How to use derma stamp for hair growth unveils a fascinating realm of hair restoration techniques. This exploration delves into the intricacies of microneedling, examining its mechanisms, practical applications, and potential benefits. We navigate the selection of appropriate derma stamps, the crucial steps of sterilization and scalp preparation, and the precise techniques for optimal results. The narrative also addresses potential risks, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making and professional consultation.
From understanding the diverse types of derma stamps available to mastering the art of microneedling, this guide provides a comprehensive overview. We will consider the advantages and disadvantages of derma stamping in comparison to other hair growth treatments, offering readers a nuanced perspective. Furthermore, the discussion extends to aftercare, maintenance, and the integration of derma stamping into broader hair growth regimens, culminating in a realistic assessment of expected outcomes and timelines.
Derma Stamping Basics
Derma stamping, also known as microneedling, is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a small, handheld device with tiny needles to create micro-injuries in the skin. This controlled injury triggers the body’s natural wound-healing response, stimulating collagen and elastin production. For hair growth, this increased production is believed to create a more favorable environment for hair follicles to thrive, potentially leading to thicker, fuller hair.
Mechanism of Action for Hair Growth
The primary mechanism behind derma stamping’s efficacy in promoting hair growth lies in its ability to stimulate various growth factors and cellular processes within the scalp. The micro-injuries created by the needles trigger the release of growth factors like vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast growth factor (FGF), which are crucial for angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) and follicular regeneration.
Increased blood flow delivers essential nutrients and oxygen to the hair follicles, improving their health and promoting anagen (growth) phase prolongation. Furthermore, the process stimulates the production of collagen and elastin, strengthening the dermal papilla – the base of the hair follicle – and providing structural support for hair growth. While the exact mechanisms are still under investigation, the observed improvements in hair density and thickness suggest a significant role for these processes.
Derma Stamp Types
Derma stamps vary in several key characteristics influencing their effectiveness and suitability for different users. The most significant variations are in needle length, stamp size, and material. Needle length typically ranges from 0.25mm to 2.0mm, with longer needles penetrating deeper into the dermis. Shorter needles are generally preferred for the scalp to avoid potential bleeding and scarring, while longer needles might be used for more advanced cases under professional supervision.
Stamp size also varies, influencing the area covered in each session. Larger stamps may be more efficient for covering larger areas of the scalp but may also be less precise. The material is usually surgical-grade stainless steel, which is durable, easily sterilized, and relatively inexpensive. Titanium derma stamps are also available, offering potential benefits in terms of durability and biocompatibility, although they are typically more costly.
Derma Stamp Sterilization
Proper sterilization is paramount to prevent infection and ensure the safety of the procedure. Before each use, the derma stamp should be thoroughly cleaned with isopropyl alcohol (70% concentration) and then sterilized using an autoclave (if available) or by submerging it in boiling water for at least 15 minutes. After use, the stamp should be immediately cleaned again with isopropyl alcohol, and then stored in a sterile, airtight container.
It’s crucial to ensure that all parts of the stamp, including the needles, are thoroughly sterilized. Improper sterilization can lead to serious skin infections, emphasizing the need for careful and meticulous cleaning procedures.
Comparison with Other Hair Growth Treatments
| Treatment | Benefits | Drawbacks | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Derma Stamping | Relatively inexpensive, minimally invasive, stimulates natural hair growth | Requires consistent use, potential for minor bleeding and scarring, effectiveness varies | Low to Moderate |
| Minoxidil (Rogaine) | FDA-approved, widely available, topical application | Requires continuous use, potential side effects (scalp irritation, unwanted hair growth), effectiveness varies | Moderate |
| Finasteride (Propecia) | FDA-approved, effective for some men with androgenetic alopecia | Oral medication, potential side effects (sexual dysfunction), not suitable for women | Moderate to High |
| Hair Transplant | Permanent results, natural-looking hair restoration | Expensive, invasive procedure, potential for scarring and complications | High |
Preparing for Derma Stamping
Derma stamping, while a promising technique for hair regrowth, demands meticulous preparation to maximize its effectiveness and minimize the risk of complications. Proper preparation ensures the procedure is both safe and yields the best possible results. This involves understanding your scalp’s condition, selecting the appropriate tools, and following a strict hygiene protocol.
