Was kostet Strom in Deutschland? Understanding the cost of electricity in Germany is crucial for both residents and businesses. Electricity prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including energy sources, market dynamics, and government regulations. This guide delves into the intricacies of German electricity costs, exploring key aspects like tariff structures, consumption patterns, and energy efficiency initiatives.
We will analyze how factors such as regional variations, household sizes, and energy-saving measures impact electricity bills. Additionally, we will compare German electricity prices with those of other European countries and discuss the potential impact of future energy policies on the cost of electricity in Germany.
Understanding Electricity Costs in Germany
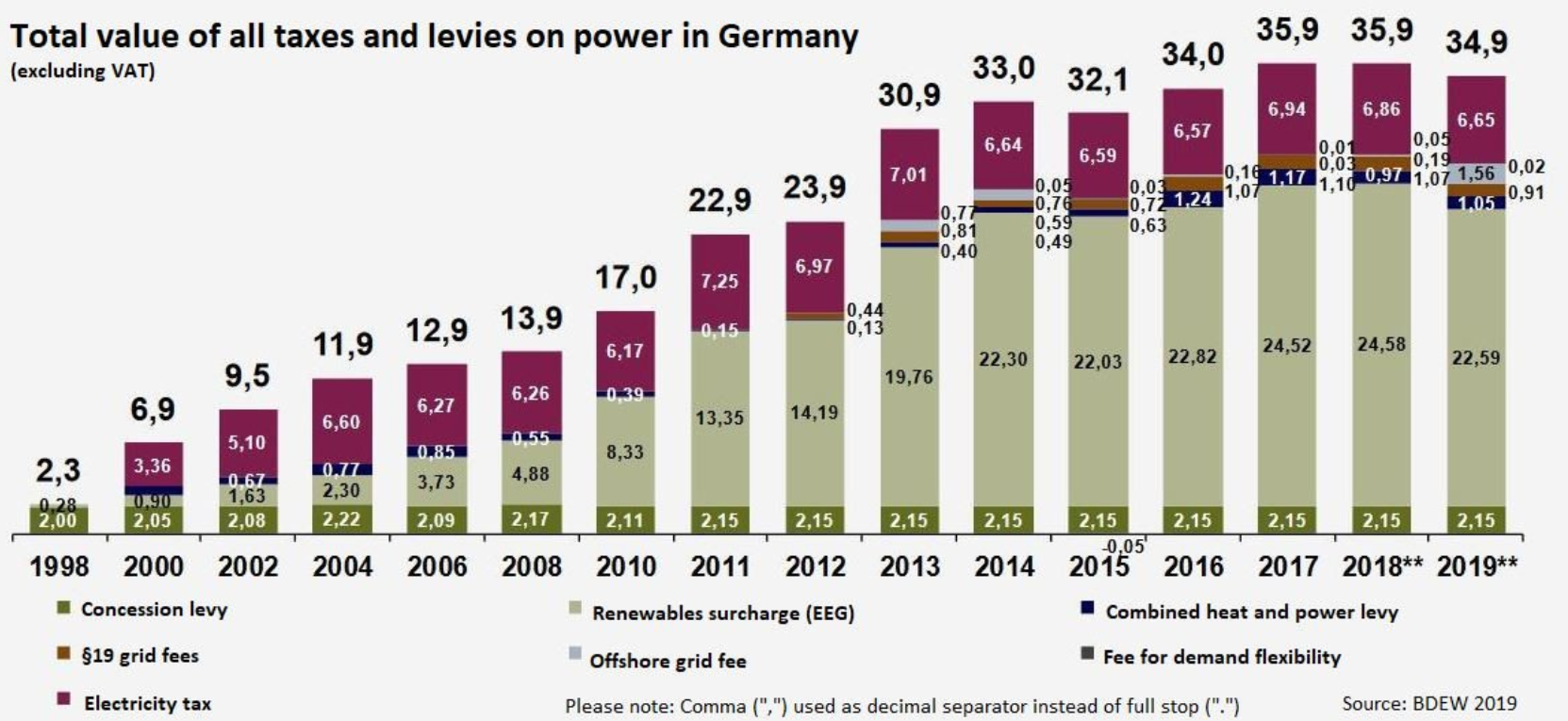
Navigating the complexities of electricity costs in Germany can feel daunting. However, by understanding the key factors that influence pricing, you can make informed decisions about your energy consumption and potentially save money.
