Are symptoms of ischemic and hemorrhagic strome different – Are ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke symptoms different? This question is crucial to understanding these devastating conditions and ensuring timely, effective treatment. While both stroke types affect the brain, their underlying mechanisms and resulting symptoms can vary significantly. Recognizing these differences is critical for healthcare professionals and individuals alike, as it can lead to faster diagnosis and more appropriate treatment, ultimately impacting recovery outcomes.
Stroke, a leading cause of disability and death worldwide, occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted. This interruption can be caused by a blood clot blocking an artery (ischemic stroke) or by a ruptured blood vessel causing bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). Understanding the distinct characteristics of each type of stroke is essential for prompt recognition and intervention, which are vital for minimizing brain damage and improving long-term outcomes.
Understanding Stroke Types
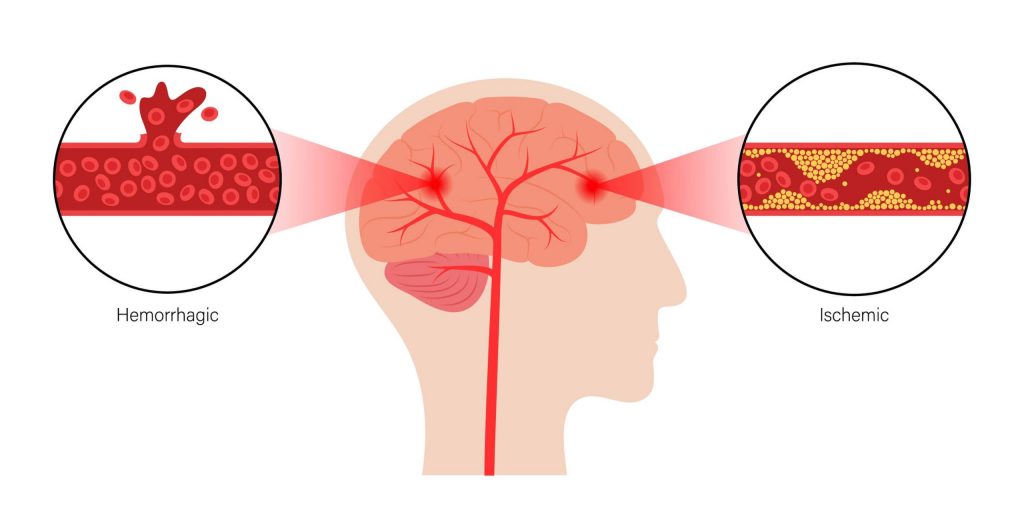
Strokes are a serious medical condition that can cause permanent brain damage. There are two main types of strokes: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. Understanding the differences between these two types is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Ischemic Stroke
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery in the brain, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. This blockage can happen in two ways:
- Thrombotic stroke: A blood clot forms inside an artery in the brain, blocking blood flow.
- Embolic stroke: A blood clot forms elsewhere in the body, travels through the bloodstream, and gets lodged in an artery in the brain.
The causes of ischemic stroke can include:
- Atherosclerosis: A buildup of plaque inside the arteries, narrowing them and increasing the risk of clot formation.
- Atrial fibrillation: An irregular heartbeat that can increase the risk of blood clots forming in the heart.
- High blood pressure: Damages the arteries and increases the risk of blood clots forming.
- Diabetes: Damages blood vessels and increases the risk of clot formation.
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and increases the risk of clot formation.
Hemorrhagic Stroke, Are symptoms of ischemic and hemorrhagic strome different
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing bleeding into the brain tissue. This bleeding can put pressure on the brain, damaging brain cells.
- Intracerebral hemorrhage: Bleeding occurs within the brain tissue itself.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Bleeding occurs in the space between the brain and the surrounding membranes.
The causes of hemorrhagic stroke can include:
- High blood pressure: Weakens blood vessels and increases the risk of rupture.
- Aneurysm: A weakened and bulging blood vessel that can rupture.
- Arteriovenous malformation (AVM): A tangle of abnormal blood vessels that can rupture.
- Blood clotting disorders: Can increase the risk of bleeding in the brain.
Differences in Mechanisms
The underlying mechanisms of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes are fundamentally different:
Ischemic stroke: Blood flow is blocked, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients.
Hemorrhagic stroke: Blood vessel ruptures, causing bleeding into the brain tissue and putting pressure on brain cells.
Symptoms of Ischemic Stroke
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery leading to the brain, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. This can cause a range of symptoms, which vary depending on the location and severity of the blockage. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention, which can significantly improve the chances of recovery.
