How to use computer camera for security – How to use computer cameras for security is a topic that’s become more important than ever, especially with the rise of home security systems and remote work. Whether you’re looking to keep an eye on your home while you’re away or monitor your business remotely, knowing how to leverage the power of your computer’s built-in camera is a valuable skill.
This guide will walk you through the basics, from understanding camera security to setting up surveillance and integrating your camera with other security systems.
Think of your computer camera as a silent guardian, ready to watch over your space and alert you to any suspicious activity. We’ll cover everything from the different types of cameras and their vulnerabilities to tips on maximizing privacy and ensuring your data is secure. Get ready to transform your computer camera from a simple webcam into a powerful security tool!
Understanding Computer Camera Security Basics: How To Use Computer Camera For Security
Computer cameras, ubiquitous in laptops, desktops, and smartphones, have become integral to our daily lives. While they offer convenience for video calls, online meetings, and entertainment, they also pose potential security risks if not properly secured. This section explores the different types of computer cameras, common vulnerabilities, and essential security measures to protect your privacy.
Types of Computer Cameras and Their Security Implications
The types of computer cameras differ based on their design, features, and intended use. Understanding these variations helps identify specific security risks associated with each type.
- Built-in Webcams: These cameras are integrated into laptops, desktops, and tablets. They are typically low-resolution and offer basic features. The convenience of built-in webcams comes with a higher risk of unauthorized access due to their accessibility and potential vulnerabilities in the software controlling them.
- External Webcams: These cameras are connected to computers via USB or other interfaces. They offer higher resolution and advanced features compared to built-in webcams. However, external webcams can be susceptible to physical tampering and malware infections if connected to insecure networks or devices.
- Smartphone Cameras: Smartphones have become the primary camera devices for many users. They offer high-resolution images and video recording capabilities, but their security relies heavily on the operating system and app permissions. Malicious apps can exploit vulnerabilities in the operating system to gain access to the camera and capture private data.
Common Vulnerabilities Associated with Computer Cameras
Computer cameras are susceptible to various vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access and compromise user privacy.
- Malware Infections: Malicious software, such as spyware and ransomware, can hijack computer cameras to record video or capture images without the user’s knowledge. This data can then be used for surveillance, extortion, or other malicious purposes.
- Driver Vulnerabilities: Camera drivers, the software that allows the camera to communicate with the computer, can contain security flaws that attackers can exploit to gain control of the camera. This can enable attackers to remotely activate the camera, record video, and even access the user’s computer system.
- Weak Security Settings: Many computer cameras come with default security settings that are easily bypassed by attackers. These settings may allow unauthorized access to the camera, enabling attackers to view and record video without the user’s consent.
- Physical Tampering: External webcams are susceptible to physical tampering, where attackers can gain access to the camera’s internal components and modify its firmware or install malicious software. This can enable attackers to remotely control the camera and use it for surveillance or other malicious purposes.
Security Measures to Protect Computer Cameras
Protecting computer cameras from unauthorized access requires implementing a multi-layered approach that combines software and hardware security measures.
- Use a Strong Password: Ensure you use a strong password for your computer and any accounts that have access to your camera. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Keep Software Up-to-Date: Regularly update your operating system, antivirus software, and camera drivers to patch security vulnerabilities and protect against malware infections. This ensures that your system is protected against known vulnerabilities and exploits.
- Enable Camera Privacy Settings: Most operating systems and camera applications offer privacy settings that allow you to disable the camera when not in use. Enabling these settings prevents attackers from accessing the camera without your knowledge. Some operating systems allow you to block specific applications from accessing the camera, providing an additional layer of security.
- Cover Your Camera When Not in Use: A simple and effective way to prevent unauthorized access is to cover your camera with a physical barrier, such as a piece of tape or a camera cover, when not in use. This physically blocks the camera’s lens, preventing attackers from viewing or recording video.
- Be Cautious About Downloads and Attachments: Avoid downloading or opening attachments from unknown sources, as they may contain malware that can hijack your camera. Always verify the sender and the content of any email or file before opening it.
- Use a VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic, making it more difficult for attackers to intercept data, including video streams from your camera. VPNs can provide an additional layer of security, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Consider Hardware Security Measures: For sensitive environments, consider using hardware security measures, such as camera covers with physical locks or tamper-proof enclosures. These measures can prevent physical tampering and unauthorized access to the camera’s internal components.
