How to stop digital secure from running in background – How to stop digital secure from running in the background sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. It’s a common question asked by many computer users who are seeking to optimize their system performance. The constant running of security programs, while essential for protection, can sometimes lead to sluggish performance and resource depletion.
This article delves into the intricate world of digital security, providing a comprehensive guide to managing and controlling these background processes, ultimately empowering you to reclaim your system’s efficiency and maintain a secure digital environment.
Understanding the purpose and function of digital security programs is crucial. These programs act as vigilant guardians, constantly monitoring your system for potential threats. They use various techniques to identify and neutralize malicious software, ensuring your data remains safe from unauthorized access. While their background operation is essential for safeguarding your system, it’s important to strike a balance between security and performance.
Understanding Digital Security Programs
Digital security programs are essential software applications designed to protect your computer and personal data from various threats, including malware, viruses, and unauthorized access. They work by constantly monitoring your system, detecting and blocking suspicious activity, and providing real-time protection.
Benefits of Running Security Programs in the Background
Running security programs in the background provides continuous protection against evolving threats. They act as a vigilant guardian, proactively identifying and mitigating potential risks before they can cause harm.
- Real-time Protection: Security programs constantly scan your system for malicious activity, providing immediate protection against emerging threats.
- Malware Detection and Removal: They identify and remove known and emerging malware, preventing it from compromising your data and system.
- Firewall Protection: Security programs act as a firewall, blocking unauthorized access to your computer and protecting sensitive data from external threats.
- Phishing and Scam Prevention: They help identify and block phishing emails and websites that aim to steal your personal information.
- Data Encryption: Security programs encrypt your data, making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
Common Digital Security Programs
There are numerous digital security programs available, each offering a range of features and protection levels. Here are some popular examples:
- Antivirus Software: Programs like McAfee, Norton, and Bitdefender are widely used to detect and remove viruses and malware from your computer.
- Firewall Software: Programs like Windows Firewall and ZoneAlarm act as a barrier between your computer and the internet, preventing unauthorized access.
- Internet Security Suites: Comprehensive packages like Norton 360 and McAfee Total Protection offer a combination of antivirus, firewall, and other security features.
- Password Managers: Programs like LastPass and 1Password securely store and manage your passwords, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Privacy Tools: Programs like Privacy Badger and Ghostery block tracking cookies and other online surveillance techniques, protecting your online privacy.
Identifying Unnecessary Background Processes
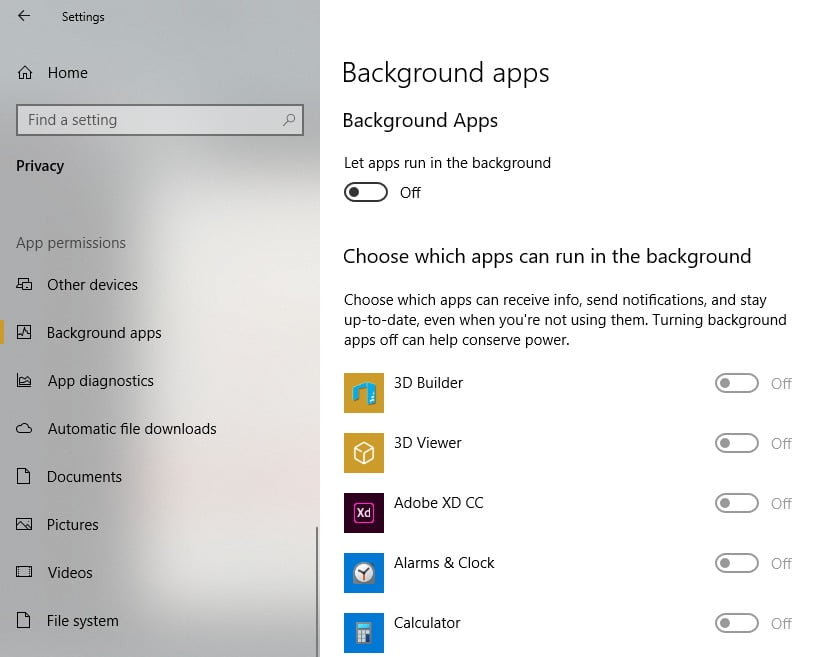
Knowing which security programs are running in the background is crucial to optimizing system performance and identifying potential resource hogs. These programs can consume valuable system resources, impacting your computer’s speed and responsiveness.