Common Ischemic Stroke Symptoms
The most common symptoms of ischemic stroke include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body. This is often described as a feeling of heaviness or tingling. It is important to note that this weakness may not be complete paralysis, but rather a difficulty in moving or controlling the affected limb.
- Sudden confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding speech. This can range from slurred speech to complete inability to communicate.
- Sudden difficulty seeing in one or both eyes. This can include blurred vision, double vision, or complete loss of vision in one eye.
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or difficulty walking. This is often accompanied by a feeling of spinning or unsteadiness.
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause. This is often described as a “thunderclap” headache and is a particularly alarming symptom.
Examples of How Ischemic Stroke Symptoms Might Present
The symptoms of an ischemic stroke can vary depending on the individual and the location of the blockage in the brain. For example:
- A person with a blockage in the left side of the brain may experience weakness or numbness on the right side of their body, difficulty speaking, and problems with understanding language.
- A person with a blockage in the back of the brain may experience dizziness, loss of balance, and double vision.
- A person with a blockage in the front of the brain may experience difficulty thinking clearly, making decisions, or planning.
Importance of Recognizing Symptoms and Seeking Immediate Medical Attention
Time is of the essence when it comes to ischemic stroke. The sooner a person receives medical attention, the better their chances of recovery. If you or someone you know experiences any of the symptoms listed above, it is crucial to call emergency services immediately.
Every minute counts when it comes to ischemic stroke.
Prompt medical attention can lead to:
- Thrombolytic therapy, which involves administering medications to dissolve the blood clot and restore blood flow to the brain.
- Endovascular therapy, which involves using a catheter to remove the blood clot or to insert a stent to keep the artery open.
These treatments can significantly reduce the risk of permanent brain damage and improve the chances of a full recovery.
Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding into the surrounding brain tissue. This bleeding puts pressure on the brain, damaging its cells and interrupting their function. Recognizing the symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke is crucial because prompt medical attention can significantly improve outcomes.
Common Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Stroke
The symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke can vary depending on the location and size of the bleed. However, some common symptoms include:
- Sudden, severe headache: This is often described as the worst headache of someone’s life and may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting. It’s important to note that a headache alone is not always indicative of a stroke, but when combined with other symptoms, it should be considered a serious warning sign.
- Sudden weakness or numbness: This can affect one side of the body, including the face, arm, or leg. For example, a person may have difficulty lifting their arm or leg on one side, or they may experience a drooping face.
- Sudden difficulty speaking or understanding speech: This can range from slurred speech to complete inability to communicate. For instance, a person may struggle to find the right words or may not understand what is being said to them.
- Sudden vision problems: This can include blurred vision, double vision, or loss of vision in one eye. For example, a person may see double or have a blind spot in their field of vision.
- Sudden dizziness or loss of balance: This can make it difficult to walk or stand steadily. For example, a person may feel lightheaded or stumble when they try to walk.
- Sudden confusion or disorientation: This can include difficulty concentrating or remembering things. For example, a person may have trouble following a conversation or may not know where they are or what day it is.
- Sudden seizures: These can be a sign of a more severe hemorrhagic stroke. Seizures are characterized by involuntary muscle contractions and loss of consciousness.
Examples of How Hemorrhagic Stroke Symptoms Might Present
- Scenario 1: A 65-year-old man suddenly develops a severe headache, accompanied by vomiting. He also experiences weakness on his right side and has difficulty speaking. These symptoms suggest a hemorrhagic stroke affecting the left side of his brain.
- Scenario 2: A 40-year-old woman suddenly feels dizzy and loses her balance. She also experiences blurred vision and has trouble understanding what her husband is saying. These symptoms suggest a hemorrhagic stroke affecting the brain stem or cerebellum.
Importance of Recognizing Symptoms and Seeking Immediate Medical Attention
Time is critical in treating a hemorrhagic stroke. Prompt medical attention can significantly improve the chances of survival and reduce the risk of long-term disability. If you or someone you know experiences any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s crucial to call 911 or your local emergency number immediately. Do not try to drive yourself to the hospital, as you may be unable to drive safely.
