Was kostet Strom kWh? This question is a crucial one for anyone seeking to understand their electricity bills and navigate the complexities of energy consumption. The cost of electricity per kilowatt-hour (kWh) is influenced by a multitude of factors, including energy source, consumption patterns, government policies, and market dynamics. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed decisions about energy usage and minimizing electricity expenses.
The cost of electricity is not a fixed value, but rather a dynamic figure that fluctuates based on several factors. These factors include the cost of generating electricity from different sources, transmission and distribution costs, taxes, and government regulations. Additionally, individual consumption patterns play a significant role in determining the final cost of electricity for each household or business.
Understanding “Was kostet Strom kWh?”

You’re probably wondering what “Was kostet Strom kWh?” means and how it affects your electricity bill. It’s all about the cost of electricity, but let’s break it down.
What is “Strom kWh”?
“Strom kWh” refers to the amount of electricity you consume, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). It’s like a unit of energy used to power your appliances, lights, and other devices. Think of it like a gallon of gas for your car – the more you use, the more it costs.
Factors Influencing Electricity Prices
Several factors influence the price of electricity per kWh. These include:* Energy Source: The type of energy source used to generate electricity (coal, natural gas, nuclear, wind, solar, etc.) influences the cost. For example, renewable energy sources like wind and solar are often cheaper in the long run, but they may have higher initial setup costs.
Market Conditions
Like any other commodity, electricity prices fluctuate based on supply and demand. If demand is high and supply is low, prices will increase.
Transmission and Distribution
The cost of transporting electricity from power plants to your home is also factored into the price.
Taxes and Fees
Local, state, and federal taxes and fees can add to the overall cost of electricity.
Energy Efficiency
Using energy-efficient appliances and devices can help you save money on your electricity bill.
Electricity Tariffs and Pricing Structures, Was kostet strom kwh
Electricity providers often offer different tariffs with varying pricing structures. These can include:* Flat Rate: A fixed price per kWh, regardless of how much electricity you use.
Time-of-Use
Different rates depending on the time of day or day of the week. For example, electricity might be cheaper during off-peak hours (like late at night or early mornings).
Tiered Rates
Different prices per kWh based on the amount of electricity you consume. The more you use, the higher the price per kWh.
Electricity prices can vary significantly depending on your location and the electricity provider you choose. It’s essential to compare different tariffs and pricing structures to find the best deal for your needs.
Factors Affecting Electricity Costs
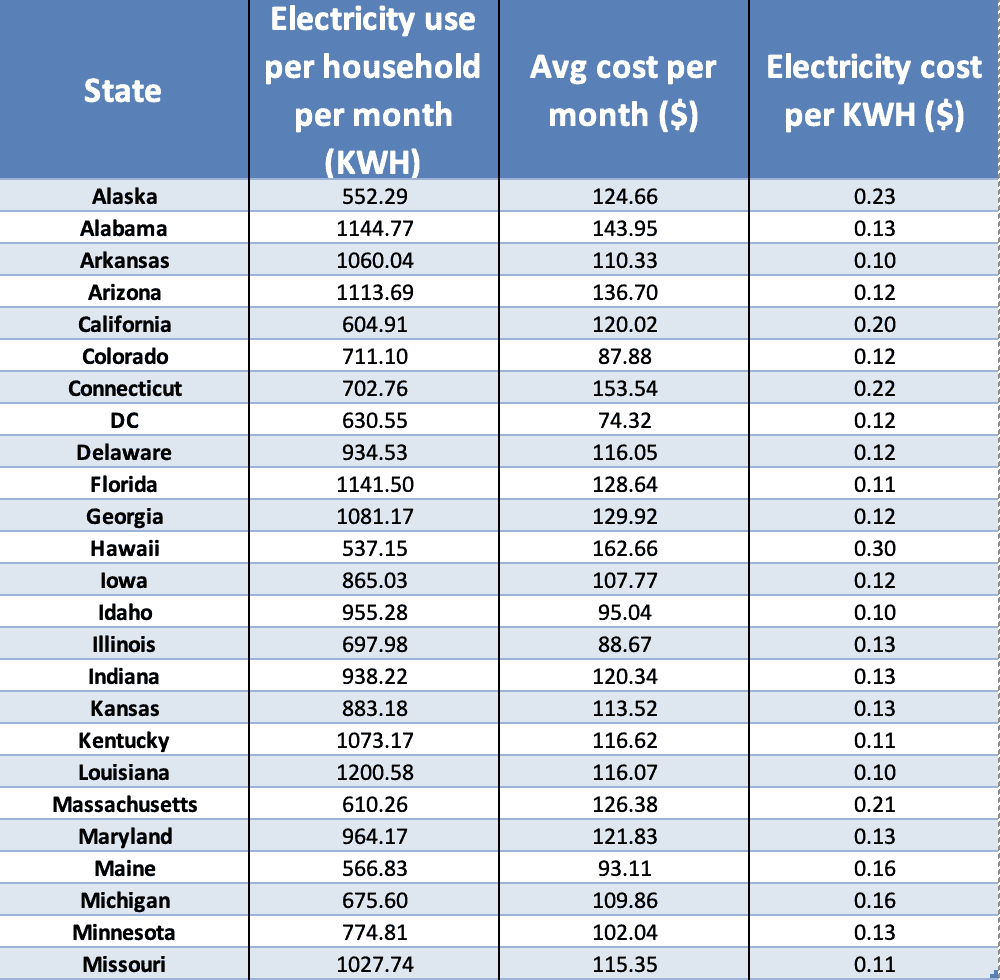
You’ve got your electricity bill in hand, and it’s got you scratching your head, wondering why it’s so high. You’re not alone! Understanding what makes up your electricity bill is key to managing your energy costs and keeping your wallet happy.