Optimal skin preparation is crucial for successful derma stamping. The goal is to create a clean, receptive environment for the microneedles to stimulate hair follicle activity without introducing infection. This involves cleansing the scalp thoroughly to remove dirt, oil, and any potential contaminants that could impede the process or lead to inflammation. Furthermore, a properly prepared scalp will minimize discomfort during the procedure.
Scalp Cleansing and Preparation
Before derma stamping, thorough cleansing is paramount. Begin by gently washing your scalp with a mild, sulfate-free cleanser. Avoid harsh chemicals or scrubs that could irritate the scalp. Rinse thoroughly with lukewarm water, ensuring all traces of cleanser are removed. Pat the scalp dry with a clean, soft towel, avoiding harsh rubbing.
This meticulous cleansing step minimizes the risk of infection and optimizes the absorption of any topical serums applied post-procedure. The clean scalp also allows for better visualization of the treatment area, aiding in the precise application of the derma stamp.
Precautions Before Derma Stamping, How to use derma stamp for hair growth
Taking necessary precautions is essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of the procedure. Ignoring these precautions can lead to complications ranging from minor skin irritation to severe infections.
- Avoid using any active topical treatments (like retinoids or strong exfoliants) on your scalp for at least 24-48 hours before derma stamping. These can increase sensitivity and the risk of irritation.
- Do not perform derma stamping if you have any active scalp infections, wounds, or skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis. The procedure could worsen these conditions.
- Ensure the derma stamp and its needles are sterilized thoroughly before and after each use to prevent infection. This typically involves autoclaving or using a medical-grade disinfectant.
- Avoid consuming alcohol or caffeine before the procedure as these can increase bleeding and sensitivity.
- Consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional before beginning derma stamping, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications that might affect your skin’s healing process.
Needle Length Selection
Choosing the correct needle length is critical for effective and safe derma stamping. Needle length is directly correlated with the depth of micro-injuries created, which in turn influences the degree of stimulation to the hair follicles. Using an inappropriately long needle can cause excessive bleeding and scarring, while too short a needle may not provide sufficient stimulation.
For example, a 0.5mm needle might be suitable for individuals with mild hair thinning, focusing primarily on superficial stimulation. However, individuals with more significant hair loss or scarring might benefit from a longer needle, such as a 1.0mm or 1.5mm needle (always under the guidance of a professional). The deeper penetration achieved with longer needles can stimulate deeper dermal layers, potentially promoting more significant hair follicle regeneration.
It is crucial to consult a dermatologist or trichologist to determine the appropriate needle length based on individual scalp condition and hair loss pattern.
Prepping the Scalp for Derma Stamping: An Infographic Description
The infographic would be visually divided into three main sections: Cleanse, Sterilize, and Prepare. Cleanse: This section would show a close-up image of a person gently washing their scalp with a mild cleanser. The text would emphasize using lukewarm water and a sulfate-free cleanser, avoiding harsh scrubbing. A visual cue could be a small icon of a soap bottle with a checkmark next to it, indicating the approval of mild cleanser.
Sterilize: This section would depict the derma stamp being submerged in a sterilizing solution (e.g., isopropyl alcohol) or placed in an autoclave. The text would highlight the importance of sterilizing both the derma stamp and the needles before and after each use to prevent infection. A visual representation could include an image of an autoclave or a container with sterilizing solution with a warning symbol indicating the need for caution.
Prepare: This section would illustrate the final steps: gently patting the scalp dry with a clean towel, and optionally, applying a topical serum or growth factor to the scalp before beginning the derma stamping process. The visual cue could be a small icon of a serum bottle with a dropper next to the image of the clean scalp.
Derma Stamping Technique
Derma stamping, also known as microneedling, involves the use of a small, handheld device with tiny needles to create micro-injuries in the scalp. These controlled injuries trigger the body’s natural wound-healing response, stimulating increased blood flow, collagen production, and potentially, hair follicle regeneration. Proper technique is crucial for maximizing benefits and minimizing risks. Incorrect technique can lead to scarring, infection, or ineffective treatment.
The effectiveness of derma stamping for hair growth is still under investigation, with studies showing mixed results. While some individuals report noticeable improvements, it’s important to manage expectations and understand that it’s not a guaranteed solution for hair loss. Its efficacy likely depends on the underlying cause of hair loss, the individual’s response to the treatment, and the consistency of application.
Always consult a dermatologist or trichologist before beginning any derma stamping regimen.
