What is the primary objective of data security controls? The answer is simple: to protect your valuable data. In today’s digital world, data is more valuable than ever before, and it’s essential to take steps to secure it from threats. Data security controls are a vital part of any organization’s security posture, and they play a critical role in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Data security controls are a set of policies, procedures, and technologies that are designed to protect data from various threats. These controls can be implemented at different levels, including administrative, technical, and physical. The goal of data security controls is to ensure that data is confidential, available, and secure. This means that only authorized users can access the data, and that the data is protected from unauthorized modification or deletion.
Data security controls are essential for any organization that handles sensitive information, and they are becoming increasingly important in today’s digital world.
The Fundamental Goal of Data Security Controls

Data security controls are like the guardians of your digital treasures, ensuring that your valuable information stays safe and sound. They act as a protective barrier against unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of data.
Protecting Sensitive Information
Data security controls play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information. They act as a shield against cyberattacks and data breaches, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical data. For example, imagine a hospital with a robust data security system in place. This system might include measures like strong passwords, access control lists, and encryption. These controls would prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive patient information, such as medical records and financial details.
Contributing to Overall Security Posture
Data security controls are not isolated entities; they work in harmony with other security measures to bolster an organization’s overall security posture. They contribute to the organization’s ability to withstand cyberattacks, maintain data integrity, and ensure business continuity.Imagine a bank implementing strong data security controls, such as multi-factor authentication, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits. These controls would help the bank to detect and prevent unauthorized access to customer accounts, protect against data breaches, and ensure the smooth functioning of its operations.
Protecting Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability: What Is The Primary Objective Of Data Security Controls
Think of data security like a fortress protecting your valuable treasure, your data. To keep that treasure safe, you need to ensure it’s secret, accurate, and accessible when you need it. These are the three pillars of data security: confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is like keeping your treasure under lock and key. It means protecting your data from unauthorized access, ensuring only authorized individuals can view and use it. This is crucial for sensitive information like personal data, financial records, or trade secrets. Data security controls play a vital role in maintaining confidentiality. Here are some examples:
- Access Control: Limiting who can access specific data based on their roles and responsibilities. This could involve using passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control (RBAC). For instance, a customer service representative might only have access to customer contact information, while a financial analyst might have access to financial reports.
- Encryption: Transforming data into an unreadable format, making it unintelligible to unauthorized individuals. This is like scrambling the treasure map, so only those with the key can decipher it. Encryption can be used to protect data at rest (stored on devices) and in transit (transmitted over networks).
- Data Masking: Replacing sensitive data with fake or masked data when sharing or displaying it. This is like using a redacted version of the treasure map, where crucial details are obscured. For example, you could mask a customer’s full credit card number by displaying only the last four digits.
Integrity
Integrity is like ensuring your treasure hasn’t been tampered with. It means protecting data from unauthorized modification, ensuring its accuracy and reliability. This is crucial for maintaining the trustworthiness of your data and preventing fraudulent activities.Data security controls help maintain data integrity through measures like:
- Hashing: Creating a unique digital fingerprint of data, allowing you to detect any unauthorized changes. If the fingerprint changes, it indicates that the data has been tampered with. This is like using a special seal on the treasure chest, where any break in the seal signifies tampering.
- Digital Signatures: Using cryptographic techniques to verify the authenticity and integrity of data. It’s like having a digital signature on the treasure map, ensuring that it hasn’t been forged.
- Input Validation: Ensuring that data entered into systems is accurate and conforms to predefined rules. This is like having a gatekeeper who checks the treasure map for authenticity before letting it into the fortress.
Availability
Availability is like ensuring your treasure is accessible whenever you need it. It means ensuring that data is readily available to authorized users when they need it. This is crucial for businesses to operate efficiently and avoid disruptions.Data security controls contribute to data availability through measures like:
- Backups and Recovery: Creating copies of data and having procedures in place to restore data in case of data loss or system failures. This is like having a backup treasure map in case the original is lost or damaged.
- Disaster Recovery: Planning and preparing for potential disasters that could disrupt data availability. This is like having a contingency plan for protecting the treasure in case of a natural disaster or attack.
- Redundancy: Using multiple systems or components to ensure that data remains accessible even if one component fails. This is like having multiple copies of the treasure map stored in different locations.