Components of an Electricity Bill
Your electricity bill is a breakdown of the costs associated with your energy usage. Think of it like a pizza with different toppings, each contributing to the final price.
- Energy Charges: This is the biggest slice of your bill, representing the cost of the actual electricity you consume. The amount you pay depends on the kilowatt-hours (kWh) you use. It’s like paying for the pizza dough and cheese – the essential stuff.
- Taxes and Fees: These are extra charges added to your bill, like taxes, regulatory fees, and other charges. Think of them as the pizza toppings – they add to the cost but can be varied.
- Other Charges: This category might include charges for things like monthly service fees, fuel adjustments, or billing adjustments. It’s like the extra toppings you might get on your pizza, like mushrooms or olives.
Energy Consumption Patterns
You know how your pizza cravings change depending on the day? The same goes for your electricity usage! Your energy consumption patterns have a major impact on your bill. Let’s break it down:
- Time of Day: Electricity prices can fluctuate throughout the day, with peak periods often costing more. Think of it like the rush hour for your energy consumption – it’s more expensive to travel during peak times.
- Seasonality: You’re more likely to crank up the AC in the summer, right? That means higher energy consumption and a bigger bill. It’s like ordering a large pizza when you’re super hungry!
- Usage Habits: The more you use electricity, the more you pay. It’s like ordering a pizza with all the toppings – the more you add, the higher the price.
Electricity Cost from Different Energy Sources
Just like you can choose different types of pizza crust, electricity comes from different sources, each with its own cost.
- Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels, like coal and natural gas, are the most common sources of electricity. While they’re often cheaper than renewable sources, they contribute to environmental pollution. Think of it like a classic pizza – it’s a familiar and reliable choice, but not necessarily the healthiest option.
- Renewable Energy: Renewable sources, like solar and wind power, are becoming increasingly popular. They’re often more expensive upfront but have lower operating costs in the long run. Think of it like a gourmet pizza – it might cost a little more, but it’s healthier and sustainable in the long run.
- Nuclear Power: Nuclear power is a low-carbon source of electricity, but it comes with safety concerns and waste disposal issues. It’s like a pizza with a unique flavor profile – it’s different, but not everyone is a fan.
Tips for Reducing Electricity Costs
You don’t have to be a superhero to save energy and lower your electricity bills. With a few simple changes, you can make a big difference in your home’s energy consumption. Let’s dive into some practical tips that can help you shrink your energy footprint and your energy bill!
Energy-Saving Habits
Making small changes in your daily routine can have a significant impact on your electricity consumption. Here are some energy-saving habits to adopt:
- Turn off lights when you leave a room: This might seem obvious, but it’s a simple and effective way to save energy. Remember, every watt counts!
- Unplug devices when not in use: Even when they’re turned off, devices like phone chargers, TVs, and computers still draw a small amount of power. Unplugging them when not in use can add up to significant savings over time. Think of it as giving your devices a mini-vacation!
- Use natural light: Open blinds and curtains during the day to take advantage of natural sunlight. This reduces your reliance on artificial light, especially during daylight hours. Let the sunshine brighten your home!
- Wash clothes in cold water: Heating water for washing accounts for a significant portion of your energy consumption. Washing clothes in cold water can save you a ton of energy, and your clothes will thank you for it!
- Air dry clothes: Skip the dryer whenever possible and let your clothes air dry. It’s a free and eco-friendly way to dry your clothes, and it can help reduce your energy bill. Think of it as a natural spa treatment for your clothes!
- Use a programmable thermostat: Set your thermostat to automatically adjust the temperature based on your schedule. This helps prevent your heating and cooling systems from running unnecessarily, saving you energy and money. It’s like giving your home a personalized energy plan!
