How companies reduce costs through contract manufacturing and outsourcing is a compelling story of strategic efficiency. It’s a tale of leveraging global expertise, optimizing production, and ultimately, boosting profitability. This exclusive interview delves into the intricacies of this cost-saving strategy, revealing the secrets behind successful implementation and the challenges companies navigate along the way. We’ll explore the various approaches, the potential pitfalls, and the remarkable results achieved by businesses that have embraced this transformative approach.
From identifying key cost-saving areas to mitigating risks and selecting reliable partners, we’ll unpack the essential elements of successful contract manufacturing and outsourcing. We’ll examine real-world case studies, showcasing the tangible benefits and offering insights into best practices. Our discussion will also touch upon the legal and ethical considerations, emphasizing the importance of responsible outsourcing and the role of technology in driving further efficiency gains.
Introduction to Contract Manufacturing and Outsourcing
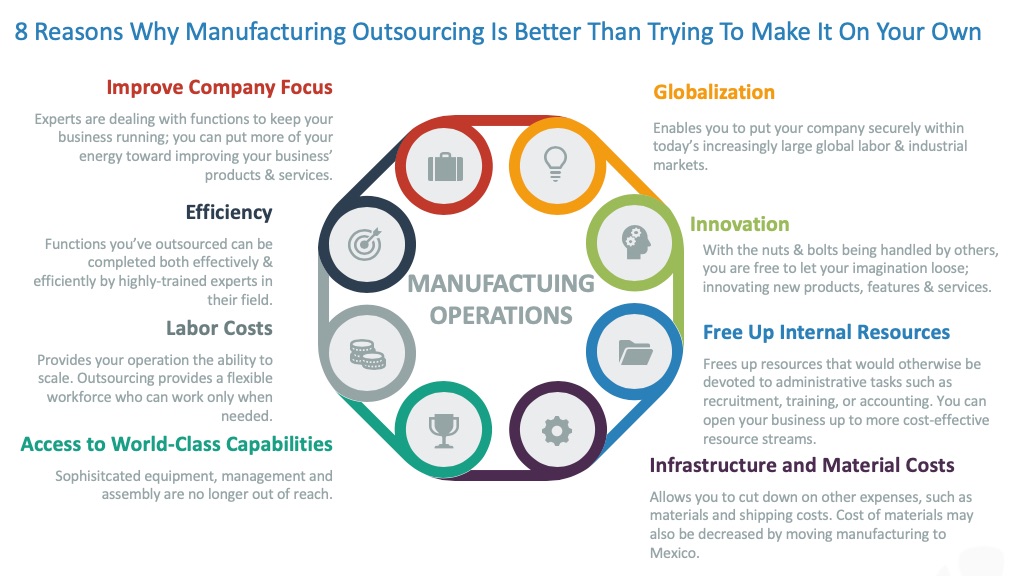
Contract manufacturing and outsourcing are two closely related strategies businesses employ to reduce costs and improve efficiency. They involve transferring some or all of a company’s manufacturing or operational processes to external providers. While often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences. Outsourcing encompasses a broader range of functions, including customer service, IT, and marketing, while contract manufacturing specifically focuses on the production of goods.
Both, however, share the common goal of leveraging external expertise and resources to streamline operations.Outsourcing and contract manufacturing allow companies to focus on their core competencies, freeing up internal resources to concentrate on strategic initiatives like research and development, marketing, and sales. This specialization can lead to significant cost savings, increased productivity, and improved product quality. However, it’s crucial to carefully select and manage external partners to mitigate potential risks such as quality control issues, intellectual property protection concerns, and supply chain disruptions.
Types of Contract Manufacturing Arrangements
Several different contract manufacturing arrangements exist, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. The best choice depends on a company’s specific needs and circumstances. Factors to consider include production volume, required level of customization, technological expertise needed, and desired level of control over the manufacturing process.
- Full-Service Contract Manufacturing: In this model, the contract manufacturer handles the entire manufacturing process, from raw material sourcing to packaging and shipping. This option offers the highest level of outsourcing but requires a significant level of trust and clear communication with the manufacturer.
