Which of the following best describes an email security gateway – Which email security gateway best describes an email security gateway? Think of it as your digital bouncer, standing guard against the spam, phishing, and malware that constantly tries to crash your inbox party. It’s the unsung hero that keeps your emails safe and your data secure.
Imagine this: you’re running a business, and suddenly, your employees start getting bombarded with phishing emails. These emails can steal sensitive information, disrupt your operations, and even damage your reputation. This is where an email security gateway comes in. It acts as a barrier, filtering out suspicious emails and blocking malicious attachments before they can reach your inbox.
What is an Email Security Gateway?
In the digital age, email is an indispensable tool for communication and collaboration. However, it also serves as a prime target for cybercriminals seeking to infiltrate systems and steal sensitive data. To combat these threats, organizations rely on email security gateways, acting as the first line of defense against malicious emails.An email security gateway is a dedicated hardware or software appliance that inspects incoming and outgoing email traffic for potential threats.
It analyzes emails for suspicious content, attachments, and sender addresses, filtering out malicious messages before they reach recipients’ inboxes.
Common Threats Mitigated by Email Security Gateways
Email security gateways are crucial for safeguarding organizations against various threats, including:
- Spam: Unwanted or unsolicited emails, often containing promotional content or phishing links.
- Phishing: Deceptive emails designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details.
- Malware: Malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware, often disguised as legitimate attachments or links.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to confidential information through email, such as customer data, financial records, or intellectual property.
- Spoofing: Emails disguised as legitimate communications from trusted sources, aiming to deceive recipients into taking actions that benefit the attacker.
Key Features and Functionalities
Email security gateways offer a comprehensive set of features to ensure email security:
- Content Filtering: Analyzing email content for s, phrases, and patterns associated with spam, phishing, or malware.
- Attachment Scanning: Examining email attachments for malicious code or suspicious file types, using antivirus engines and sandboxing technologies.
- Sender Reputation Checking: Evaluating the sender’s reputation based on their email history, blacklists, and other factors to identify potential spammers or spoofers.
- Anti-Spoofing: Detecting and blocking emails that spoof legitimate sender addresses, using techniques such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance).
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Preventing sensitive information from being leaked through email, by detecting and blocking emails containing confidential data.
- Quarantine and Reporting: Isolating suspicious emails for further analysis and providing detailed reports on email security incidents.
Types of Email Security Gateways
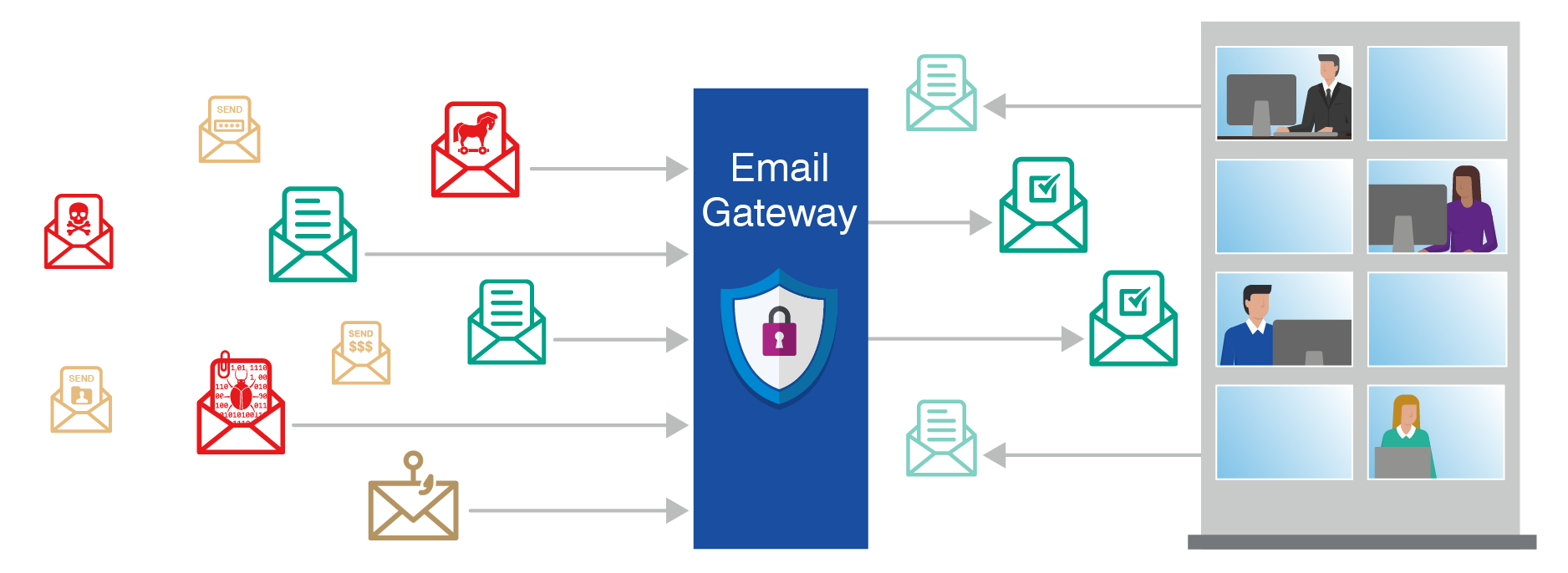
Email security gateways come in different forms, each offering unique features and functionalities to protect your organization from various email-borne threats. Understanding the different types of gateways allows you to choose the most appropriate solution for your specific needs.
Cloud-Based Email Security Gateways
Cloud-based email security gateways are hosted by a third-party provider, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure and maintenance. They offer several advantages, including:
- Scalability: Cloud-based gateways can easily scale to accommodate changing email volumes and security needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: They often offer a pay-as-you-go model, reducing upfront costs and making them a more affordable option.
- Ease of Deployment: They are typically easy to deploy and configure, requiring minimal technical expertise.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud-based gateways receive automatic updates, ensuring you always have the latest security features and protection against emerging threats.
Popular examples of cloud-based email security gateway providers include:
- Proofpoint: Proofpoint offers a comprehensive suite of email security solutions, including anti-spam, anti-virus, and data loss prevention (DLP) capabilities.
- Mimecast: Mimecast provides a cloud-based email security platform that includes email archiving, continuity, and threat protection features.
- Barracuda: Barracuda offers a range of email security solutions, including spam filtering, virus protection, and advanced threat detection.
On-Premise Email Security Gateways
On-premise email security gateways are physically installed on your organization’s network and require dedicated hardware and software resources. They offer greater control over security settings and data storage but require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
- Customization: On-premise gateways allow for greater customization of security policies and rules to meet specific organizational needs.
- Data Control: You have complete control over data storage and access, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Offline Protection: On-premise gateways can provide offline protection against email threats, as they are not dependent on an internet connection.
Popular examples of on-premise email security gateway providers include:
- Symantec: Symantec offers a comprehensive email security platform that includes anti-spam, anti-virus, and DLP capabilities.
- Trend Micro: Trend Micro provides a range of on-premise email security solutions, including spam filtering, virus protection, and advanced threat detection.
- Sophos: Sophos offers a comprehensive security suite that includes an on-premise email security gateway with advanced threat protection features.
Hybrid Email Security Gateways
Hybrid email security gateways combine the benefits of both cloud-based and on-premise solutions. They allow organizations to leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of cloud services while maintaining control over sensitive data and critical security settings.
- Flexibility: Hybrid gateways offer flexibility in choosing which functions to manage on-premise and which to delegate to the cloud.
- Best of Both Worlds: They allow organizations to benefit from the advantages of both cloud and on-premise solutions.
- Cost Optimization: They can help organizations optimize costs by utilizing cloud services for less critical functions and managing sensitive data on-premise.
Examples of hybrid email security gateway solutions include:
- Microsoft Exchange Online Protection (EOP): EOP is a cloud-based email security service that can be integrated with on-premise Exchange servers, providing a hybrid email security solution.
- Google Workspace: Google Workspace includes a range of security features, including spam filtering, virus protection, and phishing protection, which can be used in conjunction with on-premise email servers.
Email Security Gateway Implementation
Implementing an email security gateway requires careful planning and execution to ensure effective protection against email-borne threats. This process involves a series of steps, configuration considerations, and best practices for optimal performance and security.
