How to become a bloodstain pattern analyst – Have you ever watched a crime drama and wondered how investigators decipher the intricate patterns left behind by blood? Bloodstain pattern analysis is a fascinating and crucial field that uses the science of blood spatter to reconstruct crime scenes, identify weapons, and determine the sequence of events. Becoming a bloodstain pattern analyst requires a unique blend of scientific knowledge, meticulous observation, and a keen understanding of human biology.
This journey takes you through the necessary education, training, and essential skills needed to excel in this challenging and rewarding career.
This field offers a unique opportunity to contribute to justice by piecing together the puzzle of a crime. As a bloodstain pattern analyst, you will be involved in the collection and analysis of evidence, working alongside law enforcement and forensic teams to bring closure to victims and their families. It is a field that demands both intellectual curiosity and a strong sense of empathy, as you will be working with sensitive and often tragic cases.
Understanding Bloodstain Pattern Analysis: How To Become A Bloodstain Pattern Analyst
Bloodstain pattern analysis (BPA) is a forensic science discipline that involves the examination and interpretation of bloodstains at a crime scene. It helps investigators understand the events that occurred during a crime by analyzing the size, shape, and distribution of bloodstains.
History and Evolution of Bloodstain Pattern Analysis
BPA has a long and fascinating history, evolving alongside advancements in forensic science. Early investigations relied on simple observations of bloodstains, but as technology progressed, more sophisticated techniques emerged. The development of microscopy and photography allowed for detailed examination of bloodstains, while the introduction of blood typing and DNA analysis revolutionized the field.
- Early Observations: In the early days of forensic science, investigators relied on simple observations of bloodstains to determine the nature of the crime. For instance, the presence of bloodstains on a weapon or clothing could indicate the involvement of a suspect.
- Microscopy and Photography: The development of microscopy and photography in the late 19th and early 20th centuries significantly advanced BPA. These tools allowed for detailed examination of bloodstains, revealing information about their shape, size, and distribution.
- Blood Typing and DNA Analysis: The introduction of blood typing in the early 20th century and DNA analysis in the late 20th century revolutionized BPA. These techniques allowed for the identification of individuals from bloodstains, providing crucial evidence in criminal investigations.
Fundamental Principles and Concepts
BPA is based on the fundamental principles of physics, particularly the laws of motion and gravity. Blood behaves like any other liquid, following these laws when it is projected or deposited. By understanding these principles, analysts can interpret the patterns created by bloodstains and reconstruct the events that led to their formation.
- Bloodstain Characteristics: Bloodstains exhibit specific characteristics that provide information about the event that caused their formation. These characteristics include the size, shape, and distribution of the stains, as well as the presence of satellite spatter and other patterns.
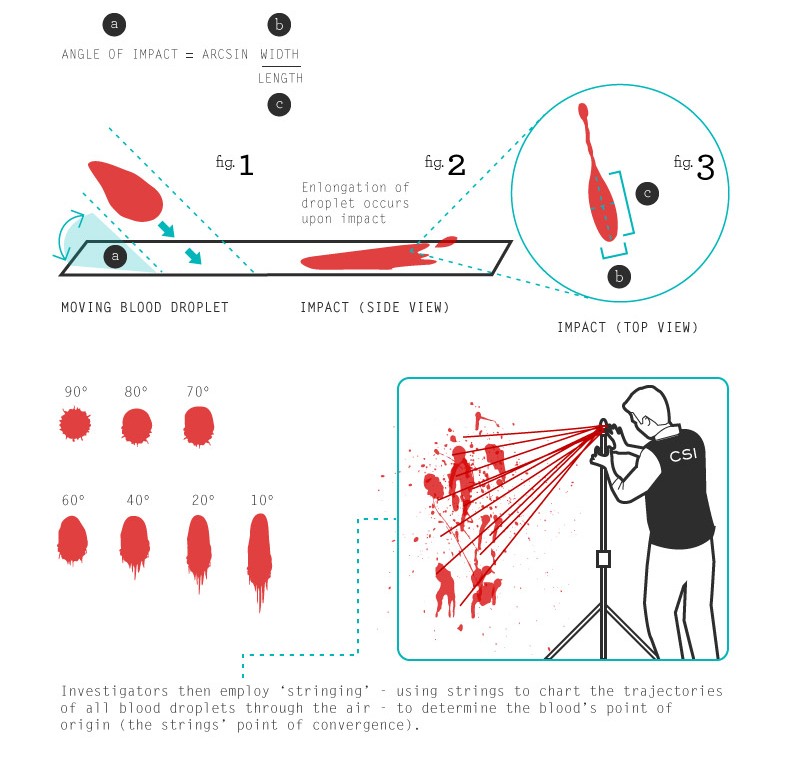
- Impact Angle: The angle at which blood strikes a surface affects the shape of the bloodstain. A high-impact angle will create a circular or nearly circular stain, while a low-impact angle will result in an elongated or elliptical stain.
