Are there any stroms i the atlantic now – Are there any storms in the Atlantic now? This question, ever-present in the minds of those living along the Atlantic coast and those who sail its waters, is a constant reminder of the powerful forces that shape our planet. The Atlantic basin, a vast expanse of ocean, is a breeding ground for storms, from gentle tropical waves to ferocious hurricanes, each with the potential to disrupt lives and reshape landscapes.
Understanding the current state of Atlantic storm activity is crucial for safety, preparedness, and appreciating the delicate balance of nature.
The Atlantic hurricane season, officially running from June 1st to November 30th, is a time of heightened vigilance. During this period, meteorologists diligently monitor the ocean, tracking the development and movement of storms using a complex array of tools and technologies. Satellites, radar, and weather buoys provide real-time data, allowing experts to predict storm paths and intensity, offering crucial information for coastal communities and maritime interests.
Current Atlantic Storm Activity
The Atlantic hurricane season officially runs from June 1st to November 30th, and we’re currently in the midst of it. While the Atlantic basin has been relatively quiet in recent weeks, there are always new areas of interest to keep an eye on. Let’s take a look at the current storm activity.
Active Tropical Storms and Hurricanes
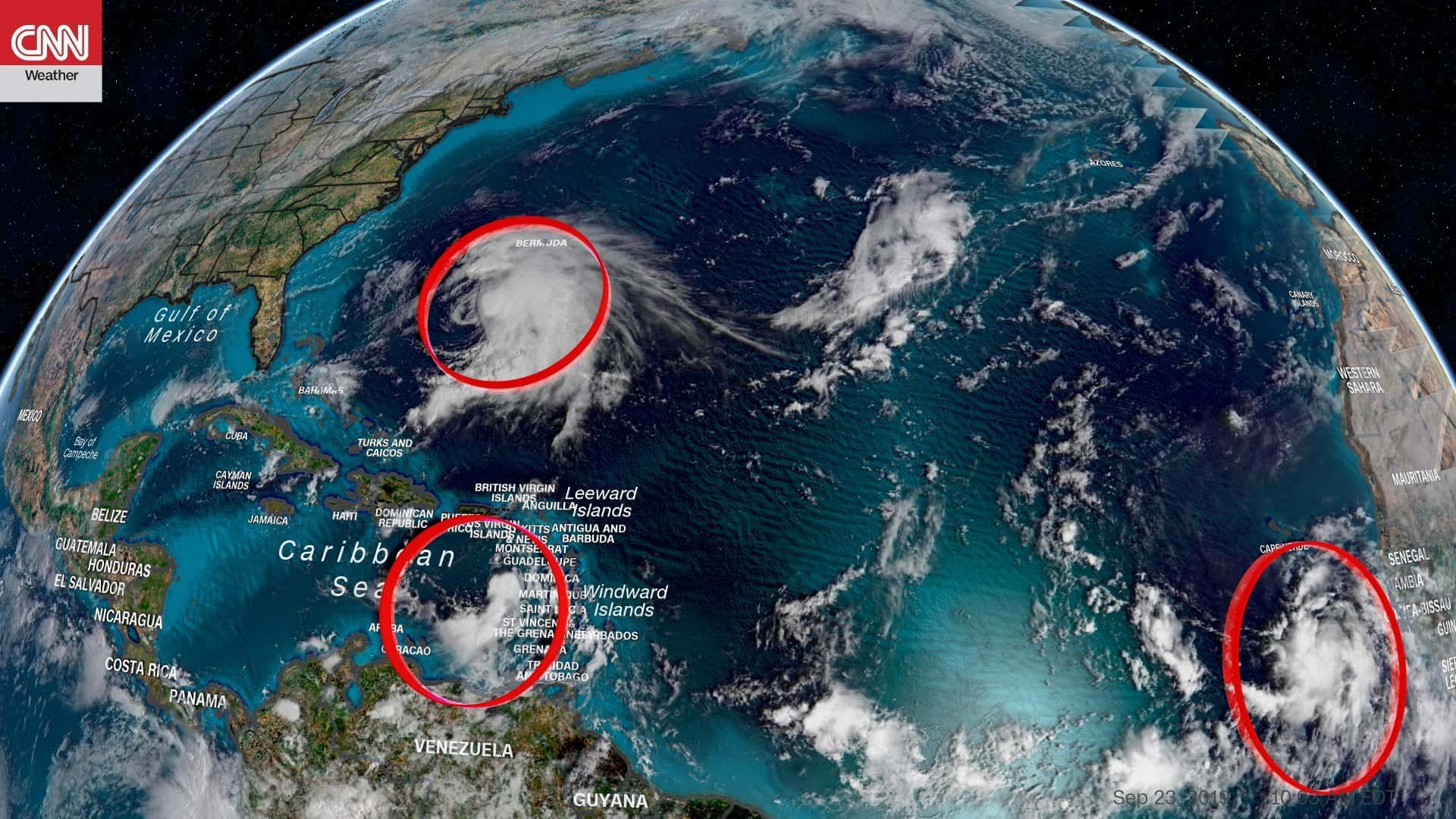
There are currently no active tropical storms or hurricanes in the Atlantic basin. However, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) is closely monitoring several areas of interest that have the potential to develop into tropical cyclones.
Areas of Interest
- Area 1: A broad area of low pressure located several hundred miles southwest of the Cabo Verde Islands is being monitored. This system has a low chance of development over the next 5 days, but it’s worth keeping an eye on as it moves westward across the Atlantic.
- Area 2: Another area of low pressure is located near the coast of Africa. This system has a slightly higher chance of development over the next 5 days. It’s important to note that even if this system develops into a tropical depression or storm, it is still too early to determine its potential track or intensity.
Storm Tracking and Forecasting: Are There Any Stroms I The Atlantic Now
