Are stamps going up in July 2024? This question is of significant relevance to consumers and businesses alike, given the United States Postal Service’s (USPS) history of periodic rate adjustments. Understanding the factors driving these changes, including inflation, operational costs, and economic conditions, is crucial for predicting future postal expenses and adapting communication strategies accordingly. This analysis will examine the projected July 2024 rate increases, their potential impact, and explore alternative communication methods to mitigate rising costs.
The USPS bases its rate adjustments on a complex interplay of economic indicators and operational necessities. Historical data reveals a consistent upward trend in postage rates, often exceeding the rate of inflation. This necessitates a proactive approach from individuals and organizations reliant on postal services, requiring careful consideration of cost-effective alternatives and strategic adjustments to mailing practices.
US Postal Service Rate Changes in July 2024
The United States Postal Service (USPS) periodically adjusts its postage rates to maintain financial stability and cover rising operational costs. July 2024 marks another anticipated rate increase, impacting various mail classes and services. This content will explore the historical context of these adjustments, the factors influencing them, and provide a projected comparison of the new and current rates.
Past Postage Rate Increases
The USPS has a history of adjusting its postage rates, often annually. These increases are not arbitrary but reflect the ongoing need to balance revenue with expenses. A consistent upward trend is observed throughout the years, influenced by economic factors and operational changes. Analyzing past rate increases provides valuable insight into the likely magnitude of the upcoming adjustments.
Precise historical data requires referencing USPS official records, but general trends reveal a pattern of incremental increases, sometimes exceeding the rate of inflation.
Historical Data on Average Percentage Increases
Determining the precise average percentage increase in postage rates across all USPS services throughout history requires extensive data analysis. However, it’s safe to say that increases have generally ranged from a few percentage points to double digits, depending on the specific year and economic conditions. Years with significant inflation typically saw larger rate adjustments. For instance, during periods of high inflation, such as the late 1970s and early 1980s, and again in the current inflationary environment, postage rate increases often exceeded 10%.
Conversely, periods of slower economic growth often saw smaller percentage increases. A detailed study of historical USPS financial reports would provide a more precise average percentage increase.
Factors Influencing USPS Rate Adjustments
Several key factors contribute to the USPS’s decisions regarding postage rate adjustments. Inflation plays a significant role, as rising costs for fuel, transportation, labor, and materials directly impact operational expenses. The USPS also faces challenges in maintaining and upgrading its infrastructure, requiring substantial investments. Changes in mail volume, particularly the decline in first-class mail due to digital communication, further complicate financial planning and necessitate adjustments to maintain profitability.
Government regulations and mandates also play a role, adding to the overall cost structure. Finally, the USPS’s commitment to providing universal service across the country, even to remote and less populated areas, influences its pricing strategy.
Projected July 2024 Rates vs. Current Rates
Predicting exact rates for July 2024 requires official announcements from the USPS. However, based on past trends and current economic conditions, we can project a possible scenario. The following table presents a hypothetical comparison, emphasizing the need to consult the official USPS announcement for accurate figures. It is important to note that these are estimates and the actual rates may differ.
