What is 5×120 bolt pattern – What is a 5×120 bolt pattern? This seemingly simple phrase holds significant meaning in the world of automotive engineering and wheel compatibility. It refers to the arrangement of lug holes on a vehicle’s wheel hub, with five holes spaced 120 millimeters apart, forming a circular pattern. Understanding this pattern is crucial for ensuring proper wheel fitment and safe driving.
The 5×120 bolt pattern is commonly found on various vehicles, including popular models from BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and other European manufacturers. It dictates which wheels can be safely and securely mounted on a car, ensuring proper alignment and preventing potential damage to the vehicle.
Understanding Bolt Patterns

A bolt pattern, also known as a wheel bolt pattern, is a crucial specification in automotive engineering and other applications that involve mounting components to a hub or a central point. It defines the arrangement and spacing of the mounting holes on a wheel or hub, ensuring proper fitment and secure attachment.
Understanding the 5×120 Bolt Pattern, What is 5×120 bolt pattern
The “5×120” bolt pattern describes the arrangement of five mounting holes on a wheel or hub, spaced at 120 millimeters (mm) apart. This pattern is commonly found in various vehicles, particularly those manufactured by BMW, Mini Cooper, and some models from other manufacturers.
Vehicles Using a 5×120 Bolt Pattern
Here are some examples of vehicles that commonly use a 5×120 bolt pattern:
- BMW 3 Series (E36, E46, E90, F30)
- BMW 5 Series (E39, E60, F10)
- BMW X3 (E83, F25)
- Mini Cooper (R50, R53, R56, R57, R58, R59, F55, F56)
- Mercedes-Benz C-Class (W203, W204)
Wheel Compatibility
Ensuring wheel compatibility with your vehicle is crucial for safe and reliable driving. The bolt pattern is a primary factor in determining whether a wheel will fit your car. Using wheels with an incompatible bolt pattern can lead to serious consequences, including wheel detachment, damage to the vehicle, and potential accidents.
Determining Wheel Compatibility
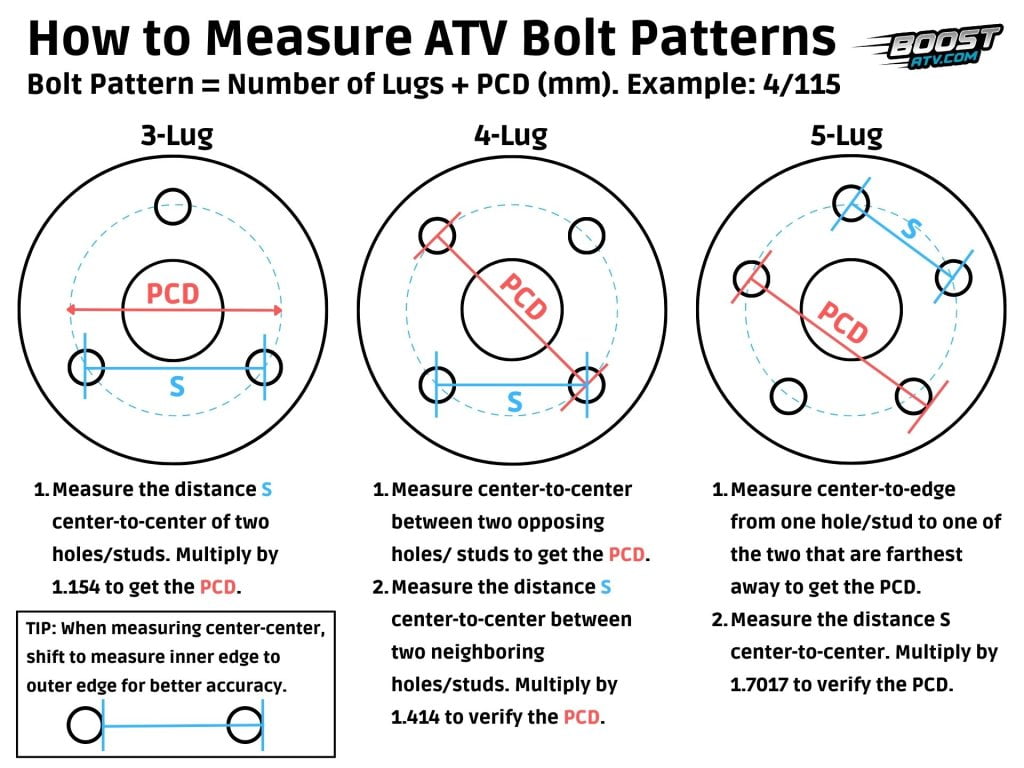
Matching the bolt pattern is essential for safe and reliable wheel installation. The bolt pattern defines the number of studs, their diameter, and the distance between them. To ensure compatibility, you need to identify the bolt pattern of your vehicle and the wheel you are considering.