Derma Stamping Patterns
Different patterns can be employed during derma stamping, each potentially offering advantages depending on the scalp area and the density of hair follicles. A common approach involves vertical passes, followed by horizontal passes, creating a grid-like pattern across the treatment area. Another approach is to use a circular motion, ensuring complete coverage of the targeted area. It’s essential to maintain consistent spacing between passes to ensure even stimulation of the scalp.
Overlapping passes can increase the risk of irritation and discomfort. A methodical approach, ensuring complete coverage without excessive pressure, is key to a successful treatment.
Optimal Pressure and Depth
The depth of penetration and the pressure applied during derma stamping are critical factors influencing the treatment’s efficacy and safety. Generally, a depth of 0.5mm to 1.5mm is recommended for the scalp. Deeper penetration might increase the risk of bleeding and scarring, while shallower penetration may not effectively stimulate hair follicle regeneration. The pressure should be consistent and firm enough to create micro-injuries but not so forceful as to cause excessive pain or bleeding.
The user should feel a slight resistance, indicating the needles are effectively penetrating the skin. Excessive pressure should be avoided, as it increases the risk of injury.
Step-by-Step Derma Stamping Procedure
A systematic approach is essential for safe and effective derma stamping. Each step plays a crucial role in maximizing benefits and minimizing potential risks. Following these steps will ensure a consistent and controlled treatment.
- Cleanse the scalp thoroughly with a mild, antibacterial cleanser to remove any dirt, oil, or debris that could lead to infection.
- Sterilize the derma stamp according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This usually involves soaking the device in a disinfectant solution or using a UV sterilizer.
- Apply a numbing cream to the scalp (optional, but recommended for increased comfort), allowing sufficient time for it to take effect before starting the procedure.
- Begin derma stamping using a chosen pattern (vertical, horizontal, or circular), maintaining consistent pressure and depth. Avoid applying excessive pressure.
- After the treatment, apply a suitable serum or growth factor to the scalp to promote hair follicle regeneration.
- Cleanse the scalp again and apply a soothing moisturizer to reduce any redness or irritation.
- Avoid touching the treated area excessively and refrain from applying harsh chemicals or products.
Aftercare and Maintenance

The success of derma stamping for hair growth hinges not only on the procedure itself but also on diligent aftercare. Proper post-procedure care minimizes the risk of infection, promotes healing, and optimizes the benefits of the micro-needling. Neglecting aftercare can lead to irritation, inflammation, and potentially hinder hair growth. This section details crucial steps and product recommendations for optimal results.
Following derma stamping, your scalp will be more susceptible to irritation and infection. The micro-injuries created by the needles provide entry points for bacteria. Therefore, maintaining a clean and healthy scalp environment is paramount to successful hair regrowth. This involves gentle cleansing, avoiding harsh products, and protecting the scalp from environmental stressors.
Post-Derma Stamping Scalp Care
Immediately after the procedure, avoid touching your scalp unnecessarily. Gently cleanse the area with a mild, fragrance-free cleanser. Avoid harsh scrubbing or aggressive rubbing. Pat the scalp dry with a clean, soft towel. Applying a thin layer of a suitable serum or lotion can help soothe the skin and promote healing.
Avoid using products containing alcohol or harsh chemicals, as these can irritate the already sensitive scalp. Instead, opt for products specifically designed for sensitive skin or post-procedure care.
Products to Support Hair Growth After Derma Stamping
Several products can enhance the benefits of derma stamping and support hair growth. These products often contain ingredients that stimulate hair follicles, improve scalp health, and promote a healthy hair growth cycle.
Examples include serums containing peptides (like copper peptides), growth factors (like epidermal growth factor), or active ingredients like minoxidil (always follow the product instructions carefully). Other beneficial ingredients include vitamins (like biotin and vitamin B5), antioxidants (like green tea extract), and essential oils (like rosemary oil and peppermint oil, but always perform a patch test before widespread application). Remember to choose products that are formulated for sensitive skin and free from harsh chemicals and fragrances.
Maintaining Scalp Hygiene After Derma Stamping
Maintaining impeccable scalp hygiene is crucial after derma stamping. This involves regular, gentle cleansing with a mild, sulfate-free shampoo. Avoid harsh scrubbing, as this can damage the newly formed micro-channels and irritate the scalp. It’s also important to avoid excessive heat styling, which can dehydrate the scalp and hair. Protecting your scalp from direct sunlight with a hat or sunscreen is also recommended, especially during the initial healing phase.
