Which of the following passwords would be considered most secure – Which password is most secure? It’s a question that plagues us all in the digital age, a constant battle between convenience and security. We’re bombarded with warnings about weak passwords, but what does that even mean? Is a longer password always better? Should we use symbols?
Let’s dive into the world of password security and uncover the secrets to crafting truly unbreakable digital fortresses.
This exploration will guide you through the labyrinth of password strength, revealing the pitfalls of common password practices and showcasing the power of informed choices. We’ll examine different password types, analyze their strengths and weaknesses, and explore security measures that can enhance your digital defenses.
Password Security Fundamentals
A strong password is your first line of defense against unauthorized access to your sensitive information. It’s like a sturdy lock on your digital door, protecting your valuable data from prying eyes.
Importance of Strong Passwords, Which of the following passwords would be considered most secure
Strong passwords are essential for safeguarding your online accounts, personal data, and financial information. They act as a barrier, preventing malicious actors from gaining access to your sensitive information. Imagine your online accounts as your virtual homes; a weak password is like leaving your front door unlocked, inviting trouble.
Risks Associated with Weak Passwords
Using weak passwords can lead to serious consequences. Imagine a thief walking into your home because you left the door unlocked; that’s essentially what happens when you use a weak password.
- Account Takeover: Hackers can easily guess or crack weak passwords, gaining unauthorized access to your accounts and potentially stealing your personal data, financial information, or even your identity.
- Data Breaches: When a website or service is compromised, weak passwords can allow hackers to access a large amount of data, including yours. This can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and other serious consequences.
- Malware Infection: Weak passwords can be used by hackers to spread malware, which can steal your data, track your online activity, or even take control of your device.
Common Password Vulnerabilities
It’s crucial to understand the weaknesses that make passwords vulnerable.
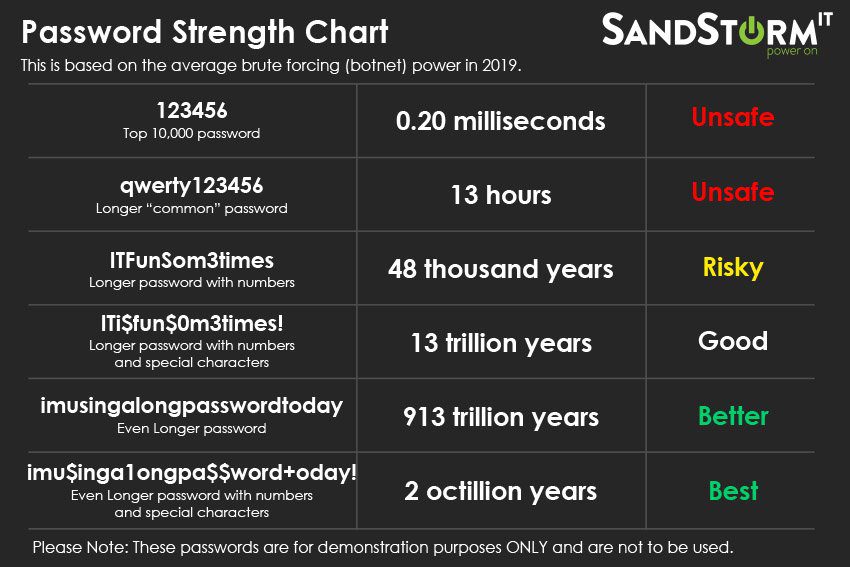
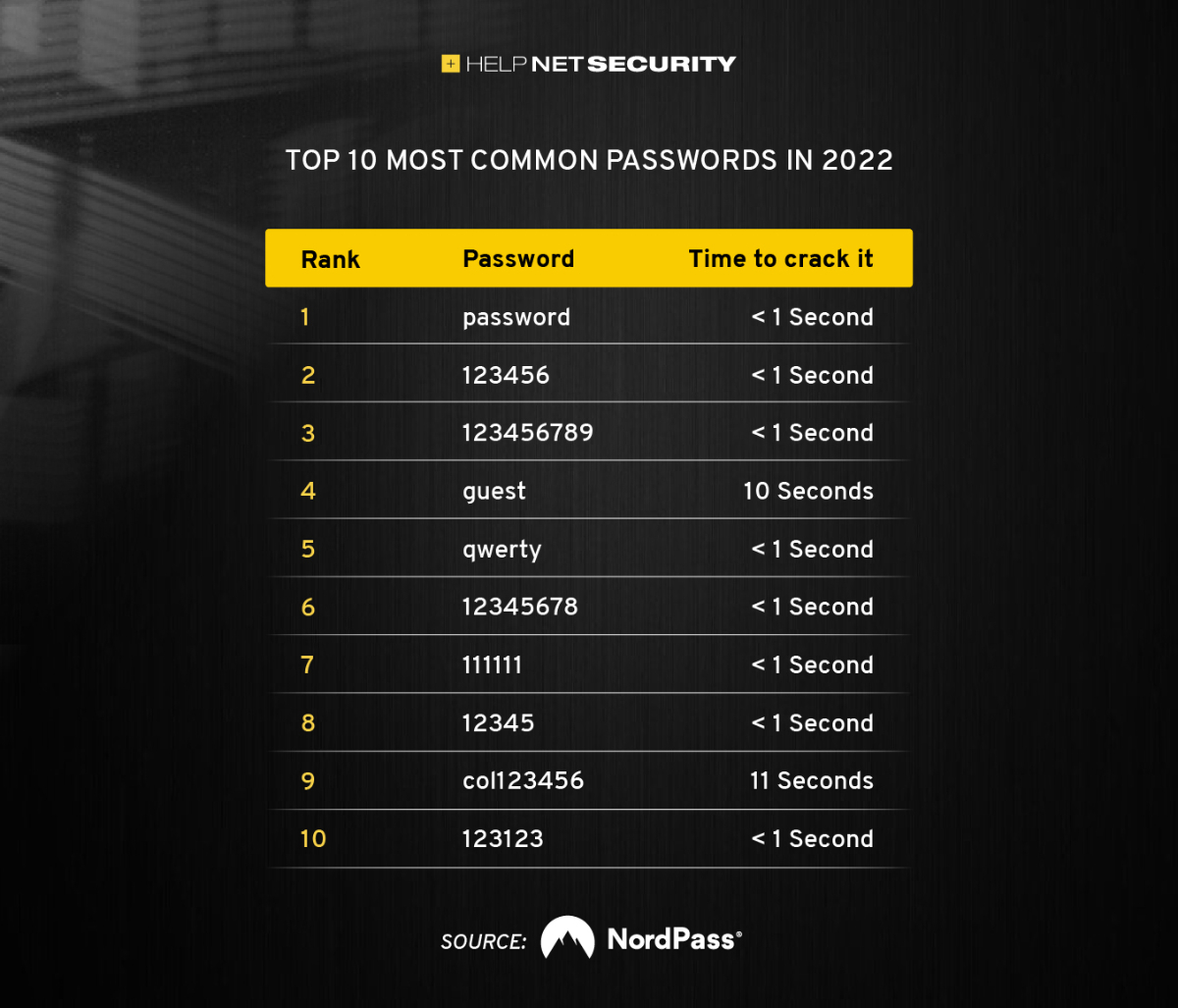
- Simple and Common Passwords: Passwords like “password,” “123456,” or “qwerty” are easily guessed by hackers using automated tools.
- Personal Information: Using personal information like your name, birthday, or pet’s name as passwords is a huge security risk. Hackers often use this information to guess your password.
- Reusing Passwords: Using the same password for multiple accounts is extremely risky. If one account is compromised, hackers can use the same password to access your other accounts.
Best Practices for Creating Strong Passwords
It’s time to step up your password game!
