What is pseudodecidualized stroma? This intriguing term refers to a specialized tissue found within the female reproductive system, playing a crucial role in the complex dance of conception, pregnancy, and even the development of certain conditions. Pseudodecidualized stroma is a fascinating example of how the body adapts and transforms to support the miracle of life.
During the menstrual cycle, the uterine lining, or endometrium, undergoes a series of changes in preparation for potential pregnancy. The stromal cells, which form the supportive framework of the endometrium, undergo a transformation known as decidualization. In this process, they enlarge, become more metabolically active, and acquire a unique set of characteristics. Pseudodecidualization is a similar process that occurs in response to hormonal signals, particularly estrogen and progesterone, but it is not associated with pregnancy.
This transformation results in the formation of a specialized tissue that shares many similarities with true decidua, the tissue that forms during pregnancy.
Cellular and Molecular Characteristics
Pseudodecidualized stroma is a fascinating example of cellular transformation, marked by distinct changes in cell composition and molecular expression. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for deciphering the complex interplay between the endometrium and the embryo during implantation.
Cellular Composition of Pseudodecidualized Stroma
The cellular landscape of pseudodecidualized stroma undergoes a dramatic shift, characterized by an influx of specific cell types and a reorganisation of existing cells.
- Decidual Cells: These are the hallmark of pseudodecidualization, derived from the transformation of stromal fibroblasts. They are larger and more rounded than their fibroblast counterparts, with increased cytoplasmic volume and a distinctive granular appearance. These cells play a pivotal role in supporting the developing embryo, providing essential nutrients and creating a conducive microenvironment for implantation.
- Immune Cells: The immune landscape of the pseudodecidualized stroma is equally dynamic, with a significant increase in immune cells, including macrophages, NK cells, and T cells. These cells are crucial for orchestrating the immune response to the implanting embryo, preventing rejection while ensuring a successful pregnancy.
- Endothelial Cells: The vascular network within the pseudodecidualized stroma undergoes significant remodelling, with increased vascular permeability and angiogenesis. This facilitates nutrient delivery and waste removal, supporting the growing embryo.
Molecular Markers of Pseudodecidualized Stroma, What is pseudodecidualized stroma
The molecular profile of pseudodecidualized stroma distinguishes it from other stromal tissues, reflecting the profound changes in gene expression and protein profiles that occur during pseudodecidualization.
- Hormone Receptors: Pseudodecidualized stroma expresses high levels of progesterone receptors (PR), estrogen receptors (ER), and growth hormone receptors (GHR). These receptors are crucial for mediating the hormonal signals that drive pseudodecidualization and subsequent implantation.
- Growth Factors and Cytokines: The expression of various growth factors and cytokines, such as IGF-1, VEGF, and IL-10, is significantly upregulated in pseudodecidualized stroma. These molecules contribute to the establishment of a receptive endometrium, promoting angiogenesis, cell proliferation, and immune modulation.
- Extracellular Matrix Components: Pseudodecidualization involves significant changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM), with increased expression of collagen, fibronectin, and laminin. These ECM components provide structural support, facilitate cell adhesion, and influence cell signaling.
Gene Expression and Protein Profiles
The molecular signature of pseudodecidualization is further reflected in the distinct changes in gene expression and protein profiles.
- Gene Expression: Studies have identified numerous genes that are upregulated or downregulated during pseudodecidualization. For example, genes involved in cell cycle regulation, growth factor signaling, and immune modulation are often upregulated, while genes associated with fibroblast function are downregulated.
- Protein Profiles: The protein profile of pseudodecidualized stroma also undergoes significant changes, with the increased expression of proteins involved in cell adhesion, angiogenesis, and immune regulation.