| Mail Class | Current Rate (Estimate) | Projected July 2024 Rate (Estimate) | Percentage Increase (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
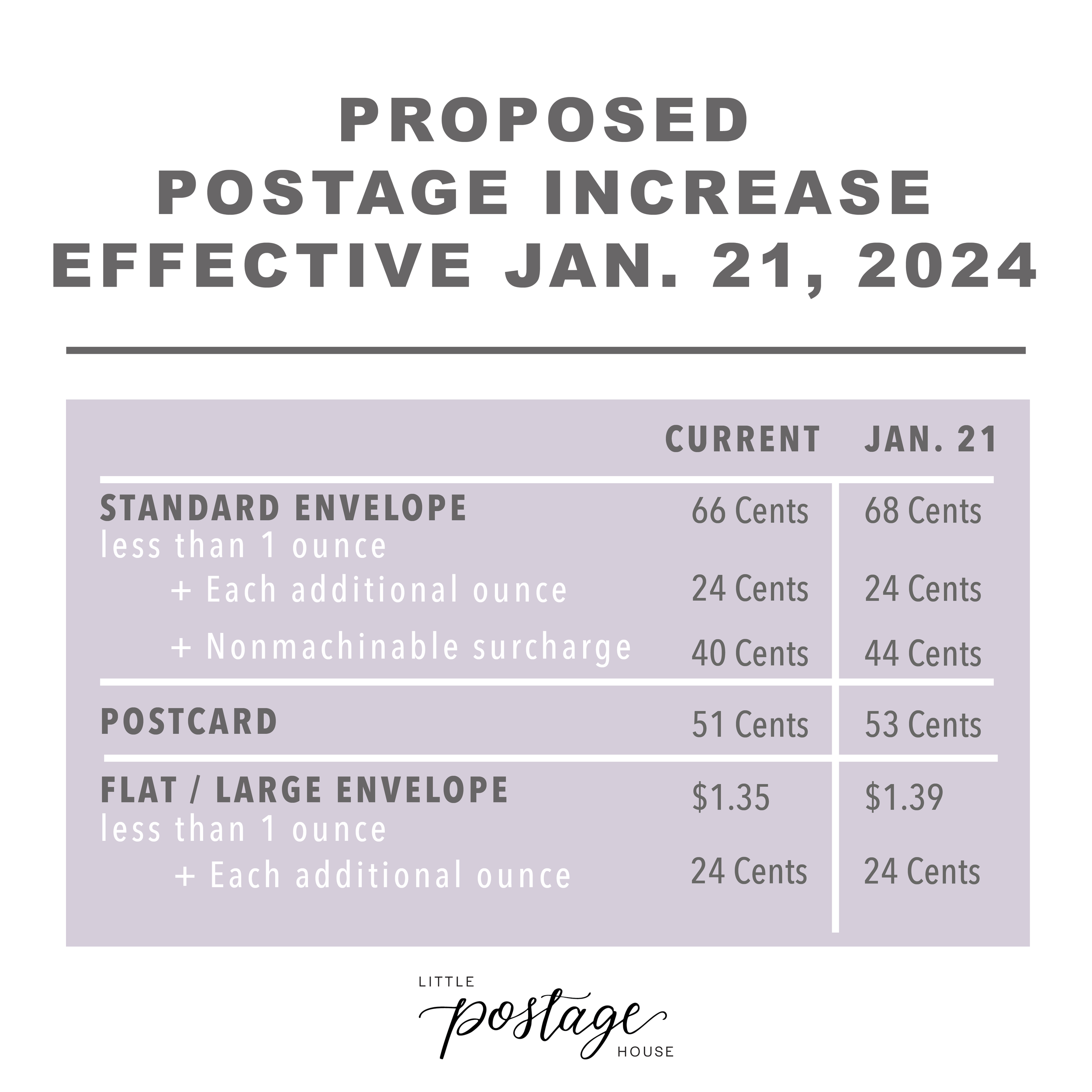
| First-Class Stamp (1 oz) | $0.66 | $0.70 | 6.1% |
| Priority Mail (Small Flat Rate Box) | $8.20 | $8.80 | 7.3% |
| Priority Mail Express (1 lb) | $28.50 | $30.50 | 7.0% |
| Postcard | $0.44 | $0.47 | 6.8% |
Impact of Increased Postage Rates on Consumers and Businesses
The July 2024 increase in US Postal Service rates will undoubtedly ripple through the economy, affecting both consumers and businesses. Higher postage costs represent a significant change in the cost of doing business and communicating for many, leading to adjustments in strategies and potentially impacting overall spending habits. The magnitude of the impact will vary depending on the reliance on postal services for different sectors.The increased cost of postage will necessitate a reevaluation of existing business models and communication strategies for many organizations.