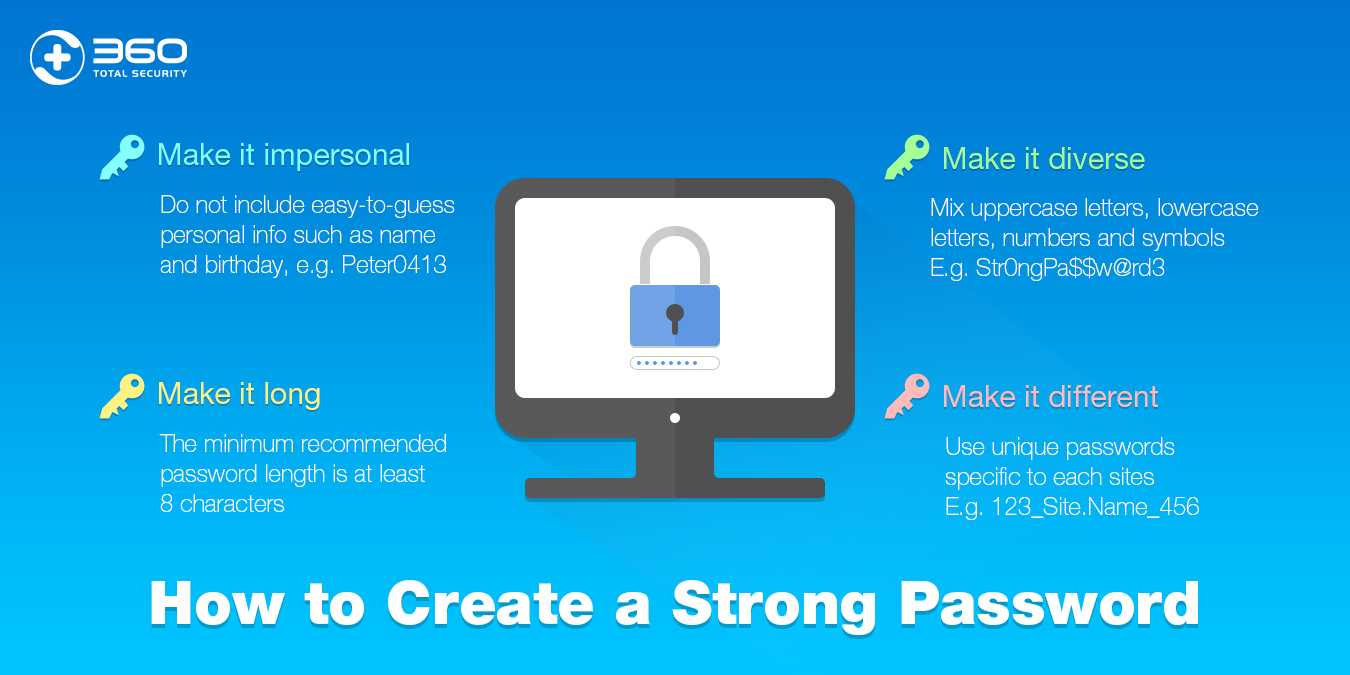
- Length: Aim for at least 12 characters or more. The longer the password, the harder it is to crack.
- Complexity: Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. This makes it much harder for hackers to guess your password.
- Uniqueness: Use a different password for each of your online accounts. This way, if one account is compromised, your other accounts will remain secure.
- Avoid Personal Information: Never use personal information like your name, birthday, or pet’s name in your passwords. This makes them easy to guess.
- Use a Password Manager: Password managers can help you create, store, and manage strong passwords for all your accounts. They are a great way to improve your password security without having to remember dozens of different passwords.
Password Complexity and Length
A strong password is like a sturdy door lock: it needs both complexity and length to be effective. Just like a simple lock can be easily picked, a weak password can be easily cracked by hackers.
Password Complexity Requirements
Different organizations and platforms often have different requirements for password complexity. Here’s a comparison:
- Basic Requirements: Many systems require a minimum length (e.g., 8 characters) and a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. These are often referred to as “strong” passwords, but they are actually quite easy to crack with modern tools.