- Seal air leaks: Check for drafts around windows and doors and seal them with weatherstripping or caulk. This prevents warm or cool air from escaping, reducing your reliance on your HVAC system. It’s like giving your home a cozy winter coat!
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Replacing older appliances with energy-efficient models can significantly reduce your electricity consumption. Look for appliances with the Energy Star label, which indicates they meet certain energy efficiency standards. It’s like upgrading your home’s energy game!
Energy-Efficient Appliances
Investing in energy-efficient appliances can be a smart move for your wallet and the environment. These appliances are designed to use less energy while still providing the same level of performance.
- Refrigerators: Modern refrigerators are much more energy-efficient than older models. Look for refrigerators with features like automatic defrost and adjustable shelves. It’s like having a refrigerator that’s always on its A-game!
- Dishwashers: Energy-efficient dishwashers use less water and energy than their predecessors. Look for models with features like a sensor that automatically adjusts the wash cycle based on the level of dirt. It’s like having a dishwasher that’s always thinking ahead!
- Washing machines: Energy-efficient washing machines use less water and energy per load. Look for models with features like a water-level sensor and a high-efficiency impeller. It’s like having a washing machine that’s always on a mission to save energy!
- Dryers: Energy-efficient dryers use less energy to dry your clothes. Look for models with features like a sensor that automatically stops the cycle when the clothes are dry. It’s like having a dryer that’s always in control!
- Lighting: Switching to LED light bulbs is one of the easiest and most effective ways to save energy. LED bulbs use significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last much longer. It’s like giving your home a bright and energy-saving makeover!
Renewable Energy Sources
Harnessing the power of the sun, wind, and other renewable resources can significantly reduce your reliance on fossil fuels and lower your electricity bills.
- Solar Panels: Installing solar panels on your roof can generate electricity from sunlight, reducing your dependence on the grid. Solar panels are a long-term investment that can pay for itself over time through reduced energy costs. It’s like having a mini power plant on your roof!
- Wind Turbines: If you live in a windy area, installing a small wind turbine can generate electricity from the wind. Wind turbines are a great way to reduce your carbon footprint and save money on your electricity bill. It’s like having a personal wind farm in your backyard!
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from the Earth’s core to generate electricity. Geothermal energy is a clean and reliable source of energy that can significantly reduce your energy costs. It’s like tapping into the Earth’s own natural energy source!
Electricity Tariffs and Pricing Structures
Electricity tariffs are the pricing structures used by energy providers to charge customers for their electricity consumption. Understanding these tariffs is crucial for making informed decisions about your electricity usage and minimizing your energy bills.
Types of Electricity Tariffs
Electricity tariffs can vary widely, offering different pricing models to cater to diverse consumption patterns and preferences.
- Fixed Tariffs: A fixed tariff offers a consistent price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) throughout the billing cycle, regardless of your energy consumption. This predictable pricing structure provides budgeting stability and eliminates fluctuations in your energy bills.
- Variable Tariffs: A variable tariff, as the name suggests, allows the price per kWh to fluctuate based on market conditions, such as changes in fuel prices or wholesale electricity costs. This can lead to unpredictable energy bills, but it may also offer potential savings if market conditions are favorable.
- Time-of-Use Tariffs: Time-of-use tariffs, often referred to as “TOU” tariffs, offer varying electricity prices based on the time of day or day of the week. These tariffs encourage consumers to shift their energy usage to off-peak hours when electricity demand is lower, often resulting in lower prices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Tariff Types
Each electricity tariff type comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it important to carefully consider your consumption patterns and budget when selecting the most suitable option.
Fixed Tariffs
- Advantages:
- Predictable energy bills, making budgeting easier.
- Protection against fluctuating electricity prices.
- Disadvantages:
- May not offer the lowest prices if market conditions are favorable.
- May not provide incentives to reduce energy consumption.
Variable Tariffs
- Advantages:
- Potential for lower prices if market conditions are favorable.
- Can incentivize consumers to reduce energy consumption during periods of high prices.
- Disadvantages:
- Unpredictable energy bills, making budgeting difficult.
- Risk of higher prices if market conditions are unfavorable.
Time-of-Use Tariffs
- Advantages:
- Potential for lower energy bills by shifting energy usage to off-peak hours.
- Encourages energy conservation and efficiency.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires careful planning and adjustment of energy usage habits.
- May not be suitable for all consumers, especially those with inflexible schedules.
Choosing the Most Suitable Electricity Tariff
The best electricity tariff for you depends on your individual energy consumption patterns, budget, and risk tolerance.
- Fixed tariffs are a good choice for consumers who value predictability and budgeting stability, even if they may not offer the lowest prices.
