Can you draw long term disability and social security – Navigating the intricate world of disability benefits can feel like traversing a labyrinth, especially when considering the potential overlap of long-term disability and Social Security. Both programs offer crucial financial support during times of hardship, but understanding their eligibility criteria, application processes, and potential for coordination is essential. This exploration will shed light on the key aspects of these programs, empowering you to make informed decisions regarding your financial well-being.
The journey towards accessing these benefits can be complex, often requiring meticulous documentation and persistent advocacy. However, with a clear understanding of the intricacies involved, individuals can navigate this process with greater confidence, ensuring they receive the support they deserve. Let us delve into the details of these programs, illuminating the path towards financial security during challenging times.
Eligibility for Long-Term Disability and Social Security
Understanding the eligibility requirements for long-term disability (LTD) and Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is crucial for individuals seeking these benefits. Both programs have distinct criteria, and qualifying for one does not automatically guarantee eligibility for the other.
Types of Disabilities
The types of disabilities that qualify for LTD and SSDI vary. Both programs require a severe impairment that prevents you from performing your usual work activities. However, SSDI focuses on a broader range of disabilities that significantly limit your ability to engage in any substantial gainful activity (SGA). LTD, on the other hand, often has specific definitions of disability based on the policy terms.
- Long-Term Disability (LTD): LTD programs typically cover disabilities that prevent you from performing your own job. Some common examples include:
- Physical Disabilities: Back injuries, spinal cord injuries, amputations, severe arthritis, chronic pain syndromes, and severe heart conditions.
- Mental Health Conditions: Severe depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Cognitive Impairments: Traumatic brain injury, stroke, dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI): SSDI covers a broader range of disabilities that significantly limit your ability to work in any job. Examples include:
- Physical Disabilities: Similar to LTD, including conditions like muscular dystrophy, multiple sclerosis, and certain types of cancer.
- Mental Health Conditions: Similar to LTD, including conditions like severe anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and personality disorders.
- Sensory Impairments: Severe vision loss, hearing loss, and chronic pain.
- Other Conditions: Epilepsy, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease.
Application Process
Applying for long-term disability or Social Security disability benefits involves a multi-step process that requires careful documentation and communication. This process can be complex and time-consuming, so it is essential to understand the steps involved and to gather all necessary information.
Long-Term Disability Benefits Application Process
The application process for long-term disability benefits typically involves the following steps:
- Contact your insurance company: The first step is to contact your insurance company and notify them that you are filing a claim. You will need to provide them with information about your disability, including the date of onset, the nature of your disability, and the medical professionals treating you. It is important to follow your insurance company’s specific instructions for filing a claim.
- Complete and submit the claim form: Your insurance company will provide you with a claim form that you will need to complete and submit. This form will ask for detailed information about your disability, your medical history, and your employment history. Be sure to provide accurate and complete information, as this will be reviewed by the insurance company to determine your eligibility.
- Provide supporting medical documentation: Along with the claim form, you will need to provide supporting medical documentation from your doctor or other healthcare providers. This documentation should include details about your disability, including the diagnosis, treatment plan, and any limitations you have due to your disability. The documentation should be clear and concise, and it should be provided in a timely manner.
- Attend a medical examination: In some cases, your insurance company may require you to undergo a medical examination by a physician chosen by the insurance company. This examination will be used to verify your disability and to assess your functional limitations. It is important to cooperate with the insurance company and to attend the medical examination as scheduled.
- Review and appeal: After your claim has been reviewed, the insurance company will make a decision regarding your eligibility for benefits. If your claim is denied, you will have the right to appeal the decision. The appeal process will involve providing additional documentation and arguments in support of your claim. It is important to consult with an attorney or other qualified professional if you are considering appealing a denial.
Social Security Disability Benefits Application Process
The application process for Social Security disability benefits involves the following steps:
- Complete and submit an application: You can apply for Social Security disability benefits online, by phone, or by mail. You will need to provide personal information, work history, and medical information. The application process can be lengthy and detailed, so it is important to gather all necessary information and to complete the application accurately.