Recommended Post-Procedure Skincare Routine
| Day | Morning | Evening | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1-3 | Gentle cleanse with mild, fragrance-free cleanser; apply thin layer of soothing aloe vera gel | Gentle cleanse with mild, fragrance-free cleanser; apply thin layer of a hyaluronic acid serum | Avoid vigorous scrubbing or rubbing |
| Day 4-7 | Gentle cleanse; apply a serum containing peptides or growth factors | Gentle cleanse; apply a lightweight moisturizer | Monitor for any signs of infection (redness, swelling, pus) |
| Day 7 onwards | Gentle cleanse; apply hair growth serum as directed | Gentle cleanse; apply a scalp-specific moisturizer or oil | Continue to maintain good scalp hygiene |
Potential Risks and Side Effects
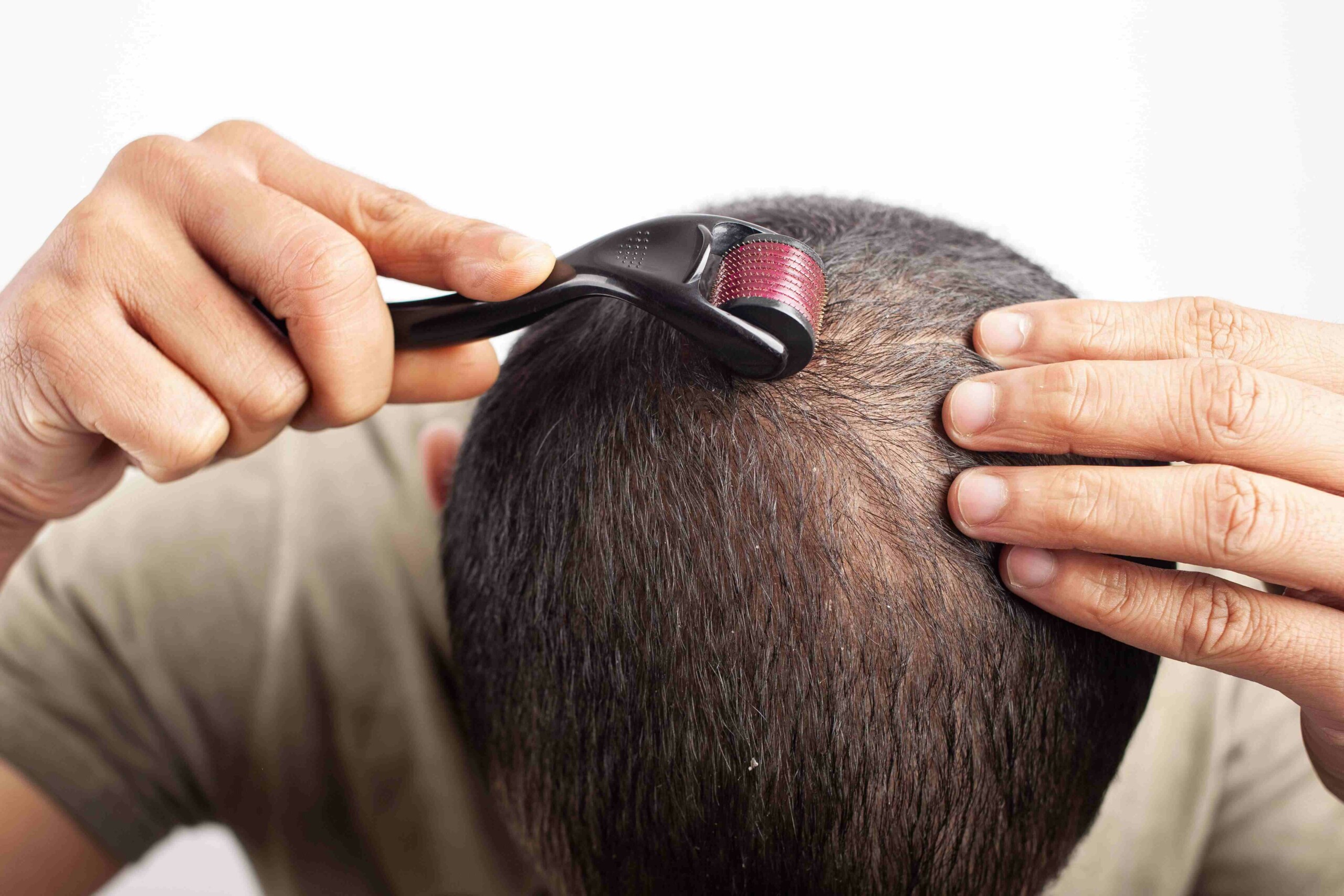
Derma stamping, while a promising technique for hair growth stimulation, is not without potential risks and side effects. Understanding these risks and taking appropriate precautions is crucial for minimizing complications and ensuring a safe and effective treatment. The procedure involves puncturing the skin, creating micro-injuries that trigger a healing response. While this response is intended to stimulate hair follicle activity, it also carries the risk of adverse reactions.