Factors Influencing Electricity Prices in Germany, Was kostet strom in deutschland
Several factors play a crucial role in shaping electricity prices in Germany. These include:
- Energy Sources: Germany’s energy mix, relying heavily on renewable sources like wind and solar, is a significant factor in electricity pricing. The fluctuating nature of these sources can impact price stability, particularly during periods of low wind or sunshine.
- Market Dynamics: The German electricity market is characterized by competition among energy providers, influencing pricing strategies. Wholesale electricity prices, influenced by factors like global energy demand and commodity prices, also play a role in retail electricity costs.
- Government Regulations: The German government actively shapes the energy landscape through policies like the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), which incentivizes renewable energy production. These regulations, while promoting sustainable energy, can also influence electricity costs for consumers.
Electricity Tariffs in Germany
Germany offers a variety of electricity tariffs catering to different needs and consumption patterns. These tariffs can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Basic Tariffs: These are standard tariffs with a fixed price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) for all electricity consumed. They are often the simplest option, suitable for households with predictable consumption patterns.
- Variable Tariffs: These tariffs fluctuate based on wholesale electricity prices, offering potential savings during periods of low prices. However, they also carry the risk of higher costs when prices rise.
- Time-of-Use Tariffs: These tariffs offer different prices depending on the time of day or day of the week. They encourage consumers to shift their energy consumption to off-peak hours, potentially leading to lower overall costs.
- Green Tariffs: These tariffs focus on electricity generated from renewable sources, offering consumers a way to support sustainable energy production. They often come at a premium compared to standard tariffs.
Average Electricity Costs in Germany
The average electricity cost per kWh in Germany varies depending on the region, household size, and chosen tariff. According to the Federal Network Agency (Bundesnetzagentur), the average electricity price for households in Germany was around 30 cents per kWh in 2022. However, this average can fluctuate significantly, with prices in some regions reaching as high as 40 cents per kWh.
The average electricity price for households in Germany was around 30 cents per kWh in 2022.
Analyzing Electricity Consumption Patterns
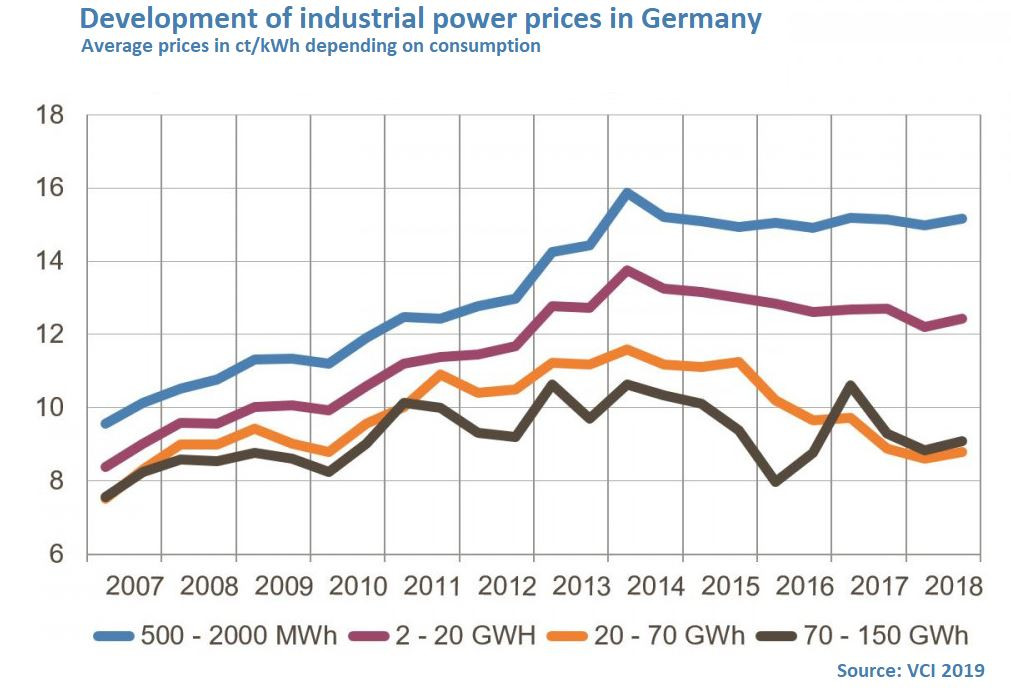
Understanding how electricity is consumed in German households is crucial for comprehending the factors that influence electricity costs. Analyzing consumption patterns reveals insights into typical usage habits, seasonal variations, and the impact of various factors on electricity bills.