- Provide medical evidence: Along with the application, you will need to provide medical evidence to support your claim. This evidence should be from a doctor or other qualified medical professional and should include details about your disability, including the diagnosis, treatment plan, and any limitations you have due to your disability. The Social Security Administration (SSA) will review your medical evidence to determine if your disability meets their definition of disability.
- Attend a consultative examination: In some cases, the SSA may require you to attend a consultative examination with a physician chosen by the SSA. This examination will be used to verify your disability and to assess your functional limitations. It is important to cooperate with the SSA and to attend the consultative examination as scheduled.
- Review and appeal: After your application has been reviewed, the SSA will make a decision regarding your eligibility for benefits. If your application is denied, you will have the right to appeal the decision. The appeal process will involve providing additional documentation and arguments in support of your claim. It is important to consult with an attorney or other qualified professional if you are considering appealing a denial.
Comparison of Application Processes
The application processes for long-term disability and Social Security disability benefits are similar in some ways, but there are also some key differences:
- Eligibility criteria: The eligibility criteria for both programs are based on the severity of your disability and your ability to work. However, the specific criteria used to determine eligibility can vary between the programs.
- Application process: The application process for long-term disability benefits is typically handled by your insurance company, while the application process for Social Security disability benefits is handled by the SSA. Both processes involve providing medical documentation and attending medical examinations, but the specific requirements can vary.
- Benefits: The benefits provided by long-term disability and Social Security disability programs are also different. Long-term disability benefits are typically based on your salary, while Social Security disability benefits are based on your work history and earnings.
- Duration of benefits: Long-term disability benefits are typically paid for a limited period of time, while Social Security disability benefits can be paid for life, depending on the severity of your disability.
Benefits and Payments
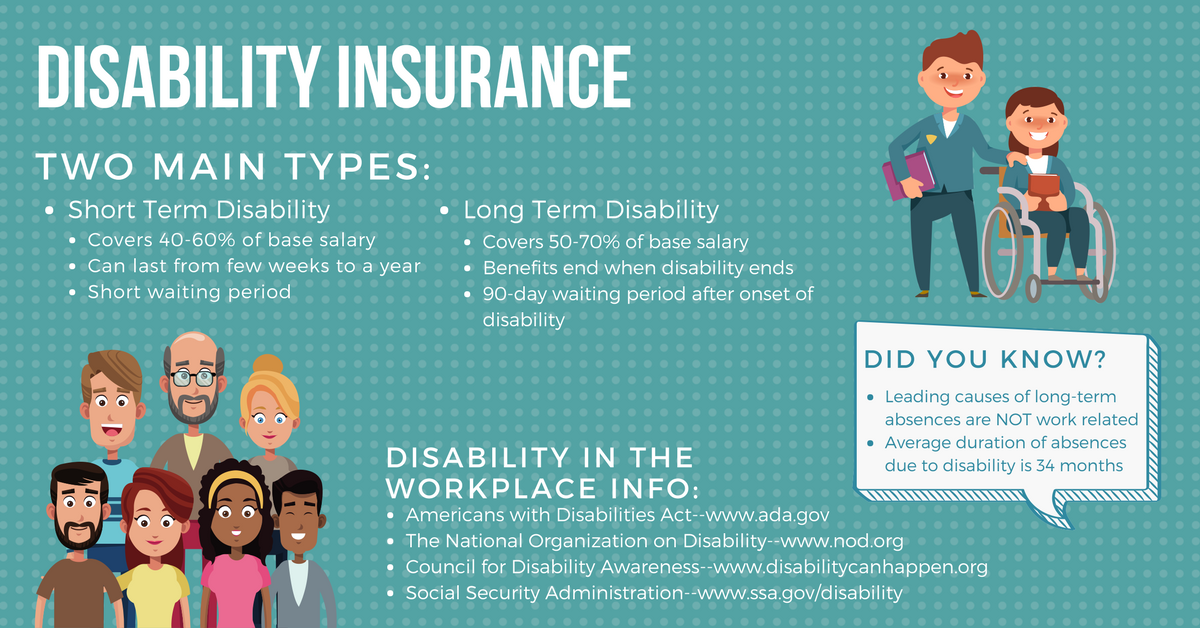
Understanding the benefits and payment structure of long-term disability insurance and Social Security disability is crucial for individuals facing prolonged health challenges. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the benefits available under each program and how payments are structured.
