What is triage in cyber security – What is triage in cybersecurity? In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, it’s the critical first step in incident response, a process that prioritizes and categorizes security incidents to guide efficient and effective resolution. Think of it as a battlefield medic assessing casualties, determining who needs immediate attention and who can wait. Triage in cybersecurity ensures that the most critical threats are addressed promptly, minimizing potential damage and mitigating risks.
This process involves a systematic evaluation of the incident, considering its severity, potential impact, and available resources. It’s a collaborative effort, bringing together security analysts, incident responders, and IT staff to assess the situation, gather information, and determine the appropriate course of action.
Introduction to Triage in Cybersecurity
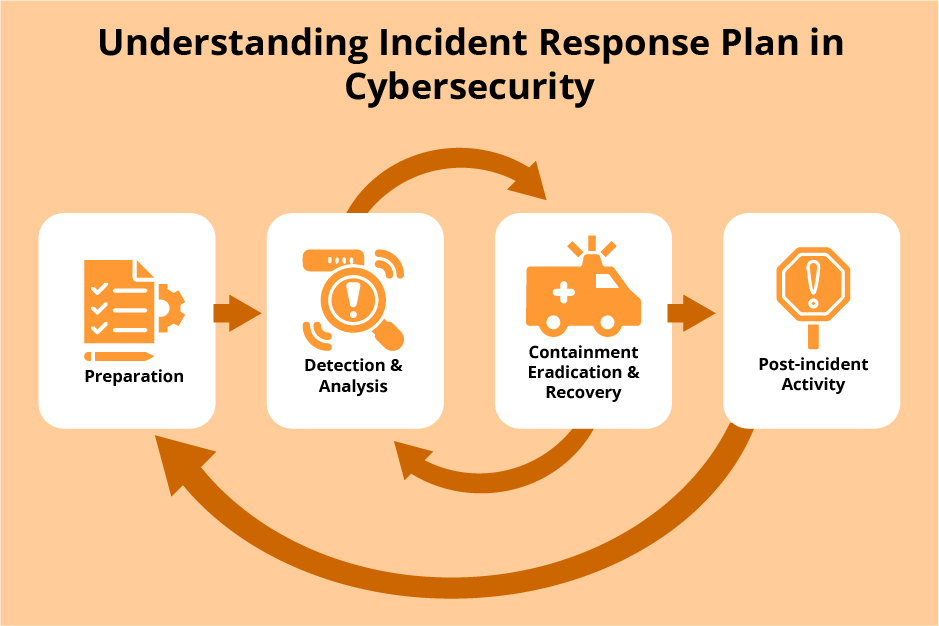
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, rapid response and efficient prioritization are paramount. Triage, a fundamental concept borrowed from the medical field, plays a crucial role in effectively managing cybersecurity incidents and mitigating potential damage. Triage in cybersecurity involves the process of quickly assessing and prioritizing cybersecurity incidents based on their severity, potential impact, and urgency. It’s a crucial first step in incident response, allowing security teams to allocate resources effectively and focus on the most critical threats.
The Importance of Triage in Incident Response and Threat Management
Triage is essential for incident response and threat management as it provides a structured framework for handling multiple security events simultaneously.
- Rapid Assessment and Prioritization: Triage enables security teams to quickly assess the nature and severity of incidents, allowing them to prioritize the most critical threats first. This ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that the most impactful incidents are addressed promptly.
- Effective Resource Allocation: By prioritizing incidents based on their severity and potential impact, triage allows security teams to allocate resources effectively. This ensures that the most critical threats are addressed with the appropriate level of attention and expertise.
- Reduced Downtime and Damage: By quickly identifying and addressing critical threats, triage helps minimize downtime and potential damage to systems and data. This is crucial for businesses that rely on their IT infrastructure for operations.
- Improved Incident Response Time: Triage streamlines the incident response process, allowing security teams to react quickly and efficiently to threats. This reduces the time it takes to contain and resolve incidents, minimizing potential damage.
