Is security facebookmail com a legitimate email – Is security.facebookmail.com a legitimate email? This question arises when you encounter an email claiming to be from Facebook, but the sender address seems a bit off. While Facebook is a well-known platform, scammers often try to mimic its appearance to trick users into giving up sensitive information. This article delves into the potential red flags associated with this domain name and explores the common phishing tactics used to target Facebook users.
Understanding the difference between official Facebook communication and phishing attempts is crucial for protecting your online security. We’ll analyze the domain name, discuss common phishing tactics, and provide best practices for safeguarding your accounts from these threats.
Understanding Email Legitimacy: Is Security Facebookmail Com A Legitimate Email

In today’s digital world, email has become an indispensable communication tool. However, with the rise of cybercrime, it is crucial to understand how to distinguish legitimate emails from fraudulent ones. This section will guide you through the key characteristics of legitimate emails, empowering you to identify potential threats and protect yourself from online scams.
Identifying Legitimate Email Characteristics, Is security facebookmail com a legitimate email
Identifying legitimate emails is crucial for safeguarding your personal and financial information. Legitimate emails typically exhibit certain characteristics that set them apart from phishing attempts and other fraudulent communications. These characteristics can be broadly categorized into sender identity, domain name, and email content.
- Sender Identity: A legitimate email will often come from a known and trusted sender. The sender’s name should be displayed clearly and accurately, matching the organization or individual you expect to be sending the email. Be wary of emails with unusual or misspelled sender names, as these could indicate a fraudulent attempt.
- Domain Name: The domain name in the email address should align with the sender’s organization. For example, an email from Facebook should have a domain name ending in “@facebook.com”. Be cautious of emails with domain names that appear similar to legitimate ones but have slight variations, as these could be phishing attempts designed to trick you into thinking the email is authentic.
- Email Content: Legitimate emails typically have well-written and grammatically correct content. They should avoid using excessive exclamation marks or overly persuasive language. The email should also be relevant to your existing relationship with the sender. If you receive an email that seems out of place or unrelated to your interactions with the sender, it could be a red flag.
Verifying Sender Information
Verifying sender information is an essential step in determining the legitimacy of an email. While many email providers offer spam filters, these filters may not always be foolproof. Therefore, it is crucial to take proactive measures to verify the sender’s identity.
- Hover over Links: Before clicking on any links within an email, hover your mouse cursor over them. This will often reveal the actual URL the link points to. If the URL appears suspicious or different from the displayed text, it could be a phishing attempt. For example, a link that appears to point to “facebook.com” might actually lead to a fraudulent website designed to steal your login credentials.
- Check for Misspellings and Typos: Legitimate emails are usually written with care and attention to detail. Look for any spelling errors or grammatical mistakes, as these can be signs of a fraudulent email. Phishing emails often contain grammatical errors or typos as they are typically created by individuals who are not native English speakers or who are trying to create a sense of urgency to prevent you from scrutinizing the email carefully.
- Contact the Sender Directly: If you are unsure about the legitimacy of an email, the safest course of action is to contact the sender directly through a verified channel, such as their official website or phone number. This will allow you to confirm the authenticity of the email and ensure that it is not a fraudulent attempt.
Examples of Legitimate Email Practices
Legitimate organizations and individuals typically adhere to certain email practices to ensure the authenticity and security of their communications. These practices include using official email addresses, avoiding generic greetings, and maintaining a professional tone.
- Official Email Addresses: Legitimate emails from organizations will typically use email addresses that align with their domain name. For example, an email from a company named “Acme Corporation” might come from an address like “info@acmecorp.com”. Be cautious of emails from addresses that are not associated with the organization’s official domain name, as these could be fraudulent attempts.
- Avoid Generic Greetings: Legitimate emails typically avoid using generic greetings such as “Dear Sir/Madam” or “To Whom It May Concern”. Instead, they will use specific greetings that address the recipient by name. Generic greetings can be a sign of a mass-mailed email that may not be personalized or legitimate.
- Professional Tone: Legitimate emails maintain a professional tone and avoid using excessive exclamation marks or overly persuasive language. If an email uses excessive exclamation marks, employs high-pressure tactics, or includes threatening language, it could be a phishing attempt or a scam.