- Blood Volume and Velocity: The volume and velocity of blood projected or deposited also influence the size and shape of the bloodstains. A high-velocity impact will create smaller, more numerous bloodstains, while a low-velocity impact will produce larger, fewer bloodstains.
Importance of Bloodstain Pattern Analysis in Crime Scene Investigations
BPA plays a crucial role in crime scene investigations by providing valuable information about the events that occurred. By analyzing bloodstains, investigators can:
- Determine the Position of the Victim and the Assailant: The location and distribution of bloodstains can indicate the positions of the victim and the assailant during the crime.
- Reconstruct the Sequence of Events: BPA can help reconstruct the sequence of events that led to the crime by analyzing the patterns of bloodstains and their relationship to other evidence.
- Identify the Type of Weapon Used: The size, shape, and distribution of bloodstains can provide clues about the type of weapon used in the crime.
- Corroborate or Disprove Witness Statements: BPA can help corroborate or disprove witness statements by providing objective evidence about the events that occurred.
Education and Training Requirements
To become a bloodstain pattern analyst, a solid foundation in science and criminal justice is essential. Aspiring analysts need to pursue a specific educational path that equips them with the necessary knowledge and skills.
Educational Pathways
The journey to becoming a bloodstain pattern analyst typically involves a combination of formal education and specialized training.
- Bachelor’s Degree: A bachelor’s degree in a science-related field, such as biology, chemistry, forensic science, or criminal justice, provides a strong foundation in the scientific principles underlying bloodstain pattern analysis. This degree equips individuals with the fundamental knowledge of biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics necessary for understanding bloodstain patterns.
- Master’s Degree: While not always mandatory, a master’s degree in forensic science or a related field can enhance career prospects and provide specialized knowledge in bloodstain pattern analysis. Master’s programs often offer advanced coursework in bloodstain pattern analysis, crime scene investigation, and forensic photography.
Essential Academic Qualifications
The educational requirements for bloodstain pattern analysts vary depending on the employer and specific job responsibilities. However, a strong academic background is crucial.
- Science Courses: A solid understanding of biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics is essential for interpreting bloodstain patterns. Courses in these subjects provide a foundation for understanding the principles of blood spatter, impact, and trajectory.
- Criminal Justice Courses: Courses in criminal justice, forensic science, and crime scene investigation provide a comprehensive understanding of the legal and investigative aspects of bloodstain pattern analysis. These courses help analysts understand the context of their findings and their role in criminal investigations.
- Statistics and Data Analysis: Bloodstain pattern analysis involves interpreting data and drawing conclusions based on evidence. Courses in statistics and data analysis help analysts develop critical thinking skills and the ability to analyze and interpret complex data sets.
Specialized Training Programs and Certifications
Specialized training programs and certifications are crucial for aspiring bloodstain pattern analysts.
- Bloodstain Pattern Analysis Training Programs: Numerous organizations offer specialized training programs in bloodstain pattern analysis. These programs provide hands-on experience in crime scene investigation, bloodstain pattern documentation, and analysis techniques. They often include workshops, lectures, and practical exercises.