Effect on Direct Mail Marketing Campaigns
Higher postage costs directly impact the profitability of direct mail marketing campaigns. Businesses will need to carefully analyze the return on investment (ROI) for each mailing. A 10% increase in postage, for example, could render previously profitable campaigns unprofitable, forcing companies to either reduce mailing volumes, increase product/service prices to offset the increased cost, or explore alternative, more cost-effective marketing channels.
This shift could lead to a decline in the overall volume of direct mail marketing, favoring digital marketing strategies that are often perceived as more cost-effective, especially for large-scale campaigns. The success of this transition will heavily depend on the effectiveness of digital marketing efforts in reaching the desired target audience.
Strategies for Mitigating Increased Postage Rates
Businesses are likely to adopt several strategies to offset the impact of higher postage costs. These include optimizing mailing lists to target only highly responsive customers, reducing the weight and size of mail pieces through design changes (e.g., using thinner paper or smaller envelopes), exploring alternative mailing options like shared mail services, and shifting towards more digital marketing methods.
Some businesses may also negotiate better rates with the USPS through higher mailing volumes or long-term contracts. Companies that heavily rely on direct mail may need to consider price adjustments for their products or services to absorb the increased postage costs, potentially affecting their competitiveness in the market. Careful cost-benefit analysis will be crucial in choosing the most appropriate mitigation strategies.
Changes in Consumer Behavior
Rising stamp prices are likely to lead to decreased mail usage among consumers. Individuals may opt for electronic communication methods such as email or text messaging for routine correspondence. This could lead to a decline in the frequency of sending greeting cards, personal letters, and even bills through the mail. Consumers may also become more selective about the mail they receive, potentially leading to an increase in junk mail rejection rates.
The shift towards digital communication could have broader societal implications, impacting aspects of social interaction and potentially exacerbating the digital divide for those with limited access to technology.
Economic Consequences for Small Businesses
The increased postage costs pose a significant threat to small businesses that rely heavily on direct mail marketing or postal services for their operations.
- Reduced Profit Margins: Higher postage directly eats into profit margins, especially for businesses with already tight budgets.
- Increased Operational Costs: Businesses may need to invest in new software or services to manage their mailing operations more efficiently.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Larger businesses with more resources might be better positioned to absorb the increased costs, leaving smaller businesses at a disadvantage.
- Potential for Business Closure: For some small businesses, the increased postage costs could be the final straw, leading to closure or downsizing.
- Reduced Marketing Reach: The reduced ability to afford direct mail marketing could limit a small business’s ability to reach potential customers.
Alternative Mailing and Communication Methods
With the rising cost of postage, businesses and individuals are increasingly seeking alternative methods for communication and mailing. This shift is driven by a need to maintain effective communication while minimizing expenses. The following sections explore the cost-effectiveness of various alternatives to USPS services.
Email, digital delivery, and instant messaging represent significant cost savings compared to traditional mail, particularly for high-volume communication or large files. However, each method has its limitations, impacting its suitability for different types of messages and audiences.