Typical Electricity Consumption Patterns in German Households
German households exhibit distinct electricity consumption patterns influenced by factors such as seasonality, appliance usage, and household size.
- Seasonal Variations: Electricity consumption tends to be higher during winter months due to increased heating demands. Conversely, consumption dips during summer months as heating requirements decrease.
- Appliance Usage: Major appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens contribute significantly to overall electricity consumption.
- Household Size: Larger households generally consume more electricity due to increased appliance usage and lighting requirements.
Electricity Consumption by Region and Income Level
Electricity consumption patterns can vary across different regions and income levels in Germany.
- Regional Differences: Regions with colder climates, such as northern Germany, tend to have higher electricity consumption due to increased heating needs.
- Income Level: Higher-income households may consume more electricity due to the ownership of energy-intensive appliances and larger living spaces.
Impact of Energy-Saving Measures and Smart Home Technologies
Energy-saving measures and smart home technologies are increasingly influencing electricity consumption in German homes.
- Energy-Saving Measures: Implementing energy-saving measures, such as using energy-efficient appliances, installing insulation, and adopting sustainable practices, can significantly reduce electricity consumption and costs.
- Smart Home Technologies: Smart home technologies, including smart thermostats, intelligent lighting systems, and energy management software, enable homeowners to monitor and optimize their electricity consumption, leading to potential savings.
Exploring Energy Efficiency Initiatives
Germany, a nation committed to environmental sustainability, has implemented a comprehensive set of policies and programs aimed at reducing energy consumption and promoting energy efficiency. These initiatives, combined with a robust renewable energy sector, play a crucial role in shaping the country’s electricity landscape.
Government Programs and Incentives
Germany’s commitment to energy efficiency is evident in its numerous government programs and incentives designed to encourage households and businesses to adopt energy-saving practices. These initiatives aim to reduce electricity consumption, lower energy bills, and minimize the country’s environmental footprint.
- The Energy Saving Ordinance (EnEV): This comprehensive regulation sets minimum energy efficiency standards for new and existing buildings, covering aspects like insulation, heating systems, and windows. The EnEV has significantly improved the energy performance of buildings, contributing to lower energy consumption and reduced CO2 emissions.
- The Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG): While primarily focused on promoting renewable energy, the EEG also includes provisions for energy efficiency. It mandates that energy suppliers invest a portion of their revenues in energy efficiency projects, fostering a more sustainable energy system.
- Financial Incentives: The German government offers various financial incentives, including subsidies and tax breaks, to encourage individuals and businesses to invest in energy-efficient technologies. These incentives cover a wide range of measures, such as installing solar panels, upgrading insulation, and replacing old appliances with energy-efficient models.
Renewable Energy Sources in Germany
Renewable energy sources, particularly solar, wind, and hydropower, have become integral to Germany’s electricity market. The country’s ambitious renewable energy targets have driven significant investments in these technologies, resulting in a substantial increase in renewable energy generation.
- Solar Energy: Germany is a global leader in solar energy, with a vast network of photovoltaic installations across the country. The sunny climate and government support have fostered the growth of the solar sector, contributing significantly to electricity generation.