Physiological Roles of Pseudodecidualized Stroma: What Is Pseudodecidualized Stroma
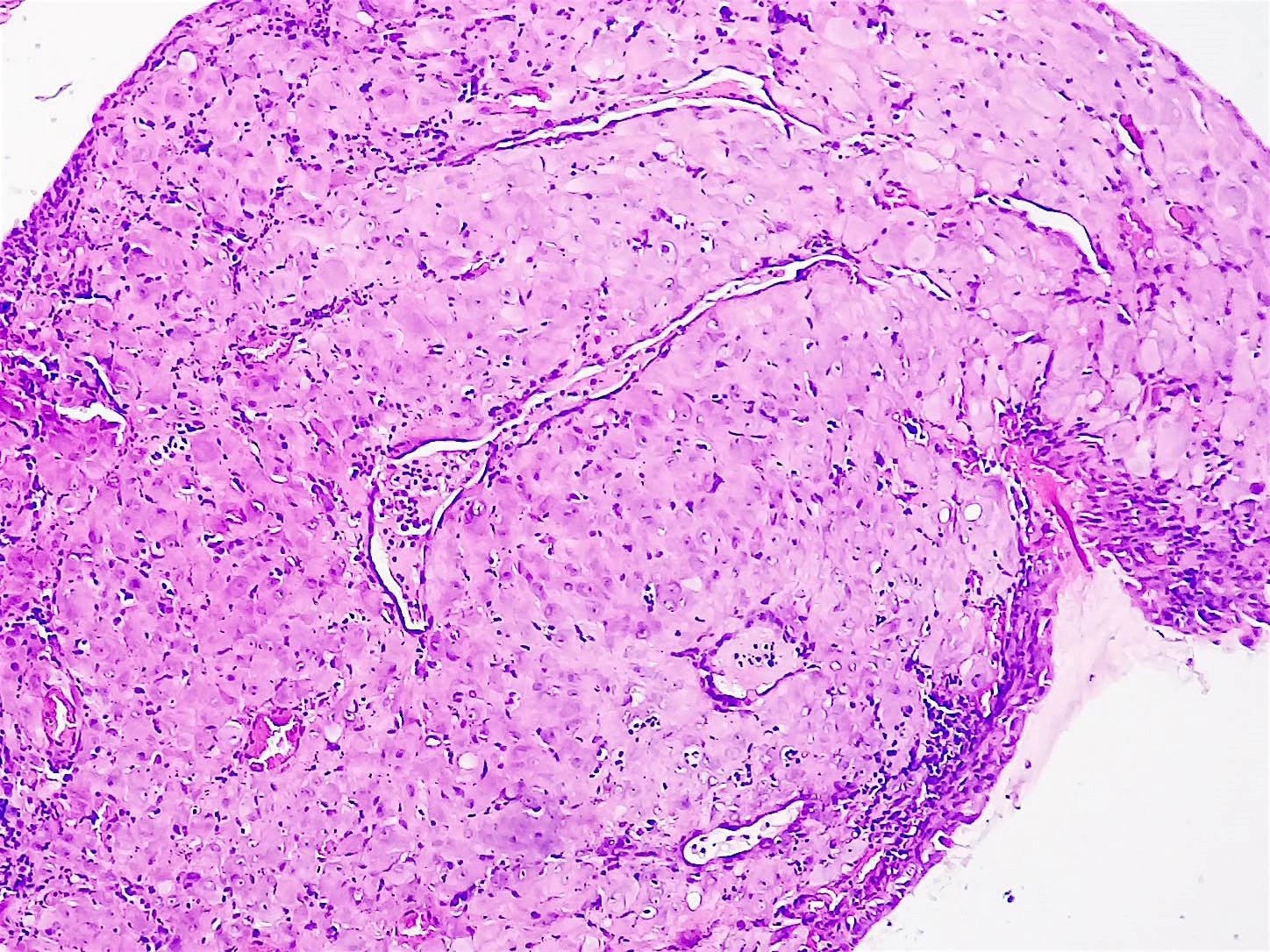
Pseudodecidualized stroma plays a crucial role in the successful establishment and maintenance of pregnancy. It undergoes significant changes during the implantation process, contributing to the development of the placenta and the regulation of uterine growth and remodeling.
Role in Implantation
Pseudodecidualized stroma plays a vital role in the implantation of a fertilized egg. When a fertilized egg reaches the uterus, it needs to attach to the uterine lining for successful implantation. This process is facilitated by the pseudodecidualized stroma.
- Increased vascularity: The pseudodecidualized stroma undergoes a dramatic increase in vascularity, providing an enriched blood supply to the implantation site. This ensures adequate nutrient and oxygen delivery to the developing embryo.
- Production of growth factors: Pseudodecidualized stromal cells produce various growth factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast growth factor (FGF), which stimulate angiogenesis and promote the growth of the placenta.
- Secretion of extracellular matrix proteins: The stromal cells secrete extracellular matrix proteins, such as fibronectin and laminin, which provide structural support and create a favorable environment for the implantation of the embryo.
Contribution to Placental Development
Pseudodecidualized stroma is essential for the development and maintenance of the placenta, the organ that provides nourishment and oxygen to the developing fetus.
- Decidualization: The pseudodecidualized stroma undergoes further differentiation, becoming a specialized tissue called the decidua. The decidua provides structural support for the placenta and serves as a barrier between the maternal and fetal circulations.