Proper technique, thorough preparation, and diligent aftercare are essential to mitigate these risks.Derma stamping involves the creation of micro-wounds, making it imperative to consult a dermatologist before initiating treatment. A dermatologist can assess your individual skin type, hair condition, and overall health to determine the suitability of derma stamping and to provide guidance on minimizing potential risks. They can also identify any pre-existing conditions that might contraindicate the procedure.
Ignoring this crucial step can lead to unforeseen complications.
Bleeding and Infection
Minor bleeding is a common occurrence during and immediately after derma stamping. The micro-needles create small punctures in the skin, leading to capillary bleeding. This bleeding is usually minimal and stops spontaneously. However, excessive bleeding, persistent bleeding, or bleeding that doesn’t clot within a reasonable time indicates a potential problem. Infection is another significant risk.
The micro-wounds created by the derma stamp provide entry points for bacteria, potentially leading to localized infections characterized by redness, swelling, pain, and pus formation. Proper sterilization of the derma stamp and adherence to strict hygiene practices during and after the procedure are paramount to prevent infection. Applying antiseptic solutions as directed and monitoring the treated area for signs of infection are crucial steps in post-procedure care.
Scarring and Hyperpigmentation
In rare cases, improper derma stamping technique or inadequate aftercare can lead to scarring. Deep or aggressive puncturing of the skin can damage the dermis, resulting in the formation of scars. Similarly, individuals with a predisposition to keloid formation (raised, thickened scars) should exercise extreme caution and potentially avoid derma stamping altogether. Hyperpigmentation, or the darkening of the skin, is another possible side effect, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones.
This occurs due to increased melanin production in response to skin injury. Using appropriate sun protection after derma stamping is essential to minimize the risk of hyperpigmentation.
Unsuitable Situations for Derma Stamping
Derma stamping is not suitable for everyone. Individuals with active acne, open wounds, or skin infections should avoid the procedure as it can exacerbate these conditions. Those with bleeding disorders or who are taking blood-thinning medications should also consult their physician before undergoing derma stamping, as increased bleeding risk exists. Conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea can also be aggravated by derma stamping, making it unsuitable for individuals with these skin conditions.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are additional contraindications, as the effects of derma stamping on fetal or infant development are not fully understood. Finally, individuals with sensitive skin or a low pain tolerance may find the procedure uncomfortable or experience prolonged irritation.
Combining Derma Stamping with Other Treatments
Derma stamping, while effective on its own, can significantly amplify its hair growth-promoting capabilities when combined with other established treatments. This synergistic approach leverages the mechanisms of action of each treatment to create a more potent and comprehensive strategy for combating hair loss. Understanding the interplay between derma stamping and other therapies is crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes and maximizing the benefits for individuals experiencing hair thinning or loss.
The effectiveness of derma stamping stems from its ability to induce controlled micro-trauma to the scalp, triggering a cascade of regenerative processes. This includes increased blood flow, stimulation of growth factors, and enhanced delivery of topical treatments. When combined with other therapies, this micro-needling effect acts as a potent facilitator, enhancing their penetration and efficacy.
Derma Stamping and Minoxidil
Minoxidil, a topical medication widely used for hair loss, works by prolonging the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle and stimulating hair follicle growth. However, its absorption can be limited by the skin’s natural barrier. Derma stamping creates microscopic channels, increasing minoxidil’s penetration and bioavailability. This leads to a higher concentration of minoxidil reaching the hair follicles, potentially resulting in accelerated hair growth and improved efficacy compared to using minoxidil alone.
Studies have not yet directly compared this combination, but the theoretical benefits are supported by the known mechanisms of both treatments. A possible regimen could involve derma stamping once a week, followed by the application of minoxidil.
