Was kostet Strom? It’s a question we all ask ourselves, especially when we see that energy bill creeping up. Electricity is essential, powering our homes, businesses, and lives, but the cost can be a real pain. Understanding how electricity costs are determined is key to making smart choices and potentially saving some serious cash. So, let’s break down the factors that influence your electricity bill and explore ways to keep those costs in check.
From the energy providers setting the prices to your own energy consumption habits, there are a lot of moving parts. We’ll dive into the different pricing structures, discuss the impact of tariffs and taxes, and even look at how regional variations and market fluctuations can affect your bottom line. Don’t worry, we’ll keep it simple and relatable – no need for complicated jargon.
By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of what drives your electricity costs and be equipped to make informed decisions about your energy use.
Understanding “Was kostet Strom?”

In the context of energy costs, “Was kostet Strom?” translates to “How much does electricity cost?”. It’s a fundamental question for anyone seeking to understand their energy bills and manage their energy consumption.This question is particularly relevant in everyday life, as electricity powers our homes, businesses, and industries. Understanding the cost of electricity helps us make informed decisions about our energy usage and find ways to save money.
Factors Influencing Electricity Costs
Electricity costs are influenced by various factors, including:
- Energy Consumption: The more electricity you use, the higher your bill will be. This is directly proportional to your usage.
- Electricity Tariff: Different energy providers offer various tariffs with different rates based on factors such as time of day, energy consumption, and contract duration.
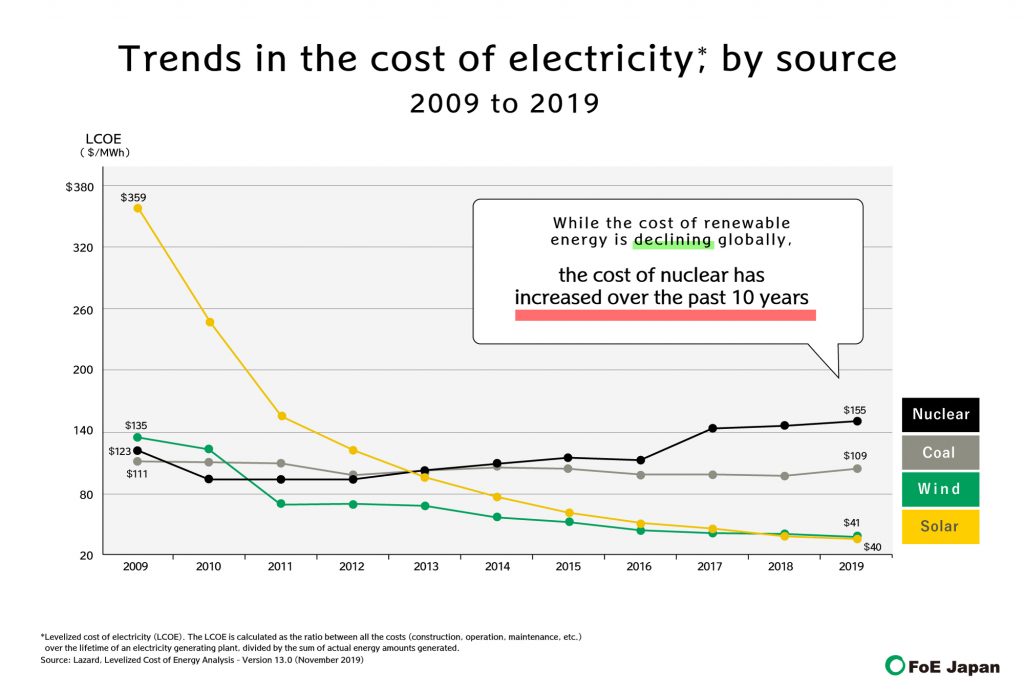
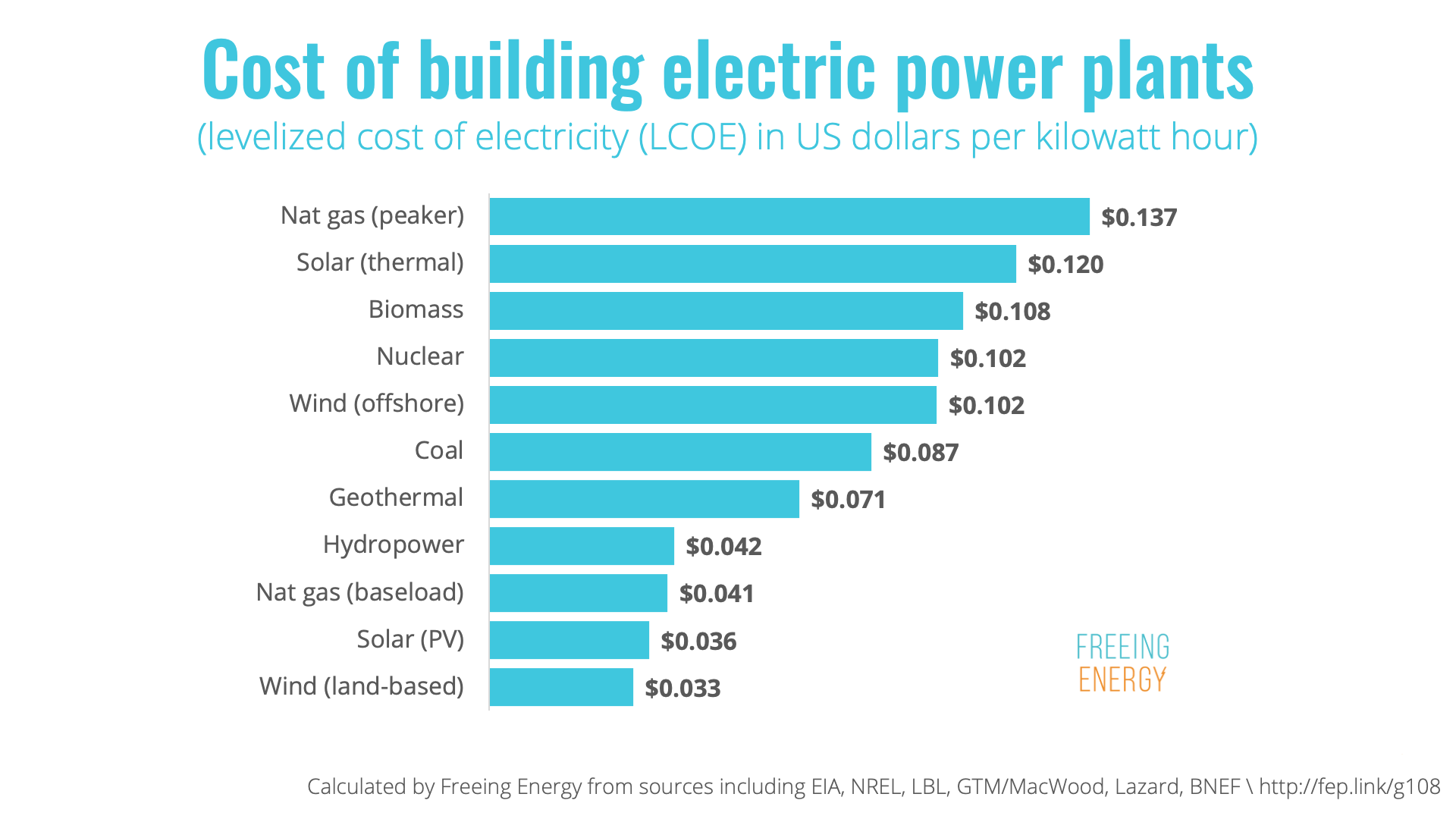
- Energy Source: The source of electricity generation, whether it’s fossil fuels, renewable energy, or nuclear power, impacts its cost.
For instance, renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are generally considered more sustainable but may have higher upfront costs.
- Government Regulations and Taxes: Government policies, including taxes and subsidies, can influence electricity prices.
- Network Costs: Costs associated with maintaining and expanding the electricity grid, including transmission and distribution, are factored into electricity prices.
Factors Determining Electricity Costs: Was Kostet Strom
Understanding the factors that influence electricity costs is crucial for making informed decisions about energy consumption and managing household budgets. Several key elements contribute to the final price you pay for electricity.
Energy Providers and Pricing Structures
Energy providers play a significant role in determining electricity costs. They generate and distribute electricity to consumers and establish pricing structures based on various factors.
- Market Competition: In regions with competitive energy markets, multiple providers offer different rates and plans, leading to potential price variations. Consumers can compare offers and choose the most suitable option.
