on the other hand, is the distance between the mounting surface and the inside of the wheel. Offset is typically measured in millimeters (mm), while backspacing is measured in inches (in). A positive offset indicates that the mounting surface is further out from the center of the wheel, while a negative offset means the mounting surface is closer to the center of the wheel.
A positive offset pushes the wheel further out from the vehicle, while a negative offset pulls the wheel closer to the vehicle.
Impact of Offset and Backspacing on Vehicle Handling and Tire Clearance
Offset and backspacing play a significant role in determining the wheel’s position relative to the vehicle’s suspension components and bodywork. * Tire Clearance: A larger offset (or smaller backspacing) can increase the risk of tire rubbing against the vehicle’s suspension or bodywork, especially when turning or encountering bumps. Conversely, a smaller offset (or larger backspacing) can create more clearance, reducing the chances of rubbing.
Handling
Offset and backspacing affect the vehicle’s track width, which is the distance between the centers of the left and right wheels. A wider track width, achieved by using wheels with a larger offset, can improve stability and handling, particularly during cornering. However, excessive offset can also lead to instability at high speeds or on uneven surfaces.
Vehicle Stability
Offset and backspacing also influence the vehicle’s camber angle, which is the angle of the wheel relative to the vertical axis. A larger offset can cause the wheel to lean inward, resulting in negative camber, which can improve handling but may also lead to uneven tire wear.
Offset and Backspacing Values and Their Impact on Wheel Fitment
The following table illustrates the relationship between offset and backspacing values and their impact on wheel fitment:| Offset (mm) | Backspacing (in) | Impact on Wheel Fitment ||—|—|—|| +40 | 4.5 | Wheel sits further out, may increase tire clearance, wider track width, potential for rubbing. || +30 | 5.0 | Balanced offset, good for most vehicles, moderate track width, minimal risk of rubbing.
|| +20 | 5.5 | Wheel sits closer to the vehicle, less tire clearance, narrower track width, less chance of rubbing. || +10 | 6.0 | Wheel sits very close to the vehicle, reduced tire clearance, narrowest track width, least chance of rubbing. || 0 | 6.5 | Wheel sits flush with the vehicle’s body, minimal clearance, can be used for custom fitments.
|| -10 | 7.0 | Wheel sits inside the vehicle’s body, potentially negative clearance, not recommended for most vehicles. | Note: These are general guidelines, and the optimal offset and backspacing values will vary depending on the specific vehicle model and desired fitment. It is crucial to consult with a qualified mechanic or wheel specialist to determine the appropriate values for your vehicle.
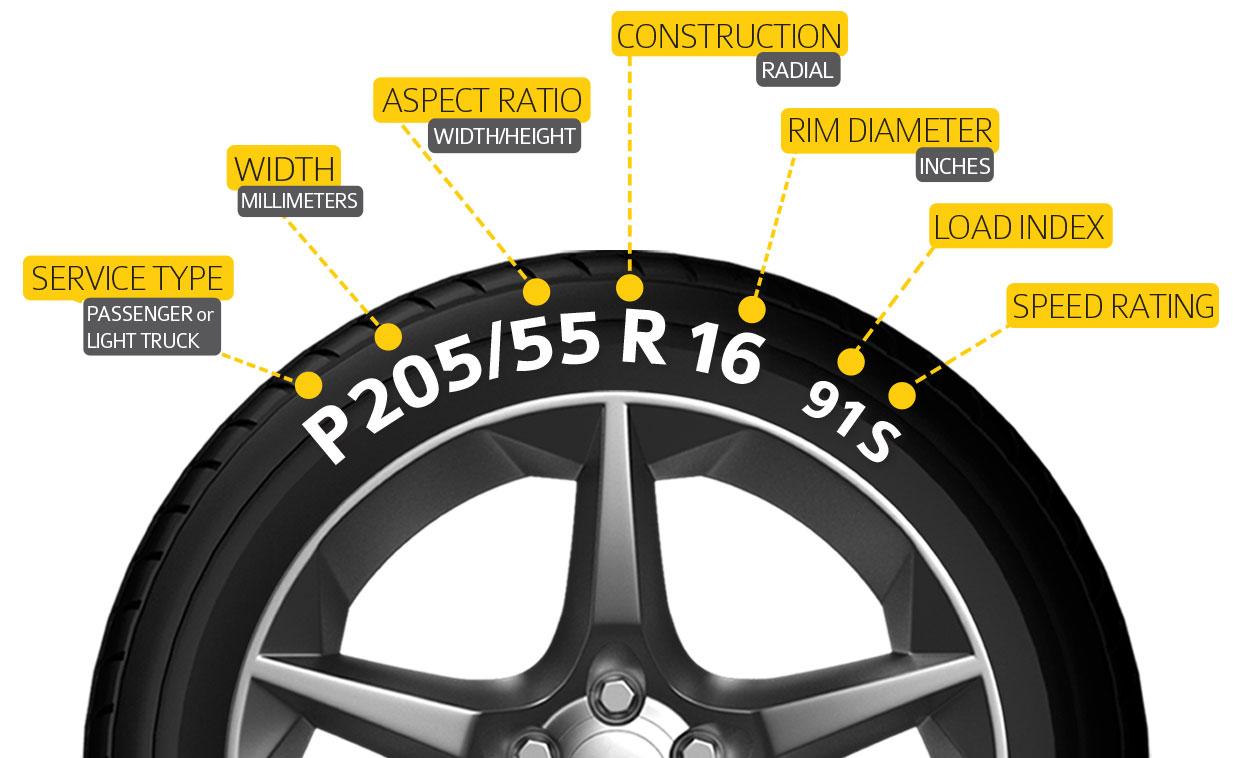
Tire Size and Load Rating
The wheel size and tire size are directly related. The wheel size determines the diameter of the tire that can be mounted, while the tire size specifies the overall dimensions of the tire, including its width, aspect ratio, and diameter. The tire size needs to be compatible with the wheel size to ensure proper fit and performance. Choosing tires with the appropriate load rating is crucial for vehicle safety and handling.