- International Association of Bloodstain Pattern Analysts (IABPA): The IABPA offers certification programs for bloodstain pattern analysts. These programs require extensive training, experience, and a rigorous examination process. Achieving IABPA certification demonstrates a high level of expertise and professionalism in the field.
- Other Certifications: Other organizations, such as the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS), also offer certifications in bloodstain pattern analysis. These certifications often require a combination of education, experience, and a successful examination.
Essential Skills and Knowledge
To become a proficient bloodstain pattern analyst, you must possess a unique blend of skills and knowledge. This field demands a keen eye for detail, a strong understanding of the science behind blood spatter, and the ability to interpret complex patterns.
Understanding Blood Dynamics
A comprehensive understanding of blood dynamics is paramount for effective bloodstain pattern analysis. Blood behaves in a predictable manner when it is ejected from a source, and understanding these dynamics is crucial for interpreting the patterns it creates.
- Blood Viscosity: Blood’s viscosity, its resistance to flow, influences the size and shape of bloodstains. Higher viscosity results in smaller, more compact stains, while lower viscosity leads to larger, more dispersed stains.
- Surface Tension: Blood’s surface tension causes it to form spherical droplets, which can then impact surfaces and create unique patterns. Understanding the relationship between surface tension and impact angle is crucial for determining the direction and origin of blood spatter.
- Gravity: Gravity plays a significant role in the trajectory of blood droplets. The force of gravity affects the shape and size of bloodstains, as well as their distribution on a surface.
- Impact Angle: The angle at which a blood droplet strikes a surface influences the shape of the stain. For example, a blood droplet striking a surface at a 90-degree angle will create a circular stain, while a droplet striking at an oblique angle will create an elongated, teardrop-shaped stain.
- Velocity: The velocity of the blood droplet at impact determines the size and distribution of the spatter. Higher velocity impacts create smaller, more dispersed spatter, while lower velocity impacts create larger, more concentrated spatter.
Knowledge of Physics and Mathematics
Bloodstain pattern analysis relies heavily on principles of physics and mathematics. A solid foundation in these subjects is essential for accurate interpretation of bloodstain patterns.
- Physics: Knowledge of motion, forces, and energy is crucial for understanding the trajectory of blood droplets and the impact they create. For example, understanding projectile motion allows analysts to determine the point of origin of blood spatter.
- Mathematics: Bloodstain pattern analysis involves using mathematical formulas to calculate impact angles, distances, and velocities. For example, the angle of impact can be calculated using the formula:
Angle of Impact = Arcsin (Width of Stain / Length of Stain)
Observational Skills, Critical Thinking, and Attention to Detail
Bloodstain pattern analysis is a highly detail-oriented field that demands keen observational skills, critical thinking, and meticulous attention to detail.
- Observational Skills: The ability to meticulously observe and document bloodstain patterns is fundamental to the analysis process. This involves identifying subtle details like the shape, size, and distribution of bloodstains, as well as the presence of any other evidence.
- Critical Thinking: Bloodstain pattern analysis requires the ability to interpret complex patterns and draw logical conclusions based on the evidence.
Analysts must be able to identify patterns, evaluate potential scenarios, and develop hypotheses based on the bloodstain evidence.
- Attention to Detail: Even the smallest details can be crucial in bloodstain pattern analysis. Analysts must be able to meticulously document the location, shape, and size of bloodstains, as well as any other relevant details, to ensure the accuracy of their findings.
Bloodstain Pattern Analysis Techniques
Bloodstain pattern analysis is a specialized field that involves the interpretation of bloodstains at a crime scene to reconstruct the events that led to the bloodshed. By carefully analyzing the size, shape, and distribution of bloodstains, analysts can determine the type of weapon used, the direction of the attack, the position of the victim and assailant, and the sequence of events.
This information can be crucial in solving crimes and bringing perpetrators to justice.