- Cost of Generation: The cost of generating electricity varies depending on the energy source used (e.g., coal, natural gas, renewable sources). Providers pass these costs onto consumers through their pricing structures.
- Distribution and Transmission: The infrastructure used to transport electricity from power plants to consumers also contributes to the final price. Costs associated with maintaining and upgrading this infrastructure are factored into pricing.
- Regulatory Costs: Governments impose regulations on energy providers to ensure safety, environmental protection, and fair competition. These regulations can influence electricity costs.
Energy Consumption
Your electricity consumption directly impacts your overall costs. Higher energy consumption translates to higher bills.
- Appliance Efficiency: Energy-efficient appliances consume less electricity, reducing your bills. Choosing appliances with higher energy star ratings can significantly impact your costs.
- Usage Patterns: Using electricity-intensive appliances during peak hours (when demand is high) often results in higher rates. Shifting usage to off-peak hours can save money.
- Household Size: Larger households typically consume more electricity due to increased appliance use and lighting needs.
Tariffs and Taxes
Energy providers often apply tariffs and taxes to electricity bills. These charges can vary based on location and government policies.
- Time-of-Use Tariffs: These tariffs charge different rates depending on the time of day or day of the week. Higher rates are typically applied during peak demand periods.
- Demand Charges: Some providers impose demand charges based on the highest level of electricity usage during a specific period.
- Sales Taxes: Most regions impose sales taxes on electricity bills, adding to the final cost.
- Environmental Fees: Some governments levy fees on electricity bills to support environmental initiatives or offset the environmental impact of electricity generation.
Regional Variations and Market Fluctuations
Electricity costs can vary significantly across different regions and are influenced by factors such as:
- Availability of Resources: Regions with abundant renewable energy sources may have lower electricity costs compared to areas relying heavily on fossil fuels.
- Market Competition: The level of competition among energy providers in a region can impact electricity prices.
- Government Policies: Government regulations and subsidies can influence electricity costs in different regions.
- Fuel Prices: Fluctuations in fuel prices, particularly for natural gas and coal, can affect the cost of electricity generation and impact consumer prices.
Calculating Electricity Costs
Understanding how electricity costs are calculated is essential for managing your energy expenses. By breaking down the factors that contribute to your electricity bill, you can make informed decisions about your energy consumption and potentially reduce your costs.
Understanding Electricity Costs
The cost of electricity is determined by the amount of energy you consume, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), and the price per kWh set by your electricity provider.
Electricity Cost = Energy Consumption (kWh) x Price per kWh
Calculating Your Electricity Bill
To estimate your energy bill, you can follow these steps:
- Identify your electricity consumption: Check your previous electricity bills or use a meter to track your energy usage. This will give you an idea of your average daily, weekly, or monthly consumption.
- Determine your electricity tariff: Your electricity provider will have a specific tariff structure, which Artikels the price per kWh for different consumption levels. This tariff may vary depending on the time of day or the season.
- Calculate your total electricity cost: Multiply your energy consumption (kWh) by the price per kWh from your tariff.
Example:
Let’s assume your monthly energy consumption is 500 kWh, and your electricity tariff is €0.25 per kWh.
Total Electricity Cost = 500 kWh x €0.25/kWh = €125
Cost Scenarios, Was kostet strom
Here is a table illustrating different cost scenarios for various consumption levels and tariffs:
| Consumption (kWh) | Tariff (€/kWh) | Total Cost (€) |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 0.25 | 125 |
| 750 | 0.25 | 187.50 |
| 500 | 0.30 | 150 |
| 750 | 0.30 | 225 |
Saving on Electricity Costs
Reducing electricity consumption is crucial for both environmental sustainability and personal finances. By implementing energy-saving strategies, you can significantly lower your electricity bills and contribute to a greener future.
Energy-Efficient Appliances and Lighting
Energy-efficient appliances and lighting play a significant role in reducing electricity consumption. These products are designed to use less energy while providing the same level of performance, leading to substantial savings over time.
Energy-Efficient Appliances
Choosing energy-efficient appliances can significantly impact your electricity bill. Look for appliances with an Energy Star label, which indicates that they meet specific energy-efficiency standards.
- Refrigerators: Modern refrigerators with advanced insulation and efficient compressors consume less energy than older models.