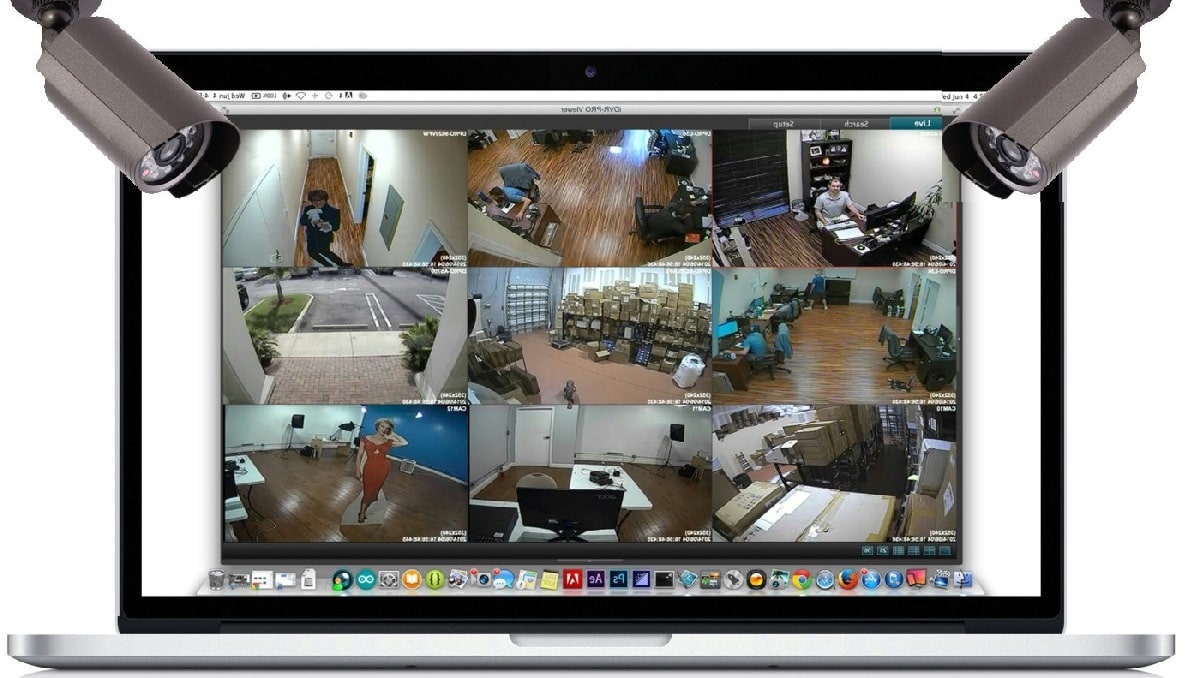
Using Computer Cameras for Surveillance
Turning your computer’s built-in camera into a surveillance tool is a surprisingly simple process, opening up possibilities for home or office security. Whether you want to keep an eye on your pets, monitor your business, or simply add an extra layer of security, this guide will walk you through the steps and best practices.
Configuring and Setting Up a Computer Camera
The initial step is to ensure your camera is working correctly. This involves verifying that the camera is recognized by your computer and that you have the necessary software installed. Most operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux) come with built-in camera drivers, but if your computer is older or has a unique camera model, you might need to download specific drivers from the manufacturer’s website.Once the camera is working, you can configure its settings for optimal surveillance.
These settings might include:* Resolution: Higher resolution (1080p or 4K) provides more detail, but requires more storage space and processing power.
Frame Rate
Higher frame rates (30fps or 60fps) result in smoother video but also increase storage requirements.
Field of View
Adjust the camera’s field of view to capture the desired area. A wider field of view covers a larger area, while a narrower field of view provides more detail on a specific subject.
Image Quality
Adjust the brightness, contrast, and color saturation to achieve the desired image quality.
Positioning and Mounting a Computer Camera
Strategic camera placement is crucial for effective surveillance. Consider these factors when choosing a location:* Coverage Area: Place the camera where it can capture the most important areas. For example, in a home, you might want to focus on entryways, valuables, or areas where pets roam. In an office, you might want to monitor the front door, work areas, or common spaces.