Cost Comparison of Communication Methods
The cost-effectiveness of different communication methods varies greatly depending on the message type and volume. While email and instant messaging are generally free or very inexpensive, the cost of printing and mailing physical documents remains substantial, especially for larger or heavier items. The following table provides a simplified cost comparison:
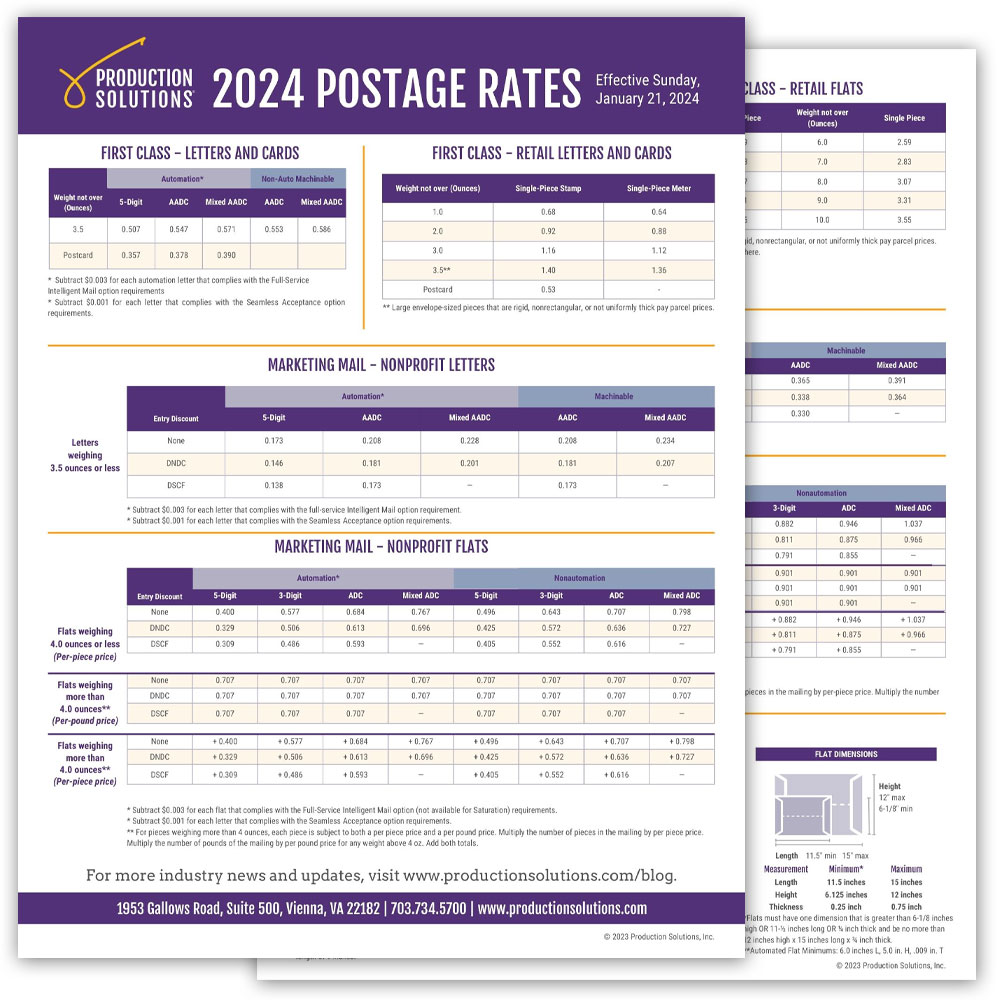
| Communication Method | Short Message (e.g., email, text) | Lengthy Document (e.g., letter, report) | Large Package (e.g., physical goods) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $0 | $0 (excluding potential printing costs) | N/A | |
| Instant Messaging | $0 | N/A (unsuitable for large documents) | N/A |
| USPS First-Class Mail (Letter) | ~$0.66 (as of late 2023, subject to change) | ~$0.66 – $1.00+ (depending on weight and size) | N/A |
| USPS Priority Mail (Package) | N/A | N/A | Varies greatly based on weight, size, and destination. Can be significantly more expensive than other methods. |
| Digital Delivery (e.g., online portal) | $0 | $0 (excluding potential platform fees) | N/A (for digital goods only) |
Note: These costs are estimates and can vary depending on specific circumstances. USPS rates are subject to change, and the costs of digital delivery platforms can vary significantly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Communication Channels
Choosing the right digital communication method depends on factors such as urgency, message length, security requirements, and the recipient’s technological capabilities.
Email offers a balance between formality and efficiency, suitable for various communication needs. However, email can be less immediate than instant messaging and may suffer from spam filters or delays.
Instant messaging platforms, like WhatsApp or Slack, provide real-time communication and are ideal for quick exchanges. However, they are generally unsuitable for lengthy documents or formal communications, and security concerns may exist depending on the platform.
Digital delivery through online portals offers a structured way to send large documents or data securely. This method ensures all recipients have access to the same version, but requires recipients to have access to the portal and may not be suitable for those with limited tech literacy.