Derma Stamping and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s own blood into the scalp. Platelets are rich in growth factors that stimulate hair follicle regeneration. Combining derma stamping with PRP can enhance the therapeutic effect of PRP. The micro-needles created by the derma stamp facilitate the even distribution of the injected PRP throughout the scalp, ensuring that a higher concentration of growth factors reaches the target hair follicles.
This combined approach may lead to improved hair density, thickness, and overall growth compared to either treatment alone. Clinical trials have shown promising results for PRP therapy alone, and the addition of derma stamping could further amplify these results. A typical protocol might involve a PRP injection session followed by derma stamping, allowing for optimal PRP distribution.
Integrating Derma Stamping into a Comprehensive Hair Growth Regimen
A comprehensive hair growth regimen integrating derma stamping should consider the individual’s specific needs and hair loss condition. The frequency of derma stamping and other treatments should be determined by a healthcare professional or dermatologist. A sample regimen could be:
Week 1: Derma stamping session.
Week 2: Minoxidil application, followed by gentle massage.
Week 3: PRP injection, followed immediately by derma stamping.
Week 4: Rest week.
Week 5: Repeat cycle.
This is just an example, and the specific regimen should be tailored to the individual’s needs and response to treatment. Regular monitoring of hair growth progress is essential, and adjustments to the regimen may be necessary based on observed results. It’s crucial to remember that consistency is key for optimal outcomes.
Expected Results and Timeframe: How To Use Derma Stamp For Hair Growth

Derma stamping, also known as microneedling, aims to stimulate hair growth by creating controlled micro-injuries to the scalp. While it can be a helpful addition to a hair growth regimen, it’s crucial to understand that results vary significantly and aren’t guaranteed. The process works by triggering the body’s natural wound-healing response, increasing collagen and elastin production, and potentially improving blood flow to hair follicles.
This enhanced environment can, in turn, support hair follicle function and potentially promote thicker, fuller hair. However, it’s not a miracle cure for hair loss.The timeframe for seeing noticeable results is highly individual and depends on various factors. Some individuals might observe subtle improvements in hair thickness or density within a few months, while others may require several months or even a year of consistent treatments to see significant changes.
It’s important to manage expectations and understand that derma stamping is typically used as a complementary therapy, often in conjunction with other treatments. The gradual nature of hair growth itself contributes to the extended timeframe for observable results.
Factors Influencing Derma Stamping Effectiveness
Several factors can significantly influence the effectiveness of derma stamping for hair growth. These include the individual’s overall health, the severity and type of hair loss, the consistency and technique of the treatments, and the use of complementary therapies. For instance, someone with androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness) might experience different results compared to someone with telogen effluvium (temporary hair shedding).
Similarly, proper technique and depth of needling are crucial for optimal stimulation without causing unnecessary damage. Furthermore, combining derma stamping with other treatments, such as minoxidil or finasteride (under medical supervision), can potentially enhance its effectiveness. The age of the individual and their genetic predisposition also play a significant role in the overall outcome. A younger individual with a strong genetic predisposition for hair growth might experience more significant results than an older individual with a weaker genetic predisposition.
For example, a 30-year-old with mild androgenetic alopecia might see noticeable improvement in hair density after six months of consistent derma stamping and minoxidil use, whereas a 60-year-old with advanced androgenetic alopecia might see only modest improvements even after a year of combined therapy. This highlights the importance of realistic expectations and individual variation in response to treatment.
Ultimately, the journey of utilizing a derma stamp for hair growth requires careful consideration and a commitment to proper technique. While promising potential for hair regeneration, the process necessitates a thorough understanding of the procedure, including appropriate preparation, execution, and aftercare. This comprehensive exploration, however, serves not merely as a procedural guide but as a critical examination of the efficacy and limitations of this approach to hair restoration, empowering readers with the knowledge to make informed choices.
FAQ Insights
Can I use a derma stamp at home?
While possible, home use requires meticulous sterilization and adherence to proper technique to minimize infection risk. Professional consultation is strongly recommended.
How often should I use a derma stamp?
Frequency depends on individual scalp response and needle length. Consult a dermatologist to establish a safe and effective treatment schedule.
What are the signs of an infection after derma stamping?
Signs include increased redness, swelling, pus, or persistent pain. Seek immediate medical attention if infection is suspected.
Does derma stamping hurt?
Mild discomfort or stinging is possible. Numbing creams can be used to mitigate pain, but consult a dermatologist first.