- Partial Contract Manufacturing: This approach involves outsourcing only specific aspects of the manufacturing process, such as assembly or packaging, while the company retains control over other stages. This offers more control but may not provide the same level of cost savings as full-service contract manufacturing.
- Joint Venture Contract Manufacturing: This involves a collaborative arrangement between the company and the contract manufacturer, often involving shared investment and risk. This can be beneficial when specialized knowledge or resources are required.
Industries Utilizing Contract Manufacturing
Numerous industries rely heavily on contract manufacturing to streamline operations and reduce costs. The flexibility and scalability of contract manufacturing make it particularly attractive to companies in industries with fluctuating demand or those needing access to specialized manufacturing capabilities.
- Electronics: Companies like Apple heavily utilize contract manufacturers like Foxconn to produce their electronic devices. This allows Apple to focus on design and marketing while outsourcing the complex and capital-intensive manufacturing process.
- Apparel and Footwear: Many clothing and shoe brands outsource manufacturing to countries with lower labor costs. This allows them to offer products at competitive prices while maintaining design and branding control.
- Automotive: Automotive manufacturers often contract out the production of specific components, such as engines or transmissions, to specialized suppliers. This enables them to leverage the expertise of specialized manufacturers and reduce their manufacturing footprint.
- Pharmaceuticals: Pharmaceutical companies frequently outsource the manufacturing of their drugs to contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) that possess the necessary expertise and facilities to produce complex medications safely and efficiently.
Cost Reduction Strategies Through Contract Manufacturing: How Companies Reduce Costs Through Contract Manufacturing And Outsourcing
Contract manufacturing, also known as outsourcing manufacturing, offers businesses significant opportunities to streamline operations and reduce costs. By transferring the responsibility of production to a specialized third-party manufacturer, companies can focus on core competencies like research and development, marketing, and sales. This strategic shift can lead to substantial savings across various aspects of the production process.
Key Cost Areas Where Contract Manufacturing Offers Savings
Several key cost areas experience significant reductions when a company opts for contract manufacturing. These savings stem from the elimination of the need for extensive capital investment in facilities, equipment, and personnel associated with in-house production. Furthermore, contract manufacturers often have established supply chains and economies of scale, resulting in lower material costs and more efficient production processes.
Specifically, savings are often seen in areas like facility overhead, labor costs, equipment maintenance, and raw material procurement.
Comparison of In-House Production Costs Versus Contract Manufacturing Costs
Directly comparing the costs of in-house production versus contract manufacturing requires a detailed analysis of individual circumstances. However, a general comparison reveals that in-house production often incurs higher fixed costs due to the need for large capital investments in facilities, equipment, and ongoing maintenance. Furthermore, in-house production carries the burden of managing a workforce, including salaries, benefits, and training costs.
In contrast, contract manufacturing shifts many of these fixed costs to the contract manufacturer, allowing the company to focus on variable costs associated with the volume of goods produced. The initial setup costs for contract manufacturing might be slightly higher, but long-term cost savings often outweigh these upfront expenses, particularly for companies with fluctuating production demands.
Economies of Scale in Contract Manufacturing and Cost Reduction
Contract manufacturers often benefit from economies of scale. This means that their production costs decrease as their production volume increases. They leverage their large-scale operations to negotiate better prices on raw materials, utilize more efficient equipment, and optimize their labor force. This efficiency translates directly into lower per-unit costs for the company outsourcing its manufacturing. For example, a small company producing 1000 units in-house might pay a significantly higher per-unit cost than a contract manufacturer producing 100,000 units, benefiting from the lower per-unit costs due to its larger scale.
