A general contracting firm experiences cost overruns on 20-unit projects, a common hurdle faced in the construction industry. These projects, with their intricate complexities and larger scale, present unique challenges that can easily lead to budget overruns if not carefully managed. From fluctuating material costs and communication breakdowns to inadequate risk mitigation and unforeseen delays, numerous factors can contribute to these financial burdens.
This exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of cost overruns on projects with 20 or more units, examining the root causes, effective risk management strategies, crucial project planning and execution techniques, contractual considerations, financial management practices, and prevailing industry trends. By understanding these factors and implementing best practices, general contracting firms can enhance their cost control capabilities and navigate the complexities of large-scale projects with greater financial stability.
Contractual Considerations

The type of contract used for a construction project can significantly impact the likelihood of cost overruns. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of different contract types is crucial for minimizing financial risks.
Impact of Different Contract Types on Cost Overruns
Different contract types place varying degrees of responsibility for cost management on the contractor and owner. The most common contract types in construction are:
- Fixed-Price Contracts: In a fixed-price contract, the contractor agrees to complete the project for a predetermined price. This type of contract offers the owner a clear budget and predictable costs. However, it also places a significant burden on the contractor to accurately estimate costs and manage risks. If unexpected issues arise, the contractor may absorb the additional expenses, potentially leading to cost overruns.
- Cost-Plus Contracts: Cost-plus contracts allow the contractor to be reimbursed for all project costs plus a predetermined fee. This type of contract provides the owner with greater flexibility, as they can make changes to the project scope throughout the construction process. However, it can lead to unpredictable costs, as the final price is not known until the project is completed. The owner also has less control over cost management, as the contractor is responsible for reimbursing all expenses.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Fixed-Price Contracts vs. Cost-Plus Contracts, A general contracting firm experiences cost overruns on 20
| Feature | Fixed-Price Contracts | Cost-Plus Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Certainty | High | Low |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Risk Allocation | High for contractor, low for owner | Low for contractor, high for owner |
| Transparency | Moderate | High |
Key Contractual Clauses to Mitigate Cost Overruns
Several contractual clauses can be incorporated to minimize the risk of cost overruns:
- Change Order Provisions: These clauses define the process for making changes to the project scope and the associated cost adjustments. Clear and specific change order provisions help prevent disputes and ensure that both parties understand the financial implications of any modifications.
- Force Majeure Clauses: These clauses address unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or government regulations, that can impact project costs. By outlining how such events will be handled, force majeure clauses can help mitigate financial risks associated with uncontrollable circumstances.
- Payment Schedules: A well-defined payment schedule ensures timely payments to the contractor, reducing the risk of delays and cost overruns. The schedule should clearly Artikel payment milestones and the associated deliverables.
- Performance Bonds: Performance bonds guarantee that the contractor will complete the project according to the specifications. They provide financial protection for the owner in case the contractor defaults on the contract.
Successful Contract Negotiations to Minimize Cost Overruns
Effective contract negotiations are essential for minimizing the risk of cost overruns. Here are some key strategies:
- Thorough Due Diligence: Before entering into a contract, both parties should conduct thorough due diligence to understand the project scope, potential risks, and available resources. This includes site investigations, cost estimates, and risk assessments.
- Clear Communication: Open and honest communication is crucial throughout the negotiation process. Both parties should clearly define their expectations, responsibilities, and potential challenges. This helps build trust and minimize misunderstandings.
- Contingency Planning: It is important to include contingency plans in the contract to address unexpected costs. This could involve establishing a reserve fund for unforeseen expenses or defining a process for handling cost overruns.
- Expert Negotiation: Both parties should engage experienced legal and financial professionals to assist in contract negotiations. This ensures that the contract is comprehensive, fair, and protects the interests of both parties.
Financial Management and Control
In the construction industry, cost overruns are a major concern for general contracting firms. Effective financial management practices are crucial to control costs, mitigate risks, and ensure project profitability. A robust financial management system provides the framework for tracking project expenses, identifying potential overruns early on, and making informed decisions to optimize project outcomes.
Importance of Robust Financial Management Practices
Robust financial management practices are essential for controlling costs and ensuring project success. They provide a structured approach to managing finances, monitoring expenses, and making informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle. A well-defined financial management system helps general contractors:
- Track project expenses accurately and in real-time. This allows for timely identification of cost deviations and the implementation of corrective measures to prevent further overruns.
