What cars have 4×100 lug pattern? This question often pops up for car enthusiasts looking to upgrade their wheels or understand the intricacies of their vehicle’s setup. The 4×100 lug pattern is a common configuration, especially for smaller and sportier vehicles, and understanding its implications can be crucial for achieving optimal performance and handling. From the iconic Honda Civic to the nimble Mazda Miata, a variety of popular vehicles utilize this pattern, opening up a world of customization and performance possibilities.
But before you dive into the exciting world of wheel upgrades, it’s essential to grasp the meaning behind the 4×100 designation and its impact on your car’s overall driving experience.
The 4×100 lug pattern refers to the arrangement of wheel bolts on a car’s hub. The “4” represents the number of bolts, while the “100” indicates the diameter of the bolt circle in millimeters. This means that the centers of the four bolts are spaced 100 millimeters apart, creating a circular pattern that secures the wheel to the hub. Understanding this pattern is crucial for ensuring compatibility and safety when selecting new wheels for your vehicle.
Understanding 4×100 Lug Pattern
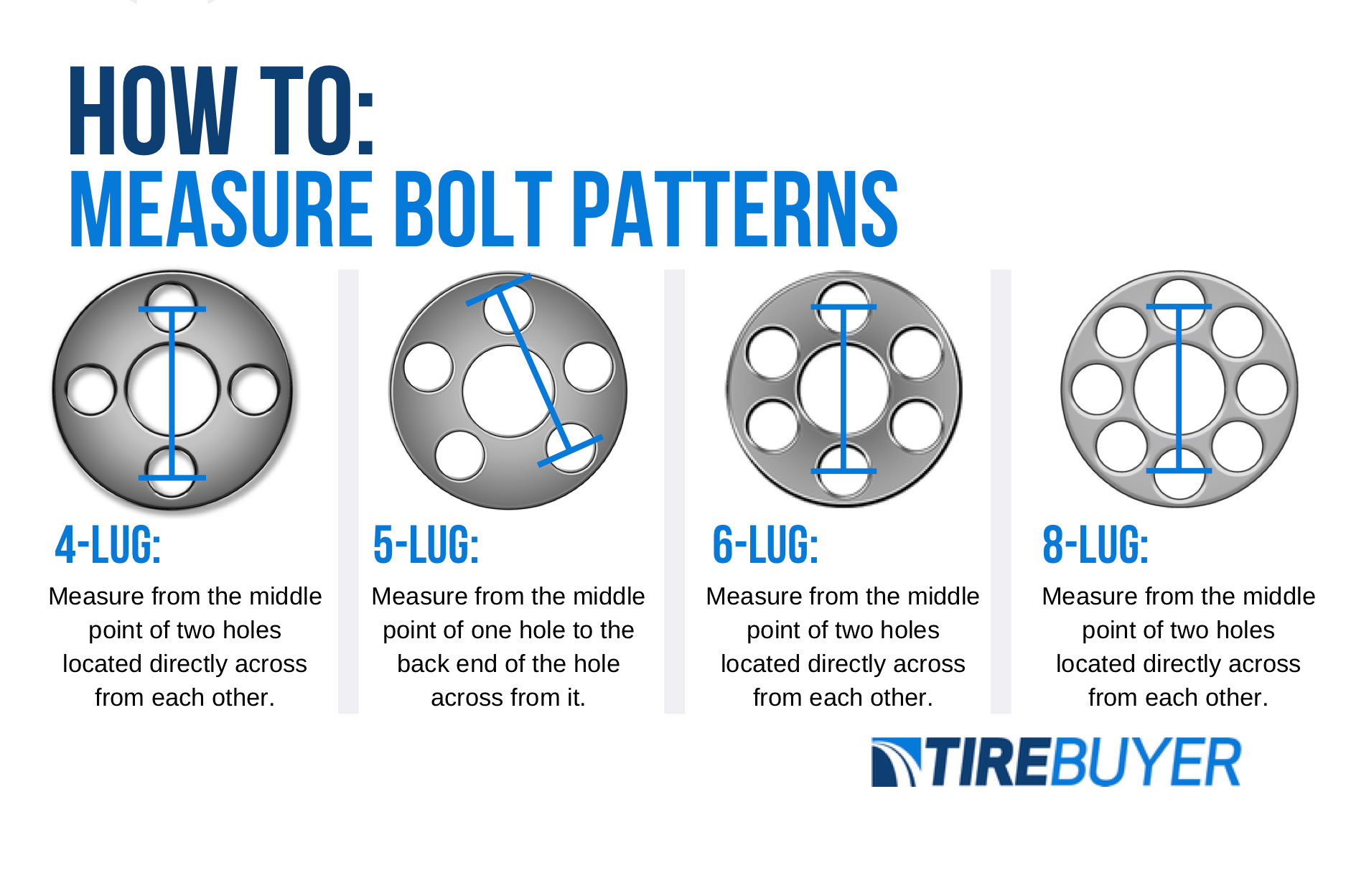
The 4×100 lug pattern is a crucial aspect of wheel and tire compatibility in automotive applications. Understanding this pattern is essential for ensuring proper fitment and safe operation of your vehicle.The “4×100” designation describes the configuration of the wheel bolts, indicating the number of bolts and their spacing. The “4” represents the number of bolts holding the wheel to the hub, while “100” refers to the bolt circle diameter (BCD) in millimeters.
This means that the centers of the four bolt holes are arranged in a circle with a diameter of 100 millimeters.
Vehicle Models with 4×100 Lug Pattern
The 4×100 lug pattern is commonly found on a variety of vehicle models, primarily smaller cars and hatchbacks. It is particularly prevalent in European and Japanese car manufacturers. Here are some examples of popular models that utilize this lug pattern:
- Honda Civic (1992-2000): The Honda Civic, a popular compact car, has been known to utilize the 4×100 lug pattern for its earlier models.
- Mazda Miata (NA and NB): The Mazda Miata, a renowned sports car, is another vehicle that utilizes the 4×100 lug pattern.