Types of Data Security Controls
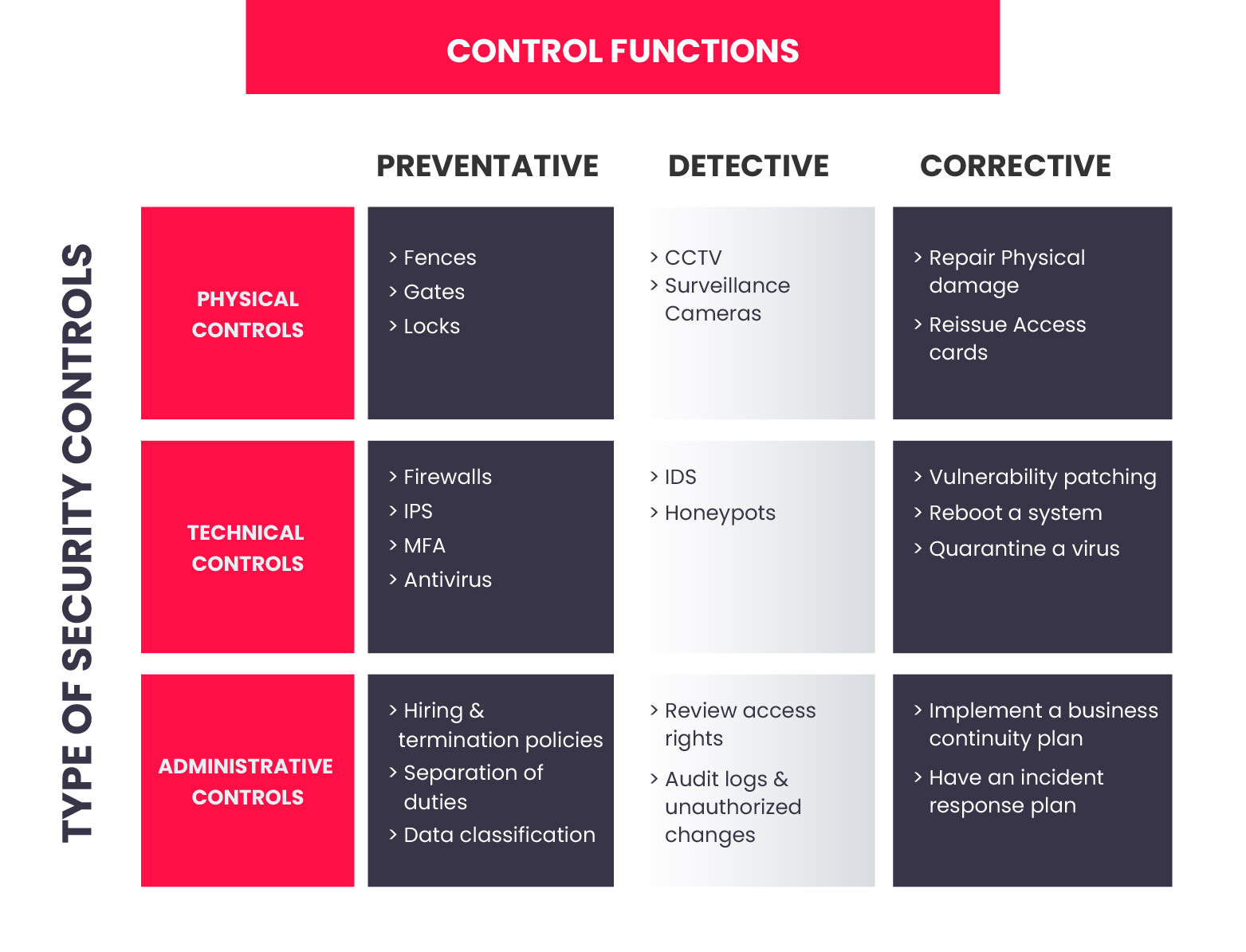
Data security controls are the measures implemented to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. These controls are crucial in maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. They are categorized into three main types: administrative, technical, and physical.
Administrative Controls
Administrative controls are policies, procedures, and guidelines that govern the management and protection of data. They are essential for establishing a strong security framework and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Security Awareness Training: This type of control involves educating employees about data security best practices, such as strong password creation, phishing awareness, and responsible data handling. It helps to reduce human error and increase awareness of potential threats.
- Data Classification and Labeling: This control involves categorizing data based on its sensitivity and assigning appropriate labels. This helps organizations prioritize protection efforts and implement controls based on the level of risk.
- Access Control Policies: These policies define who has access to specific data and what actions they are authorized to perform. They are crucial for preventing unauthorized access and maintaining data confidentiality.
- Incident Response Plan: This plan Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a data breach or security incident. It includes procedures for containment, investigation, recovery, and reporting.
