How to read sewing patterns? It’s like unlocking a secret language, full of symbols and markings that guide you to create beautiful garments! Don’t worry, it’s not as complicated as it seems. With a little bit of practice, you’ll be able to decipher these patterns like a pro, and soon you’ll be stitching up a storm!
From understanding the basics of sewing patterns, like the different types available and their components, to choosing the right pattern for your skill level and style, this guide will walk you through every step of the process. You’ll learn how to prepare your pattern and fabric, assemble the garment with confidence, and even troubleshoot common challenges along the way. So, grab your fabric, your sewing machine, and let’s get started!
Understanding Sewing Pattern Basics: How To Read Sewing Patterns
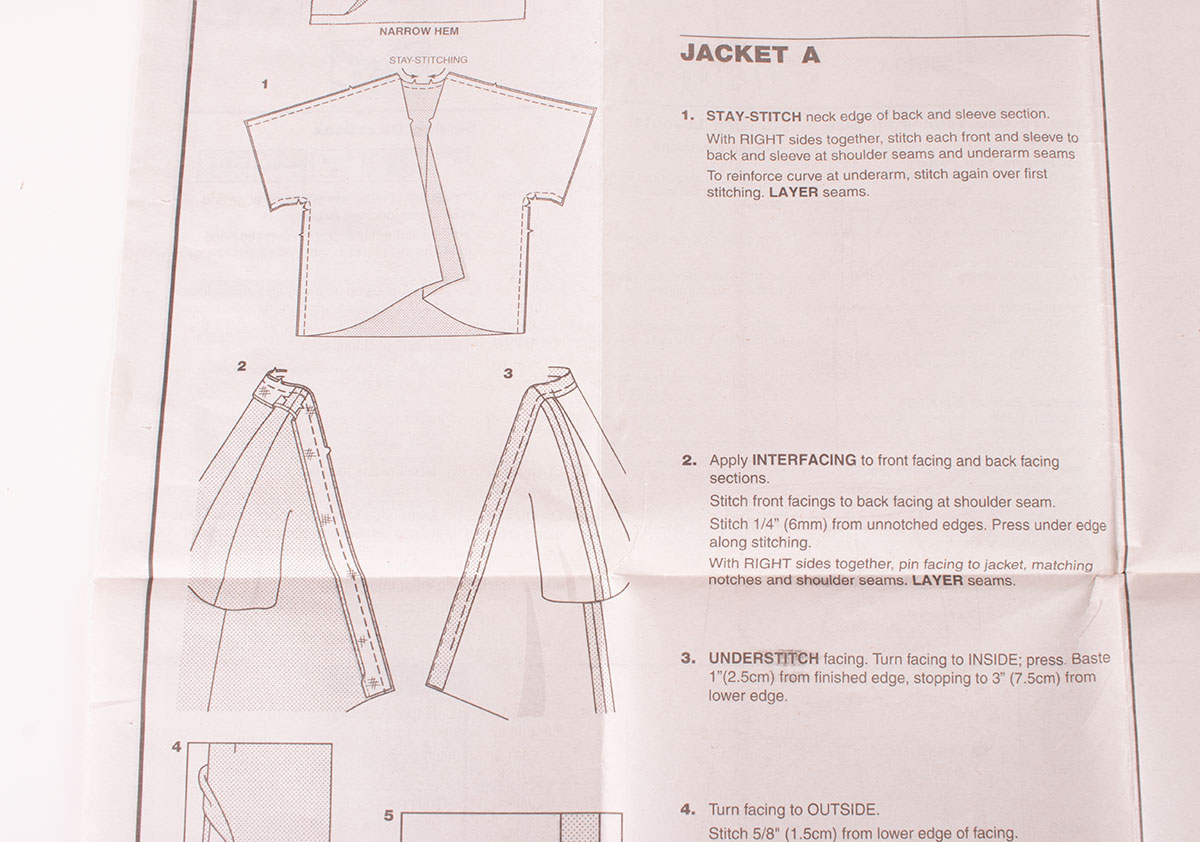
Sewing patterns are essential tools for creating garments and other sewn items. They provide detailed instructions and templates to guide you through the process. Understanding the different types of sewing patterns and their components is crucial for successful sewing projects.