- Volkswagen Golf (Mk2 and Mk3): The Volkswagen Golf, a compact hatchback, also uses the 4×100 lug pattern in its earlier generations.
- Toyota Corolla (1993-2002): The Toyota Corolla, a popular compact car, also features the 4×100 lug pattern in certain model years.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 4×100 Lug Pattern

The 4×100 lug pattern is a common wheel bolt configuration found on many smaller vehicles, particularly those produced by European manufacturers. This pattern offers a unique balance of advantages and disadvantages, making it a popular choice for some applications but not others.
Advantages of 4×100 Lug Pattern
The 4×100 lug pattern offers several advantages, particularly for smaller vehicles.
- Wide Wheel Selection: The 4×100 lug pattern enjoys a relatively wide range of wheel options, offering a variety of styles and sizes to suit different preferences and needs. This variety caters to both stock replacement and aftermarket customization.
- Lightweight Construction: Vehicles with 4×100 lug patterns often have lighter wheels, contributing to improved handling and fuel efficiency. This is especially beneficial for smaller vehicles, where weight reduction can have a significant impact on performance.
- Cost-Effective: Wheels with the 4×100 lug pattern are often more affordable compared to those with larger patterns, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious car owners.
Disadvantages of 4×100 Lug Pattern, What cars have 4×100 lug pattern
While the 4×100 lug pattern offers advantages, it also presents certain limitations.
- Limited Load Capacity: The 4×100 lug pattern is typically found on smaller vehicles with lower weight ratings. This pattern might not be suitable for heavier vehicles or those intended for off-road use, where higher load capacities are required.
- Reduced Strength: The 4×100 lug pattern may not be as strong as larger patterns, potentially leading to increased risk of wheel failure under extreme conditions. This is particularly relevant for high-performance vehicles or those subjected to heavy loads.
- Limited Availability: While the 4×100 pattern is common in smaller vehicles, it might not be readily available for larger vehicles or specialized applications. This can pose challenges when seeking replacement wheels or specific aftermarket options.