The load rating indicates the maximum weight a tire can safely carry. It is essential to select tires with a load rating that meets or exceeds the vehicle’s maximum weight capacity.
Recommended Tire Sizes
The recommended tire sizes for a 14×8 wheel depend on the vehicle’s weight, intended use, and driving conditions. Here are some general recommendations for tire sizes for a 14×8 wheel, considering load capacity and vehicle type:
For vehicles with a light load capacity (up to 2,000 lbs):
- 195/70R14
- 205/65R14
- 215/60R14
For vehicles with a moderate load capacity (2,000-3,000 lbs):
- 215/65R14
- 225/60R14
- 235/55R14
For vehicles with a heavy load capacity (over 3,000 lbs):
- 235/60R14
- 245/55R14
- 255/50R14
Note: These are just general recommendations. It is always best to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a tire specialist to determine the most appropriate tire size and load rating for your specific vehicle.
Installation and Safety
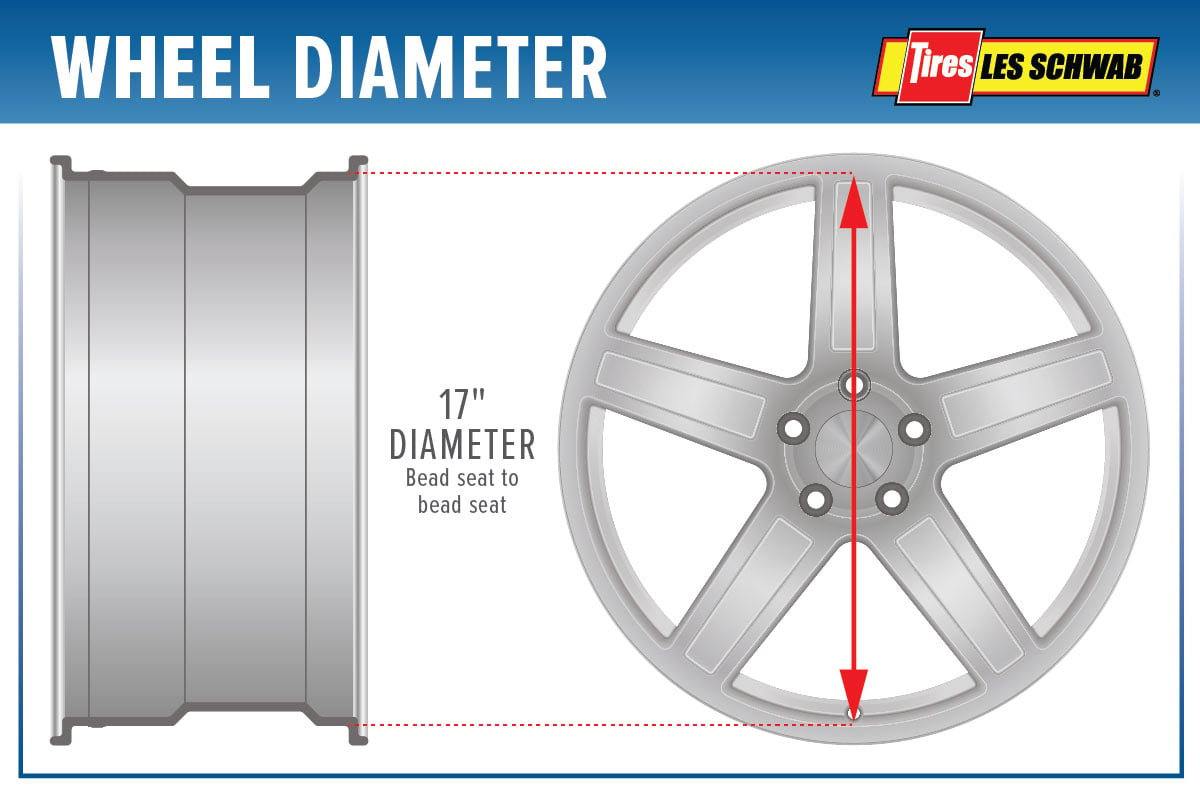
Installing 14×8 wheels with a 4/4 bolt pattern requires careful consideration of safety and proper techniques. Incorrect installation can lead to serious consequences, including accidents and damage to your vehicle. This section provides a step-by-step guide and essential safety precautions to ensure a secure and successful installation.