Bloodstain Pattern Types and Characteristics
Understanding the different types of bloodstains and their characteristics is fundamental to bloodstain pattern analysis. Here’s a table that summarizes common bloodstain patterns and their associated characteristics:| Bloodstain Pattern Type | Characteristics ||—|—|| Passive Bloodstains |
Drops
Formed when blood falls directly from a source due to gravity. The shape of the drop can indicate the angle of impact.
Pools
Accumulations of blood in a particular area.
Flows
Trails of blood that result from the movement of blood due to gravity.
Stains
Bloodstains that occur when blood comes into contact with a surface and is then transferred to another surface. || Projected Bloodstains |
Spatters
Created when blood is projected from a source, such as a weapon.
Cast-off Stains
Bloodstains created when a weapon is swung or moved, causing blood to be thrown off the weapon.
Impact Spatters
Bloodstains produced when a blunt force or projectile strikes a blood source. || Transfer Bloodstains |
Wipes
Bloodstains created when an object moves through a wet bloodstain.
Swipe
Bloodstains created when an object moves across a bloodstain, removing some of the blood.
Smudges
Bloodstains created when a wet bloodstain is dragged or smeared across a surface. |
Documenting and Photographing Bloodstains at a Crime Scene
The meticulous documentation and photography of bloodstains at a crime scene are crucial for accurate analysis. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Scene Security
The first step is to ensure the safety and security of the crime scene, preserving the integrity of the bloodstains.
Initial Observations
The analyst will make initial observations, noting the overall scene, the presence of bloodstains, and any potential weapons or other evidence.
Photography
Detailed photographs of the bloodstains are taken from various angles and distances. This includes close-up shots of individual bloodstains, as well as wider shots that show the relationship between the bloodstains and other evidence.
Measurements
The analyst will measure the size, shape, and location of the bloodstains using measuring tapes, rulers, and other tools.
Documentation
All observations, measurements, and photographs are carefully documented in a detailed report. This report will serve as a permanent record of the crime scene and the bloodstain evidence.
Methods for Measuring and Interpreting Bloodstain Patterns
Bloodstain pattern analysis relies on a combination of scientific principles and analytical techniques to interpret the meaning of bloodstains. Here are some key methods used:
Angle of Impact
This refers to the angle at which a blood drop strikes a surface. It can be determined by measuring the length and width of the bloodstain and using mathematical formulas.
Directionality
The direction from which a blood drop originated can be determined by examining the shape of the bloodstain. For example, elongated bloodstains indicate that the blood drop struck the surface at an angle.
Area of Convergence
This is the point in space where bloodstains originated. It can be determined by drawing lines from the center of each bloodstain, extending them back to a point of convergence.
Point of Origin
The point of origin is the location from which the blood was projected. It can be determined by using the area of convergence and the angle of impact of the bloodstains.
“Bloodstain pattern analysis is a valuable tool for investigators, providing insights into the events that led to a crime. By understanding the different types of bloodstains and the techniques used to analyze them, investigators can piece together the events of a crime and bring justice to victims.”
Interpreting Bloodstain Patterns
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bloodstain-pattern-analyst-job-information-974465-FINAL-5bf4617a46e0fb002671d958.png)
Bloodstain pattern analysis is a crucial aspect of crime scene investigation, providing valuable insights into the events that unfolded. By meticulously examining the distribution, shape, and size of bloodstains, analysts can reconstruct the sequence of events, identify the type of weapon used, and determine the position of the victim during the incident.
Determining the Sequence of Events
Bloodstain patterns offer a visual timeline of the events that occurred at a crime scene. By analyzing the different patterns and their relationships to one another, analysts can establish a chronological order of events. For instance, if a bloodstain pattern is found on top of another, it indicates that the first pattern was created before the second.
- Impact Spatter: This pattern is created when a blood-covered object impacts a surface. The size and distribution of the droplets can help determine the type of weapon used, the force of the impact, and the direction of the blow.