Comparison with Other Lug Patterns
The 4×100 lug pattern’s strength and durability compare differently to other common lug patterns.
- 4×114.3 (5×114.3): This pattern is commonly found on larger vehicles and offers a stronger foundation for heavier loads. The larger bolt spacing provides a more secure connection, enhancing the wheel’s ability to withstand stress and prevent loosening.
- 5×100: While similar in diameter to the 4×100 pattern, the 5×100 pattern has an additional bolt hole, offering increased strength and load capacity. This pattern is commonly found on performance-oriented vehicles and those designed for demanding applications.
Compatibility and Wheel Selection
So, you have a car with a 4×100 lug pattern and you’re looking to upgrade your wheels. Awesome! This is a popular pattern, meaning you’ve got a good range of options, but it’s crucial to choose wheels that fit properly. This ensures safety, performance, and a good look.
Wheel Sizes and Offsets
The most common wheel sizes for cars with a 4×100 lug pattern are 14, 15, 16, and 17 inches. But remember, not all wheels are created equal. The offset (ET) and backspacing are key factors to consider. Here’s a general table showing compatible wheel sizes and offsets for vehicles with a 4×100 lug pattern:| Wheel Size | Offset (ET) Range | Notes ||—|—|—|| 14 inches | 35-45 mm | Suitable for stock or slightly lowered vehicles.
|| 15 inches | 35-45 mm | A popular choice for many 4×100 cars. || 16 inches | 35-45 mm | Can provide a more aggressive look and better handling. || 17 inches | 35-45 mm | May require fender modifications for some vehicles. |
It’s important to note that these are just general guidelines. Always check the specific wheel manufacturer’s recommendations for your vehicle model.
Choosing the Right Wheels
To ensure you choose the right wheels, you need to consider several factors:
Wheel Size
The size should be compatible with your vehicle’s suspension and brake system. A larger wheel can sometimes interfere with the brake calipers.
Offset (ET)
The offset determines how far the wheel sits in or out from the hub. A higher offset pushes the wheel further inward, while a lower offset pushes it outward.
Backspacing
This is the distance between the mounting surface of the wheel and the center of the wheel.
Tire Size
The tire size needs to be compatible with the wheel size and your vehicle’s specifications.
A good rule of thumb is to stay within a 5-10mm range of the original offset for your vehicle. However, it’s always best to consult a wheel and tire specialist or your car’s owner’s manual for specific recommendations.
Understanding Offset and Backspacing
Offset (ET)
Offset is measured in millimeters and refers to the distance between the mounting surface of the wheel and the center of the wheel. A positive offset means the mounting surface is closer to the inside of the wheel, while a negative offset means it’s closer to the outside.
Backspacing
Backspacing is measured in inches and is the distance from the mounting surface of the wheel to the inside of the wheel. It’s a crucial measurement for determining how the wheel sits in the wheel well.
If you’re unsure about the offset and backspacing for your vehicle, you can use a wheel fitment calculator or consult a wheel and tire specialist.
Performance and Handling Considerations: What Cars Have 4×100 Lug Pattern

Choosing the right wheels for your car can significantly impact its handling and performance. Wheel size and offset are crucial factors that affect how your car drives, influencing everything from acceleration and braking to cornering stability and overall ride comfort. Understanding the relationship between wheel size, offset, and vehicle dynamics is essential for optimizing your car’s performance and maximizing your driving experience.
Impact of Wheel Size and Offset on Handling and Performance
Wheel size and offset play a crucial role in determining a vehicle’s handling and performance characteristics. These factors influence the car’s geometry, affecting tire contact patch, suspension travel, and overall stability.
- Wheel Diameter: Larger wheels generally offer improved handling and stability, particularly at higher speeds. This is due to the increased tire contact patch, which provides better grip and reduces tire flex. However, larger wheels can increase unsprung weight, which can negatively impact acceleration and braking.