Cost Factor Comparison: In-House vs. Outsourced Manufacturing
| Cost Factor | In-House Cost | Outsourced Cost | Cost Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facility Rent/Mortgage | High (significant fixed cost) | Low (or zero if manufacturer owns facility) | Significant Savings |
| Equipment Purchase & Maintenance | High (substantial upfront and ongoing costs) | Low (manufacturer covers costs) | Significant Savings |
| Labor Costs (Salaries, Benefits) | High (significant variable cost) | Lower (manufacturer’s labor costs are typically lower) | Moderate Savings |
| Raw Materials | Moderate (depending on purchasing power) | Potentially Lower (manufacturer’s bulk purchasing power) | Variable, potentially significant savings |
| Management Overhead | High (salaries, benefits for management staff) | Low (manufacturer handles most management) | Significant Savings |
| Utilities | High (electricity, water, gas) | Low (manufacturer covers costs) | Significant Savings |
| Insurance | High (property, liability) | Low (manufacturer handles insurance for the facility and processes) | Significant Savings |
Outsourcing Specific Functions for Cost Savings

Smart outsourcing can significantly reduce a company’s operational costs. By strategically transferring specific business functions to external providers, companies can access specialized expertise, reduce overhead, and improve efficiency. This allows internal teams to focus on core competencies and strategic initiatives, leading to overall growth and profitability.Outsourcing different functions offers a range of advantages and disadvantages that need careful consideration.
The optimal approach depends on factors such as the company’s size, industry, and strategic goals. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is crucial before making any outsourcing decisions.
Examples of Outsourced Business Functions and Their Cost-Benefit Analysis
Several business functions lend themselves well to outsourcing. These functions often involve repetitive tasks, require specialized skills that are not core to the business, or are geographically dispersed, making them ideal candidates for cost-effective external management. The decision to outsource should be based on a detailed assessment of the potential cost savings against the risks involved, such as potential loss of control or quality issues.
- Customer Service: Outsourcing customer service can reduce labor costs associated with salaries, benefits, and training. Companies can leverage call centers in lower-cost regions or utilize advanced technologies like AI-powered chatbots. However, potential disadvantages include concerns about communication barriers, quality inconsistencies, and potential damage to brand reputation if service quality is compromised. Cost savings can be substantial, potentially reaching 20-40% depending on the scale and complexity of the operation.
- Human Resources (HR): Outsourcing HR functions such as payroll processing, benefits administration, and recruitment can streamline operations and reduce administrative overhead. Specialized HR outsourcing firms often have sophisticated systems and expertise in compliance regulations, minimizing risks and costs. However, a loss of internal control over sensitive employee data and a potential decrease in employee engagement could occur. Cost savings could reach 15-30% depending on the scope of outsourced services.
- Information Technology (IT): Outsourcing IT infrastructure management, help desk support, and software development can reduce capital expenditures on hardware and software, as well as labor costs associated with maintaining an in-house IT team. This can also provide access to cutting-edge technologies and expertise that might not be readily available internally. However, companies must carefully consider data security and potential disruptions in service if the outsourcing provider experiences issues.
Cost savings can range from 10-25%, depending on the specific IT services outsourced.
- Accounting and Finance: Outsourcing accounting and finance functions, such as accounts payable, accounts receivable, and financial reporting, can reduce the need for a large in-house finance team. This allows for improved accuracy and efficiency through specialized expertise. However, maintaining data security and confidentiality is paramount, requiring rigorous vetting of potential outsourcing partners. Cost savings can amount to 10-25% by streamlining operations and reducing labor costs.
- Marketing and Sales: Outsourcing certain marketing and sales functions, like digital marketing campaigns, social media management, or lead generation, can provide access to specialized expertise and a wider reach. This can increase efficiency and reduce the costs associated with building and maintaining an in-house marketing team. However, ensuring alignment with brand messaging and achieving consistent quality across different channels can be challenging.
Cost savings can vary greatly depending on the scale and scope of the outsourced services, but can potentially reach 15-30%.