Identifying Background Processes
To identify which digital security programs are running in the background, you can use the Task Manager on Windows or Activity Monitor on macOS. Both tools provide a comprehensive list of running applications and processes, including their resource usage.
Task Manager (Windows)
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open the Task Manager.
- Click on the Processes tab to view a list of running programs.
- You can sort the list by CPU, Memory, Disk, or Network usage to identify resource-intensive processes.
Activity Monitor (macOS)
- Open the Activity Monitor by searching for it in Spotlight.
- The CPU tab shows a list of processes sorted by CPU usage.
- Other tabs, such as Memory, Energy, and Disk, provide insights into resource usage by different processes.
Understanding Resource Usage
Once you have identified the running security programs, you can analyze their resource usage.
Resource Usage Table
| Program Name | Description | Resource Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Antivirus Software | Protects your computer from malware and viruses | High CPU and memory usage during scans |
| Firewall | Blocks unauthorized network access | Moderate CPU and network usage |
| VPN | Encrypts internet traffic and masks your IP address | High network and CPU usage during active connection |
| Password Manager | Stores and manages your passwords securely | Low resource usage |
Determining Essential Processes
Not all background processes are essential. While security programs are crucial for protecting your system, some may be unnecessary or have features that can be disabled.
Essential Security Processes
- Antivirus software: Regularly scans your computer for malware and viruses.
- Firewall: Blocks unauthorized network access and protects your system from external threats.
Potentially Unnecessary Processes
- Real-time protection: Some antivirus software provides real-time protection, constantly monitoring your system for threats. This can be resource-intensive and may not be necessary for all users.
- Automatic updates: Many security programs automatically update in the background. While essential for keeping your security software up-to-date, frequent updates can consume resources.
- Background scanning: Some security programs perform background scans for threats, which can impact system performance.
Disabling Background Processes
Disabling unnecessary background processes can significantly improve your computer’s performance and battery life. This process involves identifying and deactivating programs that run in the background without your active consent, often consuming resources unnecessarily. By understanding how to manage these processes, you can optimize your system for efficiency and responsiveness.
Disabling Background Processes on Windows
To disable background processes on Windows, you can use the Task Manager.
- Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc or by right-clicking the taskbar and selecting Task Manager.
- Navigate to the Startup tab. This tab displays a list of applications that launch automatically when you start your computer.
- Review the list of applications and identify any programs you don’t need to run at startup.
- Select the program you want to disable and click Disable.
You can also disable background processes from the Settings app.
- Open the Settings app by pressing Windows key + I.
- Navigate to Apps > Startup.
- Review the list of applications and toggle the switch to Off for any programs you don’t need to run at startup.
Disabling Background Processes on macOS
Disabling background processes on macOS involves using the Activity Monitor.
- Open Activity Monitor by searching for it in Spotlight.
- Navigate to the Energy tab. This tab displays a list of applications and processes that are using the most energy.
- Identify any applications you don’t need to run in the background.
- Select the application and click Quit Process.
You can also disable background processes from the System Preferences.
- Open System Preferences by clicking the Apple menu and selecting System Preferences.
- Navigate to Users & Groups.
- Select your user account and click Login Items.
- Review the list of applications that launch automatically when you log in.
- Select the application you want to disable and click the
– button to remove it from the list.
Disabling Background Processes on Linux
To disable background processes on Linux, you can use the System Monitor.
- Open System Monitor by searching for it in the application menu.
- Navigate to the Processes tab. This tab displays a list of all running processes.
- Identify any processes you don’t need to run in the background.
- Right-click the process and select Kill Process.
You can also disable background processes by editing the systemd configuration files.
- Open a terminal window.
- Use the systemctl command to disable the service. For example, to disable the cups service, you would run the command:
systemctl disable cups.service
Consequences of Disabling Essential Security Programs
Disabling essential security programs can have significant consequences for your system’s security.
- Increased Vulnerability to Malware: Antivirus and anti-malware programs run in the background to detect and remove malicious software. Disabling these programs leaves your system vulnerable to attacks.