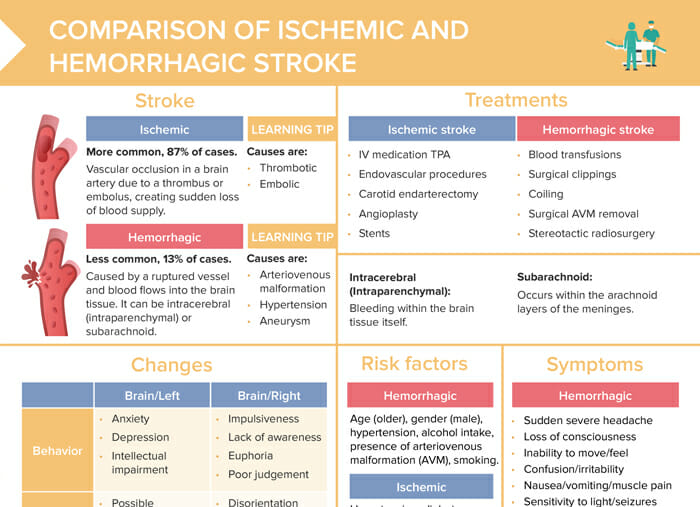
Comparing Symptoms
Understanding the differences in symptoms between ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes is crucial for timely and accurate diagnosis, which directly impacts treatment and patient outcomes. Recognizing these differences allows healthcare professionals to swiftly initiate appropriate interventions, potentially minimizing long-term neurological damage.
Distinguishing Symptoms
The symptoms of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes differ significantly, primarily due to the underlying cause of the stroke. Ischemic strokes result from a blockage in a blood vessel, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients, while hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding. This distinction leads to variations in the onset and severity of symptoms.
- Onset of Symptoms: Ischemic strokes often have a gradual onset, with symptoms developing over minutes or even hours. In contrast, hemorrhagic strokes tend to have a sudden and abrupt onset, with symptoms appearing rapidly.
- Headache: While headaches can occur in both types of strokes, they are more common and severe in hemorrhagic strokes. The headache associated with a hemorrhagic stroke is often described as sudden, intense, and “thunderclap” like.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Nausea and vomiting are more prevalent in hemorrhagic strokes, possibly due to increased pressure within the skull from the bleeding.
- Loss of Consciousness: Loss of consciousness is more common in hemorrhagic strokes, particularly in cases of significant bleeding. Ischemic strokes may lead to confusion or disorientation but are less likely to cause complete unconsciousness.
- Seizures: Seizures are more likely to occur in hemorrhagic strokes, particularly when the bleeding is near the surface of the brain.
Misdiagnosis Implications
Misdiagnosis of stroke type can have serious consequences, as treatment approaches differ significantly. For example, administering blood thinners to a patient with a hemorrhagic stroke could worsen the bleeding, leading to further brain damage. Conversely, delaying treatment for an ischemic stroke can result in irreversible brain damage.
Misdiagnosis of stroke type can have serious consequences, as treatment approaches differ significantly.
Recognizing Stroke Symptoms
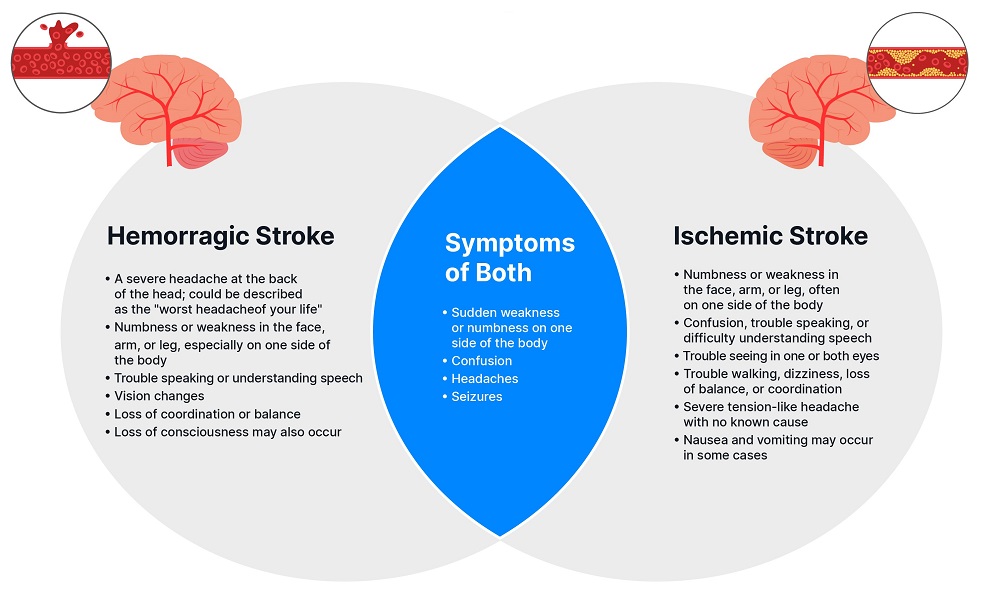
A stroke is a medical emergency that happens when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted. This can happen due to a blood clot blocking an artery (ischemic stroke) or a blood vessel bursting (hemorrhagic stroke). Prompt recognition and treatment are crucial to minimizing brain damage and improving the chances of recovery.