- Dishwashers: Energy-efficient dishwashers use less water and energy to clean dishes effectively.
- Washing Machines: High-efficiency washing machines use less water and energy per cycle, reducing both your electricity and water bills.
- Dryers: Energy-efficient dryers utilize heat pumps or other technologies to dry clothes faster and consume less energy.
Energy-Efficient Lighting
Replacing traditional incandescent bulbs with LED or CFL bulbs can dramatically reduce your electricity consumption.
- LED Bulbs: LED bulbs are highly energy-efficient, lasting longer and consuming significantly less energy than incandescent bulbs.
- CFL Bulbs: CFL bulbs are more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs but less efficient than LEDs. They last longer than incandescent bulbs but not as long as LEDs.
Alternative Energy Sources
The rising cost of electricity has prompted many to seek alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources. Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, offer a promising solution to reduce electricity costs and lessen our dependence on non-renewable resources.
Cost-Effectiveness of Renewable Energy Sources
The cost-effectiveness of renewable energy sources varies depending on the specific technology and location.
- Solar Energy: Solar panels have become increasingly affordable, with prices declining significantly in recent years. The initial investment cost for a solar panel system can be offset by long-term savings on electricity bills. In many regions, solar energy is now cost-competitive with traditional energy sources, especially when considering government incentives and tax credits. For example, in sunny regions like California, solar energy can be significantly cheaper than grid electricity, with payback periods as short as 5 years.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines are a mature technology with established costs. The cost of wind energy has been steadily decreasing, and in some locations, it is now the cheapest form of electricity generation. However, the initial investment in wind turbines can be substantial, and the cost-effectiveness depends on factors such as wind resource availability and land use. For example, offshore wind farms, while potentially generating large amounts of electricity, require significant upfront investment and can be more expensive than onshore wind farms.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy is a reliable and sustainable source of electricity, but it is geographically limited. The cost of geothermal energy is relatively high compared to other renewable sources, but it can be cost-effective in regions with abundant geothermal resources. The initial investment in geothermal power plants is significant, but the operating costs are low due to the continuous availability of geothermal heat.
For instance, Iceland, known for its geothermal activity, relies heavily on geothermal energy for electricity generation, making it one of the most cost-effective options in the country.
Benefits and Challenges of Transitioning to Alternative Energy
Transitioning to alternative energy sources presents both benefits and challenges.
- Benefits:
- Reduced Electricity Costs: Renewable energy sources can help reduce electricity costs in the long run, especially as the technology continues to improve and costs decrease.
- Environmental Sustainability: Renewable energy sources do not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants, making them a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels.
- Energy Security: Relying on renewable energy sources reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, improving energy security and reducing geopolitical risks.
- Job Creation: The renewable energy sector is creating new jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, contributing to economic growth.
- Challenges:
- Intermittency: Solar and wind energy are intermittent sources, meaning they are not always available. This requires efficient energy storage solutions and grid management systems.
- Initial Investment Costs: The initial investment in renewable energy infrastructure can be significant, requiring government support and private investment.
- Land Use: Large-scale solar and wind farms require substantial land, which can raise concerns about land use and environmental impact.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous research and development are necessary to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of renewable energy technologies.
Navigating the world of electricity costs can feel like a maze, but with a little knowledge and awareness, you can take control. By understanding the factors that influence your bill, you can make conscious choices about your energy consumption and explore ways to save money. Remember, every little bit helps! So, ditch the energy-guzzling habits and embrace a more efficient approach.
It’s time to get smart about your electricity costs and make those energy bills work for you, not against you.
Popular Questions
What are the main factors influencing electricity costs?
Electricity costs are influenced by a combination of factors including energy consumption, tariffs, taxes, energy provider pricing structures, regional variations, and market fluctuations.
How can I calculate my electricity costs?
You can calculate your electricity costs by multiplying your energy consumption (in kilowatt-hours) by your electricity tariff (price per kilowatt-hour).
Are there any government subsidies or programs available for energy savings?
Yes, many governments offer subsidies and programs to encourage energy savings. These programs can include rebates for energy-efficient appliances, tax credits for solar panels, and financial assistance for energy audits.
What are the most cost-effective renewable energy sources?
Solar and wind energy are generally considered the most cost-effective renewable energy sources, but the best option will depend on your specific location and energy needs.