- Data Loss: Security programs can help prevent data loss by encrypting your data and backing it up regularly. Disabling these programs can increase the risk of data loss due to accidental deletion, hardware failure, or malicious attacks.
- Compromised Privacy: Security programs can help protect your privacy by blocking tracking cookies and preventing websites from collecting your personal information. Disabling these programs can expose your browsing history and other personal data to unauthorized parties.
Alternative Security Measures
While disabling background processes can be a viable option to reduce resource consumption and enhance privacy, it’s crucial to understand that this approach may not always be sufficient or even advisable for comprehensive security. Alternative security measures provide a wider range of options to strengthen your digital defenses.
Comparison of Security Measures
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different security measures allows you to create a well-rounded approach to digital security. The following table compares various security measures and their effectiveness:
| Method | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Antivirus Software | Protects against malware, viruses, and other threats by scanning files and processes for malicious code. | Highly effective against known threats, but may struggle with emerging or zero-day attacks. |
| Firewall | Acts as a barrier between your computer and the internet, blocking unauthorized access and preventing malicious traffic. | Effective in preventing external threats but may not be sufficient against internal vulnerabilities or sophisticated attacks. |
| Password Manager | Stores and manages your passwords securely, reducing the risk of password compromise and enabling strong, unique passwords for each account. | Highly effective in improving password security, but relies on the security of the password manager itself. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a code from a mobile device, making it harder for attackers to gain access. | Significantly enhances account security by adding an extra layer of protection. |
| Virtual Private Network (VPN) | Encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, protecting your online activity from eavesdropping and censorship. | Effective in protecting your privacy and security while browsing the internet, but may not be effective against all threats. |
| Regular Software Updates | Patches security vulnerabilities in software, reducing the risk of exploitation by attackers. | Essential for maintaining a secure system, but requires vigilance to ensure all software is updated promptly. |
| Secure Browsing Practices | Avoiding suspicious websites, using strong passwords, and being cautious about phishing attempts. | Effective in reducing the risk of infection and compromise, but requires ongoing vigilance and awareness. |
Optimizing System Performance: How To Stop Digital Secure From Running In Background
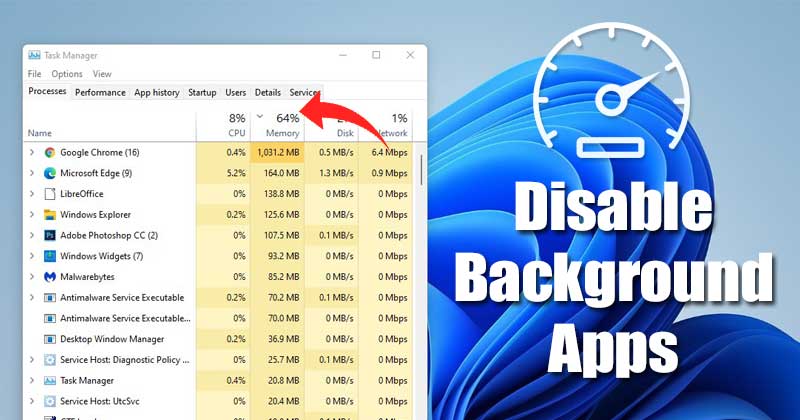
Disabling unnecessary background processes can significantly enhance your system’s performance. By reducing the load on your computer’s resources, you can experience faster application launch times, smoother multitasking, and improved overall responsiveness.
System Resource Management
Optimizing system performance involves managing system resources effectively. This includes managing CPU usage, RAM utilization, and disk space. Here are some tips for managing these resources:
- Monitor Resource Usage: Regularly monitor your system’s resource usage to identify potential bottlenecks. Tools like Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (macOS) provide insights into CPU, RAM, and disk usage. This information helps you identify resource-intensive processes that might be impacting performance.
- Close Unused Applications: Close applications you are not actively using to free up RAM and CPU resources. Minimize the number of applications running in the background, as they can consume resources even when not in focus.
- Optimize Disk Space: Regularly clear your hard drive of unnecessary files, such as temporary files, system caches, and unused programs. Consider using disk cleanup utilities or manually deleting files. Freeing up disk space can improve application loading times and overall system responsiveness.