- Advanced Requirements: Some systems may impose more stringent requirements, like prohibiting common words or requiring a specific mix of character types. These are generally more secure but can make it difficult to remember passwords.
- Password Strength Estimators: Many websites and applications include built-in password strength estimators. These tools analyze your password based on its length, character variety, and common patterns. While they can provide helpful feedback, they are not always accurate and should be used with caution.
Password Length and Security
Password length plays a crucial role in security. Longer passwords are significantly harder to crack.
Longer passwords are significantly harder to crack.
Here’s why:
- Combinations: The number of possible combinations for a password increases exponentially with its length. A 6-character password has only 62^6 possible combinations, while a 12-character password has 62^12, which is a much larger number.
- Brute-Force Attacks: Hackers use brute-force attacks to try every possible combination of characters until they find the correct password. Longer passwords significantly increase the time it takes to crack them.
Complexity vs. Memorability
Finding the right balance between complexity and memorability is essential. A password that is too complex can be difficult to remember, increasing the risk of users writing it down or using the same password for multiple accounts.
A password that is too complex can be difficult to remember, increasing the risk of users writing it down or using the same password for multiple accounts.
Here’s a table showing different complexity levels and their corresponding security strengths:
| Complexity Level | Security Strength | Memorability |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Weak | Easy |
| Medium | Moderate | Moderate |
| High | Strong | Difficult |
Password Types and Their Security
Different types of passwords offer varying levels of security, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing passwords that effectively protect your accounts.
Password Types and Their Characteristics
The following table Artikels the main types of passwords and their key characteristics:| Password Type | Description | Security Strength | Security Weaknesses ||—|—|—|—|| Alphanumeric | Consists of letters (uppercase and lowercase) and numbers. | Moderate | Can be relatively easy to guess or crack, especially with common patterns. || Symbolic | Includes special characters like !@#$%^&*()_+=-`~|[]\:;’<>,.?/ | High | Can be difficult to remember and type, increasing the risk of typos.
|| Passphrase | A short, memorable phrase that is easy to remember but difficult to guess. | High | May be susceptible to dictionary attacks if the phrase is too common. || Randomly Generated | Created using a random password generator. | Very High | Difficult to remember and may not be easily typed. |
Security Strengths and Weaknesses of Password Types
Each password type has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of security. Alphanumeric Passwords:* Strengths: Relatively easy to remember and type.
Weaknesses
Can be vulnerable to brute-force attacks, dictionary attacks, and pattern-based attacks. Symbolic Passwords:* Strengths: More difficult to guess than alphanumeric passwords, especially if they include a wide range of symbols.
Weaknesses
Can be difficult to remember and type, increasing the risk of typos. Passphrases:* Strengths: Easy to remember and relatively difficult to guess, especially if they use a unique and uncommon phrase.
Weaknesses
May be vulnerable to dictionary attacks if the phrase is too common. Randomly Generated Passwords:* Strengths: Extremely difficult to guess, even with advanced hacking techniques.
Weaknesses
Difficult to remember and may not be easily typed.
Password Types and Resistance to Attacks
The effectiveness of different password types in resisting common attacks is summarized below:* Brute-force attacks: Randomly generated passwords are most resistant to brute-force attacks, followed by symbolic passwords, then alphanumeric passwords, and lastly passphrases.
Dictionary attacks
Randomly generated passwords and unique passphrases are most resistant to dictionary attacks, followed by symbolic passwords, then alphanumeric passwords.
Pattern-based attacks
Symbolic passwords and randomly generated passwords are most resistant to pattern-based attacks, followed by passphrases, then alphanumeric passwords.
Password Security Measures: Which Of The Following Passwords Would Be Considered Most Secure
Password security measures are crucial in protecting your digital life. They act as extra layers of defense against unauthorized access to your accounts and data. Let’s dive into some of the most effective measures.
Password Managers
Password managers are software applications that store and manage your passwords securely. They encrypt your passwords and make it easier to generate strong and unique passwords for every account. Imagine trying to remember dozens of passwords for different websites – it’s a recipe for disaster. Password managers help you avoid that headache.
