Was kostet eine kWh Strom, or “What does a kilowatt-hour of electricity cost,” is a fundamental question in understanding the cost of energy consumption. Electricity, a vital resource for modern life, comes at a price that can vary depending on a multitude of factors, including energy source, distribution costs, and government regulations. These variables lead to fluctuations in electricity prices across different regions and time periods, making it essential to understand the factors that influence them.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of electricity costs, examining the concept of kilowatt-hour (kWh) as the unit of energy consumption, the various electricity tariffs and billing structures, and practical strategies for estimating and reducing electricity expenses. By understanding these key aspects, individuals can gain greater control over their energy usage and make informed decisions about their electricity consumption.
Understanding Electricity Costs: Was Kostet Eine Kwh Strom
Electricity is an essential part of modern life, powering our homes, businesses, and transportation. But have you ever wondered how much it costs to run your appliances or charge your electric car? Understanding electricity costs can help you make informed decisions about energy consumption and save money.
Electricity Consumption: The Kilowatt-Hour, Was kostet eine kwh strom
Electricity consumption is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). One kilowatt-hour represents the amount of energy used by a 1-kilowatt appliance running for one hour. For example, a 100-watt light bulb running for 10 hours consumes 1 kWh of energy.
Factors Influencing Electricity Prices
Electricity prices are influenced by several factors:
Energy Source
The cost of generating electricity varies depending on the energy source used. For example, renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are generally cheaper than fossil fuels like coal and natural gas.
Distribution Costs
The cost of transmitting and distributing electricity from power plants to consumers also contributes to electricity prices. This includes the cost of building and maintaining power lines, substations, and other infrastructure.
Government Regulations
Government policies and regulations can impact electricity prices. For example, subsidies for renewable energy sources can lower electricity costs, while taxes on fossil fuels can increase them.
Electricity Price Variations
Electricity prices can vary significantly across different regions and time periods.
Regional Variations
Electricity prices can differ based on factors like:
- Energy source availability: Regions with abundant renewable energy resources may have lower electricity prices than those reliant on fossil fuels.
- Population density: Areas with high population density may have higher distribution costs and therefore higher electricity prices.
- Competition in the electricity market: Regions with more electricity providers tend to have lower prices due to competition.
Time-of-Day Variations
Electricity prices can fluctuate throughout the day, often being higher during peak demand periods.
- Peak demand: During peak hours, when electricity demand is high, prices are usually higher to incentivize consumers to reduce their usage.
- Off-peak demand: During off-peak hours, when electricity demand is low, prices are often lower to encourage consumers to use electricity during these times.
Electricity Tariffs and Billing

Electricity tariffs are the rates at which electricity is charged to consumers. They determine the cost of electricity based on the amount consumed. Understanding electricity tariffs is crucial for managing your energy costs effectively.
Types of Electricity Tariffs
Electricity tariffs are designed to reflect the cost of producing and delivering electricity. There are various tariff structures, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Flat Rate Tariffs: This is the simplest tariff structure. You pay a fixed price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity consumed, regardless of the time of day or the amount consumed. Flat rate tariffs are straightforward but may not be the most cost-effective option, especially for consumers with fluctuating energy usage patterns.
- Tiered Rate Tariffs: Tiered rate tariffs offer different prices per kWh depending on the amount of electricity consumed. This structure encourages energy conservation by charging higher rates for higher consumption levels. For example, you might pay a lower rate for the first 500 kWh consumed and a higher rate for anything beyond that.
- Time-of-Use Tariffs: Time-of-use tariffs vary the price of electricity depending on the time of day or day of the week. Electricity is typically cheaper during off-peak hours (e.g., overnight or weekends) and more expensive during peak hours (e.g., weekdays between 4 pm and 8 pm). This structure encourages consumers to shift their energy usage to off-peak hours to save money.
Electricity Bill Calculation
Your electricity bill is calculated based on your electricity consumption and the applicable tariff. The calculation typically involves the following steps:
- Meter Reading: Your electricity meter tracks your total electricity consumption. Your electricity provider takes meter readings at regular intervals to determine your consumption.
- Consumption Calculation: The difference between two consecutive meter readings represents your electricity consumption for the billing period.
- Tariff Application: The electricity consumption is then multiplied by the applicable tariff rate to calculate the cost of electricity.
- Other Charges: Your electricity bill may include additional charges, such as taxes, network charges, and supply charges. These charges are typically fixed or based on your connection capacity.
- Total Bill: The cost of electricity, plus any additional charges, equals your total electricity bill.