Tracking and forecasting Atlantic storms is a complex and vital process, involving a sophisticated network of technologies and expert analysis. This process helps us understand the path, intensity, and potential impact of these weather events, enabling us to prepare and protect ourselves.
Satellites and Radar
Satellites provide a broad view of the Atlantic basin, capturing images of storms from space. These images reveal the size, shape, and movement of storms, offering valuable insights into their development. Radar systems, positioned on land and in the air, provide more detailed information about storm structure, precipitation intensity, and wind patterns. By combining data from satellites and radar, meteorologists gain a comprehensive understanding of storm dynamics.
Importance of Accurate Forecasting, Are there any stroms i the atlantic now
Accurate storm forecasting is crucial for public safety and preparedness. Timely and reliable predictions allow communities to take necessary steps to minimize risks, including evacuations, securing property, and preparing emergency supplies. For example, accurate forecasts during Hurricane Katrina in 2005 could have potentially saved lives and reduced damage. The ability to predict a storm’s path, intensity, and potential impact allows for better decision-making and a more effective response.
Potential Impacts of Storms
Storms, particularly hurricanes and tropical storms, can have devastating impacts on coastal areas and beyond. These impacts are multifaceted, affecting not only the immediate environment but also infrastructure, economies, and communities.
Coastal Impacts
Coastal areas are particularly vulnerable to storm surges, high winds, and heavy rainfall. These factors can lead to a range of destructive consequences:
- Flooding: Storm surges, a rise in sea level caused by the storm’s powerful winds, can inundate low-lying coastal areas, causing extensive flooding. This can damage homes, businesses, and infrastructure, displacing residents and disrupting daily life. For example, Hurricane Katrina in 2005 caused catastrophic flooding in New Orleans, displacing hundreds of thousands of people and causing billions of dollars in damage.
- Wind Damage: Strong winds associated with storms can cause significant damage to buildings, trees, and power lines. This can lead to power outages, structural damage, and injuries. The 2017 hurricane season in the Caribbean saw widespread wind damage, including the destruction of roofs, power lines, and entire buildings.