Technical Controls
Technical controls are implemented using software and hardware to protect data. They are essential for securing data in transit and at rest.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between a network and the outside world, blocking unauthorized access to sensitive data. They examine incoming and outgoing network traffic and only allow authorized communication.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can block or alert on potential threats. They are essential for detecting and preventing attacks like malware infections and denial-of-service attacks.
- Encryption: Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, protecting it from unauthorized access. It is crucial for securing data both in transit (e.g., during transmission over the internet) and at rest (e.g., on hard drives).
- Anti-Malware Software: This software detects and removes malware, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware, that can compromise data security. It is essential for protecting systems from malicious attacks and preventing data loss.
Physical Controls
Physical controls are measures implemented to secure physical access to data and computing devices. They are essential for preventing unauthorized physical access to sensitive information.
- Security Cameras: Security cameras provide visual monitoring of physical spaces, deterring unauthorized access and providing evidence in case of a security breach.
- Access Control Systems: These systems restrict physical access to specific areas, such as data centers or server rooms, using key cards, biometrics, or other authentication methods.
- Environmental Controls: These controls ensure the proper functioning of data centers and other computing environments by maintaining optimal temperature, humidity, and power supply.
- Physical Security Guards: Security guards provide physical protection of facilities and can respond to security incidents. They are essential for deterring unauthorized access and ensuring the safety of personnel and data.
Comparison of Data Security Controls
| Control Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative | Cost-effective, flexible, can be tailored to specific needs. | Reliance on human behavior, difficult to enforce, can be time-consuming to implement. |
| Technical | Automated, effective in preventing attacks, can be easily scaled. | Can be complex to manage, require expertise to implement, may not be effective against sophisticated attacks. |
| Physical | Provides a physical barrier to unauthorized access, effective against physical threats. | Can be expensive to implement, may not be effective against internal threats, can be difficult to maintain. |
Implementing Effective Data Security Controls
Implementing effective data security controls is crucial for protecting your organization’s valuable data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. A well-designed and implemented framework for data security controls ensures that your data remains confidential, integral, and available when you need it.
Designing a Framework for Implementing Data Security Controls
A robust framework for implementing data security controls involves a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. The framework should be tailored to the specific needs of your organization, considering factors such as the type of data you handle, the sensitivity of the information, and the potential threats you face.
- Identify Data Assets and Their Sensitivity: Begin by identifying all the data assets your organization holds, including databases, applications, files, and other digital information. Categorize each asset based on its sensitivity, such as confidential, private, or public, to prioritize protection efforts.
- Conduct Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Analysis: A comprehensive risk assessment involves identifying potential threats to your data assets and evaluating the likelihood and impact of those threats. Vulnerability analysis focuses on identifying weaknesses in your systems and applications that could be exploited by attackers.
- Define Security Objectives and Control Measures: Based on the risk assessment and vulnerability analysis, define clear security objectives for each data asset. For example, you might aim to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data. Then, select appropriate security controls to achieve those objectives.
- Implement and Configure Controls: Once you have chosen your controls, implement them effectively and configure them properly. This includes installing software, configuring hardware, and training employees on security policies and procedures.
- Monitor and Evaluate Controls: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of your implemented controls. Use tools and techniques to track security events, detect anomalies, and identify areas for improvement. Continuously evaluate your controls and make adjustments as needed to ensure they remain effective.
The Importance of Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Analysis
Risk assessment and vulnerability analysis are fundamental to designing effective data security controls. They provide valuable insights into the threats your organization faces and the vulnerabilities that could be exploited. By understanding these factors, you can prioritize your security efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Risk assessment helps you identify potential threats and evaluate their likelihood and impact, while vulnerability analysis reveals weaknesses in your systems and applications.
Monitoring and Evaluating the Effectiveness of Implemented Controls
Continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential to ensure that your data security controls remain effective. This involves:
- Security Event Monitoring: Use security information and event management (SIEM) tools to track security events, such as login attempts, file access, and network traffic.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scan your systems and applications for known vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing: Simulate real-world attacks to assess the effectiveness of your security controls.
- Security Audits: Conduct regular audits to verify that your security policies and procedures are being followed.
- Performance Metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to your data security controls, such as the number of security incidents, the time it takes to respond to incidents, and the percentage of vulnerabilities patched.
Addressing Common Data Security Threats

Data security threats are a constant reality in the digital world. It’s like living in a jungle, you gotta be prepared for anything! These threats can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your valuable data. But don’t worry, with the right security controls, you can protect yourself from these threats.
Malware
Malware is like a sneaky ninja that enters your system without your permission. It can cause all sorts of havoc, from stealing your data to crashing your computer.
