How can IMAP be a security threat to a company? It’s a question that’s probably not on everyone’s minds, but it should be. IMAP, the Internet Message Access Protocol, is a standard protocol for accessing email. While it’s a convenient and popular way to manage emails, it also presents some security risks that companies need to be aware of.
Think of it like this: if IMAP is a door to your company’s email, you need to make sure that door is locked and secure, or else you’re inviting trouble.
IMAP allows users to access their email from multiple devices and locations, which can be a huge advantage for businesses. But this flexibility also opens up opportunities for attackers. If someone can get into your IMAP server, they can potentially read, delete, or even modify your emails. This can be a huge problem for businesses that rely on email for sensitive communications.
It’s like having a key to your company’s vault sitting on a public bench – not a good idea.
IMAP Protocol Overview
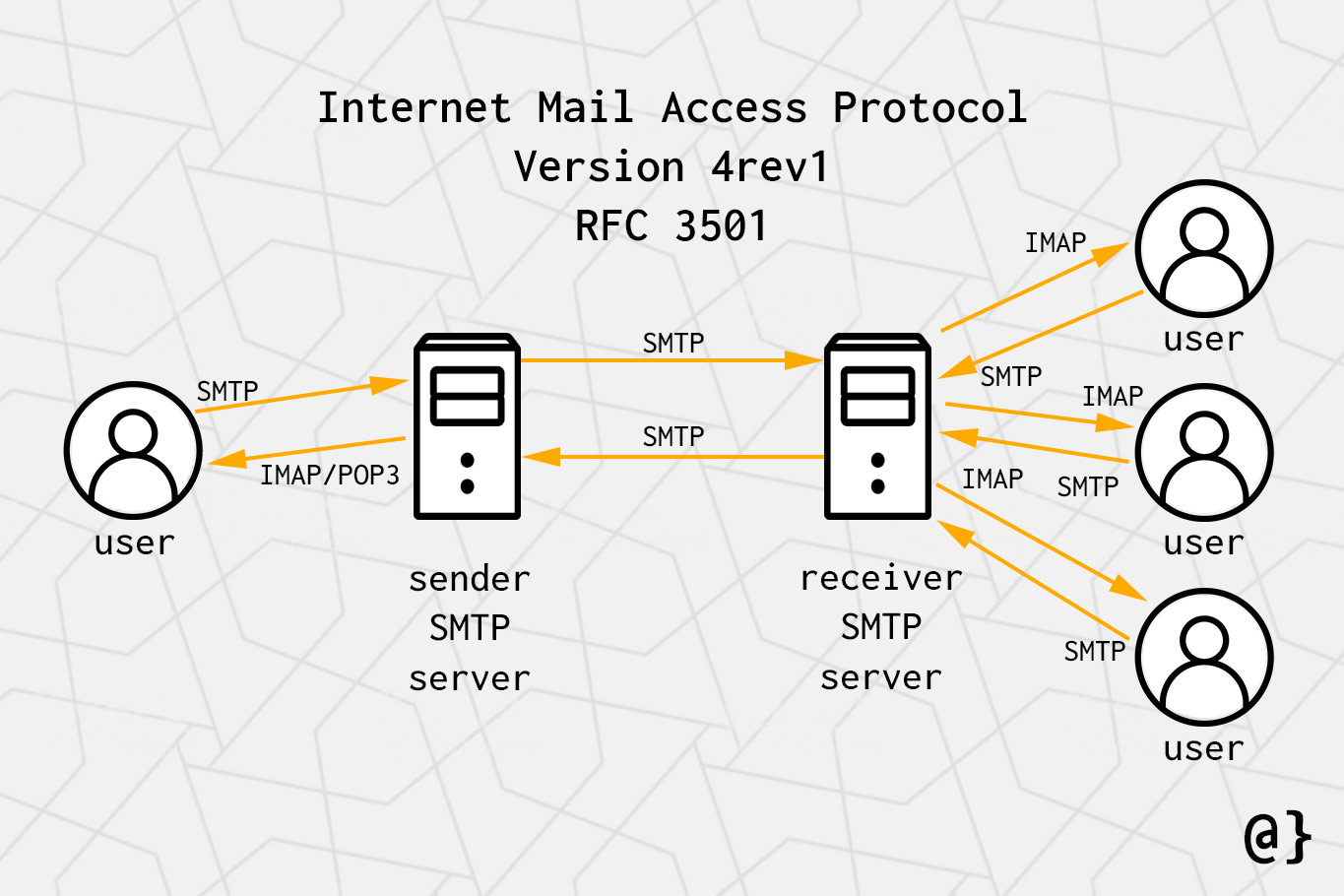
The Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) is a standard protocol used for accessing and managing email messages on a mail server. It allows users to interact with their emails remotely, enabling them to read, send, organize, and delete messages from any device with an internet connection. IMAP’s core functionalities empower users with a robust and flexible approach to email management.