Common Stroke Symptoms
Recognizing stroke symptoms quickly is essential for seeking immediate medical attention. The faster a stroke is treated, the better the chances of recovery. Here are some common stroke symptoms to be aware of:
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body. This could manifest as a drooping face, difficulty raising one arm, or inability to lift one leg.
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or understanding. This could include slurred speech, difficulty finding words, or inability to follow simple instructions.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes. This could be blurry vision, double vision, or complete loss of vision in one eye.
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination. This could include feeling unsteady on your feet, difficulty walking, or stumbling.
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause. This could be a sudden, intense headache that is unlike any previous headaches.
Visual Guide to Stroke Symptoms
Here is a visual guide to help you understand how stroke symptoms might appear:
- Facial Drooping: Imagine a person smiling. One side of the face may droop or sag, making it difficult to smile evenly.
- Arm Weakness: Imagine a person raising both arms above their head. One arm may be weak or unable to lift, while the other arm can raise normally.
- Speech Difficulty: Imagine a person trying to speak a simple phrase like “The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.” Their speech may be slurred, jumbled, or difficult to understand.
- Vision Loss: Imagine a person looking straight ahead. One eye may see blurry, double, or nothing at all.
The Importance of Time
Time is of the essence when it comes to stroke treatment. The sooner a stroke is recognized and treated, the better the chances of recovery and minimizing long-term disability.
Time-Sensitive Treatment for Ischemic Stroke
Prompt treatment for ischemic stroke is crucial to prevent permanent brain damage. The most effective treatment for ischemic stroke is administering clot-busting medications, also known as thrombolytics. These medications work by dissolving the blood clot that is blocking blood flow to the brain.
To be effective, thrombolytics must be administered within a specific time window. The ideal time frame is within 4.5 hours of the onset of stroke symptoms.
However, in certain cases, this window can be extended up to 24 hours if specific criteria are met, such as the use of a specialized imaging technique called perfusion imaging.
This imaging technique helps determine the extent of brain tissue still at risk of damage.
Surgical Interventions for Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, leading to bleeding. Treatment for hemorrhagic stroke often involves surgical interventions to stop the bleeding and relieve pressure on the brain.
Surgical options may include:
- Craniotomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of the skull to access the bleeding site and control the hemorrhage.
- Coiling: This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible catheter into the blood vessel and deploying a coil to block the aneurysm, preventing further bleeding.
- Clipping: This procedure involves placing a small clip at the base of the aneurysm to prevent blood flow into the aneurysm and stop bleeding.
Stroke Prevention
Taking proactive steps to prevent stroke is crucial for safeguarding your health and well-being. While some risk factors for stroke are beyond our control, many others are modifiable through lifestyle changes. By adopting healthy habits, you can significantly reduce your risk of experiencing this life-altering event.
Lifestyle Factors and Stroke Prevention
Understanding the role of lifestyle factors in stroke prevention is essential. Modifying these factors can significantly reduce your risk of both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Maintaining a healthy blood pressure is critical. High blood pressure puts extra strain on your arteries, making them more likely to narrow and harden. This can lead to blockages, increasing the risk of ischemic stroke.
- High Cholesterol: High cholesterol levels contribute to the buildup of plaque in your arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This plaque can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of ischemic stroke.
- Diabetes: Diabetes damages blood vessels, making them more susceptible to blockages. It also increases the risk of blood clots, both of which contribute to ischemic stroke.
- Obesity: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of which contribute to stroke.
- Physical Inactivity: Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight, lowering blood pressure, and improving cholesterol levels.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots, both of which contribute to stroke.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption increases the risk of high blood pressure and stroke.
- Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help lower blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of stroke.
The ability to differentiate between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke symptoms is vital for timely and appropriate medical intervention. While both types of stroke require immediate medical attention, the treatment strategies differ significantly. Understanding the distinct symptoms associated with each type can help healthcare professionals make accurate diagnoses and initiate the most effective treatment plans, ultimately impacting the recovery process and improving patient outcomes.
Q&A: Are Symptoms Of Ischemic And Hemorrhagic Strome Different
What is the most common type of stroke?
Ischemic stroke is the most common type, accounting for about 87% of all strokes.
What are the risk factors for ischemic stroke?
Risk factors for ischemic stroke include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, heart disease, and atrial fibrillation.
What are the risk factors for hemorrhagic stroke?
Risk factors for hemorrhagic stroke include high blood pressure, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and certain blood disorders.
Can stroke symptoms be reversed?
The extent of recovery from stroke depends on the severity of the stroke, the location of the brain damage, and the promptness of treatment. Some symptoms may improve over time with rehabilitation therapy, while others may be permanent.