Example Electricity Bill
Here is an example of a typical electricity bill and its breakdown of costs:
| Item | Cost |
|---|---|
| Electricity Consumption (500 kWh) | $50 |
| Network Charges | $10 |
| Supply Charges | $5 |
| Taxes | $5 |
| Total Bill | $70 |
The specific breakdown of your electricity bill may vary depending on your electricity provider and tariff plan.
Estimating Electricity Costs
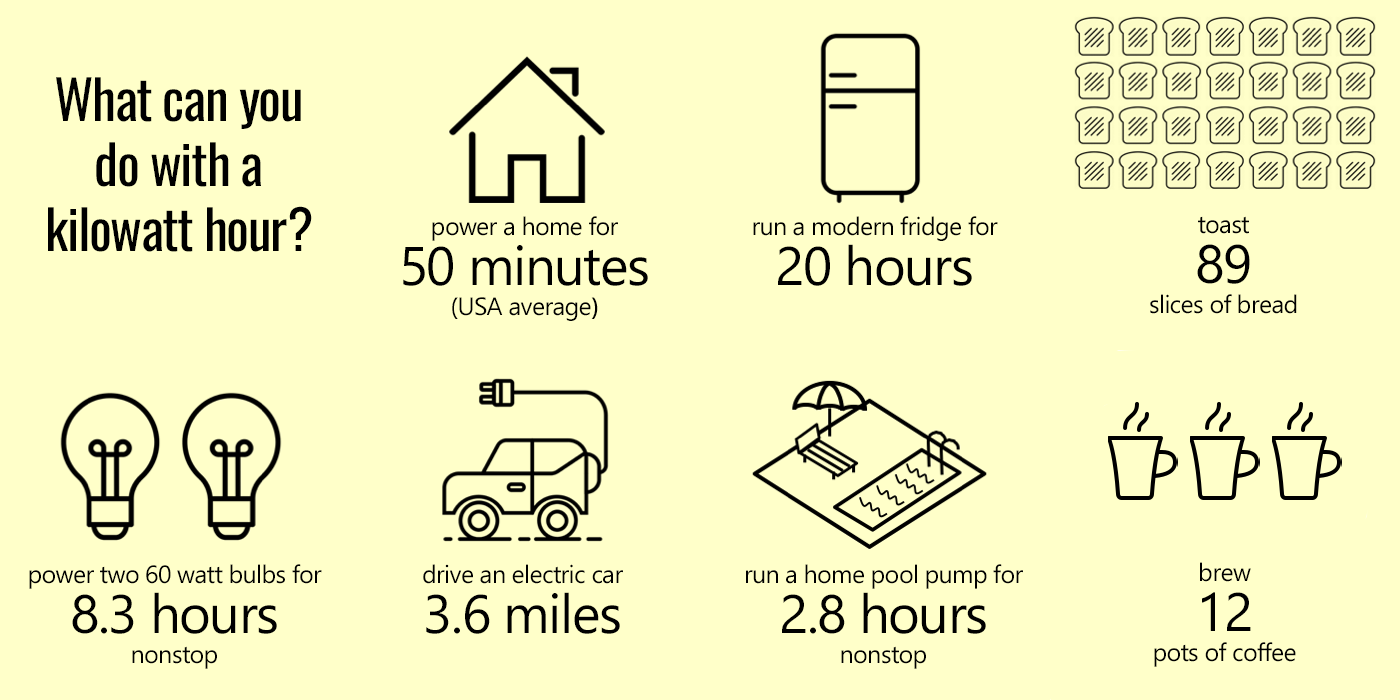
Understanding how much electricity you use and its cost is crucial for managing your energy consumption and expenses. By estimating your electricity consumption for different appliances and devices, you can gain insight into your energy usage patterns and identify areas for potential savings.
Estimating Electricity Consumption
Accurately estimating your electricity consumption for different appliances and devices is a key step in understanding your electricity costs. To do this, you can use the following methods:
- Check Appliance Labels: Most appliances come with energy labels that provide information about their power consumption in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). This information can be used to calculate the energy consumption of the appliance over a specific period.
- Use Online Calculators: Numerous online calculators are available that allow you to estimate the electricity consumption of different appliances based on their wattage, usage time, and electricity tariff. These calculators can be helpful for quickly determining the energy consumption of common household appliances.
- Monitor Electricity Consumption: Smart meters or energy monitors can provide real-time data on your electricity consumption. By analyzing this data, you can identify appliances that consume the most energy and make informed decisions about their usage.