- Cast-off Patterns: These patterns occur when a blood-covered object is swung or moved, causing blood to be flung off in a characteristic arc. The shape and size of the cast-off pattern can indicate the type of weapon, the number of blows, and the direction of movement.
- Transfer Patterns: This pattern occurs when a bloody object comes into contact with a surface, leaving behind a blood imprint. Transfer patterns can reveal the shape of the object and the direction of movement.
Identifying the Type of Weapon Used
Bloodstain patterns can provide clues about the type of weapon used in an assault. For example, a sharp weapon like a knife will typically create a smaller, more concentrated bloodstain pattern, while a blunt weapon like a hammer will produce a larger, more dispersed pattern.
- Sharp Force Injuries: These injuries often result in a smaller, more concentrated bloodstain pattern, with a distinct “tail” indicating the direction of the blade’s movement.
- Blunt Force Injuries: These injuries typically create a larger, more dispersed bloodstain pattern, with a variety of droplet sizes and shapes.
- Gunshot Wounds: Bloodstain patterns from gunshot wounds are characterized by a distinctive “backspatter” pattern, which is created when blood is forced backward from the wound as the bullet exits the body.
Determining the Position of the Victim
Bloodstain patterns can also provide information about the position of the victim during the incident. For instance, the presence of bloodstains on the ceiling can indicate that the victim was standing upright when they were injured, while bloodstains on the floor could suggest that the victim was lying down or kneeling.
Real-World Case Studies
Bloodstain pattern analysis has played a pivotal role in countless criminal investigations, helping to solve crimes and bring justice to victims. One notable case involved the investigation of a murder where the victim was found in a pool of blood. Bloodstain pattern analysis revealed that the victim had been stabbed multiple times, and the direction of the bloodstains indicated that the attacker had been standing over the victim during the assault.
This evidence was instrumental in identifying and convicting the perpetrator.Another case involved a hit-and-run accident where the victim was found lying in the street. Bloodstain pattern analysis revealed that the victim had been struck by a vehicle, and the pattern of bloodstains on the road surface indicated the direction of the vehicle’s movement. This information was crucial in helping investigators identify the vehicle involved in the accident.
Advanced Techniques and Technologies

The field of bloodstain pattern analysis has evolved significantly with the advent of advanced techniques and technologies. These advancements have enhanced the accuracy, precision, and efficiency of bloodstain analysis, leading to more robust and reliable interpretations.
3D Modeling and Computer Software
D modeling and computer software play a crucial role in reconstructing crime scenes and analyzing bloodstain patterns. These tools enable analysts to create virtual representations of the crime scene, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of the events that transpired. By incorporating bloodstain data into these models, analysts can simulate the trajectory of blood droplets, determine the position of the victim and the assailant, and identify potential impact points.
- Software Applications: Several specialized software applications are available for bloodstain pattern analysis, such as:
- Bloodstain Pattern Analysis Software (BPA): This software allows analysts to simulate blood spatter patterns based on various parameters, including impact angle, velocity, and distance. It provides visual representations of the bloodstain patterns, helping analysts interpret the events that led to their formation.
- 3D Crime Scene Reconstruction Software: This software enables analysts to create virtual 3D models of crime scenes, incorporating data from various sources, including photographs, measurements, and bloodstain patterns. These models allow for a more realistic and comprehensive reconstruction of the crime scene.
- Benefits of 3D Modeling:
- Enhanced visualization: 3D models provide a more realistic and immersive view of the crime scene, allowing analysts to better understand the spatial relationships between bloodstains and other evidence.
- Improved accuracy: 3D modeling can help improve the accuracy of bloodstain pattern analysis by simulating the movement of blood droplets and providing a more precise understanding of the impact angles and velocities involved.
- Enhanced communication: 3D models can be used to communicate findings to juries and other stakeholders in a clear and concise manner, enhancing the understanding and impact of the analysis.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging techniques, such as infrared and ultraviolet imaging, provide valuable insights into bloodstain patterns that may not be visible under normal lighting conditions. These techniques can reveal hidden details, enhance contrast, and identify specific components within the bloodstains.