Steps Involved in Implementation
Implementing an email security gateway typically involves the following steps:
- Needs Assessment: Determine the specific email security needs of your organization, including the types of threats you face, the volume of email traffic, and the level of security required.
- Solution Selection: Choose an email security gateway solution that aligns with your needs, considering factors such as features, pricing, ease of use, and scalability.
- Deployment: Deploy the email security gateway solution, either on-premises or in the cloud, depending on your infrastructure and preferences.
- Configuration: Configure the email security gateway, including settings for spam filtering, virus scanning, content filtering, and other security features.
- Testing and Tuning: Thoroughly test the email security gateway to ensure it is working as intended and fine-tune the configuration for optimal performance.
- Integration: Integrate the email security gateway with your existing email infrastructure, including email servers, mail clients, and other relevant systems.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitor the email security gateway for performance, security, and compliance issues, and regularly update the solution and its security policies.
Considerations for Configuration and Customization
Configuration and customization of an email security gateway are critical to achieving optimal security and performance. Key considerations include:
- Spam Filtering: Configure spam filtering rules to block unwanted emails, including blacklists, whitelists, and reputation-based filtering.
- Virus Scanning: Implement robust virus scanning to detect and prevent malware from entering your network. This involves selecting an effective antivirus engine and regularly updating the virus signature database.
- Content Filtering: Establish content filtering policies to block inappropriate content, such as phishing links, malware attachments, and objectionable material.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP rules to prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization through email. This includes policies for identifying and blocking emails containing confidential information, such as credit card numbers or social security numbers.
- Encryption: Configure email encryption to protect sensitive data in transit and at rest. This ensures that emails cannot be intercepted and read by unauthorized individuals.
- User Management: Establish robust user management policies to control access to the email security gateway and ensure that only authorized personnel can make changes to the configuration.
- Reporting and Analytics: Enable reporting and analytics features to monitor email security activity, identify trends, and evaluate the effectiveness of the email security gateway.
Best Practices for Management and Maintenance
Managing and maintaining an email security gateway is essential for ensuring ongoing security and optimal performance. Best practices include:
- Regular Updates: Keep the email security gateway software and virus signatures updated to protect against the latest threats. Regularly check for updates and apply them promptly.
- Security Policy Review: Periodically review and update your email security policies to reflect evolving threats and industry best practices.
- Monitoring and Analysis: Monitor the email security gateway for suspicious activity and analyze logs to identify trends and potential threats. This includes tracking the volume of spam, malware, and other threats blocked by the gateway.
- Incident Response: Develop and test incident response plans to address security incidents promptly and effectively. This involves having procedures in place for identifying, containing, and resolving email security breaches.
- Training: Train users on email security best practices to help them identify and avoid phishing scams, malware, and other threats. This includes educating users about safe email practices, such as not clicking on suspicious links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
Benefits of Email Security Gateways

Email security gateways are essential tools for businesses of all sizes, providing a critical layer of protection against various email-borne threats. By implementing an email security gateway, organizations can significantly enhance their data security, improve compliance with industry regulations, and safeguard their reputation.
Impact on Data Security and Compliance
Email security gateways play a vital role in protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. They act as a barrier against malicious emails, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. By filtering out spam, phishing attacks, and malware, these gateways ensure that only legitimate emails reach users’ inboxes. This significantly reduces the risk of data theft, ransomware attacks, and other cyber threats that can compromise sensitive information.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Email security gateways can be configured to identify and block emails containing sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, or confidential business information. This helps prevent accidental or intentional data leaks and ensures compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Compliance with Industry Regulations: Many industries have strict regulations regarding data security and email communication. Email security gateways help organizations comply with these regulations by providing features like encryption, message authentication, and content filtering. This ensures that sensitive data is handled securely and in accordance with legal requirements.
Real-World Examples of Protection
Email security gateways have proven to be effective in protecting organizations from various attacks. For example, in 2020, a major healthcare provider successfully thwarted a sophisticated phishing attack targeting its employees. The email security gateway detected the malicious emails, preventing them from reaching user inboxes and protecting sensitive patient data from unauthorized access.
“Our email security gateway was instrumental in stopping a targeted phishing attack that could have compromised our entire network. The gateway detected the malicious emails and blocked them before they could reach our employees. This prevented a potential data breach and saved us significant time and resources,” said the organization’s Chief Information Security Officer.