The bolt pattern is typically expressed as a sequence of numbers, such as 5×120. The first number indicates the number of studs, and the second number represents the diameter of the bolt circle in millimeters.
For instance, a 5×120 bolt pattern indicates that the wheel has five studs spaced evenly around a circle with a diameter of 120 millimeters.Here’s how to determine compatibility:
- Vehicle Bolt Pattern: Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual, VIN plate, or a reliable online resource to find the bolt pattern for your car.
- Wheel Bolt Pattern: Look for the bolt pattern information on the wheel itself, its packaging, or the manufacturer’s website.
- Matching Bolt Patterns: Compare the bolt patterns of your vehicle and the wheel. They must match precisely for compatibility.
Consequences of Incompatible Bolt Patterns
Using wheels with an incompatible bolt pattern can lead to serious problems:
- Wheel Detachment: The most dangerous consequence is wheel detachment. If the studs don’t fit correctly, the wheel can come loose during driving, causing a catastrophic accident.
- Vehicle Damage: Misaligned wheels can stress the suspension components, leading to premature wear and damage to the vehicle’s chassis.
- Ride Quality Issues: Incompatible bolt patterns can cause vibration, uneven tire wear, and a compromised ride quality.
- Safety Concerns: Wheel detachment and other issues caused by incompatible bolt patterns significantly compromise the safety of the vehicle and its occupants.
Wheel Specifications
Beyond the bolt pattern, other wheel specifications are crucial for compatibility:
- Center Bore: The center bore is the diameter of the hole in the wheel that fits over the hub of the vehicle. The center bore must match the hub diameter for a secure fit.
- Offset: Offset refers to the distance between the wheel’s mounting surface and the center of the wheel. Offset influences the wheel’s position relative to the vehicle’s suspension.
- Wheel Diameter: The wheel diameter should be compatible with the vehicle’s tire size.
Wheel Offset and Backspacing
Wheel offset and backspacing are crucial aspects of wheel compatibility that directly impact a vehicle’s handling, aesthetics, and overall performance. Understanding these concepts is essential when choosing new wheels for your vehicle.
Defining Wheel Offset and Backspacing
Wheel offset, denoted by ET, refers to the distance between the wheel’s mounting surface (where the wheel bolts to the hub) and the center line of the wheel. Backspacing, on the other hand, measures the distance between the mounting surface and the innermost point of the wheel rim. While these two measurements are related, they provide different perspectives on the wheel’s positioning.
Impact of Offset and Backspacing on Vehicle Handling and Aesthetics
Wheel offset and backspacing significantly influence a vehicle’s handling and aesthetics.
- Increased offset (positive offset): Pushes the wheel further inwards, potentially leading to improved stability and reduced tire wear but may affect steering feel and potentially cause rubbing issues.
- Decreased offset (negative offset): Moves the wheel outwards, potentially enhancing steering response and visual appeal, but may increase the risk of tire rub, affecting suspension travel and potentially causing premature tire wear.
Aesthetics are also affected by offset and backspacing. A wider stance achieved by negative offset can enhance a vehicle’s appearance, while a more tucked-in look is possible with a positive offset.
Measuring and Understanding Wheel Offset and Backspacing
- Wheel Offset: Offset is typically stamped on the back of the wheel, usually denoted by “ET” followed by a number (e.g., ET35). A positive offset indicates the mounting surface is further inward from the wheel’s center line, while a negative offset means it’s further outward.
- Backspacing: Backspacing can be calculated using the wheel’s diameter, offset, and rim width.
Backspacing = (Wheel Diameter / 2)
-(Rim Width / 2)
-OffsetFor example, a 17-inch wheel with a 7-inch rim width and a +35 offset would have a backspacing of 4.5 inches.