Types of Sewing Patterns
Sewing patterns come in various forms, each with its own advantages and drawbacks. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
- Commercial Patterns: These are widely available patterns from companies like Simplicity, McCall’s, and Butterick. They often offer a wide range of styles and sizes, making them a popular choice for beginners and experienced sewers alike. Commercial patterns typically include detailed instructions, pattern pieces, and fabric recommendations.
- Independent Patterns: Independent designers often create unique and innovative patterns that may not be found in mainstream stores. These patterns are typically available online or through specialized shops. They often feature more detailed instructions and offer a higher level of customization.
- Vintage Patterns: Vintage patterns offer a glimpse into past fashion trends and styles. They can be found at flea markets, antique shops, and online. Vintage patterns may require some adjustments to fit modern sizes and sewing techniques.
Standard Components of a Sewing Pattern
Sewing patterns typically include the following components:
- Pattern Pieces: These are the templates used to cut out the fabric for your garment. They are usually printed on tissue paper or a similar material.
- Instructions: The instructions guide you through the sewing process, step-by-step. They include information on cutting, sewing, finishing, and fitting the garment.
- Size Chart: The size chart provides measurements for each pattern size, allowing you to choose the appropriate size for your body.
- Fabric Recommendations: The pattern will usually recommend specific fabrics for the garment. These recommendations are based on the style, fit, and intended use of the garment.
- Notions: The pattern may list additional notions needed for the project, such as buttons, zippers, thread, or interfacing.
Symbols and Markings
Sewing patterns use various symbols and markings to convey instructions and information. Understanding these symbols is essential for accurate sewing.
- Cutting Lines: These lines indicate where to cut the fabric. They are usually solid lines.
- Sewing Lines: These lines indicate where to sew. They are usually dashed lines.
- Grain Lines: These lines indicate the direction of the fabric’s warp and weft threads. They ensure that the fabric is cut and sewn correctly.
- Fold Lines: These lines indicate where to fold the fabric before cutting.
- Dart Lines: These lines indicate where to sew darts, which are used to shape the garment.
- Pleat Lines: These lines indicate where to sew pleats, which are folds of fabric used for decoration or shaping.
- Ease Markings: These markings indicate where to add extra fabric for ease of movement.
- Notches: These markings are small triangles or circles used to match pattern pieces together.
- Arrows: These indicate the direction of the grain line or the direction of stitching.
- Numbers: These numbers may indicate the order of sewing steps or the size of the pattern piece.
Choosing the Right Sewing Pattern
The first step to a successful sewing project is choosing the right pattern. This involves considering your skill level, desired garment style, and fabric choice.
Skill Level
Before you start browsing patterns, it’s crucial to be honest about your sewing experience. Sewing patterns come with difficulty ratings, typically ranging from beginner to advanced. Beginner-friendly patterns are often simple in design and construction, with straightforward instructions and minimal pattern pieces. They are ideal for those starting their sewing journey and looking to build confidence. Advanced patterns, on the other hand, might involve complex techniques, multiple fabric types, and intricate details, requiring a higher level of skill and experience.
Beginner-Friendly Sewing Patterns
Here are some examples of beginner-friendly sewing patterns:
- Simple skirts: A-line skirts, gathered skirts, or pencil skirts are excellent starting points for beginners. These patterns usually involve basic sewing techniques and require minimal fabric.
- T-shirts: Basic T-shirt patterns are straightforward and allow you to experiment with different necklines, sleeve lengths, and fabric choices.
- Pillowcases: These are excellent projects for beginners, as they involve simple sewing techniques and require minimal fabric.
More Advanced Sewing Patterns
For those with more experience, there are numerous challenging and rewarding patterns to explore:
- Dresses with intricate details: Patterns with ruffles, pleats, or elaborate necklines can test your sewing skills and create stunning garments.
- Coats and jackets: These patterns involve complex tailoring techniques and require careful fabric selection.