- Production of hormones: Pseudodecidualized stromal cells produce various hormones, such as progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which are essential for maintaining pregnancy.
- Immune regulation: Pseudodecidualized stroma plays a crucial role in regulating the maternal immune response to the developing embryo, preventing rejection of the fetus.
Regulation of Uterine Growth and Remodeling
Pseudodecidualized stroma contributes to the regulation of uterine growth and remodeling during pregnancy.
- Uterine growth: The pseudodecidualized stroma promotes uterine growth by producing growth factors and stimulating angiogenesis. This ensures that the uterus can accommodate the growing fetus.
- Uterine remodeling: Pseudodecidualized stroma also plays a role in uterine remodeling, which involves changes in the structure and function of the uterine wall to accommodate the developing fetus.
- Postpartum recovery: After delivery, pseudodecidualized stroma contributes to the process of uterine involution, which involves the return of the uterus to its non-pregnant state.
Clinical Significance of Pseudodecidualized Stroma
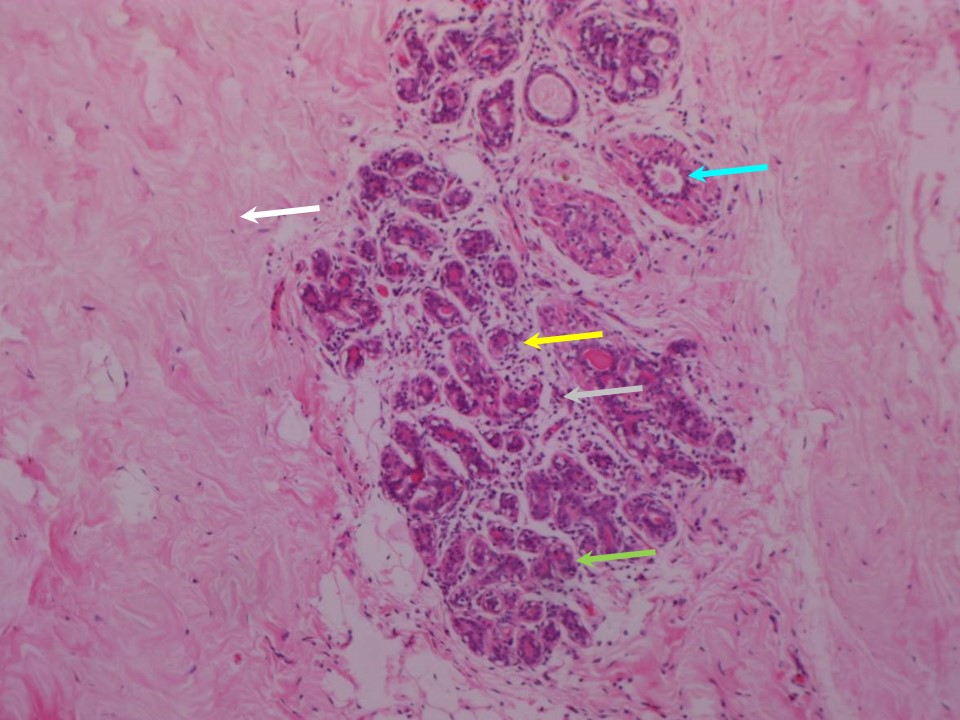
Pseudodecidualized stroma, despite its relatively obscure name, plays a crucial role in reproductive health, particularly in the context of certain conditions. Understanding its behaviour and implications can be super helpful in diagnosing and managing these conditions.
Association with Endometriosis and Uterine Fibroids
Pseudodecidualized stroma is often found in the context of endometriosis, a condition where endometrial-like tissue grows outside the uterus. This can be a bit of a head-scratcher, as it suggests that the process of decidualization, normally associated with pregnancy, might be involved in the development of endometriosis. Some studies have shown that pseudodecidualized stroma can be found in endometrial implants, which are the hallmark of endometriosis.
This suggests that pseudodecidualization might be a key player in the development and progression of this condition.Pseudodecidualized stroma is also associated with uterine fibroids, benign tumours that grow in the uterus. It’s been shown that fibroids can undergo decidualization, which can contribute to their growth and symptoms. This association highlights the importance of pseudodecidualization in the context of uterine fibroids and suggests potential avenues for their treatment.
Potential Implications of Abnormal Pseudodecidualization in Reproductive Health
Abnormal pseudodecidualization can have a significant impact on reproductive health. For example, it can contribute to infertility, miscarriage, and ectopic pregnancy. This is because abnormal pseudodecidualization can disrupt the normal implantation process, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant in the uterus. It can also affect the development of the placenta, which is crucial for the health of the fetus.In some cases, pseudodecidualization can even lead to the formation of pseudodecidual tumours, which can be benign or malignant.