IMAP’s Core Functionalities
IMAP operates by maintaining a copy of the user’s email messages on the server, ensuring that the data is synchronized across multiple devices. This allows users to access their emails from any location without the need to download all messages onto their device. IMAP’s key functionalities include:
- Message Access and Management: IMAP enables users to read, send, delete, and organize email messages directly on the server. This eliminates the need to download entire mailboxes onto their devices, improving efficiency and reducing storage requirements.
- Folder Synchronization: IMAP allows users to create and manage folders on the server, and these folders are synchronized across all devices. This enables users to organize their emails into different categories and access them seamlessly from any location.
- Offline Access: IMAP allows users to download email messages to their devices for offline access. This feature is particularly useful for users who frequently work offline or have limited internet connectivity.
- Multiple Client Support: IMAP is designed to support multiple email clients simultaneously. This means users can access their emails from different devices and applications without compromising data integrity.
Advantages of IMAP over POP3
IMAP offers several advantages over the Post Office Protocol (POP3), which is another email protocol. These advantages include:
- Server-Side Email Storage: IMAP stores emails on the server, ensuring that they are accessible from any device. POP3, on the other hand, downloads emails to the user’s device, making them unavailable on other devices.
- Email Synchronization: IMAP synchronizes emails across multiple devices, providing a consistent experience. POP3 only downloads emails to the device they are accessed from, leading to potential data inconsistencies.
- Folder Management: IMAP allows users to create and manage folders on the server, enabling better email organization. POP3 does not offer folder management capabilities, forcing users to rely on their device’s email client for organization.
IMAP Use Cases in Corporate Environments, How can imap be a security threat to a company
IMAP is widely used in corporate environments for various email management tasks. These use cases include:
- Shared Mailboxes: IMAP enables multiple users to access and manage shared mailboxes, facilitating team collaboration and communication.
- Email Archiving: IMAP allows organizations to archive emails on the server, ensuring long-term data retention and compliance with regulations.
- Centralized Email Management: IMAP provides a centralized platform for managing email accounts and policies across an organization, simplifying administration and security measures.
Security Vulnerabilities in IMAP
IMAP, despite its advantages in email management, presents inherent security vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. These vulnerabilities arise from the protocol’s design and implementation, making it crucial to understand and mitigate these risks to safeguard sensitive data.
Vulnerabilities in IMAP Authentication
Authentication is a fundamental security mechanism in IMAP, ensuring only authorized users can access email accounts. However, weaknesses in authentication mechanisms can compromise the integrity of the system.
- Weak Passwords: Users often choose easily guessable passwords, making it easier for attackers to brute-force their way into accounts. This vulnerability can be mitigated by implementing strong password policies and encouraging users to use complex passwords.
- Password Storage: Storing passwords in plain text is a significant security risk. Attackers can steal passwords from compromised servers or databases, granting them access to email accounts. Employing secure password hashing algorithms like bcrypt or Argon2 can prevent attackers from easily accessing passwords even if they gain access to the database.
- Credential Stuffing: Attackers use stolen credentials from other breaches to try accessing email accounts. This attack leverages lists of usernames and passwords obtained from other compromised services, making it crucial to implement measures like account lockout policies and multi-factor authentication to prevent credential stuffing attacks.
Vulnerabilities in IMAP Communication
IMAP communication between email clients and servers is vulnerable to interception and manipulation, posing a significant risk to data confidentiality and integrity.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Attackers can intercept communication between clients and servers, eavesdropping on sensitive information or injecting malicious code. This can be mitigated by using secure communication protocols like TLS/SSL to encrypt communication channels.
- Unencrypted Communication: IMAP communication is often unencrypted, making it susceptible to eavesdropping by anyone on the network. Implementing TLS/SSL encryption ensures data confidentiality and integrity, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Command Injection: Attackers can inject malicious commands into IMAP requests, potentially causing harm to the server or accessing sensitive information. Implementing input validation and sanitization techniques can help mitigate this vulnerability.
Vulnerabilities in IMAP Server Configuration
Improper server configuration can create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to email accounts or compromise the server itself.
- Default Credentials: Servers often come with default credentials that attackers can exploit if not changed. Regularly updating default credentials and implementing strong password policies can mitigate this risk.
- Open Ports: Leaving IMAP ports open to the public internet without proper security measures can expose servers to attacks. Restricting access to specific IP addresses or using firewalls can prevent unauthorized access.
- Outdated Software: Outdated server software may contain known vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Regularly updating server software with the latest security patches can protect against known vulnerabilities.
Common IMAP Attack Vectors: How Can Imap Be A Security Threat To A Company
Attackers employ various methods to exploit vulnerabilities in IMAP servers, gaining unauthorized access to sensitive data. These methods often leverage weaknesses in security protocols, user behavior, or system configurations.