Analyzing “security.facebookmail.com”
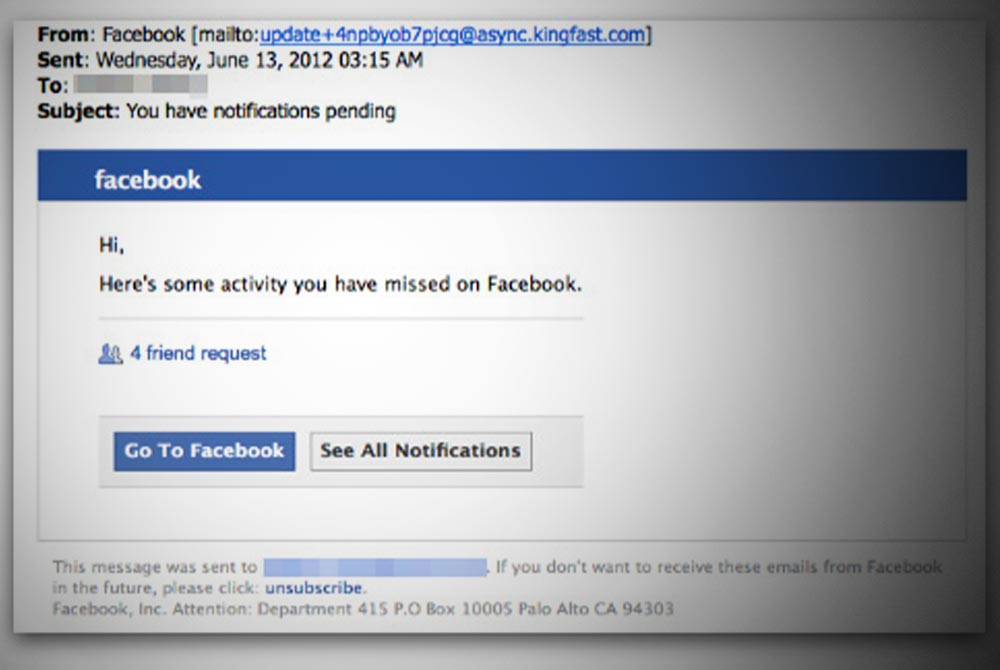
The domain name “security.facebookmail.com” appears to be a deliberate attempt to mimic the official Facebook domain, “facebook.com.” This tactic is commonly employed by phishing websites and malicious actors to deceive unsuspecting users. Examining the domain name reveals several potential red flags that raise concerns about its legitimacy.
Domain Name Analysis
The use of “security” in the domain name is a common tactic used by phishing websites. It creates a sense of urgency and trustworthiness, suggesting that the website is related to Facebook’s security measures. However, Facebook would never use a subdomain like “security.facebookmail.com” for its security-related communications. Furthermore, the inclusion of “facebookmail” in the domain name is misleading. Facebook does not use “facebookmail.com” as its email service.
This suggests that the website is attempting to impersonate Facebook’s email service to gain access to user credentials.
Implications of Mimicking the Official Domain
The use of a domain name that closely resembles the official Facebook domain is a clear indication of phishing. Phishing websites often mimic the look and feel of legitimate websites to trick users into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card details, or personal data. When users visit a website that appears to be legitimate, they are more likely to trust it and provide their personal information.
This is precisely what phishing websites exploit to steal sensitive data.In conclusion, the domain name “security.facebookmail.com” exhibits several red flags that strongly suggest it is a phishing website. Users should be extremely cautious when encountering this domain name and avoid providing any personal information.
Recognizing Official Facebook Communication

It is crucial to distinguish between genuine communication from Facebook and fraudulent attempts to impersonate the social media platform. Understanding Facebook’s official communication channels and practices can help users identify and avoid phishing scams.
Official Facebook Communication Channels
Facebook primarily communicates with users through its website, mobile apps, and email. Here are the key communication channels and their corresponding addresses:
- Facebook Website: www.facebook.com
- Facebook Mobile App: Available on iOS and Android devices
- Facebook Email Addresses:
- General Inquiries: support@facebook.com
- Security Concerns: security@facebook.com
- Advertising Inquiries: ads@facebook.com
- Business Inquiries: business@facebook.com
Standard Practices for Official Facebook Communication
Facebook employs specific practices to ensure the authenticity of its communication:
- Official Branding: Facebook consistently uses its official logo, colors, and fonts in all communication materials, including emails, website pages, and app notifications.
- Clear Subject Lines: Subject lines in official Facebook emails are typically clear and concise, accurately reflecting the email’s content. They avoid using generic or misleading language.
- Personalization: Official Facebook emails often include personalized information, such as the user’s name or profile picture. This helps verify the email’s legitimacy.
- Links to Official Website: All links in official Facebook communication direct users to the official Facebook website (www.facebook.com). Avoid clicking on links that lead to unfamiliar or suspicious domains.
- Secure Connection: Official Facebook emails are sent from secure servers, indicated by the “https://” prefix in the website address. This ensures that the communication is encrypted and protected.
- No Urgent Action Required: Legitimate Facebook communication rarely requires users to take immediate action, such as clicking on a link or providing sensitive information. Be wary of emails that demand urgent attention or threaten account suspension.