- Wind Energy: Wind power is another crucial component of Germany’s renewable energy mix. The country’s geographical location, with its extensive coastlines and wind-swept landscapes, provides ideal conditions for wind energy development. Wind turbines are a common sight across Germany, generating clean electricity on a large scale.
- Hydropower: While less prominent than solar and wind, hydropower remains an important source of renewable energy in Germany. The country’s numerous rivers and lakes provide opportunities for hydroelectric power generation, contributing to the overall renewable energy mix.
Future Energy Policies and Their Impact on Electricity Costs
Germany’s commitment to transitioning towards a carbon-neutral energy system by 2045 has significant implications for future energy policies and electricity costs. The country’s energy transition involves a complex interplay of factors, including the expansion of renewable energy, the phasing out of fossil fuels, and the modernization of the electricity grid.
- Expansion of Renewable Energy: To achieve its carbon neutrality goals, Germany plans to significantly expand its renewable energy capacity. This expansion will involve investing in new wind and solar farms, as well as exploring other renewable energy sources like geothermal and biomass.
- Phasing Out Fossil Fuels: Germany aims to phase out coal-fired power plants by 2038 and gradually reduce its reliance on natural gas. This transition will require investments in renewable energy and energy storage solutions to ensure a reliable and stable electricity supply.
- Modernization of the Electricity Grid: The expansion of renewable energy and the shift towards a decentralized energy system necessitate a modern and flexible electricity grid. Germany is investing in smart grid technologies to improve grid efficiency, integrate renewable energy sources, and manage energy flows more effectively.
The transition towards a carbon-neutral energy system will likely involve both challenges and opportunities for Germany. While the shift away from fossil fuels may initially lead to higher electricity costs, the long-term benefits of a sustainable energy system are expected to outweigh the short-term costs. The government’s commitment to energy efficiency and renewable energy will play a crucial role in shaping the future of Germany’s electricity market, balancing environmental sustainability with economic competitiveness.
Comparing Electricity Costs with Other Countries: Was Kostet Strom In Deutschland
Understanding the cost of electricity in Germany requires a comparative perspective. By examining electricity prices in other European countries, we can gain valuable insights into the factors influencing electricity costs and identify potential areas for improvement.
Comparison with Other European Countries
Electricity prices in Germany are relatively high compared to many other European countries. The following table provides a comparison of average household electricity prices in 2022:
| Country | Average Household Electricity Price (EUR/kWh) |
|---|---|
| Germany | 0.35 |
| France | 0.25 |
| Italy | 0.28 |
| Spain | 0.24 |
| United Kingdom | 0.29 |
Several factors contribute to these price differences, including:
- Energy Mix: Germany’s reliance on renewable energy sources, particularly wind and solar, can lead to higher electricity prices due to the intermittency of these sources.
- Energy Taxes and Regulations: Germany has a relatively high level of energy taxes and regulations, including the Renewable Energy Act (EEG), which aims to promote renewable energy development. These measures can contribute to higher electricity prices.
- Nuclear Power: Germany’s decision to phase out nuclear power has resulted in a higher reliance on fossil fuels, which can impact electricity prices.
- Transmission and Distribution Costs: Germany has a well-developed electricity grid, which can lead to higher transmission and distribution costs compared to countries with less extensive grids.
Impact of International Energy Markets and Geopolitical Events
Electricity prices in Germany are also influenced by international energy markets and geopolitical events. For example, the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine significantly impacted energy prices across Europe, including Germany. This event led to increased reliance on alternative energy sources, such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), and resulted in higher energy prices.
Potential for Cross-Border Electricity Trade
Cross-border electricity trade can play a significant role in stabilizing electricity prices in Germany. By connecting to other countries’ electricity grids, Germany can access cheaper electricity sources during peak demand periods or when renewable energy production is low. The European Union’s internal energy market promotes cross-border electricity trade, and initiatives such as the European Supergrid aim to further enhance cross-border electricity connections.