Long-Term Disability Insurance Benefits
Long-term disability insurance, often purchased through employers or independently, provides financial support to individuals who are unable to work due to a disability. The benefits typically replace a portion of the insured’s income, helping them maintain financial stability during their recovery.
- Disability Income Benefits: These are the primary benefits offered by long-term disability insurance. They provide a monthly payment to the insured, typically calculated as a percentage of their pre-disability income, for the duration of their disability.
- Other Benefits: Depending on the specific policy, long-term disability insurance may also offer additional benefits, such as:
- Rehabilitation Benefits: Coverage for vocational rehabilitation services, helping individuals return to work.
- Medical Expense Benefits: Coverage for medical expenses related to the disability, although this is less common.
- Death Benefits: A lump-sum payment to beneficiaries in case of death during the disability period.
Social Security Disability Benefits, Can you draw long term disability and social security
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is a federal program that provides monthly income benefits to individuals who are unable to work due to a severe medical condition. The program is funded through payroll taxes and is available to eligible workers who have paid into the system.
- Disability Insurance Benefits (DIB): These benefits are available to workers who have paid enough Social Security taxes to be insured. The amount of benefits received is based on the individual’s earnings history and the age at which they become disabled.
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI): SSI is a needs-based program available to individuals with disabilities who have limited income and resources. The monthly payment amount is determined by the individual’s financial situation and the state in which they reside.
- Other Benefits: In addition to monthly income benefits, Social Security disability recipients may also be eligible for other benefits, such as:
- Medicare: Individuals receiving SSDI benefits are automatically eligible for Medicare coverage after a 24-month waiting period.
- Medicaid: Individuals receiving SSI benefits may be eligible for Medicaid, a state-funded program that provides health insurance coverage.
Payment Structure and Frequency
The payment structure and frequency for both long-term disability insurance and Social Security disability benefits vary depending on the specific program and individual circumstances.
- Long-Term Disability Insurance: Payments are typically made monthly and are calculated based on the insured’s pre-disability income and the percentage of coverage provided by the policy. The duration of payments depends on the policy’s terms and the individual’s disability status.
- Social Security Disability Insurance: Payments are made monthly and are calculated based on the individual’s earnings history. The amount of benefits received is capped at a maximum amount set by the Social Security Administration each year. Payments continue as long as the individual remains disabled and meets the program’s eligibility requirements.
- Supplemental Security Income: Payments are made monthly and are based on the individual’s financial situation and the state in which they reside. The amount of benefits received is capped at a maximum amount set by the Social Security Administration each year.
Appeals and Reconsideration

If your claim for long-term disability or Social Security disability benefits is denied, you have the right to appeal the decision. The appeals process allows you to present additional evidence and argue your case to an administrative law judge or other decision-maker.
Appealing a Long-Term Disability Benefits Decision
The appeals process for long-term disability benefits varies depending on the insurance company or plan. Generally, the process involves the following steps:
- Internal Appeal: You will typically have a set period of time (usually 60-180 days) to file an internal appeal with the insurance company. This appeal should include any new evidence or information that supports your claim.
- External Appeal: If the internal appeal is denied, you may be able to appeal to an external review board or an independent arbitrator. This process will vary depending on the specific terms of your policy.
- Court Appeal: In some cases, you may be able to appeal the decision to a court of law. However, this is typically only an option if the insurance company has violated the terms of the policy or acted in bad faith.