Comparison of Official Facebook Communication and Phishing Tactics
The following table highlights the key differences between official Facebook communication and common phishing tactics:
| Feature | Official Facebook Communication | Phishing Tactics |
|---|---|---|
| Sender Email Address | Typically uses a Facebook domain (e.g., @facebook.com, @facebookmail.com) | May use a fake or unrelated domain (e.g., @facebookmail.net, @facebook-login.com) |
| Subject Line | Clear and concise, accurately reflecting the email’s content | Generic, misleading, or urgent, often using fear tactics |
| Email Content | Well-written, grammatically correct, and free of spelling errors | Poorly written, with grammatical errors, typos, or strange formatting |
| Links | Direct to the official Facebook website (www.facebook.com) | May lead to fake websites designed to steal user information |
| Branding | Uses official Facebook branding, logos, and fonts | May use similar but slightly different branding or no branding at all |
| Request for Personal Information | Rarely asks for sensitive information unless necessary for account verification or security purposes | Often asks for passwords, credit card details, or other sensitive information |
| Urgency | Does not create a sense of urgency or pressure to take immediate action | Often creates a sense of urgency, threatening account suspension or other consequences |
Best Practices for Email Security
In today’s digital age, email has become an indispensable tool for communication and information sharing. However, the convenience of email also comes with inherent risks, particularly phishing attacks, which aim to deceive users into revealing sensitive information or installing malicious software. To safeguard your online security, it is crucial to adopt best practices for email security.
Being Cautious of Suspicious Emails
Suspicious emails often exhibit telltale signs that can alert you to their malicious nature. These emails may contain grammatical errors, misspellings, or inconsistent formatting, which can indicate that they are not from a legitimate source. Additionally, suspicious emails may request personal information, such as passwords or credit card details, or urge you to click on links that lead to phishing websites.
- Pay attention to the sender’s email address: If the email address appears strange or unfamiliar, it could be a phishing attempt. Legitimate companies and organizations typically use official email addresses that match their website domain.
- Hover over links before clicking: Before clicking on any links in an email, hover your mouse over them to see the actual URL in the status bar. If the URL appears suspicious or different from the expected destination, it is best to avoid clicking on it.
- Be wary of urgent requests: Phishing emails often use urgency as a tactic to pressure you into acting quickly without thinking. If an email requests immediate action, take a moment to verify the request before proceeding.
- Check for typos and grammatical errors: Legitimate emails are typically well-written and free from errors. If an email contains multiple typos or grammatical mistakes, it could be a sign of a phishing attempt.
Verifying Information Before Clicking on Links
Before clicking on any link in an email, it is essential to verify the information and ensure that it is legitimate. If you are unsure about the legitimacy of a link, it is always best to err on the side of caution and avoid clicking on it. You can verify the legitimacy of a link by:
- Checking the URL: The URL should match the expected website domain. For example, if you receive an email from Facebook, the link should lead to facebook.com. If the URL is different, it could be a phishing attempt.
- Looking for security indicators: Legitimate websites often have security indicators, such as a padlock icon in the address bar, to indicate that the connection is secure. If a website lacks these indicators, it could be a phishing website.
- Contacting the sender directly: If you are unsure about the legitimacy of an email, you can contact the sender directly through a known and trusted channel, such as their website or phone number, to verify the information.
Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication
Strong passwords are crucial for securing your online accounts, including your email account. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information, such as your name, birthdate, or common phrases. Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring you to provide two forms of authentication before granting access.
This can be done through a combination of something you know (your password) and something you have (a code generated by an authenticator app or sent to your phone). 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to your accounts, even if your password is compromised.
Security Software and Anti-Phishing Tools
Security software, such as antivirus and anti-malware programs, can help protect your computer from malware and other threats that can be spread through email. Anti-phishing tools, which are often included in security software packages, can help identify and block phishing emails before they reach your inbox. These tools use various techniques, such as analyzing email content, identifying suspicious links, and comparing email addresses to known phishing databases, to identify and block phishing attempts.
Navigating the digital world requires vigilance, especially when it comes to email communication. Remember, if an email seems suspicious, even if it appears to be from a familiar source, it’s always best to err on the side of caution. By understanding the tactics employed by phishers and adopting best practices for email security, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these online scams.
Essential FAQs
What are some other ways to identify a phishing email?
Besides the sender address, look for grammatical errors, urgent requests for personal information, and links that don’t match the expected website.
What should I do if I accidentally click on a link in a phishing email?
If you suspect you’ve clicked on a phishing link, change your passwords immediately and contact Facebook’s support team to report the incident.
How can I report a phishing email?
Most email providers have a “report spam” or “report phishing” option. You can also report the email directly to Facebook through their website.






