What is a secured bond in North Carolina? This question delves into the realm of financial instruments where security and collateral play a crucial role. In essence, a secured bond in North Carolina is a debt security backed by specific assets, providing an extra layer of protection for investors. Unlike unsecured bonds, where investors rely solely on the issuer’s creditworthiness, secured bonds offer the comfort of knowing that they can claim specific assets in case of default.
These assets, known as collateral, can range from real estate and equipment to intellectual property, depending on the nature of the bond. The use of collateral in secured bonds significantly reduces the risk for investors, making them a popular choice for those seeking a balance between potential returns and risk mitigation.
North Carolina law recognizes various types of secured bonds, each tailored to specific purposes and industries. These bonds play a vital role in facilitating economic growth by providing businesses and government entities with access to capital. Understanding the nuances of secured bonds, their issuance process, and the regulatory framework governing them is crucial for investors seeking to navigate this segment of the North Carolina financial market.
Definition of Secured Bonds in North Carolina
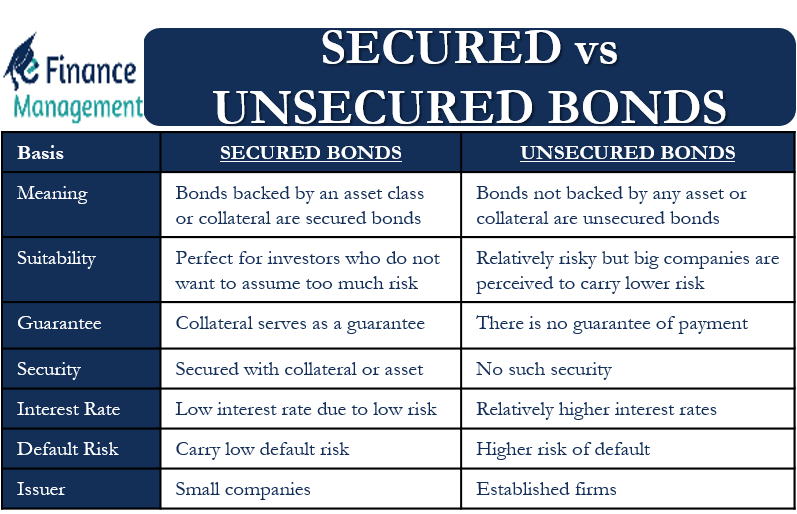
In North Carolina, a secured bond is a type of debt instrument that is backed by specific assets, known as collateral. This collateral provides an extra layer of security for bondholders, ensuring that they can recover their investment even if the issuer defaults on their payments. Secured bonds are generally considered less risky than unsecured bonds, as investors have a claim on specific assets in the event of default.
Key Characteristics of Secured Bonds
Secured bonds are distinguished from unsecured bonds by the presence of collateral. This collateral serves as a guarantee for bondholders, providing them with a legal right to claim the assets if the issuer fails to meet their obligations.
- Collateralization: Secured bonds are backed by specific assets, such as real estate, equipment, or inventory. This collateral is pledged to bondholders as a guarantee of repayment.
- Priority of Claim: In the event of default, secured bondholders have a higher priority claim on the collateral than unsecured bondholders. This means they are more likely to recover their investment.
- Lower Interest Rates: Because secured bonds are considered less risky, they typically carry lower interest rates than unsecured bonds. This reflects the reduced risk for investors.
Examples of Collateral for Secured Bonds
In North Carolina, a wide range of assets can be used as collateral for secured bonds. Here are some common examples:
- Real Estate: This is a common form of collateral for secured bonds, particularly for mortgage-backed securities.
- Equipment: Businesses often use equipment, such as machinery or vehicles, as collateral for secured bonds.
- Inventory: Companies may use their inventory of goods as collateral, particularly for bonds issued by retailers or manufacturers.
- Accounts Receivable: A company’s accounts receivable, which represent money owed to them by customers, can also be used as collateral.
Secured bonds provide investors with an extra layer of protection, making them a less risky investment option compared to unsecured bonds.
Types of Secured Bonds in North Carolina

Secured bonds in North Carolina offer investors a level of protection by being backed by specific assets, making them less risky than unsecured bonds. Understanding the various types of secured bonds and their features is crucial for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios and manage risk effectively.
Types of Secured Bonds in North Carolina
Secured bonds in North Carolina are categorized based on the type of asset backing them. This categorization helps investors understand the specific risks and potential returns associated with each type of bond.