- Wheel Width: Wider wheels offer a larger contact patch, improving grip and stability. However, wider wheels can also increase rolling resistance, reducing fuel efficiency and potentially affecting steering responsiveness.
- Offset: Offset refers to the distance between the wheel mounting surface and the center of the wheel. A positive offset pushes the wheel further outward, while a negative offset moves it inward. Offset affects the wheel’s position relative to the suspension, impacting steering response, camber angle, and overall handling.
Performance Benefits and Drawbacks of Specific Wheel Sizes
Different wheel sizes offer specific advantages and disadvantages depending on the intended use and driving style.
- Larger Wheels (16″ or More): Larger wheels typically provide improved handling and stability, especially at higher speeds. The larger contact patch contributes to better grip, enhancing cornering performance and reducing tire flex. However, larger wheels can increase unsprung weight, negatively impacting acceleration and braking. They can also increase ride harshness and potentially affect fuel efficiency.
- Smaller Wheels (14″ or Less): Smaller wheels generally offer better acceleration and braking due to reduced unsprung weight. They also tend to be more affordable and have a wider selection of tires available. However, smaller wheels can compromise handling and stability, particularly at higher speeds, as they offer a smaller contact patch and are more prone to tire flex.
Impact of Wheel Selection on Braking, Cornering, and Overall Driving Experience
Wheel selection can significantly impact braking, cornering, and overall driving experience.
- Braking: Larger wheels, while offering a larger contact patch, can increase unsprung weight, potentially leading to a longer braking distance. Smaller wheels, on the other hand, can improve braking performance due to reduced unsprung weight.
- Cornering: Larger wheels provide better stability and grip, improving cornering performance. However, larger wheels can also increase the car’s tendency to understeer, where the front wheels lose grip and the car fails to turn as sharply as intended.
- Overall Driving Experience: The overall driving experience is influenced by the combination of wheel size, offset, and tire selection. Larger wheels generally offer a more planted and stable ride, while smaller wheels can provide a more agile and responsive feel.
Popular Applications of 4×100 Lug Pattern
The 4×100 lug pattern is a common configuration found on a wide range of vehicles, particularly smaller and more compact models. This pattern’s prevalence stems from its suitability for smaller vehicles, offering a balance between strength and weight optimization.
Popular Vehicle Makes and Models
The 4×100 lug pattern is widely used in the automotive industry, particularly for smaller and more compact vehicles. Here are some popular examples:
- Honda: Civic (1992-2000), CRX (1984-1991), Del Sol (1992-1997), Fit (2007-present)
- Mazda: Miata (1990-present), MX-5 (1990-present), Protegé (1990-2003), 323 (1985-1998)
- Toyota: Corolla (1993-2002), Tercel (1988-1999), MR2 (1985-2007)
- Volkswagen: Golf (1974-present), Jetta (1979-present), Polo (1975-present)
- Ford: Fiesta (1976-present), Focus (1998-present)
- Mitsubishi: Lancer (1973-present), Eclipse (1989-2012)
- Subaru: Impreza (1993-present), Legacy (1989-present)
Applications within the Automotive Industry
The 4×100 lug pattern finds application in various segments of the automotive industry:
- Compact Cars: Due to its lighter weight and suitability for smaller vehicles, it is commonly found on compact cars, hatchbacks, and sedans. This pattern effectively balances strength with weight reduction, crucial for enhancing fuel efficiency and handling in smaller vehicles.
- Sports Cars: The 4×100 lug pattern is also prevalent in sports cars, particularly in models known for their lightweight construction and agile handling. The pattern allows for the use of lightweight wheels while maintaining sufficient strength for high-performance driving.
- Performance Vehicles: The 4×100 lug pattern is also used in performance vehicles, particularly in models with aftermarket modifications that emphasize handling and track performance. The pattern offers a balance between strength and weight optimization, allowing for the use of wider and lighter wheels.