- Formal wear: Evening gowns, suits, and other formal garments often require advanced sewing skills and a high level of precision.
Desired Garment Style
Once you’ve assessed your skill level, consider the style of garment you want to sew. Are you looking for a casual, everyday outfit, a special occasion piece, or something in between? Do you have a specific design in mind, or are you open to exploring different options? Browsing through pattern books, online pattern shops, or sewing magazines can provide inspiration and help you narrow down your choices.
Fabric Choice, How to read sewing patterns
The fabric you choose will significantly impact the final look and feel of your garment. Consider the intended use of the garment, the desired drape and texture, and the ease of sewing with the chosen fabric. For beginners, it’s recommended to start with fabrics that are easy to work with, such as cotton, linen, or jersey. These fabrics are generally forgiving and less likely to cause frustration for novice sewers.
Determining the Correct Size
Sewing patterns typically come in a range of sizes, and choosing the right size is crucial for a comfortable and well-fitting garment. Most patterns provide a measurement chart that you can use to determine your size. It’s essential to take accurate measurements, using a flexible tape measure and following the instructions provided in the pattern.
Adjusting Patterns for a Custom Fit
Even if you choose the correct size, you may need to adjust the pattern to achieve a perfect fit. This is particularly true for individuals with unique body shapes or who prefer a specific fit. Pattern adjustments can involve adding or subtracting fabric, altering seam allowances, or making other modifications to the pattern pieces. There are numerous resources available to help you with pattern adjustments, including books, online tutorials, and sewing classes.
Preparing the Pattern and Fabric

Now that you have chosen the perfect pattern and fabric, it’s time to prepare them for sewing. This involves transferring the pattern pieces onto your fabric and cutting them out. It also involves understanding and utilizing grain lines for accurate garment construction.
Transferring Pattern Pieces to Fabric
Transferring pattern pieces to fabric is essential for accurate cutting. There are various techniques for this, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Tracing: This method involves tracing the pattern pieces onto the fabric using a tracing wheel and tracing paper. It’s suitable for delicate fabrics where pins can cause holes.
- Pinning: This is the most common method. Pin the pattern pieces to the fabric, ensuring the pattern is aligned with the grain line. Use plenty of pins to secure the pattern in place.
- Weights: For larger pieces, you can use weights to hold the pattern in place instead of pins. This minimizes the risk of fabric slippage.
After transferring the pattern pieces, you can cut them out with sharp fabric shears. Always cut along the marked lines, ensuring the fabric is smooth and flat to avoid any distortion.
Understanding Grain Lines
Grain lines are essential for fabric stability and garment fit. They represent the direction of the fabric’s warp and weft threads, which are the lengthwise and crosswise threads woven together to create the fabric.
- Warp: The lengthwise threads, which are stronger and less prone to stretching.
- Weft: The crosswise threads, which are generally weaker and more prone to stretching.
Pattern pieces are designed to be cut along the grain lines, ensuring the garment hangs correctly and retains its shape. The grain lines are typically marked on pattern pieces with arrows or a straight line. When placing the pattern on the fabric, align the grain lines of the pattern with the grain lines of the fabric.
Preparing Different Types of Fabrics for Sewing
Different fabrics require different preparation techniques before sewing. Here are some tips for preparing common fabric types:
- Woven Fabrics: These fabrics are typically pre-washed and pressed before cutting. This helps to prevent shrinkage and set the fabric’s weave.
- Knit Fabrics: These fabrics are generally more forgiving and can be sewn without pre-washing. However, if you are concerned about shrinkage, it’s best to pre-wash and dry the fabric before cutting.
- Silk Fabrics: These fabrics are delicate and require special handling. Avoid pinning them directly as it can cause holes. Instead, use weights or tracing methods. Silk should also be pressed with a low heat setting to avoid scorching.
- Linen Fabrics: These fabrics are prone to wrinkling. To minimize wrinkling, pre-wash and press the fabric before cutting.
Preparing the pattern and fabric correctly is crucial for a successful sewing project. By understanding grain lines and using appropriate cutting and preparation techniques, you can ensure your garment fits well and hangs beautifully.