- Identify and analyze potential cost risks. By assessing potential cost risks early on, contractors can develop mitigation strategies to minimize their impact on the project budget.
- Make informed decisions about project scope and budget. Data-driven financial analysis supports informed decision-making, allowing contractors to adjust project scope and budget based on changing market conditions and unforeseen circumstances.
- Improve project profitability and financial performance. By effectively managing costs and maximizing efficiency, general contractors can enhance project profitability and achieve better financial outcomes.
Financial Reporting System
A comprehensive financial reporting system is crucial for tracking project costs and identifying potential overruns early on. It should provide timely and accurate information about project expenses, budget variances, and potential risks. The system should include:
- Regular cost reports: These reports should provide a detailed breakdown of project expenses, including labor, materials, equipment, and subcontracts. They should also compare actual costs to the budgeted amounts, highlighting any significant variances.
- Budget tracking tools: These tools allow contractors to monitor project expenses against the approved budget, identifying potential overruns before they become significant. They can include spreadsheets, project management software, or specialized financial reporting systems.
- Cost variance analysis: This involves analyzing the reasons behind cost variances and identifying potential areas for improvement. By understanding the root causes of cost overruns, contractors can implement corrective measures to prevent similar issues in future projects.
- Performance metrics: These metrics provide insights into project performance, including cost efficiency, schedule adherence, and overall profitability. By tracking key performance indicators, contractors can identify areas for improvement and optimize project outcomes.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost-benefit analysis is a crucial tool for making informed decisions about project scope and budget. It involves evaluating the potential benefits of a project against its estimated costs. By comparing the expected returns on investment with the project expenses, contractors can determine whether a project is financially viable and whether it aligns with their business objectives.
Cost-benefit analysis helps ensure that the project’s benefits outweigh its costs.
Cost Control Measures
General contracting firms implement various cost control measures to minimize expenses and ensure project profitability. Some common examples include:
- Competitive bidding: Obtaining quotes from multiple vendors for materials, equipment, and subcontractors helps secure the best prices and ensures cost-effective procurement.
- Value engineering: This involves identifying potential cost savings without compromising project quality or functionality. It can include exploring alternative materials, construction methods, or design modifications.
- Project scheduling and planning: Effective project planning and scheduling helps minimize delays and rework, which can significantly impact project costs.
- Inventory management: Efficient inventory management practices, including just-in-time delivery and minimizing waste, can significantly reduce material costs.
- Labor productivity: Implementing measures to improve labor productivity, such as training and incentives, can help reduce labor costs and enhance project efficiency.
Industry Trends and Best Practices
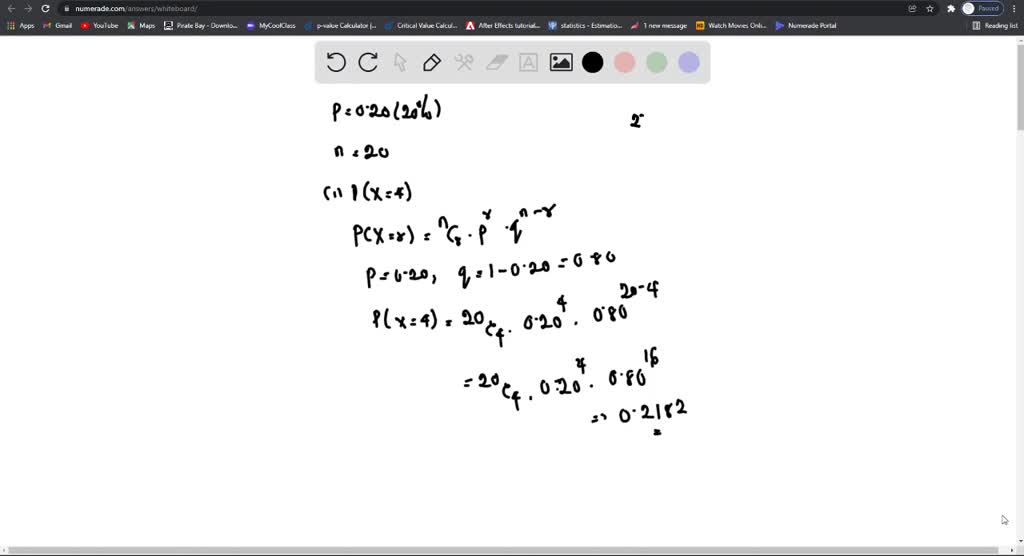
The construction industry is constantly evolving, and understanding current trends is crucial for general contracting firms to manage costs effectively and remain competitive. This section will explore key industry trends related to cost overruns and discuss how technological advancements, sustainability, and best practices are impacting project management and cost control.