Impact of Energy Efficiency on Electricity Costs
Energy efficiency plays a significant role in reducing electricity consumption and costs. By using energy-efficient appliances, you can significantly reduce your electricity bill.
- Energy Star Rating: Look for appliances with an Energy Star rating, which indicates that they meet certain energy efficiency standards. These appliances typically consume less energy than standard models, resulting in lower electricity bills.
- LED Lighting: Replacing traditional incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs can significantly reduce your lighting energy consumption. LED bulbs consume significantly less energy than incandescent bulbs while providing similar brightness.
- Insulation: Proper insulation in your home can prevent heat loss during winter and heat gain during summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems, and subsequently, electricity consumption.
Average Cost of Electricity for Common Household Appliances
The following table Artikels the average cost of electricity for common household appliances based on their wattage and usage time.
| Appliance | Wattage (W) | Usage Time (Hours) | Daily Cost (€) | Monthly Cost (€) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 100 | 24 | 0.24 | 7.20 |
| Washing Machine | 1500 | 1 | 0.36 | 10.80 |
| Television | 100 | 4 | 0.04 | 1.20 |
| Computer | 100 | 8 | 0.08 | 2.40 |
| Electric Kettle | 1500 | 0.5 | 0.09 | 2.70 |
Note: These costs are estimates and may vary depending on your electricity tariff and usage patterns.
Saving on Electricity Costs

Reducing your electricity consumption can significantly lower your energy bills and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle. This section explores practical strategies and technologies for saving energy at home.
Energy-Efficient Appliances
Energy-efficient appliances are designed to consume less electricity while providing the same or even better performance. Choosing appliances with the Energy Star label is a good starting point.
- Refrigerators: Look for models with high energy efficiency ratings (EERs) and consider features like automatic defrosting and door alarms.
- Washing Machines and Dryers: Opt for front-loading washing machines, as they use less water and energy than top-loading models. Consider using a clothesline for drying, which is the most energy-efficient option.
- Dishwashers: Choose energy-efficient models with features like air drying and delayed start timers.
- Lighting: Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with LED lights, which consume significantly less energy and last much longer.
Turning Off Lights and Unplugging Devices
Simple habits can make a difference. Turning off lights when you leave a room and unplugging devices when not in use can significantly reduce phantom load – the electricity consumed by devices that are plugged in but not actively in use.
Energy-Saving Options
- Solar Panels: Installing solar panels on your roof can generate clean electricity from sunlight, reducing your reliance on the grid and lowering your electricity bills. The cost of solar panels has decreased significantly in recent years, making them a more accessible option for many homeowners.
- Smart Home Technologies: Smart thermostats, smart plugs, and other smart home devices can help you monitor and control your energy consumption. For example, a smart thermostat can automatically adjust your heating and cooling system based on your schedule and preferences, optimizing energy efficiency.
Conducting an Energy Audit at Home
An energy audit can help you identify areas where you can save energy and money. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Gather Information: Collect your recent electricity bills and make a list of your major appliances and their energy consumption ratings.
- Inspect Your Home: Walk through your home and identify areas where you can improve energy efficiency, such as drafty windows and doors, poorly insulated attics and basements, and inefficient lighting.
- Consider Professional Help: If you want a more comprehensive energy audit, you can hire a qualified energy auditor. They can use specialized equipment to identify areas of energy loss and recommend specific solutions.
Navigating the complexities of electricity costs requires a comprehensive understanding of the factors at play. By grasping the concept of kilowatt-hour, exploring different electricity tariffs and billing structures, and adopting practical strategies for estimating and reducing consumption, individuals can empower themselves to make informed decisions about their energy usage. This knowledge fosters a greater awareness of electricity costs, promoting responsible consumption and potentially leading to significant savings on energy bills.
Questions and Answers
How do I read my electricity bill?
Electricity bills typically include information about your energy consumption (kWh), the tariff applied, and the total cost. It may also provide a breakdown of costs for different periods or usage patterns.
What are some examples of energy-efficient appliances?
Energy-efficient appliances are often labeled with Energy Star ratings. Examples include LED light bulbs, Energy Star refrigerators, and high-efficiency washing machines and dryers.
How can I find out my local electricity rates?
You can usually find your local electricity rates on the website of your electricity provider or by contacting their customer service department.
What are the benefits of solar panels?
Solar panels can reduce your reliance on the electricity grid, potentially lowering your electricity bills and reducing your carbon footprint.