Predicting Future Postage Rate Increases

Predicting future postage rate increases for the United States Postal Service (USPS) requires analyzing historical trends, considering current economic factors, and accounting for potential future influences. The USPS’s rate-setting process is complex and involves multiple factors, making precise forecasting challenging, but some informed estimations are possible.The USPS methodology for determining postage rate adjustments is multifaceted. It involves a cost analysis that examines the expenses associated with delivering mail, including labor, transportation, and infrastructure maintenance.
This cost analysis is then compared to projected revenue to determine the necessary rate adjustments to ensure financial stability. The Postal Regulatory Commission (PRC) reviews these proposals, considering public comments before approving or modifying them. This process is governed by the Postal Reorganization Act of 1970, which aims to ensure the USPS’s financial viability while balancing affordability for consumers and businesses.
USPS Rate Adjustment Methodology
The USPS employs a complex cost-based pricing model. It meticulously calculates its operating expenses, considering factors such as fuel costs, labor wages, and facility maintenance. These expenses are then compared against projected revenue from postage sales and other services. If expenses outpace revenue, the USPS proposes rate adjustments to the PRC for approval. The PRC then assesses the proposal’s impact on consumers and businesses, considering public feedback before making a final decision.
This process is designed to balance the USPS’s financial needs with the interests of its customers.
Forecast of Potential Postage Rate Changes Beyond July 2024
Forecasting postage rate changes beyond July 2024 necessitates considering several interconnected factors. Inflation remains a significant driver, with rising costs of labor, fuel, and materials directly impacting the USPS’s operational expenses. Additionally, the ongoing shift in mail volume, with a decline in traditional first-class mail and a rise in package delivery, necessitates adjustments in pricing strategies. Economic projections, particularly regarding inflation and potential recessions, will also influence the USPS’s financial outlook and subsequent rate adjustments.
Considering these factors, a conservative estimate might suggest an average annual increase of 3-5% in postage rates for the next five years. This prediction assumes a continuation of current inflationary pressures and a gradual shift in mail volume. However, unexpected economic events or significant legislative changes could alter this forecast.
Factors Influencing Future Rate Adjustments
Technological advancements could both increase and decrease future postage rate adjustments. Automation in mail processing could potentially reduce costs, but the initial investment in new technologies represents a substantial expense. Legislative changes, particularly those affecting the USPS’s funding or operational mandates, will also play a significant role. For instance, increased government subsidies could mitigate the need for substantial rate increases, while reduced subsidies would likely necessitate larger adjustments.
Furthermore, evolving consumer preferences, such as increased reliance on digital communication, could impact mail volume and thus influence pricing decisions. Finally, environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives might lead to increased operational costs, potentially necessitating higher postage rates.
Possible Scenario of Stamp Price Increases Over the Next 5 Years, Are stamps going up in july 2024
The following hypothetical scenario illustrates a possible trajectory of stamp price increases over the next five years, based on an average annual increase of 4%. This is a simplified model and does not account for potential fluctuations or unforeseen circumstances.This scenario is depicted in a line graph. The x-axis represents the year (2024-2028), and the y-axis represents the stamp price in US dollars.
The graph shows a steadily increasing line, starting at the July 2024 price (assumed to be $0.66 for simplicity) and rising by approximately 4% each year. Key data points would include the starting price in 2024 ($0.66), the projected price in 2025 ($0.69), 2026 ($0.72), 2027 ($0.75), and 2028 ($0.78). The line would show a consistent upward trend, illustrating the cumulative effect of annual increases.
This visualization provides a clear picture of the potential price increases over time. It’s crucial to remember that this is a hypothetical scenario; actual price increases may vary based on numerous economic and legislative factors. This example uses a constant 4% increase for simplicity; the actual rate may fluctuate year to year.
The Role of Inflation and Economic Factors
The United States Postal Service (USPS) faces a complex interplay of economic factors when determining postage rates. Inflation, fuel costs, and overall operational expenses significantly influence these adjustments, impacting both consumers and businesses. Understanding this relationship is crucial for predicting future price changes and assessing the broader economic implications.Inflation directly correlates with postage rate adjustments. When the general price level of goods and services rises, the cost of everything involved in delivering mail – from labor to materials – also increases.