Lighting
Ensure adequate lighting in the area where the camera is placed. Poor lighting can result in blurry or grainy footage.
Obstructions
Avoid placing the camera in areas where it might be obstructed by furniture, plants, or other objects.
Stability
Securely mount the camera to prevent it from moving or falling. You can use a tripod, a wall mount, or a desk stand.
Tip: Consider using a camera cover or physical barrier to protect the camera lens when not in use. This helps prevent unauthorized access to the camera.
Software Options for Recording and Monitoring
Several software options are available for recording and monitoring computer camera footage. Some popular choices include:* Free and Open Source:
OBS Studio
A powerful and versatile streaming software that can also be used for recording.
OpenCV
A computer vision library that offers a wide range of features for image and video processing.
Paid Software
Blue Iris
A comprehensive surveillance software with features like motion detection, recording, and remote access.
IP Cam Viewer
A user-friendly application that supports a wide range of IP cameras, including computer cameras.
Cloud-Based Services
Amazon CloudWatch
A cloud-based monitoring and logging service that can be used to store and analyze camera footage.
Google Cloud Vision API
A cloud-based image analysis service that can be used to detect objects, faces, and other features in camera footage.
Note: When choosing software, consider factors like ease of use, features, cost, and security.
Integrating Computer Cameras with Security Systems

Integrating computer cameras into your existing security systems can significantly enhance your home or business security. By connecting your cameras to alarm systems, access control, and cloud storage services, you gain a comprehensive and remotely accessible security solution.
Connecting to Alarm Systems, How to use computer camera for security
Integrating computer cameras with alarm systems creates a powerful security system that can deter crime and provide evidence in case of an incident. When an alarm is triggered, the connected cameras can automatically start recording, capturing footage of the event. This footage can be used to identify intruders, provide evidence to law enforcement, and help to prevent future incidents.
Connecting to Access Control
Connecting computer cameras to access control systems allows you to monitor entry and exit points in real-time. This integration enables you to see who is entering and leaving your property, verify access permissions, and identify potential security threats. You can also use the cameras to record footage of unauthorized entry attempts, providing valuable evidence in case of security breaches.
Connecting to Cloud Storage Services
Connecting your computer cameras to cloud storage services offers numerous benefits. You can store your camera footage securely off-site, ensuring that it is protected from damage or theft. Cloud storage also allows you to access your camera footage from anywhere with an internet connection, providing remote monitoring capabilities. This is particularly useful for businesses with multiple locations or for homeowners who want to keep an eye on their property while they are away.
Using Motion Detection and Facial Recognition
Motion detection and facial recognition software can enhance the functionality of your computer cameras. Motion detection can trigger recordings when movement is detected, allowing you to focus on events that matter. Facial recognition software can identify individuals in the camera’s field of view, enabling you to create personalized alerts or restrict access to specific individuals.
Examples of Integration
Here are some examples of how computer cameras can be integrated with security systems:
- A home security system can be set up to trigger recordings from a security camera when an alarm is triggered. This footage can be used to identify the intruder and provide evidence to the police.
- A business can use facial recognition software to identify employees and grant access to restricted areas. This can help to prevent unauthorized access and improve security.
- A school can use computer cameras with motion detection to monitor hallways and playgrounds. This can help to deter vandalism and ensure the safety of students.
Ensuring Privacy and Data Protection
Using computer cameras for security can be a powerful tool, but it’s crucial to prioritize privacy and data protection. This involves taking proactive measures to safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
Password Protection and Encryption
Strong passwords and encryption are essential for protecting camera footage. A robust password acts as the first line of defense, preventing unauthorized individuals from accessing the camera’s settings or recordings. Encryption adds an extra layer of security by scrambling the data, making it unreadable to anyone without the proper decryption key. This is particularly important if the footage contains sensitive information, such as personal details or financial transactions.
Ethical Considerations and Legal Implications
Using computer cameras for security purposes raises important ethical and legal considerations. It’s essential to be mindful of the potential impact on individuals’ privacy and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations. For instance, in many jurisdictions, it’s illegal to record individuals without their consent, especially in private spaces.
Minimizing the Risk of Unauthorized Access and Data Breaches
Several steps can be taken to minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches:
- Regularly Update Software and Firmware: Keeping software and firmware up-to-date helps patch vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers. This is crucial for both the camera itself and any associated software, such as recording software or network devices.
- Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Strong passwords, ideally using a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, make it difficult for unauthorized individuals to guess. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification, such as a password and a code sent to their phone.
- Secure Network Connections: Ensure that the network connection used by the camera is secure. This includes using a strong password for the router and enabling encryption protocols like WPA2 or WPA3.
- Limit Access to the Camera: Only grant access to the camera to authorized individuals. This can be achieved through user accounts and permissions. Regularly review access privileges to ensure they are still appropriate.
- Use a Secure Storage Solution: Store camera footage in a secure location, ideally on a dedicated server with appropriate security measures in place. Consider using cloud storage with strong encryption and access controls.
- Implement a Data Retention Policy: Establish a clear data retention policy that specifies how long camera footage will be stored and how it will be disposed of. This helps minimize the risk of data breaches and ensures compliance with regulations.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance

Just like any other technology, computer cameras require regular maintenance and troubleshooting to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This section delves into common issues and provides practical solutions for maintaining your camera’s health and maximizing its lifespan.
Troubleshooting Common Computer Camera Issues
Troubleshooting computer camera issues involves identifying the root cause and implementing appropriate solutions. This section provides a step-by-step guide for resolving common problems.
- Camera Not Detected: If your computer cannot detect the camera, check if it is properly connected and powered on. Verify the camera driver is up-to-date and compatible with your operating system. Restart your computer to refresh system resources.
- Image Distortion or Blurriness: Ensure the camera lens is clean and free of obstructions. Check the camera settings for resolution, focus, and exposure adjustments. If the issue persists, consider updating the camera driver or checking for hardware malfunctions.
- Poor Video Quality: Low lighting conditions can affect video quality. Adjust the camera’s brightness and contrast settings. Consider using an external light source for better illumination. Ensure your internet connection is stable and fast enough for high-quality video streaming.
- Camera Freeze or Lag: High CPU usage or insufficient RAM can cause camera freezes or lag. Close unnecessary programs and applications. Ensure your computer meets the minimum system requirements for the camera software.
- No Audio: Verify that the camera’s microphone is enabled and not muted. Check the audio settings in your operating system and camera software. Ensure the microphone is connected properly and not damaged.
Regular Software Updates and Camera Maintenance
Keeping your camera software up-to-date is crucial for security and performance. Software updates often include bug fixes, performance enhancements, and security patches. Regularly check for updates and install them promptly.
- Software Updates: Manufacturers release software updates to address vulnerabilities and improve camera performance. Install updates promptly to ensure optimal functionality and security.
- Cleaning: Dust and debris can accumulate on the camera lens, affecting image quality. Use a soft, microfiber cloth to gently clean the lens. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
- Storage Conditions: Store the camera in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Avoid storing the camera in environments with high humidity or dust levels.
Maximizing Lifespan and Performance
Following these tips can help prolong the lifespan and maintain optimal performance of your computer camera:
- Avoid Overheating: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can damage the camera’s internal components. Ensure adequate ventilation and avoid placing the camera in direct sunlight or near heat sources.
- Proper Handling: Handle the camera with care to prevent damage to the lens, casing, or internal components. Avoid dropping or subjecting it to excessive force.
- Use a Protective Case: When not in use, store the camera in a protective case to shield it from dust, scratches, and other environmental factors.
By understanding the basics of computer camera security, you can take control of your digital environment and ensure your safety and privacy. Remember, your computer camera is a powerful tool that can be used for both good and bad. By following the tips and advice in this guide, you can use it to enhance your security, protect your data, and feel confident about your digital footprint.
Expert Answers
Can I use my computer camera for outdoor surveillance?
While it’s possible to use a computer camera outdoors, it’s not recommended. Outdoor cameras are designed to withstand weather conditions and have wider viewing angles. Using an indoor camera outdoors could damage it and compromise its performance.
Is it legal to use a computer camera for security purposes?
The legality of using a computer camera for security purposes varies depending on your location. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the laws in your area regarding surveillance and data privacy.
How can I tell if my computer camera is being hacked?
Look for signs like unusual activity on your computer, unexpected software installations, or a blinking light on your camera when it’s not in use. If you suspect your camera is being hacked, immediately change your passwords and contact a security professional.