Wheel Installation Process
Installing wheels involves several steps that need to be performed correctly. Here’s a detailed guide:
- Prepare the Vehicle: Park your vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. Ensure the vehicle is in park (automatic transmission) or neutral (manual transmission). Chock the front wheels to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
- Loosen Lug Nuts: Using a breaker bar or lug wrench, loosen the lug nuts on the wheel you’re replacing. Do not remove the lug nuts completely at this stage.
- Raise the Vehicle: Using a jack, safely raise the vehicle until the tire is slightly off the ground. Ensure the jack is properly positioned under a designated jacking point on the vehicle’s frame.
- Remove the Wheel: Remove the lug nuts completely and carefully remove the old wheel.
- Install the New Wheel: Position the new 14×8 wheel onto the hub. Ensure the wheel is properly centered and sits flush against the brake rotor.
- Tighten Lug Nuts: Hand-tighten the lug nuts to ensure the wheel is secure. Do not overtighten at this stage.
- Lower the Vehicle: Lower the vehicle until the tire touches the ground.
- Tighten Lug Nuts (Final): Using a torque wrench, tighten the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specifications. This is crucial for ensuring the wheel is securely attached and prevents loosening during driving.
- Final Check: Once all lug nuts are tightened, double-check that the wheel is securely installed and the vehicle is safe to drive.
Safety Precautions During Wheel Installation
Safety should always be prioritized during wheel installation. Here are essential precautions:
- Use Proper Tools: Always use a breaker bar or lug wrench designed for your vehicle’s lug nuts. Avoid using damaged or mismatched tools, as they can slip and cause injury.
- Use a Jack Stand: Never rely solely on the jack to support the vehicle. Use a jack stand to ensure the vehicle is securely lifted and prevents it from falling.
- Proper Lifting Points: Ensure the jack is positioned under a designated jacking point on the vehicle’s frame. Lifting the vehicle from other areas can damage the frame.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris during the installation process.
- Avoid Distractions: Focus on the task at hand and avoid distractions that could lead to errors or accidents.
Risks Associated with Improper Wheel Installation
Improper wheel installation poses significant risks, including:
- Wheel Detachment: Loose lug nuts can cause the wheel to detach from the vehicle while driving, leading to a catastrophic accident.
- Tire Damage: Improper wheel installation can damage the tire, causing premature wear and potential blowouts.
- Brake System Damage: If the wheel is not properly centered on the hub, it can interfere with the brake system, leading to reduced braking performance or damage to the brakes.
- Suspension Damage: Incorrect wheel installation can strain the suspension components, leading to premature wear and damage.
Choosing the right wheels for your vehicle can be a daunting task, but with the right information, it doesn’t have to be a headache. Understanding wheel size, bolt pattern, offset, and backspacing are all crucial factors to consider. With a little research and the right guidance, you’ll be rolling in style and confidence, knowing that your wheels are the perfect fit for your ride.
Top FAQs: What Size Wheel 14×8 4/4 Bolt Pattern
What are the risks of installing wheels with the wrong bolt pattern?
Installing wheels with the wrong bolt pattern can be extremely dangerous. The wheels may not be securely attached to the vehicle, potentially leading to wheel separation while driving. This could cause a serious accident.
How do I know if my vehicle has a 4/4 bolt pattern?
The bolt pattern is usually found on a sticker or label inside your vehicle’s driver’s side doorjamb. You can also consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or online resources.
What are the benefits of upgrading to larger wheels?
Larger wheels can offer a number of benefits, including improved handling, a more aggressive look, and the ability to fit larger tires. However, it’s important to consider the potential drawbacks, such as increased unsprung weight and a harsher ride.