Real-World Examples of Cybersecurity Incidents Where Triage Was Crucial
- Data Breach at Equifax: In 2017, Equifax experienced a massive data breach that affected millions of individuals. Triage was crucial in identifying and containing the breach, preventing further damage and allowing Equifax to begin the process of recovery.
- WannaCry Ransomware Attack: The WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 targeted organizations worldwide, encrypting their data and demanding ransom payments. Triage played a vital role in identifying affected systems and implementing mitigation measures to prevent further spread of the ransomware.
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: DDoS attacks overwhelm targeted systems with traffic, rendering them inaccessible. Triage is essential in identifying and mitigating DDoS attacks, ensuring the continued availability of critical systems and services.
The Triage Process in Cybersecurity
Triage is the initial phase of incident response, where security professionals assess the situation and determine the urgency and severity of a potential security breach. This critical step helps prioritize actions and allocate resources effectively to mitigate the impact of the incident.
Steps Involved in Cybersecurity Triage
The triage process typically involves a series of steps that help security teams quickly understand the situation and make informed decisions. These steps are designed to provide a structured approach to incident response, ensuring that critical actions are taken in a timely manner.
- Detection: The triage process begins with the detection of a potential security incident. This could be triggered by various sources, such as security tools, system logs, user reports, or external threat intelligence.
- Initial Assessment: Once an incident is detected, the next step is to gather preliminary information to assess the severity and potential impact of the incident. This includes identifying the affected systems, the nature of the attack, and the potential data compromised.
- Confirmation: After the initial assessment, security teams need to confirm whether the detected event is indeed a genuine security incident. This involves further investigation, analyzing logs, and potentially running additional tools to verify the nature of the event.
- Impact Assessment: Once the incident is confirmed, security teams need to determine the potential impact of the incident on the organization’s business operations, reputation, and financial stability. This involves assessing the compromised data, the affected systems, and the potential consequences of the incident.
- Prioritization: Based on the impact assessment, security teams need to prioritize the incident and determine the appropriate response. High-impact incidents require immediate attention and a rapid response, while low-impact incidents might be addressed later or with less urgency.
- Communication: Effective communication is crucial throughout the triage process. Security teams need to keep stakeholders informed about the incident, including the affected systems, the potential impact, and the response plan.
- Escalation: If the incident requires expertise beyond the immediate team, it needs to be escalated to appropriate stakeholders, such as senior management, legal counsel, or external security consultants.
Role of Stakeholders in Triage
The triage process involves the collaboration of various stakeholders, each playing a critical role in ensuring a timely and effective response.
- Security Analysts: Security analysts are responsible for monitoring security tools, analyzing logs, and identifying potential security incidents. They play a crucial role in the initial detection and assessment of incidents.
- Incident Responders: Incident responders are specialized security professionals who are responsible for investigating and resolving security incidents. They are typically involved in the confirmation, impact assessment, and prioritization of incidents.
- IT Staff: IT staff, such as system administrators and network engineers, play a vital role in implementing technical solutions to mitigate the impact of incidents. They may be involved in isolating affected systems, restoring backups, or implementing security patches.
- Legal Counsel: Legal counsel provides guidance on legal implications of security incidents, such as data breach notifications, regulatory compliance, and potential litigation.
- Senior Management: Senior management provides overall direction and support for incident response activities. They are responsible for making critical decisions, such as allocating resources, communicating with stakeholders, and managing the public image of the organization.
Tools and Techniques Used in Triage
Security teams rely on various tools and techniques to effectively conduct triage and incident response. These tools provide the necessary information and insights to make informed decisions.
- Log Analysis: Log analysis involves examining system logs to identify suspicious activities, network traffic patterns, and potential security threats. This helps security teams understand the timeline of events, the source of the attack, and the potential impact of the incident.