- Viruses: Think of these like contagious diseases that can spread from one computer to another. They can corrupt files, delete data, or even take control of your computer.
- Worms: These bad boys can replicate themselves and spread from one computer to another without any human intervention. They can slow down your computer, steal your data, or even give hackers access to your network.
- Trojan horses: These sneaky guys disguise themselves as legitimate software but contain malicious code. They can steal your passwords, track your online activity, or even give hackers remote access to your computer.
- Ransomware: This is like a digital hostage situation. Ransomware encrypts your files and demands payment to unlock them.
To protect yourself from malware, you can use antivirus software, firewalls, and keep your software up to date. It’s like having a security guard for your computer!
Phishing
Phishing is a social engineering attack that uses deceptive emails, texts, or websites to trick you into revealing personal information, like your passwords or credit card numbers. Think of it like a fake online store that wants to steal your credit card details.
- Email phishing: This is the most common type of phishing attack. Hackers send emails that look like they’re from a legitimate source, like your bank or a social media platform. These emails usually contain links to fake websites that ask you to log in or enter your personal information.
- SMS phishing (Smishing): This is similar to email phishing, but it uses text messages. Hackers send text messages that appear to be from a legitimate source, like a bank or a delivery company. These messages usually contain links to fake websites that ask you to log in or enter your personal information.
- Vishing: This type of phishing uses phone calls to trick you into revealing personal information. Hackers call you pretending to be from a legitimate source, like your bank or a government agency. They may ask you to verify your personal information or to give them remote access to your computer.
To protect yourself from phishing, be wary of suspicious emails, text messages, and phone calls. Never click on links in emails or text messages from unknown sources, and never give out your personal information over the phone unless you are sure you are talking to a legitimate source.
Unauthorized Access, What is the primary objective of data security controls
Unauthorized access is like someone breaking into your house while you’re away. Hackers can gain unauthorized access to your computer, network, or data in various ways.
- Weak passwords: Using weak passwords like “password” or “12345” is like leaving your door unlocked. Hackers can easily guess these passwords and gain access to your accounts.
- Social engineering: This is a technique that uses psychological manipulation to trick people into revealing sensitive information. For example, a hacker might pretend to be a technical support representative and ask for your password.
- Brute-force attacks: This is a method that uses automated software to try different combinations of passwords until the correct one is found.
- Exploiting vulnerabilities: Hackers can exploit security vulnerabilities in software to gain unauthorized access to your computer or network.
To protect yourself from unauthorized access, use strong passwords, be wary of social engineering attacks, and keep your software up to date.
Data Security Controls to Mitigate Threats
| Threat | Data Security Controls || ————————————- | ————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— || Malware | Antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), network segmentation, regular software updates, user education, and data backups.
|| Phishing | User education, email filtering, anti-phishing software, two-factor authentication (2FA), and strong passwords.
|| Unauthorized Access | Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), access control lists (ACLs), intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), network segmentation, regular security audits, and employee training.
|| Data Loss | Data encryption, data backups, data retention policies, and data disposal procedures.
|| Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks | Firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), load balancing, and network segmentation.
|| Insider Threats | Background checks, employee training, access control lists (ACLs), data loss prevention (DLP) software, and regular security audits.
|| Physical Security Breaches | Security cameras, access control systems, alarm systems, and physical barriers.
|| Natural Disasters | Data backups, disaster recovery plans, and data centers in geographically diverse locations.
|| Software Vulnerabilities | Regular software updates, vulnerability scanning, and patch management.
|| Improper Configuration | Security configuration management tools, regular security audits, and employee training.
|
The Role of Data Security Controls in Compliance
Data security controls play a vital role in ensuring that organizations comply with various regulations and legal requirements. They act as a shield, protecting sensitive information and helping organizations avoid hefty fines and reputational damage. Let’s delve into how data security controls contribute to compliance.
Compliance with Regulations and Legal Requirements
Data security controls are essential for meeting the mandates of numerous regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). These regulations Artikel specific requirements for protecting personal and sensitive data, and organizations must demonstrate their compliance through robust data security practices.
Examples of Data Security Controls for Compliance
- Access Control: Implementing strong access control measures, like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC), ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. This directly addresses the GDPR’s requirement for data minimization and access control.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit is a fundamental requirement for compliance with regulations like HIPAA. This safeguards sensitive patient information from unauthorized access, meeting the HIPAA Security Rule’s requirement for protecting electronic protected health information (ePHI).