Historical Evolution of the 4×100 Lug Pattern
The 4×100 lug pattern emerged as a response to the growing popularity of smaller and more fuel-efficient vehicles in the 1970s and 1980s. The pattern’s smaller diameter and lighter weight compared to larger patterns like 5×114.3 made it a suitable option for these vehicles. The widespread adoption of the 4×100 lug pattern by manufacturers like Honda, Mazda, and Toyota further cemented its significance in the automotive industry.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
Proper maintenance and safety precautions are crucial when dealing with wheels and lug nuts, especially when working with a 4×100 lug pattern. While the pattern itself doesn’t pose any unique challenges, understanding the importance of proper maintenance and safety practices is vital for ensuring a smooth and safe driving experience.
Wheel Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your wheels is essential for their longevity and safety. This includes:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean your wheels with a dedicated wheel cleaner to remove brake dust, dirt, and grime. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners that can damage the finish.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect your wheels for any signs of damage, cracks, or corrosion. Look for any unusual wear patterns or damage to the lug nut holes.
- Lubrication: Lubricate the lug nuts with a thread lubricant to prevent corrosion and ensure smooth removal and installation. This will help prevent damage to the lug nuts and wheel studs.
Lug Nut Safety
Lug nuts play a crucial role in securing your wheels to the vehicle. It’s essential to follow these safety practices:
- Proper Torque: Always tighten lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specified torque using a torque wrench. Over-tightening can damage the wheel studs or lug nuts, while under-tightening can lead to loose wheels.
- Regular Tightening: Regularly check the tightness of your lug nuts, especially after driving on rough roads or after a wheel change.
- Correct Lug Nuts: Use only lug nuts that are specifically designed for your vehicle’s wheel studs and lug pattern. Using the wrong lug nuts can lead to improper fit and potentially cause a wheel to detach.
Risks of Incorrect Wheel Size or Lug Pattern
Using the wrong wheel size or lug pattern can have serious consequences:
- Wheel Detachment: Using wheels with a different lug pattern can result in the wheels not being properly secured, leading to a potential wheel detachment while driving. This can be extremely dangerous, potentially causing an accident.
- Handling Issues: Incorrect wheel size can affect your vehicle’s handling and braking performance. This can lead to instability, reduced braking efficiency, and difficulty controlling the vehicle.
- Suspension Damage: Mismatched wheels can put undue stress on your suspension components, leading to premature wear and tear. This can result in expensive repairs and potentially affect the overall ride quality.
As you delve deeper into the world of 4×100 lug patterns, you’ll discover a fascinating blend of technical specifications, performance enhancements, and customization options. From understanding the advantages and disadvantages of this pattern to navigating the intricate world of wheel offset and backspacing, this exploration empowers you to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s setup. Remember, choosing the right wheels for your 4×100 lug pattern is not just about aesthetics; it’s about optimizing performance, enhancing handling, and ensuring a safe and enjoyable driving experience.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the benefits of a 4×100 lug pattern?
The 4×100 lug pattern is commonly found on smaller and lighter vehicles, which often translates to a more agile and responsive driving experience. This pattern can also offer a wider range of wheel choices, especially for those seeking aftermarket upgrades.
Are there any drawbacks to using a 4×100 lug pattern?
While offering a range of advantages, the 4×100 lug pattern may be less robust than larger patterns, particularly for heavier vehicles. This can lead to potential concerns regarding strength and durability under extreme conditions.
How do I know if my car has a 4×100 lug pattern?
You can usually find the lug pattern information on your vehicle’s owner’s manual or on a sticker located on the driver’s side doorjamb. Alternatively, you can check online resources or consult with a mechanic.
What are some popular cars that use a 4×100 lug pattern?
Some popular cars that use a 4×100 lug pattern include the Honda Civic, Mazda Miata, Toyota Corolla, and Volkswagen Golf.
What is the best way to maintain wheels with a 4×100 lug pattern?
Regularly inspect your wheels for any signs of damage, cracks, or corrosion. Ensure that the lug nuts are properly tightened to the specified torque. It’s also essential to clean your wheels regularly to remove dirt and debris.