Recommended System Settings
Implementing these recommended settings can further enhance your system’s performance:
- Disable Visual Effects: Reduce visual effects like animations and transparency to improve performance, especially on older or less powerful computers. These effects can consume unnecessary CPU and GPU resources.
- Adjust Power Settings: Configure your power settings to prioritize performance over energy saving. This can increase CPU speed and improve responsiveness, but it might consume more battery power on laptops.
- Enable Disk Defragmentation: Regularly defragment your hard drive to improve file access speeds and system responsiveness. This process reorganizes fragmented files on your disk, making them easier to access.
- Limit Startup Programs: Reduce the number of programs that automatically launch at startup. These programs can consume resources and slow down your system’s boot time. Use the Task Manager (Windows) or System Preferences (macOS) to manage startup programs.
Improving System Responsiveness, How to stop digital secure from running in background
- Increase Virtual Memory: If your system frequently runs out of RAM, consider increasing the virtual memory size. This allows the system to use a portion of your hard drive as temporary RAM, but it can be slower than actual RAM.
- Disable Background Downloads and Updates: Pause background downloads and updates when you need maximum system performance. These processes can consume bandwidth and CPU resources, impacting your overall experience.
Monitoring Security Programs
Monitoring the performance and effectiveness of your security programs is essential for maintaining a secure system. Regular monitoring helps identify potential vulnerabilities, track program effectiveness, and ensure your security measures are working as intended.
Security Program Logs
Security program logs provide valuable insights into the activities and events that occur within your system. These logs serve as a record of security-related events, including successful and failed login attempts, file access attempts, system changes, and malware detection.
- System Logs: System logs capture information about system events, including startup and shutdown, hardware failures, and software errors. These logs can help identify potential security breaches related to system instability or malfunction.
- Firewall Logs: Firewall logs record all incoming and outgoing network traffic, including blocked connections, allowed connections, and suspicious activity. These logs can be used to identify and block malicious network traffic.
- Antivirus Logs: Antivirus logs track the detection and removal of malware, including viruses, worms, and Trojans. These logs can help identify infected files and track the effectiveness of your antivirus software.
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Logs: IDS logs record suspicious network activity that may indicate an attempted intrusion. These logs can help identify potential security threats and respond accordingly.
Regularly reviewing security program logs can help identify patterns of suspicious activity, track the effectiveness of your security measures, and respond promptly to security incidents.
Updating Security Programs
Keeping your security programs up-to-date is crucial for maintaining a secure system. Security software updates often include patches that address newly discovered vulnerabilities and improve program effectiveness.
- Vulnerability Patches: Security updates often include patches that fix vulnerabilities in software, operating systems, and applications. These patches are essential for preventing attackers from exploiting known weaknesses.
- New Threat Detection: Security updates often include new threat signatures and detection methods that help identify and block emerging malware and threats.
- Performance Enhancements: Security updates can also improve the performance and efficiency of security programs, ensuring they run smoothly and effectively.
Regularly updating your security programs ensures that you have the latest protection against emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Maintaining Security Best Practices

Proactive measures are essential for safeguarding personal information in the digital world. By implementing strong security practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats and maintain control over your sensitive data.
Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication
Strong passwords are the foundation of online security. They should be complex, unique, and difficult to guess. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of protection by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone or email, in addition to your password.
A strong password is at least 12 characters long, includes a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and is not based on personal information.
- Use a password manager to generate and store strong passwords for different accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication wherever possible, especially for sensitive accounts like banking and email.
- Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
By understanding how to control background processes, you can optimize your system performance without compromising security. Remember, a balanced approach is key. Regularly update your security programs, monitor their performance, and implement security best practices to maintain a robust digital shield. Take charge of your digital security and reclaim your system’s speed and efficiency.
Question Bank
How do I know if a background process is essential?
Essential security programs are usually developed by reputable companies and are designed to provide critical protection against known threats. If you’re unsure, research the program online to determine its purpose and reputation.
What if I disable an essential security program?
Disabling an essential security program can leave your system vulnerable to attacks. If you’re unsure about a program’s importance, it’s best to leave it running. You can always contact the program’s developer for guidance.
What are some security best practices?
Always use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, keep your software up to date, be cautious about suspicious emails and links, and install a reputable antivirus program.