Cross-border electricity trade can help to mitigate price volatility and ensure a more stable electricity supply for Germany.
Practical Tips for Managing Electricity Costs
In Germany, households can significantly reduce their electricity bills by implementing energy-saving measures and adopting smart consumption habits. This section will provide practical tips categorized by appliance type, a step-by-step guide for choosing the right electricity tariff, and recommendations for smart home devices and energy management tools.
Energy-Saving Tips for Appliances
By adopting these energy-saving tips for different appliances, German households can significantly reduce their electricity consumption and lower their energy bills. These measures are simple to implement and can make a noticeable difference over time.
| Appliance | Energy-Saving Tips |
|---|---|
| Lighting |
|
| Refrigerator and Freezer |
|
| Washing Machine and Dryer |
|
| Dishwasher |
|
| Heating and Cooling |
|
| Electronics |
|
Choosing the Right Electricity Tariff
Selecting the most suitable electricity tariff for your consumption patterns and budget is crucial for managing electricity costs effectively. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed decision.
- Analyze your electricity consumption: Review your past energy bills to understand your average monthly consumption and identify peak usage times. You can use online tools or apps to track your consumption data in real-time.
- Compare electricity tariffs: Visit online comparison websites or contact energy providers directly to compare different tariffs and their terms and conditions.
- Consider your consumption patterns: Choose a tariff that aligns with your usage habits. For example, if you use a lot of electricity during peak hours, a variable tariff might be more cost-effective. Conversely, if you consume more during off-peak hours, a fixed tariff could be a better option.
- Factor in your budget: Compare tariffs based on their monthly costs and consider any additional fees or charges. Choose a tariff that fits your budget and meets your energy needs.
- Check for special offers and discounts: Some energy providers offer discounts for switching to their services or for signing up for long-term contracts. Take advantage of these incentives to potentially reduce your electricity costs.
Smart Home Devices and Energy Management Tools
Smart home devices and energy management tools can help you optimize electricity usage and reduce costs by providing real-time data and insights into your consumption patterns. These tools can automate energy-saving measures and help you make informed decisions about your energy use.
- Smart plugs: These devices can be plugged into any electrical outlet and allow you to control and monitor the power consumption of connected appliances remotely. You can schedule appliances to turn on or off automatically, reducing unnecessary energy use.
- Smart thermostats: Programmable thermostats can adjust the temperature of your home automatically based on your schedule and preferences, optimizing heating and cooling efficiency.
- Energy monitoring systems: These systems provide detailed information about your electricity consumption in real-time, allowing you to identify areas where you can save energy.
- Home energy management software: This software can analyze your energy usage data and provide personalized recommendations for reducing consumption and saving money.
Navigating the complexities of electricity costs in Germany requires a comprehensive understanding of the factors at play. By analyzing consumption patterns, exploring energy efficiency initiatives, and comparing prices with other countries, we can gain valuable insights into managing electricity costs effectively. Whether you’re a homeowner seeking to optimize your energy usage or a business looking to reduce operational expenses, this guide provides essential information and practical tips to navigate the German electricity landscape.
Key Questions Answered
What are the main types of electricity tariffs in Germany?
Germany offers a variety of electricity tariffs, including basic tariffs, variable tariffs, and fixed tariffs. Each type has its own pricing structure and benefits, catering to different consumption patterns and preferences.
How can I find the cheapest electricity tariff in Germany?
To find the most affordable electricity tariff, consider your annual energy consumption, your budget, and your preferred payment method. Online comparison websites and energy consultants can assist in finding the best tariff for your needs.
Are there any government subsidies available for energy-efficient appliances in Germany?
Yes, the German government offers various subsidies and incentives for energy-efficient appliances and home improvements. These programs aim to promote energy conservation and reduce electricity consumption.
What is the future outlook for electricity prices in Germany?
Future electricity prices in Germany are expected to be influenced by factors such as the transition to renewable energy sources, geopolitical events, and technological advancements. The overall trend suggests a gradual increase in electricity prices, driven by the need to invest in sustainable energy infrastructure.