- Erosion: Storms can cause significant coastal erosion, eroding beaches and altering shorelines. This can damage coastal properties and infrastructure, and disrupt ecosystems. For example, Hurricane Sandy in 2012 caused extensive erosion along the New Jersey coastline, damaging beaches and coastal communities.
Economic Impacts
Storms can have significant economic impacts on affected regions. These impacts can include:
- Property Damage: The destruction of homes, businesses, and infrastructure can result in significant property damage, leading to insurance claims and economic losses. The 2017 hurricane season in the United States resulted in billions of dollars in property damage, impacting insurance companies and the economy.
- Business Disruptions: Storms can disrupt businesses, causing closures, supply chain disruptions, and loss of revenue. For example, Hurricane Harvey in 2017 caused widespread business closures in Houston, leading to economic losses and unemployment.
- Tourism Impacts: Storms can deter tourism, leading to cancellations and reduced visitor spending. This can impact local businesses and economies reliant on tourism. For example, Hurricane Irma in 2017 significantly impacted tourism in the Caribbean, causing economic losses for hotels, restaurants, and other businesses.
Social Impacts
Storms can have significant social impacts on affected communities, including:
- Displacement: Flooding and damage to homes can lead to displacement of residents, creating a need for temporary housing and support services. The 2017 hurricane season in the Caribbean saw the displacement of thousands of people, requiring humanitarian assistance and long-term recovery efforts.
- Health Impacts: Storms can cause injuries, health problems, and mental health issues. The stress and trauma associated with storms can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges. The aftermath of Hurricane Maria in 2017 led to widespread health issues in Puerto Rico, including outbreaks of diseases and mental health challenges.
- Community Disruption: Storms can disrupt community life, leading to social isolation, loss of social networks, and challenges in rebuilding community infrastructure. The recovery process following a storm can be long and complex, requiring community resilience and support.
Safety Measures and Preparedness
Storms can be unpredictable and dangerous, so it’s crucial to take steps to ensure your safety and preparedness. Whether you’re at home, work, or on the go, there are several measures you can take to minimize risks and protect yourself and your loved ones.
Safety Measures During Storms
Being aware of your surroundings and taking precautions during storms is essential. This section will discuss various safety measures you can take to protect yourself and your property.
- Stay Informed: Keep a close eye on weather forecasts and warnings from reliable sources like the National Weather Service. This information will help you make informed decisions about your safety.
- Seek Shelter: During a storm, it’s crucial to find a safe shelter. Avoid areas prone to flooding, landslides, or high winds. If you’re in a building, move to a lower level, away from windows, and seek a sturdy room like a basement or interior hallway.
- Stay Away from Water: Never attempt to drive or walk through floodwaters. Even a few inches of water can be dangerous and can sweep you off your feet.
- Be Aware of Falling Debris: Secure loose objects outside your home, like patio furniture and trash cans, to prevent them from becoming projectiles during high winds. If you’re indoors, stay away from windows and doors that could shatter.
- Power Outages: Be prepared for power outages by having flashlights, batteries, and a battery-powered radio readily available. If you have a generator, ensure it’s properly maintained and fueled up before a storm hits.
- Stay Calm: During a storm, it’s important to remain calm and collected. Avoid panicking and follow instructions from authorities.
Preparing for Potential Storm Impacts
Preparation is key to minimizing the impact of a storm. This section will discuss essential steps you can take to prepare for potential storm impacts.
- Emergency Kit: Assemble an emergency kit that includes essential supplies like water, non-perishable food, a first-aid kit, a flashlight, batteries, a whistle, a weather radio, and copies of important documents. This kit should be readily accessible and should be reviewed and replenished regularly.
- Evacuation Plan: If you live in an area prone to flooding or other storm-related hazards, have an evacuation plan in place. Determine a safe evacuation route and a designated meeting place for your family.
- Secure Your Home: Before a storm hits, secure your home by bringing in loose objects, closing and securing windows and doors, and covering or boarding up windows. If you have a garage door opener, unplug it to prevent it from being damaged by power surges.
