How much does a contract manufacturing facility cost? That’s the million-dollar question, baby! Building your own manufacturing empire isn’t cheap – think serious investment, like launching a rocket to the moon (but hopefully with fewer explosions). From land acquisition and construction to snagging top-notch equipment and navigating the regulatory jungle, the costs can be mind-boggling. But don’t sweat it; we’re breaking down the numbers, offering a backstage pass to the financial realities of setting up your own contract manufacturing facility.
Get ready to roll up your sleeves and dive into the nitty-gritty!
This deep dive explores every facet of the cost, from the initial setup – think land, buildings, and the essential gear – to ongoing operational expenses such as staff salaries, utilities, and maintenance. We’ll also look at the costs associated with technology, regulatory compliance, and the crucial decision of location. Plus, we’ll help you plan for the unexpected with contingency planning.
It’s a complete guide to help you budget and strategize, ensuring your manufacturing dream takes flight without crashing and burning.
Initial Setup Costs
Building a contract manufacturing facility is a significant undertaking, requiring substantial upfront investment. The initial setup costs encompass a wide range of expenses, from land acquisition to equipment installation. Careful planning and budgeting are crucial for success.
Land Acquisition Costs
The cost of land varies dramatically depending on location, size, and zoning regulations. Prime industrial areas in major cities will command significantly higher prices per square foot than more rural locations. For example, a 10-acre plot in a bustling industrial park could cost millions of dollars, while a similar-sized parcel in a less developed region might cost considerably less.
Factors like proximity to transportation hubs, utilities, and skilled labor also influence land value. Legal fees and environmental assessments further add to the overall expense.
Building Construction Costs
Construction costs are heavily influenced by the size and complexity of the facility, the choice of materials, and prevailing labor rates. A basic warehouse might cost less per square foot than a highly specialized facility requiring clean rooms or specific environmental controls. The type of construction (steel frame, concrete, etc.) also plays a role. Labor costs, which include skilled tradespeople like electricians, plumbers, and welders, can fluctuate regionally.
Unexpected delays or changes in design can also increase construction costs significantly. A conservative estimate might range from $100 to $300+ per square foot, depending on the factors mentioned.
Utility Installation Costs
Connecting the facility to essential utilities – water, electricity, and gas – involves significant upfront investment. The costs depend on the distance to existing infrastructure, the required capacity, and the complexity of the installation. For example, a facility requiring high-voltage power lines might incur substantially higher costs than one with more modest energy needs. Permits and inspections also contribute to the overall expense.
It’s crucial to obtain accurate quotes from utility providers early in the planning process.
Initial Equipment Purchases