- Network Monitoring: Network monitoring tools provide real-time visibility into network traffic, allowing security teams to identify anomalies, suspicious connections, and potential attacks. This helps in detecting and responding to incidents quickly.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Vulnerability scanning tools help identify weaknesses in systems and applications that could be exploited by attackers. This helps security teams prioritize patching efforts and address vulnerabilities that could lead to security incidents.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM solutions centralize security data from various sources, allowing security teams to correlate events, identify patterns, and detect security incidents. SIEM tools are essential for effective triage and incident response.
- Threat Intelligence: Threat intelligence provides insights into the latest threats, attack methods, and attacker tactics. This helps security teams stay ahead of emerging threats and proactively mitigate potential risks.
Key Considerations in Cybersecurity Triage
Cybersecurity triage is a critical process that involves quickly assessing and prioritizing security incidents to ensure the most effective response. During triage, it is crucial to consider several factors that will influence the direction and speed of the response. These factors help determine the urgency and severity of the incident, guiding the allocation of resources and the necessary steps to mitigate the risk.
Incident Severity and Potential Impact
The severity of a security incident and its potential impact are paramount considerations in triage. A high-severity incident, such as a data breach or a ransomware attack, requires immediate attention and a swift response to minimize damage. Conversely, a low-severity incident, like a minor configuration error, might not warrant immediate action and can be addressed at a later time.
Assessing the potential impact involves considering the affected systems, the volume of data at risk, and the potential financial or reputational consequences.
Available Resources
Effective triage requires a realistic assessment of available resources. This includes considering the expertise of the security team, the availability of tools and technologies, and the allocated budget. Limited resources might necessitate prioritizing incidents based on their severity and impact, focusing on the most critical issues first. A well-equipped and experienced team can handle a broader range of incidents simultaneously, while a smaller team may need to prioritize based on urgency.
Communication and Collaboration
Communication and collaboration are essential for successful triage. Open and timely communication among security personnel, stakeholders, and other relevant teams is crucial to ensure everyone is aware of the situation and understands the response plan. Collaboration fosters a shared understanding of the incident, facilitates the sharing of information, and enables a more coordinated and effective response. Regular updates and status reports help keep everyone informed and aligned.
Types of Cybersecurity Triage
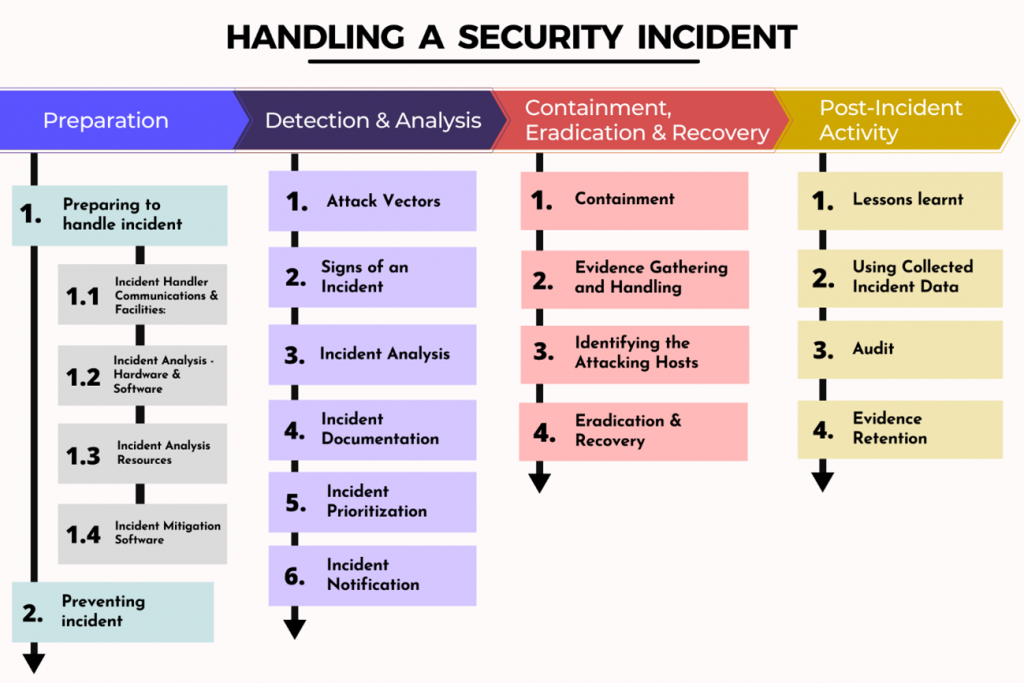
Cybersecurity triage is a crucial process for quickly identifying and responding to security incidents. The approach to triage can vary depending on the type of incident, the severity of the threat, and the resources available.