- Mortgage Bonds: These bonds are secured by real estate, typically residential or commercial properties. Investors in mortgage bonds have a claim on the property if the borrower defaults on their loan. In case of default, the bondholder can foreclose on the property and sell it to recover their investment.
- Collateralized Bonds: These bonds are secured by a specific asset other than real estate, such as equipment, inventory, or accounts receivable. The specific collateral backing the bond is clearly defined in the bond agreement, providing investors with a tangible asset to claim in case of default.
- Revenue Bonds: These bonds are secured by the revenue generated by a specific project or facility, such as a toll road, airport, or water treatment plant. Investors in revenue bonds rely on the project’s ability to generate sufficient revenue to cover debt payments.
Examples of Secured Bonds in North Carolina
Here are some examples of how secured bonds are used in real-world scenarios in North Carolina:
- Mortgage Bonds: A homeowner seeking to refinance their mortgage may issue a mortgage bond secured by their home. This bond allows investors to lend money to the homeowner while having a claim on the property in case of default.
- Collateralized Bonds: A manufacturing company might issue collateralized bonds secured by its equipment. Investors in these bonds would have a claim on the equipment if the company defaults on its debt obligations.
- Revenue Bonds: A city in North Carolina might issue revenue bonds to finance the construction of a new sports stadium. The bonds would be secured by the revenue generated from ticket sales, concessions, and other stadium-related activities.
Issuance and Regulation of Secured Bonds in North Carolina: What Is A Secured Bond In North Carolina
Issuing secured bonds in North Carolina involves a specific process, legal requirements, and regulatory oversight. This section delves into the process of issuing secured bonds, the role of the North Carolina Securities Division, and the legal framework governing these bonds.
Issuance Process of Secured Bonds
Issuing secured bonds in North Carolina typically involves the following steps:
- Authorization: The entity intending to issue secured bonds must obtain authorization from the relevant governing body, such as a city council, county commission, or state legislature. This authorization typically involves a resolution or ordinance outlining the purpose of the bonds, the amount to be issued, and the terms of the bond offering.
- Underwriting: An underwriter, typically an investment bank or financial institution, is hired to assist in the issuance process. The underwriter helps determine the interest rate, maturity date, and other terms of the bonds, and assists in marketing the bonds to potential investors.
- Registration: In most cases, the issuance of secured bonds in North Carolina requires registration with the North Carolina Securities Division. This registration process involves filing a prospectus, which provides detailed information about the bonds, the issuing entity, and the underlying collateral.
- Sale: Once the bonds are registered, they are offered for sale to investors. The underwriter typically plays a key role in this process, distributing the bonds to investors and managing the overall sale.
- Closing: The issuance process concludes with the closing, where the issuing entity receives the proceeds from the sale of the bonds. At this stage, the legal documents related to the bonds are finalized, and the collateral is pledged to secure the bonds.
Role of the North Carolina Securities Division
The North Carolina Securities Division plays a critical role in regulating the issuance and trading of secured bonds. The Division’s primary objectives include:
- Protecting investors: The Division ensures that investors have access to accurate and complete information about secured bonds before making investment decisions. This is achieved through the registration process, which requires issuers to provide detailed information about the bonds and their underlying collateral.
- Maintaining market integrity: The Division oversees the trading of secured bonds to prevent fraud and other unethical practices. This includes monitoring trading activity, investigating potential violations, and enforcing relevant securities laws.
- Promoting transparency: The Division requires issuers to disclose information about their financial condition, the purpose of the bond issuance, and the terms of the bonds. This transparency helps investors make informed decisions and promotes confidence in the bond market.
Legal Framework for Secured Bonds, What is a secured bond in north carolina
The legal framework governing secured bonds in North Carolina is complex and involves a variety of statutes and regulations. Some key statutes and regulations include:
- North Carolina Securities Act of 1959: This act establishes the general framework for regulating the issuance and trading of securities in North Carolina, including secured bonds. The Act requires registration of securities offerings, imposes disclosure requirements on issuers, and provides investors with certain remedies in case of fraud or other violations.
- North Carolina Local Government Finance Act: This act specifically addresses the issuance of bonds by local governments in North Carolina. The Act Artikels the procedures for authorizing and issuing bonds, the types of bonds that can be issued, and the requirements for securing the bonds.