- Enhanced Security: Password managers encrypt your passwords, making them virtually impossible to decipher even if someone gains access to your device.
- Convenience: No more struggling to recall passwords! Password managers can automatically fill in your login credentials on websites, saving you time and frustration.
- Stronger Passwords: They can generate complex and unique passwords for each account, ensuring your accounts are protected with strong passwords.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring you to provide two forms of authentication. This means that even if someone gets hold of your password, they won’t be able to access your account without the second factor. Think of it like having a physical key and a combination lock – you need both to open the door.
- Increased Security: 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access by requiring two distinct forms of authentication. It’s like having a double-lock on your accounts.
- Reduced Risk of Phishing: 2FA makes it much harder for attackers to gain access to your accounts through phishing scams, as they need more than just your password.
- Widely Available: 2FA is widely supported by major websites and services, making it a readily available security measure.
Biometrics
Biometric authentication uses unique biological characteristics to verify your identity. Think fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, or iris scans. These methods offer a convenient and secure way to authenticate yourself, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to access your accounts.
- Enhanced Security: Biometrics relies on unique biological traits, making it extremely difficult for someone to impersonate you. It’s like having a built-in security system that’s uniquely yours.
- Convenience: Biometric authentication is often faster and more convenient than traditional password-based authentication. Just a quick scan, and you’re in!
- Growing Adoption: Biometric authentication is becoming increasingly popular, with smartphones, laptops, and even payment systems incorporating these technologies.
Password Security Measures: Benefits and Limitations
| Security Measure | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Password Managers | Enhanced security, convenience, stronger passwords | Requires trust in the password manager, can be vulnerable to malware |
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Increased security, reduced risk of phishing, widely available | Can be inconvenient if you lose your phone or forget your backup code |
| Biometrics | Enhanced security, convenience, growing adoption | Privacy concerns, potential for spoofing attacks |
Password Security Best Practices
Protecting your passwords is crucial in today’s digital world. It’s like locking your house, but instead of a physical key, it’s a virtual one. A strong password is your shield against unauthorized access to your online accounts.
Using Unique Passwords
It’s important to use unique passwords for each of your online accounts. Imagine if someone got hold of your password for one account, they could potentially access all your other accounts if you use the same password everywhere. It’s like having one key to open all the doors in your house – not a good idea, right?
Regular Password Changes
Regularly changing your passwords is like changing the locks on your house every few months. It reduces the risk of someone using a compromised password to access your accounts. Even if your password hasn’t been compromised, changing it periodically is a good practice to stay ahead of potential threats.
Secure Password Storage and Management
Storing your passwords in a safe and secure way is critical. Writing them down on sticky notes or in a notebook is like leaving your house key under the welcome mat. It’s easy for someone to find and use it. A good solution is to use a password manager, which is like a digital safe for your passwords.
- Password Managers: These tools encrypt and store your passwords securely, allowing you to access them easily and securely. Think of it as a digital vault for your passwords.
- Two-Factor Authentication: This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone or email, in addition to your password. It’s like having a second lock on your door, making it harder for someone to break in.
- Biometric Authentication: This uses unique biological characteristics, like your fingerprint or facial recognition, to verify your identity. It’s like using your unique DNA as a password, making it very difficult for someone to impersonate you.
Ultimately, securing your digital life hinges on a commitment to strong password practices. It’s about understanding the risks, embracing best practices, and continuously evolving your approach to password security. Remember, a strong password is your first line of defense against the ever-evolving threats of the digital world. So, let’s build those fortresses, one secure password at a time.
Common Queries
What are some common password vulnerabilities?
Common password vulnerabilities include using easily guessable information like birthdays, names, or pet names, using the same password for multiple accounts, and choosing passwords that are too short or simple.
How often should I change my passwords?
It’s generally recommended to change your passwords every 90 days or whenever you suspect a security breach.
What are some good password managers?
Some popular and reputable password managers include LastPass, 1Password, and Dashlane.