- Infrared Imaging: Infrared imaging utilizes infrared radiation to capture images that highlight differences in temperature. This technique can be used to detect bloodstains that have been concealed or cleaned, as blood absorbs infrared radiation differently than other materials.
- Ultraviolet Imaging: Ultraviolet imaging uses ultraviolet light to illuminate the scene, causing certain substances, including blood, to fluoresce. This technique can be used to enhance the visibility of bloodstains, especially those that have been diluted or aged.
Forensic Laboratories and Specialized Equipment
Forensic laboratories play a crucial role in bloodstain pattern analysis, providing specialized equipment and expertise to analyze bloodstains and extract relevant information. These laboratories are equipped with advanced technologies and instrumentation that enable analysts to conduct comprehensive examinations.
- Microscopy: Microscopes are essential tools in bloodstain pattern analysis, allowing analysts to examine the morphology of bloodstains, identify the presence of foreign materials, and determine the type of blood.
- Light Microscopy: This type of microscopy uses visible light to illuminate the specimen, providing a magnified view of the bloodstain’s structure and any embedded particles.
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): SEM uses a focused beam of electrons to scan the surface of the bloodstain, providing high-resolution images of the bloodstain’s morphology and any microscopic details.
- Spectrophotometry: Spectrophotometry is a technique that measures the absorption and transmission of light through a sample. In bloodstain analysis, spectrophotometry can be used to identify the presence of blood, determine its concentration, and identify any potential adulterants.
- DNA Analysis: DNA analysis is used to identify the source of bloodstains, providing valuable information about the individuals involved in a crime. This technique involves extracting DNA from the bloodstain and comparing it to known DNA profiles.
Ethical Considerations and Professional Standards
Bloodstain pattern analysis, as a crucial tool in criminal investigations, demands adherence to strict ethical guidelines and professional standards to ensure the integrity and validity of the analysis. This section explores the ethical considerations that guide bloodstain pattern analysts in their work, highlighting the importance of objectivity, integrity, and the avoidance of biases in interpreting bloodstain patterns.
Potential Biases and Limitations in Bloodstain Pattern Interpretation
The interpretation of bloodstain patterns can be influenced by various factors, leading to potential biases and limitations.
- Confirmation Bias: This bias occurs when analysts tend to focus on evidence that supports their pre-existing beliefs or hypotheses, potentially overlooking contradictory information. It’s crucial to remain objective and consider all available evidence, regardless of whether it supports or contradicts the initial assumptions.
- Cognitive Biases: Other cognitive biases, such as anchoring bias (over-reliance on initial information) and availability bias (overestimating the likelihood of events based on easily recalled examples), can also affect interpretation. Analysts must be aware of these biases and actively work to mitigate their influence.
- Lack of Standardization: The field of bloodstain pattern analysis is still evolving, and there is no universally accepted standard for interpretation. Different analysts may interpret the same pattern differently, leading to inconsistencies. This underscores the need for ongoing research and development of standardized methodologies.
- Limited Data: The interpretation of bloodstain patterns often relies on limited data, such as the size, shape, and distribution of bloodstains. This can make it challenging to reach definitive conclusions, especially in complex cases.
Maintaining Objectivity and Integrity in Bloodstain Pattern Analysis
Maintaining objectivity and integrity is paramount in bloodstain pattern analysis.
- Adherence to Scientific Principles: Analysts must adhere to the scientific method, conducting thorough examinations, using validated techniques, and drawing conclusions based on evidence, not personal opinions or assumptions.
- Transparency and Documentation: The analysis process should be transparent, with detailed documentation of the methods used, observations made, and conclusions reached. This ensures accountability and allows for independent verification.
- Continuing Education and Training: Bloodstain pattern analysis is a dynamic field, and analysts must engage in ongoing education and training to stay abreast of the latest advancements, techniques, and ethical considerations.