- North Carolina Uniform Commercial Code (UCC): The UCC governs the creation and enforcement of security interests, including those used to secure bonds. The UCC provides a framework for perfecting security interests, which is essential for ensuring that bondholders have a valid claim against the collateral in case of default.
Benefits and Risks of Investing in Secured Bonds in North Carolina

Investing in secured bonds in North Carolina offers potential benefits, but it’s crucial to understand the associated risks before making any investment decisions. Secured bonds, backed by specific assets, provide investors with a higher level of protection compared to unsecured bonds. However, even with collateral, certain risks remain.
Advantages of Secured Bonds in North Carolina
Secured bonds in North Carolina offer advantages over unsecured bonds, primarily due to the presence of collateral. This collateral acts as a safety net for investors, reducing the risk of losing their investment in case of default.
- Reduced Risk of Default: In the event of a borrower’s default, secured bondholders have a claim on the specific assets pledged as collateral. This prioritizes their claim over unsecured creditors, increasing the likelihood of recovering their investment.
- Higher Creditworthiness: The presence of collateral often signals a borrower’s higher creditworthiness, as it demonstrates a willingness to back their obligations with valuable assets. This can translate to lower interest rates on secured bonds compared to unsecured bonds.
- Greater Investment Security: The collateral provides a tangible asset that can be liquidated to recover the investment in case of default. This offers a greater level of security for investors, especially in situations where the borrower’s financial situation deteriorates.
Potential Risks of Secured Bonds in North Carolina
While secured bonds offer advantages, investors should be aware of potential risks. Although collateral provides a degree of protection, it doesn’t completely eliminate the risk of loss.
- Valuation of Collateral: The value of collateral can fluctuate over time. If the collateral’s value declines below the bond’s principal amount, investors may not fully recover their investment upon default. It’s crucial to assess the collateral’s market value and potential depreciation.
- Cost of Liquidation: Liquidating collateral to recover the investment can incur significant costs, such as legal fees, appraisal fees, and auction expenses. These costs can reduce the net recovery for investors.
- Complexity of Collateral: The nature of collateral can vary significantly, ranging from real estate to equipment. Understanding the specific type of collateral and its potential risks is essential before investing in secured bonds.
Secured Bonds in Specific Sectors in North Carolina
Secured bonds play a significant role in financing various sectors of the North Carolina economy, particularly in real estate, infrastructure, and energy. These sectors rely heavily on long-term capital, and secured bonds provide a stable and predictable source of funding, often with lower interest rates compared to unsecured debt.
Real Estate
Secured bonds are widely used in the North Carolina real estate market to finance various projects, including commercial and residential developments, infrastructure projects, and property acquisitions. The bonds are typically secured by a mortgage or deed of trust on the underlying real estate, providing investors with a higher level of security in case of default. Real estate developers utilize secured bonds to raise capital for projects, often relying on the stability and predictability of the bond market.
For instance, a developer might issue secured bonds backed by a mortgage on a newly constructed office building. Investors are attracted to these bonds due to the tangible collateral, which minimizes their risk.
In conclusion, secured bonds in North Carolina offer a unique investment opportunity that combines potential returns with a heightened level of security. By understanding the intricacies of collateral, the various types of secured bonds, and the regulatory landscape, investors can make informed decisions that align with their risk tolerance and financial goals. As the North Carolina economy continues to evolve, secured bonds will likely play an increasingly significant role in supporting growth and development across diverse sectors.
Whether it’s real estate, infrastructure, or energy, secured bonds provide a vital link between investors and businesses seeking to achieve their financial objectives.
Query Resolution
What are some common examples of assets used as collateral for secured bonds in North Carolina?
Common examples include real estate, equipment, inventory, and accounts receivable. The specific type of collateral will depend on the nature of the bond and the industry in which the issuer operates.
How does the North Carolina Securities Division regulate the issuance of secured bonds?
The North Carolina Securities Division ensures that the issuance of secured bonds complies with state laws and regulations. This includes reviewing offering documents, verifying the collateral, and monitoring the activities of bond issuers.
What are the main benefits of investing in secured bonds in North Carolina?
The main benefits include reduced risk due to the presence of collateral, potentially higher returns compared to unsecured bonds, and the ability to diversify investment portfolios.
What are some potential risks associated with investing in secured bonds in North Carolina?
Potential risks include the value of the collateral declining, the issuer defaulting on its obligations, and the difficulty in liquidating the collateral in case of default.