The initial equipment purchase represents a substantial portion of the setup costs. The specific equipment needed will vary greatly depending on the type of manufacturing. The following table provides examples of equipment costs, keeping in mind that these are estimates and can vary widely based on brand, specifications, and features.
| Equipment Type | Quantity | Unit Cost (USD) | Total Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Machines (e.g., CNC machines) | 5 | 100,000 | 500,000 |
| Material Handling Equipment (e.g., forklifts) | 3 | 50,000 | 150,000 |
| Packaging Equipment (e.g., automated packaging lines) | 2 | 75,000 | 150,000 |
| Testing and Inspection Equipment | 4 | 25,000 | 100,000 |
Scalability and Expansion: How Much Does A Contract Manufacturing Facility Cost
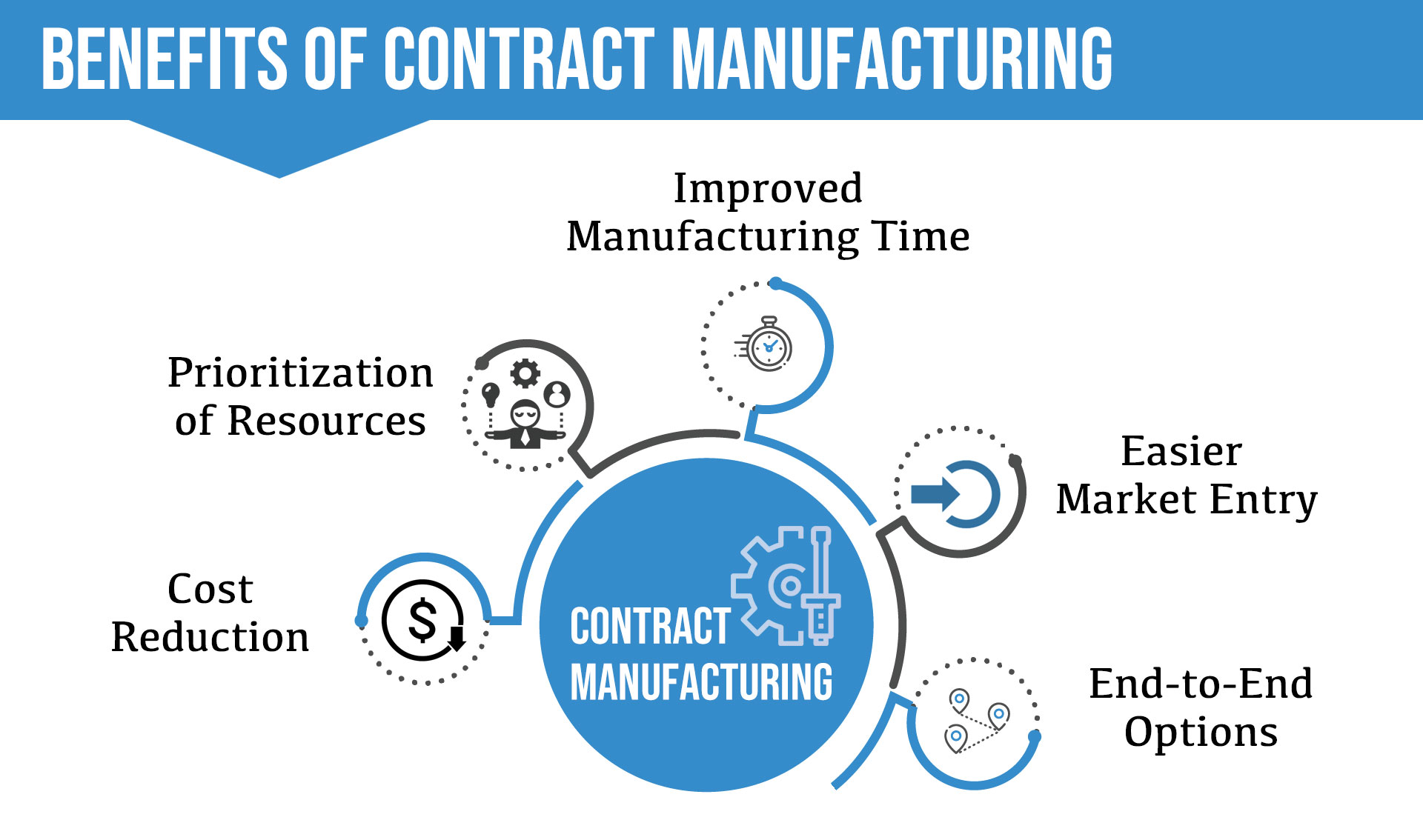
Growing a contract manufacturing facility isn’t just about meeting today’s demands; it’s about preparing for tomorrow’s growth. This involves careful planning and investment to ensure smooth scaling and expansion without compromising efficiency or profitability. Understanding the associated costs and implementing smart strategies are crucial for sustained success.Expanding your contract manufacturing facility requires careful consideration of several key financial aspects.
Simply put, growth means increased expenses, but also the potential for significantly higher returns. The key is to balance these factors effectively.
Costs Associated with Scaling Up Operations
Increased production volume necessitates investments in additional equipment, more skilled labor, and potentially upgraded infrastructure. This might include purchasing new machinery, expanding warehouse space, or investing in advanced automation systems. The cost of training new employees and implementing new software also contributes significantly to scaling-up expenses. For example, a company producing 10,000 units monthly might need to double its equipment and workforce to reach 20,000 units, resulting in substantial capital expenditures and operational costs.
Financial Implications of Expanding the Facility’s Physical Footprint
Expanding the physical footprint of your facility involves significant upfront capital costs. These include land acquisition or lease payments, construction or renovation expenses, and the cost of installing necessary utilities and infrastructure. Consider a scenario where a company needs to add a new wing to its existing building to accommodate increased production. This would entail architectural plans, construction permits, building materials, and labor costs, all adding up to a substantial investment.
Moreover, ongoing expenses like property taxes and insurance will also increase.
Return on Investment (ROI) Calculation for Facility Expansion, How much does a contract manufacturing facility cost
Calculating the ROI for facility expansion projects requires a careful assessment of both the costs and the benefits. The formula is straightforward:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100%
. To determine the net profit, you need to project future revenue increases resulting from the expansion, deducting all associated expenses, including operating costs, maintenance, and depreciation. For instance, if a $1 million expansion leads to a $200,000 annual increase in net profit, the ROI would be 20%. This calculation should consider a reasonable timeframe, perhaps 3-5 years, to accurately reflect the return on the investment.