Appealing a Social Security Disability Benefits Decision
The Social Security Administration (SSA) has a five-step appeals process for disability benefits:
- Reconsideration: This is the first level of appeal. You can request reconsideration within 60 days of receiving the initial denial. The SSA will review your case and consider any new evidence you submit.
- Hearing Before an Administrative Law Judge (ALJ): If your reconsideration is denied, you can request a hearing before an ALJ. The ALJ will review your case and hear testimony from you, your doctors, and other witnesses. The ALJ will then issue a decision on your claim.
- Appeals Council Review: If the ALJ denies your claim, you can appeal the decision to the Appeals Council. The Appeals Council will review the ALJ’s decision and may decide to grant your claim, deny your claim, or send your case back to the ALJ for further review.
- Federal Court Review: If the Appeals Council denies your claim, you can file a lawsuit in federal court. The court will review the SSA’s decision and may decide to grant your claim, deny your claim, or send your case back to the SSA for further review.
Potential Outcomes of Appeals
The outcome of an appeal depends on the specific circumstances of your case and the evidence you present. Some possible outcomes include:
- Approval of Benefits: The appeals process may result in the approval of your disability benefits. This can happen if you present new evidence that supports your claim or if the decision-maker finds that the initial decision was incorrect.
- Denial of Benefits: The appeals process may also result in the denial of your disability benefits. This can happen if the decision-maker finds that you do not meet the eligibility criteria for disability benefits or if you fail to present sufficient evidence to support your claim.
- Remand: The appeals process may result in a remand, which means that the decision-maker sends your case back to the original decision-maker for further review. This can happen if the decision-maker finds that the original decision was not properly supported by the evidence.
Overlap and Coordination of Benefits

It is possible to receive benefits from both long-term disability (LTD) insurance and Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) simultaneously. However, the amount of benefits you receive from each program may be reduced or eliminated due to coordination rules. These rules are designed to prevent individuals from receiving duplicate benefits for the same disability.
Coordination of Benefits
If you are receiving benefits from both LTD and SSDI, the amount of SSDI benefits you receive will be reduced by the amount of LTD benefits you receive. This is known as the “offset” rule.
The offset rule is calculated by subtracting your LTD benefits from your SSDI benefits.
The following are some examples of how the offset rule works:
- If you are receiving $2,000 per month in LTD benefits and $3,000 per month in SSDI benefits, your SSDI benefits will be reduced to $1,000 per month.
- If you are receiving $1,500 per month in LTD benefits and $1,000 per month in SSDI benefits, your SSDI benefits will be reduced to $0, meaning you will not receive any SSDI benefits.
It is important to note that the offset rule only applies to SSDI benefits. It does not affect your LTD benefits. You will continue to receive your full LTD benefits regardless of how much SSDI benefits you receive.
Understanding the intricacies of long-term disability and Social Security benefits is a crucial step towards ensuring financial stability during periods of disability. By navigating the application processes, understanding eligibility criteria, and exploring the potential for coordination, individuals can gain clarity and empower themselves to seek the support they need. Remember, seeking guidance from qualified professionals can be invaluable in navigating the complexities of these programs, ensuring that your rights are protected and your needs are met.
Common Queries: Can You Draw Long Term Disability And Social Security
What are the main differences between long-term disability and Social Security benefits?
Long-term disability benefits are typically provided by private insurance companies and are based on your individual policy. Social Security disability benefits are a federal program funded by payroll taxes. The eligibility criteria, benefit amounts, and application processes differ between the two.
Can I receive both long-term disability and Social Security benefits at the same time?
In some cases, you may be eligible to receive both types of benefits. However, the benefits may be coordinated to avoid duplicate payments. The specific rules for coordination vary depending on the circumstances.
How long does it typically take to receive disability benefits?
The processing time for both long-term disability and Social Security benefits can vary significantly. It can take several months or even years to receive a decision. It is important to be patient and persistent throughout the process.
What happens if my disability benefits application is denied?
If your application is denied, you have the right to appeal the decision. The appeals process can be complex, so it is essential to seek legal advice if necessary.