Malware Infection Triage
Malware infections are common cybersecurity incidents. Triage in this scenario involves identifying the type of malware, the extent of its spread, and the potential impact on the organization.
- Initial Assessment: The first step is to determine if the system is infected and the type of malware. This can be done by analyzing system logs, network traffic, and using antivirus software.
- Containment: Once the malware is identified, the next step is to contain the infection. This may involve isolating the infected system from the network, shutting down affected services, or implementing other security measures.
- Remediation: After containment, the infected system needs to be remediated. This may involve removing the malware, restoring data, and patching vulnerabilities.
Data Breach Triage
Data breaches can have significant financial and reputational consequences for organizations. Triage in this scenario involves determining the scope of the breach, the type of data compromised, and the potential impact on affected individuals.
- Incident Response: The initial step is to activate the incident response plan and notify relevant stakeholders, including legal counsel and law enforcement.
- Data Identification: The next step is to identify the data that has been compromised. This may involve reviewing system logs, network traffic, and other relevant data sources.
- Impact Assessment: Once the compromised data is identified, the next step is to assess the impact of the breach. This may involve determining the number of individuals affected, the sensitivity of the compromised data, and the potential financial and reputational consequences.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack Triage
DoS attacks are designed to overwhelm a system or network with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users. Triage in this scenario involves identifying the source of the attack, mitigating the impact, and restoring service.
- Attack Detection: The first step is to detect the DoS attack. This can be done by monitoring network traffic and looking for unusual patterns.
- Mitigation: Once the attack is detected, the next step is to mitigate its impact. This may involve blocking the attacker’s IP address, using a firewall to filter traffic, or implementing other security measures.
- Recovery: After the attack is mitigated, the next step is to restore service. This may involve restarting affected services, clearing network congestion, and restoring data.
Benefits of Effective Triage in Cybersecurity: What Is Triage In Cyber Security

Effective triage is the cornerstone of a robust cybersecurity incident response strategy. A well-structured triage process streamlines the incident response lifecycle, allowing security teams to prioritize and address threats efficiently. This, in turn, translates to tangible benefits, including faster incident resolution, minimized business disruption, and a fortified overall security posture.
Improved Incident Resolution Times
A streamlined triage process significantly reduces the time it takes to resolve security incidents. By rapidly identifying the nature and severity of the incident, security teams can prioritize their efforts and deploy the appropriate resources. This proactive approach prevents incidents from escalating and causing widespread damage, ensuring swift containment and mitigation.
Reduced Business Disruption
Cybersecurity incidents can disrupt business operations, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and customer dissatisfaction. Effective triage minimizes downtime by enabling security teams to quickly identify and address critical threats. By prioritizing incidents that pose the greatest risk to business continuity, security teams can ensure minimal disruption to operations and maintain business productivity.
Enhanced Security Posture
A well-defined triage process enhances the overall security posture of an organization. By systematically analyzing and responding to incidents, security teams gain valuable insights into threat patterns and vulnerabilities. This data-driven approach informs security policies and practices, enabling organizations to proactively identify and address potential threats before they exploit vulnerabilities.