- Variable tariffs are suitable for those who are comfortable with price fluctuations and are willing to take a risk for the potential of lower prices.
- Time-of-Use tariffs are ideal for consumers who can adjust their energy usage habits to take advantage of off-peak hours and lower prices.
It’s also important to consider the following factors:
- Your energy consumption patterns: How much energy do you use on average? Do you have a consistent energy usage pattern, or does it vary significantly?
- Your budget: How much are you willing to spend on electricity?
- Your risk tolerance: Are you comfortable with unpredictable energy bills, or do you prefer a consistent price?
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the electricity tariff that best suits your needs and helps you manage your energy costs effectively.
Electricity Market Dynamics
The price of electricity is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, making it a dynamic and often unpredictable market. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for both consumers and energy providers.
Factors Influencing Electricity Prices
The price of electricity is determined by the forces of supply and demand. Here are some key factors that affect the cost of electricity:
- Fuel Costs: The primary fuel source for electricity generation, such as coal, natural gas, or nuclear power, significantly impacts the cost of production. Fluctuations in fuel prices due to global market conditions, geopolitical events, or weather patterns directly affect electricity prices. For example, a rise in natural gas prices due to increased demand during a cold winter will likely lead to higher electricity prices.
- Generation Capacity: The availability of electricity generation capacity plays a vital role in price determination. If the demand for electricity exceeds the available generation capacity, prices can surge as power companies scramble to meet the demand. Conversely, if there is excess generation capacity, prices may fall as companies compete for customers.
- Transmission and Distribution Costs: The cost of transmitting electricity from power plants to consumers and distributing it within a region is factored into the final price. This includes maintenance of power lines, transformers, and other infrastructure.
- Renewable Energy Sources: The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power can influence electricity prices. While these sources are often seen as cost-effective in the long run, their intermittent nature (dependent on weather conditions) can create challenges for grid management and affect prices.
- Government Policies and Regulations: Government policies and regulations can have a significant impact on electricity prices. Carbon taxes, subsidies for renewable energy, and regulations on emissions can affect the cost of production and influence market dynamics.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies play a critical role in shaping the electricity market and influencing electricity costs. Here are some key areas where government intervention impacts prices:
- Renewable Energy Mandates: Many governments have set targets for the share of renewable energy in their electricity mix. These mandates can incentivize the development of renewable energy sources, potentially driving down costs over time. However, in the short term, they can also lead to higher prices as utilities comply with the mandates.
- Emissions Regulations: Regulations on carbon emissions, such as cap-and-trade programs, can influence electricity prices. By placing a price on carbon emissions, these regulations incentivize power companies to adopt cleaner technologies and reduce their environmental impact. This can lead to higher electricity prices in the short term but encourage long-term investments in cleaner energy sources.
- Market Structure and Regulation: Governments often regulate the structure and operation of electricity markets. This can include setting rules for competition, ensuring reliability of supply, and promoting consumer protection. These regulations can influence electricity prices by affecting the behavior of power companies and the overall market dynamics.
Trends in Electricity Prices
Electricity prices have been on an upward trend in recent years, driven by a combination of factors.
- Rising Fuel Costs: The global demand for energy has been steadily increasing, leading to higher prices for fossil fuels, which are used to generate electricity. This trend is expected to continue in the foreseeable future, potentially putting upward pressure on electricity prices.
- Increased Demand: As economies grow and populations expand, the demand for electricity continues to rise. This increasing demand can lead to higher prices, particularly during peak hours when generation capacity is strained.
- Transition to Renewable Energy: While the transition to renewable energy sources is generally seen as beneficial in the long run, it can also create challenges in the short term. The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, requires adjustments to grid management and can lead to price volatility.
Understanding the factors that influence the cost of electricity per kilowatt-hour (kWh) empowers consumers to make informed decisions about energy usage and potentially reduce their electricity bills. By implementing energy-saving strategies, choosing energy-efficient appliances, and exploring renewable energy options, individuals can contribute to a more sustainable future while managing their electricity costs effectively.
FAQ
How can I reduce my electricity consumption?
There are several ways to reduce your electricity consumption. Start by identifying your energy-intensive appliances and habits. Consider using energy-efficient appliances, switching to LED lighting, unplugging devices when not in use, and taking advantage of natural light.
What are the different types of electricity tariffs?
Electricity tariffs can be fixed, variable, or time-of-use. Fixed tariffs offer a consistent price per kWh, while variable tariffs fluctuate based on market conditions. Time-of-use tariffs charge different rates for electricity consumed at different times of the day.
What is the role of government policies in electricity costs?
Government policies play a significant role in shaping electricity costs. These policies include subsidies for renewable energy, regulations on emissions, and taxes on energy consumption. These policies aim to promote energy efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and ensure affordability.