Emerging Trends in Email Security

The landscape of email security is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the emergence of new threats. This dynamic environment necessitates a proactive approach to safeguarding email communications from malicious actors. This section explores the latest trends and advancements in email security technology, focusing on the impact of artificial intelligence and machine learning and the challenges and opportunities presented by emerging threats.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Email Security
AI and ML are revolutionizing email security by enhancing threat detection and response capabilities. These technologies are employed in various aspects of email security, including:
- Threat Detection: AI and ML algorithms analyze email content, sender behavior, and network traffic patterns to identify suspicious activities. They can detect sophisticated phishing attacks, malware distribution, and other malicious emails that traditional security solutions may miss.
- Spam Filtering: AI-powered spam filters learn from user feedback and historical data to identify and block unwanted emails with greater accuracy. They can adapt to evolving spam tactics, such as spoofed sender addresses and social engineering techniques.
- Zero-Day Threat Detection: AI and ML algorithms can identify zero-day threats, which are new and previously unknown vulnerabilities. These technologies can analyze email attachments and code to detect malicious patterns and prevent the spread of unknown threats.
- Automated Response: AI and ML can automate security responses to threats, such as quarantining infected emails or blocking suspicious senders. This reduces the time and effort required for human intervention, enabling faster and more effective threat mitigation.
Emerging Threats to Email Security
The threat landscape for email security is constantly evolving, with attackers continuously developing new techniques to bypass traditional security measures. Some of the emerging threats include:
- BEC (Business Email Compromise): BEC attacks target businesses by impersonating legitimate senders, often executives, to request financial transactions or sensitive information. These attacks can be highly effective, as they leverage social engineering and exploit trust within organizations.
- Advanced Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks are becoming more sophisticated, using techniques like spear phishing, whaling, and watering hole attacks to target specific individuals or organizations. These attacks often exploit vulnerabilities in user behavior and rely on social engineering to gain access to sensitive information.
- Malware Distribution: Attackers are using email as a primary means to distribute malware, such as ransomware, trojans, and spyware. These attacks often exploit vulnerabilities in software or user behavior to gain access to systems and steal data.
- Data Breaches: Email security breaches can lead to data leaks, exposing sensitive information such as customer data, financial records, and intellectual property. These breaches can have significant financial and reputational consequences for organizations.
Challenges and Opportunities, Which of the following best describes an email security gateway
The emergence of new threats and advancements in technology presents both challenges and opportunities for email security.
- Keeping Pace with Evolving Threats: Staying ahead of evolving threats requires continuous monitoring, research, and development of new security solutions. Organizations need to adapt their security strategies to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Balancing Security and Usability: Email security solutions should be effective in protecting against threats while maintaining a positive user experience. Balancing security measures with usability is crucial to ensure user adoption and minimize disruption to business operations.
- Leveraging AI and ML: Implementing AI and ML solutions can significantly enhance threat detection and response capabilities. Organizations should invest in these technologies to stay ahead of the curve in email security.
- Building a Culture of Security Awareness: Educating users about email security threats and best practices is essential to prevent phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics. Organizations should invest in training programs and awareness campaigns to empower users to identify and report suspicious emails.
So, in a nutshell, an email security gateway is like having a personal bodyguard for your inbox. It’s essential for any organization that wants to keep its data safe and its operations running smoothly. With the ever-evolving threat landscape, investing in a robust email security gateway is no longer an option but a necessity.
FAQ Resource: Which Of The Following Best Describes An Email Security Gateway
What are some common threats that email security gateways protect against?
Email security gateways protect against a wide range of threats, including spam, phishing, malware, ransomware, and even data leaks. They can also help prevent the spread of viruses and other malicious software.
How do email security gateways work?
Email security gateways work by inspecting incoming and outgoing emails for suspicious content. They use a variety of techniques, such as spam filtering, malware detection, and data loss prevention, to identify and block threats. They can also be configured to enforce email policies and compliance regulations.
Are email security gateways expensive?
The cost of email security gateways varies depending on the features and functionality you need. There are both free and paid options available, so you can choose a solution that fits your budget and security needs.