Technological Advancements in Cost Management
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the way general contracting firms manage projects and costs. Here are some of the key trends:
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM software enables contractors to create virtual models of projects, facilitating better planning, coordination, and cost estimation. This allows for early identification of potential cost overruns and reduces the risk of costly rework.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools are being used for cost forecasting, risk assessment, and project scheduling. By analyzing historical data and industry trends, AI can provide insights into potential cost overruns and help contractors make more informed decisions.
- Cloud-Based Project Management: Cloud-based platforms offer real-time collaboration, data sharing, and improved communication among project stakeholders. This enhances transparency, reduces errors, and facilitates better cost control.
Sustainability and Green Building Practices
Sustainability and green building practices are gaining increasing importance in the construction industry. These practices not only contribute to environmental responsibility but also impact project costs.
- Energy-Efficient Materials: Using energy-efficient materials and technologies can reduce operational costs for building owners. While these materials may have higher upfront costs, they can lead to long-term savings and reduce the overall project budget.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or geothermal systems, can reduce reliance on traditional energy sources and minimize energy bills. However, careful planning and integration are essential to avoid potential cost overruns.
- Waste Reduction and Recycling: Implementing waste reduction and recycling programs can minimize disposal costs and contribute to a more sustainable construction process. This requires careful planning and coordination with subcontractors and suppliers.
Best Practices for Cost Overrun Prevention
Leading general contracting firms have adopted several best practices to minimize cost overruns. Here are some examples:
- Thorough Pre-Construction Planning: Detailed pre-construction planning is essential to identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies. This includes conducting site surveys, reviewing plans and specifications, and estimating project costs accurately.
- Value Engineering: Value engineering involves analyzing project designs and specifications to identify cost-saving opportunities without compromising quality. This can lead to significant cost reductions while maintaining project functionality.
- Effective Communication and Collaboration: Clear communication and collaboration among project stakeholders, including owners, architects, engineers, and subcontractors, are crucial for avoiding misunderstandings and ensuring that everyone is working towards the same goals.
- Regular Cost Monitoring and Reporting: Regularly tracking and reporting project costs allows contractors to identify potential cost overruns early on and take corrective actions. This involves using cost management software and implementing a system for regular cost reviews.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential risks is essential for cost control. This includes developing contingency plans for unforeseen events, such as weather delays or material shortages.
In the dynamic world of construction, where projects with 20 or more units present significant challenges, navigating cost overruns is paramount. This comprehensive analysis has shed light on the key drivers of these financial burdens, emphasizing the importance of robust risk management, meticulous project planning, effective contract negotiation, and robust financial control. By implementing these strategies, general contracting firms can mitigate the risks of cost overruns, ensuring successful project delivery and maintaining financial stability.
Essential Questionnaire: A General Contracting Firm Experiences Cost Overruns On 20
What are some common signs of potential cost overruns?
Signs include: increased material costs, labor shortages, delays in project completion, unexpected changes in project scope, and inadequate communication among stakeholders.
How can technology help mitigate cost overruns?
Technology can assist in various ways, including: using project management software for efficient planning and tracking, leveraging BIM (Building Information Modeling) for accurate cost estimations, and employing drone technology for site inspections and progress monitoring.
What are the best practices for negotiating contracts to minimize cost overruns?
Best practices include: clearly defining project scope and deliverables, incorporating contingency clauses for unforeseen circumstances, establishing a detailed payment schedule, and utilizing experienced legal counsel for contract review.
What are some examples of successful cost control measures implemented by general contracting firms?
Examples include: adopting lean construction principles, implementing value engineering techniques, establishing strong cost control systems, and fostering a culture of cost awareness among employees.