It’s crucial to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a reputable wheel and tire guide to determine the recommended offset and backspacing for your specific model. Using the wrong offset or backspacing can lead to issues with handling, suspension travel, and tire wear.
Types of Wheels: What Is 5×120 Bolt Pattern
Wheels are essential components of any vehicle, playing a crucial role in supporting the vehicle’s weight, providing traction, and facilitating movement. They come in a variety of types, each with unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. This section explores the different types of wheels based on their materials, designs, and applications.
Wheel Materials
Wheel materials significantly influence a wheel’s performance, durability, and weight. Common wheel materials include:
- Steel: Steel wheels are the most affordable and widely used type. They are robust and durable, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications and off-road vehicles. However, they are heavier than other materials, which can negatively impact fuel efficiency.
- Aluminum: Aluminum wheels are lighter than steel wheels, contributing to improved fuel economy and handling. They are also more resistant to corrosion and offer a wider range of designs. However, aluminum wheels are more susceptible to damage and can be more expensive than steel wheels.
- Magnesium: Magnesium wheels are the lightest and strongest type of wheel, offering significant advantages in terms of performance and fuel efficiency. However, they are also the most expensive and require specialized manufacturing processes.
Wheel Designs
Wheel designs vary widely, influencing aesthetics, performance, and functionality.
- Spoke Wheels: Spoke wheels feature a central hub connected to the rim by spokes, offering a classic and stylish look. They are lightweight and provide good ventilation, improving brake cooling. However, they can be more susceptible to damage and require more maintenance.
- Split Spoke Wheels: These wheels feature spokes that are split into multiple sections, offering a more modern and aggressive look. They are typically stronger than standard spoke wheels and offer better brake cooling. However, they can be more complex to clean and maintain.
- Multi-Spoke Wheels: Multi-spoke wheels feature a large number of thin spokes, creating a sleek and sporty appearance. They offer excellent weight distribution and brake cooling but can be more susceptible to damage and require more frequent cleaning.
- Mesh Wheels: Mesh wheels feature a complex network of interconnected spokes, creating a unique and eye-catching design. They are lightweight and offer good ventilation but can be more expensive and difficult to clean.
Wheel Applications
Wheel types are often chosen based on the specific application or vehicle type.
- Passenger Vehicles: Passenger vehicles typically use aluminum wheels, offering a balance of performance, aesthetics, and affordability.
- Off-Road Vehicles: Off-road vehicles often use steel wheels, providing durability and resistance to damage in rugged terrain.
- Performance Vehicles: Performance vehicles may use lightweight magnesium wheels or high-performance aluminum wheels to enhance handling and acceleration.
- Commercial Vehicles: Commercial vehicles often use steel wheels due to their durability and cost-effectiveness.
Popular Wheel Brands and Manufacturers
Several reputable wheel brands and manufacturers cater to various vehicle types and preferences. Some popular brands include:
- BBS: Known for its high-performance and lightweight wheels, often used in motorsport.
- Enkei: Offers a wide range of wheels for passenger cars, SUVs, and trucks, known for their durability and performance.
- HRE: Specializes in custom-made wheels, known for their exquisite designs and high-quality craftsmanship.
- OZ Racing: A renowned manufacturer of motorsport wheels, offering high-performance and lightweight options.
- Vossen: Known for its stylish and innovative wheel designs, popular among luxury car owners.
In conclusion, understanding the 5×120 bolt pattern is essential for anyone seeking to replace or upgrade their vehicle’s wheels. By ensuring proper compatibility, drivers can maintain safe and optimal handling, while also enhancing the aesthetics of their car. Remember, always prioritize safety and consult with professionals when selecting and installing wheels, as a mismatch can lead to serious consequences.
Q&A
What are the benefits of using the correct bolt pattern?
Using the correct bolt pattern ensures secure wheel fitment, prevents wheel wobble, and maintains proper alignment for safe and optimal handling.
Can I use a wheel with a different bolt pattern on my car?
No, using a wheel with a different bolt pattern is extremely dangerous and can lead to wheel detachment, causing accidents. It is crucial to match the bolt pattern to your vehicle’s specifications.
How can I determine the bolt pattern of my car?
You can find the bolt pattern information on your vehicle’s owner’s manual, on the wheel hub itself, or by contacting your car’s manufacturer or a reputable mechanic.