Strategies for Managing Growth While Controlling Costs
Effective management of growth requires a multi-pronged approach. This includes optimizing existing processes for efficiency, leveraging technology for automation, and strategically outsourcing non-core functions. For example, a company might invest in robotics to automate repetitive tasks, reducing labor costs and increasing productivity. Outsourcing logistics or certain aspects of production to specialized third-party providers can also help manage costs while maintaining a focus on core competencies.
Careful financial planning and budgeting are also critical to ensuring that expansion projects remain within budget and deliver the expected ROI.
Contingency Planning

Building a contract manufacturing facility is a significant investment, and unforeseen challenges are an inherent part of the process. A robust contingency plan is crucial to navigate these hurdles and minimize potential financial losses. Proactive planning can significantly reduce the impact of unexpected events, ensuring the facility’s long-term viability and success.Unexpected events can significantly impact a contract manufacturing facility’s operations and profitability.
Therefore, a well-defined contingency plan is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring business continuity. This plan should encompass a range of scenarios, from minor equipment malfunctions to major natural disasters. A proactive approach, involving detailed risk assessment and resource allocation, is key to effective contingency planning.
Unforeseen Expenses
Potential unforeseen expenses during a facility’s lifecycle are numerous and varied. These can include unexpected repairs to existing equipment, higher-than-anticipated utility costs, changes in regulatory compliance requirements necessitating costly upgrades, and unanticipated material price increases. For example, a sudden surge in the price of a crucial raw material could significantly impact production costs. Similarly, an unexpected equipment breakdown might necessitate costly repairs or even complete replacement, leading to production downtime and lost revenue.
To mitigate these risks, regular equipment maintenance, close monitoring of market prices for raw materials, and building relationships with reliable suppliers are crucial.
Handling Equipment Failures and Operational Disruptions
A comprehensive contingency plan should detail procedures for handling equipment failures and operational disruptions. This includes having backup equipment or systems in place, establishing clear communication protocols for reporting and addressing issues, and having a pre-defined process for bringing in external expertise if needed. For instance, a manufacturing facility could have a spare part inventory for critical equipment, or contracts with specialized repair services.
A clear escalation process for reporting and resolving issues, involving both technical and management personnel, will ensure a timely response to disruptions. Furthermore, a plan for temporary alternative production arrangements (such as subcontracting) should be in place to minimize production downtime in case of major failures.
Risk Mitigation and Financial Loss Minimization
Strategies for mitigating risks and minimizing financial losses should be proactive and multi-faceted. This includes robust insurance coverage tailored to the specific risks of the facility, such as property damage, business interruption, and product liability. Diversifying suppliers to avoid dependence on a single source can also significantly reduce the risk of supply chain disruptions. Regular risk assessments, identifying potential vulnerabilities, and implementing corrective actions are essential for continuous improvement.
Moreover, building strong relationships with key stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, and regulatory bodies, can help mitigate risks and foster collaboration during challenging times.
Contingency Budget
A dedicated contingency budget is crucial for absorbing unexpected costs. This budget should be a percentage of the overall project budget, allocated to address unforeseen expenses. The percentage allocated will depend on the project’s complexity and inherent risks. For instance, a facility located in a seismically active zone might require a larger contingency budget than one located in a stable region.
Regular review and adjustments to the contingency budget based on risk assessments and actual expenditures are essential to ensure its effectiveness. This allows for flexible adaptation to changing circumstances and prevents financial strain during unexpected events.
So, how much
-does* a contract manufacturing facility cost? The truth is, there’s no single answer. It’s a wildly variable number, dependent on factors like location, scale, and the level of automation. But after navigating the complexities of land acquisition, construction, equipment, staffing, and regulations, one thing is clear: thorough planning and a realistic budget are your secret weapons.
This isn’t a get-rich-quick scheme; it’s a long-term investment that demands careful consideration of every detail. With smart planning and a dash of entrepreneurial grit, you can build your manufacturing dream into a profitable reality. Now go out there and make it happen!
FAQ Overview
What are some hidden costs I might not think of?
Unexpected repairs, permit delays, and fluctuating material prices are just a few. Always build in a contingency fund!
Can I lease equipment instead of buying?
Absolutely! Leasing can offer flexibility, especially when starting out. Weigh the long-term costs of leasing versus buying to determine what’s best for your situation.
How important is location?
Location is HUGE! Consider labor costs, proximity to suppliers, and access to transportation when choosing your site. It can drastically impact your bottom line.
What about insurance?
Manufacturing facilities require specialized insurance coverage to protect against accidents, liability, and property damage. Factor this into your budget early on.