These tumours can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, bleeding, and infertility.
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Features
The table below summarizes the clinical manifestations and diagnostic features of disorders associated with pseudodecidualized stroma:
| Disorder | Clinical Manifestations | Diagnostic Features |
|---|---|---|
| Endometriosis | Pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, infertility, dyspareunia | Presence of endometrial implants, pseudodecidualized stroma in implants |
| Uterine Fibroids | Heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, pressure, infertility | Presence of fibroids, pseudodecidualized stroma in fibroids |
| Pseudodecidual Tumours | Pain, bleeding, infertility | Presence of pseudodecidual tumours, histological examination |
Future Research Directions
Although we’ve come a long way in understanding pseudodecidualized stroma, there’s still loads of stuff we don’t know. It’s like, there’s a whole load of mysteries about how it works and how it’s involved in different bits of reproductive biology and diseases. So, it’s time to get our thinking caps on and figure out what’s next!
Identifying Current Research Gaps
There’s a bunch of areas where we need to get more clued up on pseudodecidualized stroma. Like, we need to understand how it interacts with different cells and molecules, how it changes during different stages of pregnancy, and how it’s involved in conditions like endometriosis and infertility. It’s a whole new world to explore!
- We need to get a better understanding of the specific molecular mechanisms that drive pseudodecidualization. What genes are involved? What are the signalling pathways that are activated?
- We need to figure out how pseudodecidualized stroma interacts with other cell types in the reproductive system. What are the signals it sends and receives?
- We need to explore how pseudodecidualization changes throughout pregnancy. Does it evolve over time? Does it differ in different parts of the uterus?
- We need to figure out the role of pseudodecidualized stroma in reproductive diseases like endometriosis and infertility. Does it play a role in the development of these conditions?
Proposing Novel Research Questions and Approaches
So, we’ve got these research gaps, now we need to come up with some fresh ideas to tackle them. This is where it gets exciting, like, we can use all sorts of cool techniques to investigate this stuff!
- We could use single-cell RNA sequencing to map the molecular landscape of pseudodecidualized stroma. This would give us a detailed picture of the genes that are expressed in these cells and how they change over time.
- We could use 3D cell culture models to study the interactions between pseudodecidualized stroma and other cell types in the reproductive system. This would allow us to see how they communicate and how they affect each other’s behaviour.
- We could use animal models to study the role of pseudodecidualized stroma in pregnancy and reproductive diseases. This would give us a better understanding of how these processes work in a whole organism.
- We could use bioinformatics tools to analyse large datasets of genomic and clinical data to identify potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for pseudodecidualization.
Designing a Study to Investigate Potential Therapeutic Targets
Right, now we need to get practical and think about how we can use this research to actually help people. It’s like, we need to find ways to manipulate pseudodecidualization to treat conditions like endometriosis and infertility.
“The aim of this study is to identify potential therapeutic targets for modulating pseudodecidualization in women with endometriosis and infertility.”
This study would involve a few key steps:
- We’d start by identifying the molecular pathways that are involved in pseudodecidualization in endometriosis and infertility.
- Then, we’d screen for drugs or other compounds that can target these pathways.
- We’d test these compounds in cell culture models and animal models to see if they can modulate pseudodecidualization.
- Finally, we’d conduct clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of these compounds in humans.
The study of pseudodecidualized stroma reveals the remarkable complexity of the female reproductive system and highlights the delicate balance of hormones and cellular interactions that govern fertility. As we continue to unravel the intricacies of this tissue, we gain valuable insights into the mechanisms of reproduction, the origins of certain reproductive disorders, and potential therapeutic targets for managing these conditions.
Pseudodecidualized stroma stands as a testament to the body’s remarkable ability to adapt and transform in support of life’s grand design.
FAQ Section
What are the clinical implications of abnormal pseudodecidualization?
Abnormal pseudodecidualization can contribute to conditions like endometriosis and uterine fibroids. It can also lead to complications during pregnancy, such as implantation failure or placental abnormalities.
How does pseudodecidualization differ from decidualization?
Pseudodecidualization is a similar process to decidualization, but it occurs in response to hormonal signals without the presence of pregnancy. True decidualization occurs only during pregnancy and is essential for implantation and placental development.
Are there any treatments for disorders associated with pseudodecidualization?
Treatments for disorders associated with pseudodecidualization vary depending on the specific condition. Options include hormonal therapy, surgical interventions, and lifestyle modifications.