Assembling the Garment
Now that you’ve prepared your pattern pieces and fabric, it’s time to bring your garment to life! This section will guide you through the process of sewing your garment, from stitching the first seam to adding those final finishing touches.
Sewing the Garment
Sewing a garment involves a series of steps, each with its own purpose. Follow these steps to assemble your garment:
- Prepare Your Work Area: Ensure you have a clean and well-lit workspace with a flat surface. Gather your sewing machine, thread, scissors, pins, measuring tape, and any other tools you might need.
- Stitch the First Seam: Start by stitching the seams that are marked on the pattern pieces. Begin with the seams that are most critical for the garment’s shape and fit. For example, if you are making a dress, you might start with the side seams.
- Pressing Seams: After stitching each seam, press it open with a hot iron. This helps to flatten the seam and create a smooth, professional finish. Pressing also helps to set the fabric and prevent puckering.
- Attaching Other Components: Follow the pattern instructions to attach other components, such as sleeves, collars, pockets, or closures. Be sure to align the pieces carefully and use the correct stitching methods.
- Finishing Seams: Finish seams to prevent fraying and create a polished look. Common finishing techniques include serging, zigzag stitching, or using a seam binding.
- Adding Embellishments: If your pattern includes embellishments, such as buttons, zippers, or appliques, attach them according to the instructions.
- Final Pressing: Press the entire garment after all the components have been attached. This helps to create a smooth, professional finish.
Common Sewing Techniques
Various sewing techniques are used in pattern construction, each serving a specific purpose. Here’s a table showcasing common sewing techniques and their applications:
| Sewing Technique | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Straight Stitch | A basic stitch that creates a straight line of stitching. | Seams, hems, attaching components |
| Zigzag Stitch | A stitch that creates a zig-zag pattern, often used for finishing seams or attaching elastic. | Finishing seams, attaching elastic, creating decorative effects |
| Backstitch | A stitch that reinforces the beginning and end of a seam, preventing it from unraveling. | Securing the beginning and end of seams |
| Serging | A technique that uses a special machine to create a finished edge on fabric. | Finishing seams, preventing fraying |
| Topstitch | A stitch that is sewn on the right side of the fabric, creating a decorative or functional element. | Attaching buttons, creating decorative accents |
Importance of Pressing Seams
Pressing seams is a crucial step in garment construction, often overlooked. Here’s why it’s essential:
Pressing helps to flatten the seam and create a smooth, professional finish.
Pressing sets the fabric and prevents puckering, resulting in a better-fitting garment.
Pressing helps to create crisp edges and define the garment’s shape.
Pressing makes it easier to sew subsequent seams accurately.
Troubleshooting and Tips
Sewing patterns can be a wonderful guide to creating your own garments, but they can also be a source of frustration for beginners. This section addresses common challenges and offers solutions to help you navigate the world of sewing patterns with confidence.
Common Challenges Faced by Beginners
While sewing patterns provide a roadmap for garment creation, beginners often encounter obstacles that can hinder their progress. Here are some common challenges and their solutions:
- Understanding Pattern Symbols: Sewing patterns utilize a variety of symbols to convey instructions. These symbols can be confusing for beginners.
- Solution: Familiarize yourself with the standard sewing pattern symbols. Many pattern companies provide a symbol chart on their website or on the pattern envelope. You can also find comprehensive symbol charts online.
- Choosing the Right Size: Determining the correct pattern size can be tricky. Often, you may need to adjust the pattern based on your measurements.
- Solution: Take accurate body measurements and compare them to the pattern size chart. If your measurements fall between sizes, choose the larger size for a more comfortable fit. Remember that pattern sizes can vary across brands, so it’s always best to check the size chart for each pattern you purchase.
- Fabric Selection: Selecting the right fabric for your project can be overwhelming. Not all fabrics are suitable for every pattern.
- Solution: Read the pattern instructions carefully to determine the recommended fabric type and weight. The pattern will often specify the best fabric choices for the garment’s intended use and design.