“Effective triage is not just about identifying and responding to incidents; it’s about learning from them to improve our security posture.”
Neil Patel
Case Studies Demonstrating the Impact of Successful Triage, What is triage in cyber security
- In a recent case study, a large financial institution implemented a comprehensive triage process. This resulted in a 50% reduction in incident resolution times and a 20% decrease in business disruption caused by security incidents.
- Another example involves a healthcare organization that experienced a ransomware attack. Their well-defined triage process enabled them to isolate the infected systems and restore critical data within 24 hours, minimizing patient disruption and financial losses.
Challenges and Best Practices in Cybersecurity Triage
Cybersecurity triage is a critical process for any organization facing a potential security incident. However, several challenges can hinder the effectiveness of triage, impacting the organization’s ability to respond promptly and effectively. Understanding these challenges and implementing best practices is essential for optimizing the triage process.
Common Challenges in Cybersecurity Triage
Understanding the common challenges associated with cybersecurity triage is crucial for organizations to develop effective strategies for mitigating these issues.
- Limited Resources: Organizations often face limited resources, including personnel, budget, and technology, which can hinder their ability to conduct thorough triage. This can lead to delayed incident response, inadequate investigation, and potentially missed security threats.
- Information Overload: In today’s complex security landscape, organizations are inundated with security alerts and logs, making it challenging to prioritize and analyze relevant information. This information overload can overwhelm security teams, leading to delayed incident response and potentially missed critical events.
- Complex Incident Scenarios: Cybersecurity incidents can be complex, involving multiple systems, networks, and potential attackers. Analyzing these incidents requires specialized expertise and tools, which may not always be readily available, leading to prolonged triage and difficulty in understanding the full scope of the incident.
- Lack of Standardization: Inconsistent triage processes across different teams or departments can lead to confusion, duplication of effort, and inefficient response. Establishing standardized processes for incident reporting, analysis, and escalation can streamline the triage process and improve efficiency.
Best Practices for Effective Cybersecurity Triage
To overcome the challenges of cybersecurity triage, organizations should implement best practices to streamline the process and ensure effectiveness.
- Establish Clear Incident Response Processes: Defining clear and documented incident response processes, including roles, responsibilities, and escalation procedures, is crucial for efficient triage. This ensures that all team members understand their roles and responsibilities, leading to a coordinated and effective response.
- Invest in Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Implementing a SIEM solution can help organizations centralize security data from multiple sources, enabling efficient analysis and correlation of events. This can significantly reduce the time needed for triage and improve the accuracy of incident assessment.
- Utilize Automation and Orchestration: Automating repetitive tasks and using orchestration tools can streamline the triage process and free up security teams to focus on more complex tasks. This can include automating incident detection, data collection, and initial analysis, significantly reducing the time needed for triage.
- Prioritize Incident Response: Developing a clear incident prioritization system based on factors like potential impact, criticality, and urgency can help security teams focus on the most critical incidents first. This ensures that resources are allocated effectively and the most significant threats are addressed promptly.
- Conduct Regular Triage Process Reviews: Regularly reviewing and improving the triage process is essential for maintaining its effectiveness. This includes gathering feedback from security teams, analyzing incident response data, and identifying areas for improvement. Continuous improvement ensures that the triage process remains relevant and efficient in a constantly evolving security landscape.
Continuous Improvement of Triage Processes
To ensure that the triage process remains effective, organizations should continuously strive to improve their processes.
- Regularly Evaluate and Update Triage Processes: Conduct periodic reviews of the triage process to identify areas for improvement. This can include analyzing incident response data, gathering feedback from security teams, and benchmarking against industry best practices.
- Invest in Training and Skill Development: Provide security teams with ongoing training and skill development opportunities to enhance their knowledge and expertise in incident response and triage. This includes training on new technologies, incident analysis techniques, and best practices.
- Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement within the security team by promoting open communication, feedback mechanisms, and a willingness to learn from past incidents. This helps create a proactive and adaptable security team that can effectively respond to evolving threats.
Future Trends in Cybersecurity Triage
Cybersecurity triage is constantly evolving, driven by the ever-changing threat landscape and the emergence of new technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is poised to significantly transform triage processes, leading to faster, more accurate, and efficient incident response.
AI and ML in Cybersecurity Triage
AI and ML are revolutionizing cybersecurity triage by automating tasks, improving threat detection, and enabling faster response times. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security breach.
- Automated Threat Detection and Prioritization: AI and ML algorithms can analyze security logs, network traffic, and other data sources to detect suspicious activities in real-time. They can then prioritize alerts based on their severity and potential impact, allowing security teams to focus on the most critical threats first.
- Enhanced Incident Response: AI and ML can assist in automating incident response tasks, such as containment, remediation, and post-incident analysis. For example, AI-powered tools can identify and isolate infected systems, patch vulnerabilities, and even suggest corrective actions.
- Predictive Security: AI and ML algorithms can analyze historical data to identify patterns and predict future security threats. This proactive approach enables organizations to take preventative measures before attacks occur.
Benefits of AI and ML in Cybersecurity Triage
The integration of AI and ML in cybersecurity triage offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Efficiency and Speed: AI and ML can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up security analysts to focus on more complex and strategic activities. This results in faster incident response times and reduced downtime.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Precision: AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns that may be missed by human analysts. This leads to more accurate threat detection and prioritization.
- Proactive Security Posture: AI and ML can help organizations proactively identify and mitigate security risks, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks.
Challenges of Integrating AI and ML in Cybersecurity Triage
While AI and ML offer significant benefits, integrating these technologies into cybersecurity triage also presents challenges:
- Data Quality and Bias: The effectiveness of AI and ML algorithms depends heavily on the quality and completeness of the training data. Biased or incomplete data can lead to inaccurate results and compromised security.
- Explainability and Transparency: AI and ML models can be complex and difficult to understand. This lack of transparency can make it challenging to interpret their decisions and trust their outputs.
- Security Risks: AI and ML models themselves can be targets of attacks. Adversaries may attempt to manipulate or compromise these models to gain unauthorized access or disrupt security operations.
Predictions for the Future of Cybersecurity Triage
Cybersecurity triage is expected to become increasingly automated and intelligent in the future.
- AI-powered Security Orchestration and Automation (SOAR): SOAR platforms will leverage AI and ML to automate incident response workflows, enabling security teams to respond to threats more effectively and efficiently.
- Increased Use of Threat Intelligence: AI and ML will play a crucial role in analyzing and sharing threat intelligence, providing security teams with real-time insights into emerging threats and attack patterns.
- Adaptive Security: AI and ML will enable organizations to build adaptive security systems that can automatically adjust to evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
Effective triage in cybersecurity is not merely about reacting to incidents; it’s about building a proactive security posture. By understanding the critical factors, prioritizing incidents based on risk, and continuously refining triage processes, organizations can minimize the impact of cyberattacks, protect their valuable assets, and ensure business continuity. In the ever-changing world of cybersecurity, triage is the cornerstone of a successful incident response strategy.
Popular Questions
What is the difference between triage and incident response?
Triage is the initial assessment and prioritization phase of incident response. Incident response encompasses the full process of handling a security incident, from detection to recovery.
How often should triage be conducted?
Triage should be conducted whenever a security incident is detected, regardless of its perceived severity. It’s a continuous process that helps ensure the most critical issues are addressed promptly.
What are some common tools used in triage?
Common tools include security information and event management (SIEM) systems, intrusion detection systems (IDS), vulnerability scanners, and log analysis tools.
How can I improve my organization’s triage process?
Regularly review and update triage procedures, conduct training for security personnel, and implement automation tools to streamline the process.