Risk Mitigation in Contract Manufacturing and Outsourcing
Outsourcing and contract manufacturing offer significant cost advantages, but they also introduce new risks to a company’s supply chain and operations. Successfully leveraging these strategies requires a proactive approach to risk management, focusing on identifying potential problems and implementing effective mitigation strategies. Failing to do so can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and even business failure.Successfully mitigating risks in contract manufacturing and outsourcing hinges on careful planning, robust due diligence, and ongoing monitoring of the chosen partners.
This involves clearly defining expectations, establishing strong communication channels, and building a relationship based on mutual trust and transparency. The following sections delve into specific risk areas and practical mitigation techniques.
Supply Chain Disruptions, How companies reduce costs through contract manufacturing and outsourcing
Supply chain disruptions, such as natural disasters, political instability, or pandemics, can severely impact a company’s ability to deliver products. These disruptions can lead to production delays, increased costs, and unmet customer demands. Mitigating these risks requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes diversifying sourcing, building strategic inventory buffers, and establishing contingency plans to quickly adapt to unforeseen circumstances.
For example, a company might source raw materials from multiple suppliers in different geographical locations to reduce reliance on a single source. Similarly, maintaining a safety stock of critical components can help buffer against temporary shortages.
Quality Control Issues
Maintaining consistent product quality when outsourcing manufacturing is crucial. Poor quality control can result in product recalls, damaged brand reputation, and significant financial losses. Effective mitigation strategies include rigorous quality audits, clear quality standards and specifications, and the implementation of robust quality management systems. Companies should thoroughly vet potential manufacturing partners, ensuring they have the necessary certifications and a proven track record of quality.
Regular on-site inspections and the use of statistical process control (SPC) techniques can help monitor quality throughout the manufacturing process.
Intellectual Property Protection
Protecting intellectual property (IP) is a major concern when outsourcing manufacturing. There’s a risk of unauthorized copying or disclosure of proprietary designs, processes, or technologies. Mitigation strategies involve establishing strong non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) with contract manufacturers, implementing secure data management practices, and carefully selecting partners with a proven commitment to IP protection. Regular audits and legal counsel can further safeguard a company’s IP.
Table of Risk Factors and Mitigation Strategies
| Risk Factor | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Disruption (e.g., natural disaster) | Medium to High (depending on location and industry) | High (production delays, increased costs, lost revenue) | Diversify sourcing, build safety stock, develop contingency plans, utilize risk assessment tools |
| Quality Control Issues | Medium | Medium to High (product recalls, reputational damage, legal liabilities) | Rigorous supplier selection, clear quality standards, regular audits, robust quality management system |
| Intellectual Property Theft | Low to Medium (depending on supplier and industry) | High (loss of competitive advantage, legal costs) | Strong NDAs, secure data management, IP audits, choose reputable suppliers |
| Political or Economic Instability in Manufacturing Location | Low to Medium (depending on location) | Medium to High (production delays, increased costs, political risks) | Geopolitical risk assessment, diversification of manufacturing locations, robust contract clauses |
In conclusion, the journey to reduce costs through contract manufacturing and outsourcing requires careful planning, strategic partnerships, and a proactive approach to risk management. While challenges exist, the potential rewards – including significant cost savings, increased efficiency, and access to specialized expertise – are substantial. By understanding the nuances of this strategy and implementing best practices, companies can unlock significant competitive advantages and pave the way for sustainable growth and profitability.
The key takeaway is that it’s not just about cutting costs; it’s about strategically optimizing operations for long-term success.
Key Questions Answered
What are the hidden costs associated with outsourcing?
Hidden costs can include unexpected transportation fees, communication barriers leading to delays, and potential difficulties in quality control oversight.
How do I ensure intellectual property protection when outsourcing?
Strong contracts with clear clauses on intellectual property rights, confidentiality agreements, and regular audits are crucial.
What are the best ways to manage cultural differences when working with overseas manufacturers?
Effective communication strategies, cultural sensitivity training for teams, and clear, well-defined communication protocols are vital.
What happens if my outsourced manufacturer goes bankrupt?
Having contingency plans, multiple sourcing options, and robust insurance policies are critical to mitigate such risks.