- Protect Your Electronics: Unplug sensitive electronics like computers, TVs, and appliances to protect them from power surges during a storm.
- Communicate: Keep a list of emergency contact numbers handy and ensure you have a way to communicate with family and friends during a storm. This could include a battery-powered radio, a cell phone with a charged battery, or a satellite phone.
Staying Informed About Storm Warnings and Advisories
Staying informed about storm warnings and advisories is crucial for your safety. This section will discuss the importance of staying updated and the various sources of information available.
- National Weather Service: The National Weather Service (NWS) is the official source for weather forecasts and warnings in the United States. You can access their information through their website, mobile app, or local news channels.
- Local Media: Stay tuned to local news channels, radio stations, and newspapers for the latest weather updates and storm warnings. These sources will provide information tailored to your specific location.
- Emergency Alerts: Sign up for emergency alerts from your local government or emergency management agency. These alerts will notify you of impending storms, evacuations, and other critical information.
- Weather Apps: Several weather apps provide detailed forecasts, radar maps, and storm warnings. Choose a reliable app and ensure it’s set to receive notifications for your location.
Historical Storm Activity
The Atlantic Ocean has a long and storied history of powerful storms, each leaving its mark on the coastlines and communities they have impacted. Understanding the historical activity of these storms helps us learn from the past and better prepare for future events.
Significant Atlantic Storms
The following table provides a glimpse into the historical records of some of the most notable Atlantic storms.
| Storm Name | Date | Category | Affected Areas | Notable Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hurricane Katrina | August 23-30, 2005 | Category 3 | Gulf Coast of the United States (Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama) | Devastating flooding in New Orleans, over 1,800 fatalities, widespread damage to infrastructure and property. |
| Hurricane Andrew | August 23-26, 1992 | Category 5 | South Florida, Louisiana | Considered one of the costliest hurricanes in US history, causing billions in damages and leaving thousands homeless. |
| Hurricane Sandy | October 22-29, 2012 | Post-tropical cyclone | Eastern United States, Caribbean | Record storm surge, widespread power outages, significant damage to infrastructure and property. |
| Hurricane Dorian | August 28 – September 6, 2019 | Category 5 | Bahamas, Eastern United States | Devastating damage to the Bahamas, particularly Abaco and Grand Bahama, significant coastal flooding and power outages. |
| Hurricane Harvey | August 25 – September 2, 2017 | Category 4 | Texas, Louisiana | Record-breaking rainfall and flooding in Houston, widespread damage to infrastructure and property. |
Historical Storm Trends and Patterns
The Atlantic hurricane season, which runs from June 1st to November 30th, exhibits certain trends and patterns. Analyzing historical data helps us understand the frequency, intensity, and geographical distribution of storms over time. For example, some years have seen a higher number of storms than others, while certain regions may experience more intense storms. These trends and patterns are valuable tools for forecasting and preparing for future hurricane seasons.
The Atlantic, a force of nature both beautiful and formidable, reminds us of our vulnerability and the importance of preparedness. Understanding the nuances of storm activity, from tracking their genesis to anticipating their potential impacts, empowers us to navigate these challenges with greater awareness and resilience. As we learn from the past and embrace the tools of modern science, we can strive to mitigate the risks associated with storms and protect our communities from their wrath.
FAQ Guide
What is the difference between a tropical storm and a hurricane?
A tropical storm has sustained wind speeds of 39 to 73 mph, while a hurricane has sustained wind speeds of 74 mph or higher.
How can I stay informed about storms?
Stay tuned to local news channels, weather websites, and official advisories from agencies like the National Hurricane Center.
What are the most common impacts of storms?
Storms can cause flooding, wind damage, storm surge, power outages, and disruptions to transportation.
What are some ways to prepare for a storm?
Gather emergency supplies, develop an evacuation plan, secure your property, and stay informed about storm warnings.