- Collaboration and Peer Review: Collaboration with other experts and peer review of findings are essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of bloodstain pattern analysis. This fosters a culture of critical thinking and helps to identify and mitigate potential biases.
“The goal of bloodstain pattern analysis is not to prove a particular theory but to provide objective, scientific evidence that can assist in the investigation and prosecution of crime.”
Career Opportunities and Advancement
A career in bloodstain pattern analysis offers a unique blend of scientific inquiry, forensic investigation, and courtroom testimony. This specialized field provides numerous opportunities for individuals with a keen interest in crime scene investigation and a passion for unraveling the mysteries behind bloodstains.
Career Paths for Bloodstain Pattern Analysts, How to become a bloodstain pattern analyst
The demand for qualified bloodstain pattern analysts continues to grow, opening doors to diverse career paths within law enforcement, forensic science, and private consulting.
- Forensic Scientist: This role involves analyzing bloodstains and other biological evidence to reconstruct crime scenes, determine the sequence of events, and provide expert testimony in court. Forensic scientists often work in crime labs, medical examiner’s offices, or private consulting firms.
- Crime Scene Investigator: Crime scene investigators play a crucial role in collecting and documenting evidence at crime scenes. Bloodstain pattern analysis is an integral part of their work, as they use their expertise to interpret bloodstain patterns and contribute to the overall investigation.
- Law Enforcement Officer: Some law enforcement agencies employ bloodstain pattern analysts to support their investigations. These analysts work closely with detectives and other officers to interpret bloodstain patterns and provide valuable insights into crime scene reconstruction.
- Private Consultant: Independent bloodstain pattern analysts offer their expertise to attorneys, insurance companies, and other organizations. They provide expert testimony, conduct independent investigations, and offer consulting services related to bloodstain analysis.
Typical Work Environment and Potential Employers
The work environment for bloodstain pattern analysts can vary depending on their specific role and employer. However, most analysts work in controlled laboratory settings, crime scenes, or courtrooms.
- Crime Laboratories: Public and private crime laboratories are major employers of bloodstain pattern analysts. These laboratories provide forensic services to law enforcement agencies and other organizations.
- Medical Examiner’s Offices: Medical examiners often employ bloodstain pattern analysts to investigate homicides, suicides, and other deaths involving bloodstains.
- Law Enforcement Agencies: Police departments, sheriff’s offices, and other law enforcement agencies may have dedicated bloodstain pattern analysts on staff or may consult with experts from outside agencies.
- Private Consulting Firms: Independent bloodstain pattern analysts often establish their own consulting firms, offering their expertise to attorneys, insurance companies, and other organizations.
Opportunities for Career Growth and Specialization
The field of bloodstain pattern analysis offers numerous opportunities for career advancement and specialization. Analysts can pursue advanced training, certifications, and specialized areas of expertise.
- Advanced Training and Certifications: Bloodstain pattern analysts can enhance their skills and credentials by pursuing advanced training programs and certifications. The International Association of Bloodstain Pattern Analysts (IABPA) offers certification programs that recognize expertise in this field.
- Specialization: Analysts can specialize in specific areas of bloodstain pattern analysis, such as:
- Firearms and Ballistics: Analyzing bloodstains associated with gunshot wounds and projectile trajectories.
- Spatter Analysis: Interpreting bloodstains caused by impact, cast-off, and other forms of spatter.
- Pattern Recognition: Developing expertise in recognizing and interpreting various bloodstain patterns.
Resources and Further Learning
Continuing your journey as a bloodstain pattern analyst requires access to a wealth of resources that can enhance your knowledge, skills, and professional development. This section will guide you to valuable organizations, publications, and training programs that can support your growth in this field.
Reputable Organizations and Associations
Joining professional organizations is an excellent way to stay informed about advancements in bloodstain pattern analysis, network with colleagues, and participate in continuing education opportunities. Here are some of the most prominent organizations dedicated to this field:
- International Association of Bloodstain Pattern Analysts (IABPA): The IABPA is a leading organization for bloodstain pattern analysts worldwide. It offers certification programs, conferences, and publications to promote professional standards and knowledge sharing.