- Cutting and Marking: Precise cutting and marking are essential for a successful sewing project. Incorrectly cut or marked fabric can lead to fitting issues and a poorly constructed garment.
- Solution: Use sharp fabric shears and a cutting mat to ensure clean cuts. Use fabric marking tools, such as tailor’s chalk or a fabric marker, to transfer pattern markings onto the fabric. Be sure to mark the fabric on the wrong side, as the marks will be hidden once the garment is assembled.
- Sewing Techniques: Sewing patterns may require specific techniques that you may not be familiar with.
- Solution: Practice basic sewing techniques before tackling more complex patterns. There are numerous online tutorials and videos that can guide you through various sewing techniques. Consider taking a beginner sewing class to learn essential skills from a qualified instructor.
Achieving a Professional Finish
Even if you follow the pattern instructions precisely, your finished garment can be elevated to a professional level with attention to detail. Here are some tips to achieve a professional finish:
- Pressing: Pressing your seams as you sew helps to create a smooth, professional finish.
- Solution: Use a steam iron and a pressing cloth to prevent shine on delicate fabrics. Press each seam open before stitching the next seam.
- Finishing Seams: Finishing seams prevents them from fraying and adds durability to your garment.
- Solution: Use a serger, zigzag stitch, or overlock stitch to finish raw edges. You can also use a bias tape or seam binding for a clean and professional finish.
- Topstitch: Topstitching adds a decorative touch and helps to secure seams.
- Solution: Use a contrasting thread color to create a bold statement or match the fabric color for a subtle finish. Topstitch along the seam lines or create decorative stitching patterns.
- Finishing Edges: Cleanly finished edges are essential for a professional look.
- Solution: Use a seam ripper to remove any loose threads or imperfections. Fold and press hems neatly. Use a blind stitch to secure hems invisibly.
- Choosing the Right Notions: The right notions, such as buttons, zippers, and interfacing, can make a significant difference in the overall quality of your garment.
- Solution: Select high-quality notions that are compatible with your fabric and project. Match button colors and sizes to the garment’s design.
Resources for Further Learning and Inspiration
The world of sewing is vast and offers endless opportunities for learning and inspiration. Here are some resources to help you continue your sewing journey:
- Online Sewing Communities: Online forums and social media groups dedicated to sewing provide a platform for connecting with other sewers, sharing tips, and seeking advice.
- Solution: Join online sewing communities to learn from experienced sewers and get feedback on your projects.
- Sewing Blogs and Websites: Numerous sewing blogs and websites offer tutorials, pattern reviews, and sewing tips.
- Solution: Explore these resources to expand your sewing knowledge and find inspiration for new projects.
- Sewing Books: Sewing books provide comprehensive information on various sewing techniques, garment construction, and pattern drafting.
- Solution: Browse your local library or bookstore for sewing books that align with your interests and skill level.
- Sewing Classes: Sewing classes offer hands-on instruction and personalized guidance from experienced instructors.
- Solution: Enroll in a sewing class to learn new skills, improve your technique, and gain confidence in your sewing abilities.
Sewing patterns are your roadmap to creating amazing garments. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be able to tackle any pattern with ease, from simple projects to intricate designs. Remember, practice makes perfect! So, don’t be afraid to experiment, have fun, and enjoy the journey of learning to sew! Who knows, maybe you’ll even discover a hidden talent for creating beautiful and unique pieces!
Essential Questionnaire
What is a “grainline” and why is it important?
The grainline is a line on the pattern piece that indicates the direction of the fabric’s warp threads. It’s important to align the grainline with the fabric’s warp threads to ensure that the garment hangs properly and doesn’t distort.
How do I know what size pattern to choose?
Every pattern has a size chart. Measure yourself carefully and choose the size that corresponds to your measurements. Remember, patterns can be adjusted for a custom fit.
What if I make a mistake while sewing?
Don’t worry, everyone makes mistakes! It’s part of the learning process. Use a seam ripper to carefully remove any mistakes and try again. Don’t be afraid to ask for help if you need it!