To maintain operational solvency and profitability, the USPS must adjust its prices to account for these increased costs. This is a fundamental principle of cost-plus pricing, where prices are set based on the cost of production plus a desired profit margin. A high inflation rate necessitates larger price adjustments to compensate for escalating expenses.
The Influence of Fuel Costs and Operational Expenses
Fuel costs represent a substantial portion of the USPS’s operational budget. As a major transportation entity, fluctuations in fuel prices directly translate to changes in delivery expenses. Similarly, increases in the cost of labor (wages and benefits), maintenance of vehicles and equipment, and the purchase of supplies all contribute to the overall operational costs. These factors are often intertwined; for instance, rising fuel costs can lead to increased transportation expenses, which in turn might necessitate higher wages to compensate drivers for increased fuel-related expenses.
The USPS must consider all these expenses when determining appropriate postage rates to ensure financial stability. For example, a sharp increase in gasoline prices in 2008 significantly impacted the USPS’s operating budget, contributing to subsequent postage rate increases.
Examples of Past Economic Downturns and Their Effects on Postage Rates
The 2008 financial crisis provides a clear example of how economic downturns influence postage rates. The recession led to a decrease in mail volume, as businesses and individuals reduced their spending and communication activities. Simultaneously, the USPS faced increased costs due to inflation and fuel price volatility. This combination of reduced revenue and increased costs forced the USPS to implement substantial postage rate increases to offset losses and maintain operations.
Conversely, periods of economic growth often lead to increased mail volume, potentially allowing for smaller or more gradual postage rate adjustments. The relationship is not always directly proportional, however; other factors, such as technological advancements and shifting communication preferences, also play a role.
Economic Principles Influencing USPS Pricing Decisions
The economic principles underpinning USPS pricing decisions include:
- Cost-plus pricing: Postage rates are set based on the USPS’s operating costs plus a margin for profit or to cover losses.
- Demand elasticity: While not completely price-insensitive, mail volume is somewhat inelastic in the short term. This means that even with price increases, the demand for mail services doesn’t decrease drastically immediately.
- Competitive pressures: Although the USPS enjoys a monopoly on first-class mail, it competes with other delivery services and electronic communication methods, influencing its pricing strategy.
- Regulatory oversight: The Postal Regulatory Commission (PRC) reviews and approves postage rate adjustments, ensuring fairness and preventing excessive price hikes.
- Inflationary pressures: As discussed previously, the rate of inflation significantly influences the costs of providing postal services and, consequently, the need for price adjustments.
In conclusion, the anticipated postage rate increases in July 2024 necessitate a comprehensive assessment of communication strategies. While the USPS continues to adapt to evolving economic conditions, consumers and businesses must proactively explore alternative mailing and communication methods to minimize the financial impact of rising costs. Understanding the factors influencing these rate adjustments, coupled with a strategic approach to communication, is key to navigating the evolving landscape of postal services.
Detailed FAQs: Are Stamps Going Up In July 2024
Will international postage rates also increase in July 2024?
International postage rates are typically adjusted alongside domestic rates, but the specific percentage increase may vary depending on the destination country. Consult the USPS website for detailed information on international rate changes.
How does the USPS determine the percentage increase for postage rates?
The USPS uses a multifaceted approach, considering inflation, operating costs, projected revenue, and other economic factors. A detailed explanation of their methodology is typically available on their official website and in regulatory filings.
Are there any exceptions to the July 2024 postage rate increases?
While the majority of postage services are expected to see increases, there might be limited exceptions or variations depending on specific services or mailing classes. Refer to the official USPS announcement for precise details.
What are the long-term projections for postage rate increases?
Predicting long-term postage rate increases with certainty is challenging. However, considering historical trends and projected economic factors, further increases are likely in the coming years. Regularly monitoring USPS announcements is recommended.