- American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS): The AAFS is a multidisciplinary organization that includes a bloodstain pattern analysis section. Members have access to resources, networking opportunities, and educational programs within this specialized area.
- Canadian Society of Forensic Science (CSFS): The CSFS is a national organization that provides a platform for forensic scientists in Canada, including those specializing in bloodstain pattern analysis. It offers conferences, workshops, and publications.
Relevant Books, Journals, and Online Resources
Staying current with the latest research and advancements in bloodstain pattern analysis is essential for professional growth. These resources provide valuable insights and information:
- “Bloodstain Pattern Analysis” by Robert W. DeHaan: This comprehensive textbook covers the fundamentals of bloodstain pattern analysis, from basic principles to advanced techniques. It’s a must-have for students and professionals alike.
- “Forensic Science Communications”: This journal, published by the AAFS, features articles on a wide range of forensic science topics, including bloodstain pattern analysis. It provides a platform for researchers to share their findings and insights.
- “Journal of Forensic Sciences”: Another reputable journal, the “Journal of Forensic Sciences” publishes articles on various aspects of forensic science, including bloodstain pattern analysis. It’s a valuable resource for staying informed about cutting-edge research and methodologies.
- “Bloodstain Pattern Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide” by Stuart H. James: This book offers a detailed exploration of the principles, techniques, and applications of bloodstain pattern analysis. It’s a valuable resource for both beginners and experienced analysts.
- “Bloodstain Pattern Analysis: Theory and Practice” by David R. Brant: This textbook provides a comprehensive overview of the theory and practice of bloodstain pattern analysis. It’s a valuable resource for students and professionals in the field.
- “Bloodstain Pattern Analysis: A Practical Guide” by Tom Bevel and Ross M. Gardner: This book offers a practical approach to bloodstain pattern analysis, with numerous case studies and illustrations. It’s a valuable resource for both students and professionals in the field.
- “Bloodstain Pattern Analysis: An Introduction” by James A. Osterburg: This book provides a concise introduction to the principles and techniques of bloodstain pattern analysis. It’s a good starting point for those new to the field.
Educational Programs and Training Courses
Formal education and specialized training are essential for becoming a competent bloodstain pattern analyst. These programs provide the necessary knowledge, skills, and practical experience:
- University Programs: Many universities offer undergraduate and graduate programs in forensic science, with specializations in bloodstain pattern analysis. These programs provide a strong foundation in the scientific principles, techniques, and legal aspects of the field.
- Specialized Training Courses: Numerous organizations, including the IABPA and AAFS, offer specialized training courses in bloodstain pattern analysis. These courses cover various topics, from basic principles to advanced techniques, and provide hands-on experience.
- Certification Programs: The IABPA offers certification programs for bloodstain pattern analysts. These programs demonstrate a high level of competence and knowledge in the field and are often required for employment in law enforcement and forensic science laboratories.
The path to becoming a bloodstain pattern analyst is not without its challenges, but the rewards are immense. It’s a field that demands dedication, continuous learning, and a passion for unraveling the mysteries of crime scenes. By embracing the complexities of bloodstain pattern analysis, you can contribute to a more just and equitable society, while forging a career that is both intellectually stimulating and deeply meaningful.
FAQ Corner
What is the typical salary for a bloodstain pattern analyst?
Salaries for bloodstain pattern analysts vary depending on experience, location, and employer. However, they generally earn a competitive salary, often comparable to other forensic science professionals.
Are there any specific personality traits that are beneficial for this career?
Strong attention to detail, analytical thinking, and a methodical approach are essential for success in this field. Additionally, being able to work independently and as part of a team is crucial.
What are the job prospects like for bloodstain pattern analysts?
The demand for skilled bloodstain pattern analysts is growing as forensic science continues to evolve. Opportunities exist in law enforcement agencies, forensic laboratories, and private consulting firms.