- Regular Security Assessments: Performing regular security assessments, including vulnerability scans and penetration testing, helps identify and address security weaknesses proactively. This aligns with the GDPR’s principle of accountability, demonstrating that organizations are taking reasonable steps to protect personal data.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with data security regulations can result in severe consequences. Organizations may face hefty fines, legal action, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
Mitigating Risks with Effective Controls
By implementing effective data security controls, organizations can mitigate these risks. These controls act as a proactive defense mechanism, reducing the likelihood of data breaches and ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
The Future of Data Security Controls
The world of data security is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging and advancements in technology driving the need for innovative solutions. As we look ahead, it’s clear that data security controls will play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information in the digital age.
Emerging Trends and Advancements in Data Security Controls
The landscape of data security is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the emergence of new technologies and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. This section explores some of the key trends and advancements shaping the future of data security controls.
- Zero Trust Security: This approach assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organization’s network. Zero trust security relies on continuous authentication and authorization, granular access controls, and robust security monitoring to protect data. This approach is gaining popularity as organizations recognize the importance of protecting data at every point in its lifecycle.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are revolutionizing data security by enabling automated threat detection, anomaly detection, and predictive analysis. AI-powered security tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate malicious activity. This allows security teams to proactively address threats and prevent breaches.
- Behavioral Analytics: Behavioral analytics focuses on analyzing user behavior patterns to identify potential security risks. By monitoring user activity, security teams can detect deviations from normal behavior, such as unusual login attempts, excessive data access, or suspicious file downloads. This approach helps to identify insider threats and other security vulnerabilities.
- Security Orchestration and Automation (SOAR): SOAR platforms streamline security operations by automating repetitive tasks, integrating security tools, and improving incident response times. By automating security processes, SOAR solutions free up security teams to focus on more strategic tasks and enhance overall security posture.
Impact of Evolving Technologies on Data Security
Emerging technologies like cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence are significantly impacting data security. These technologies present both opportunities and challenges for organizations seeking to protect sensitive information.
- Cloud Computing: The adoption of cloud computing has significantly changed how organizations store and manage data. Cloud providers offer a range of security features, but organizations still need to implement robust data security controls to protect their data in the cloud. This includes encrypting data at rest and in transit, using strong access controls, and regularly auditing cloud security configurations.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices has created a new attack surface for cybercriminals. IoT devices often have limited security features and can be vulnerable to attacks. Organizations need to implement security measures specifically designed for IoT devices, such as secure firmware updates, encryption, and access controls.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can be used to enhance data security, but it also presents new security challenges. AI-powered attacks are becoming more sophisticated, and organizations need to develop defenses against AI-based threats. This includes using AI to detect and respond to AI-powered attacks and implementing robust AI security frameworks.
Emerging Security Challenges and Future Data Security Controls
As technology continues to evolve, so do the threats to data security. Here are some emerging security challenges and how future data security controls might address them:
- Data Privacy Regulations: Data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), are becoming increasingly stringent. Organizations need to implement robust data security controls to comply with these regulations and protect consumer data. Future data security controls will likely incorporate features that automate compliance tasks, simplify data privacy management, and ensure continuous monitoring of data security practices.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing has the potential to break current encryption algorithms, posing a significant threat to data security. Future data security controls will need to incorporate quantum-resistant encryption algorithms to protect data from attacks by quantum computers. This includes developing new encryption methods that are resistant to quantum attacks and implementing these methods across organizational systems.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Supply chain attacks target vulnerabilities in software or hardware used by organizations. These attacks can be difficult to detect and can compromise sensitive data. Future data security controls will need to focus on securing the entire supply chain, including software development, hardware manufacturing, and distribution. This involves implementing security measures at every stage of the supply chain to prevent attacks and mitigate the impact of successful attacks.
By understanding the primary objective of data security controls and implementing them effectively, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of data breaches and protect their valuable information. Data security is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance and adaptation to new threats. By staying informed about the latest security threats and best practices, organizations can ensure that their data is protected from harm.
The future of data security is evolving rapidly, and organizations need to stay ahead of the curve to ensure that their data is protected from emerging threats.
Helpful Answers
What are some examples of data security controls?
Examples of data security controls include access control lists, firewalls, encryption, data loss prevention software, and security awareness training. These controls can be implemented at different levels, including administrative, technical, and physical.
Why are data security controls important?
Data security controls are important because they help to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Without data security controls, organizations would be at a much higher risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
What are the different types of data security controls?
There are three main types of data security controls: administrative, technical, and physical. Administrative controls are policies and procedures that govern the use of data. Technical controls are technologies that are used to protect data. Physical controls are measures that are taken to protect data from physical threats, such as theft or damage.