Password Brute-forcing
Password brute-forcing is a common technique where attackers use automated tools to systematically try different password combinations until they find the correct one. This method relies on weak passwords, easily guessed combinations, or stolen password lists. Attackers can use specialized software that can quickly test numerous password variations, leveraging readily available password lists or dictionaries. This technique can be particularly effective against accounts with simple or commonly used passwords.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks target unsuspecting users by tricking them into revealing their login credentials. Attackers often send emails that appear legitimate, mimicking official communications from trusted sources. These emails may contain malicious links or attachments that lead to fake login pages designed to steal user credentials. Once attackers obtain the credentials, they can gain access to the user’s email account, compromising sensitive information.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks involve an attacker intercepting communication between a user and an IMAP server. The attacker can then eavesdrop on the communication, potentially capturing sensitive information like passwords, emails, or attachments. This type of attack often relies on compromised network infrastructure or vulnerabilities in the user’s software. The attacker can manipulate the communication flow, redirecting the user to a fake server or injecting malicious code into the communication stream.
Weak or Stolen Credentials
Weak or stolen credentials significantly contribute to IMAP attacks. Users often choose weak passwords that are easy to guess, making their accounts vulnerable to brute-forcing attempts. Stolen credentials, often obtained through phishing attacks or data breaches, provide attackers with direct access to email accounts. Additionally, the use of shared accounts or inadequate password management practices can further exacerbate security risks.
Mitigating IMAP Security Threats
Protecting your company’s sensitive data stored in emails is crucial, especially with the growing threat of IMAP-based attacks. By implementing a robust security strategy, you can significantly minimize these risks and safeguard your communication infrastructure.
Strong Authentication Mechanisms
Secure authentication is the cornerstone of IMAP security. By implementing strong authentication mechanisms, you can effectively prevent unauthorized access to your email accounts.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This method requires users to provide two forms of authentication, such as a password and a code generated by a mobile app, before granting access. This significantly enhances security by adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized logins, even if the password is compromised.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Similar to 2FA, MFA uses multiple authentication factors, such as passwords, biometrics, security tokens, or one-time passwords, to verify the identity of users. This approach adds an extra layer of security, making it more challenging for attackers to gain access to accounts.
- Password Complexity Requirements: Implementing strong password policies, such as requiring a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, can make it more difficult for attackers to guess or brute-force passwords.
- Password Expiration Policies: Regularly forcing users to change their passwords helps mitigate the risk of compromised passwords being used for extended periods. This practice encourages users to create more secure passwords and reduces the window of vulnerability for attackers.
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Proactive security measures are essential for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in your IMAP systems. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help ensure that your systems are protected against known and emerging threats.
- Penetration Testing: Simulating real-world attacks can help identify security weaknesses in your IMAP infrastructure. This process involves ethical hackers attempting to exploit vulnerabilities to understand potential attack vectors and recommend mitigation strategies.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Automated tools can scan your IMAP servers for known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. This process helps identify potential weaknesses that attackers could exploit, enabling you to take corrective actions promptly.
- Regular Patching and Updates: Keeping your IMAP server software and operating system up-to-date is crucial for patching known vulnerabilities and improving security. Regularly applying security patches and updates helps protect your system from known exploits and vulnerabilities.
Secure Configuration and Best Practices
Properly configuring your IMAP server and adhering to best practices can significantly enhance your system’s security.
- Restrict Access to IMAP Ports: By limiting access to IMAP ports (143 for standard IMAP and 993 for IMAP over SSL/TLS) to authorized users and applications, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized connections. Consider using firewalls to block access to these ports from untrusted networks or devices.
- Enable SSL/TLS Encryption: Using SSL/TLS encryption for IMAP communication helps protect sensitive data from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. This ensures that data transmitted between clients and the IMAP server is encrypted, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Limit Access Permissions: Implement granular access control policies to restrict users’ permissions based on their roles and responsibilities. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and reduces the potential impact of compromised accounts.
- Implement Strong Password Policies: Encourage users to create strong and unique passwords for their email accounts. Consider using a password manager to help users generate and store strong passwords securely.
- Regularly Monitor for Suspicious Activity: Implement logging and monitoring systems to track user activity and identify potential security breaches. Regularly review logs for suspicious patterns or anomalies, such as unusual login attempts, large data transfers, or unauthorized access to sensitive folders.
Impact of IMAP Security Breaches on Businesses

A successful IMAP security breach can have severe consequences for businesses, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal ramifications. The unauthorized access to sensitive email communications can compromise confidential information, disrupt operations, and erode customer trust.
Financial Losses
Financial losses from IMAP security breaches can stem from various sources. Stolen credentials can be used to access and manipulate financial data, leading to fraudulent transactions or unauthorized fund transfers. Furthermore, breaches can disrupt business operations, causing downtime and lost productivity.
Reputational Damage
Data breaches involving sensitive email communications can severely damage a company’s reputation. Customers and partners may lose trust in the organization’s ability to protect their data, leading to a decline in business and brand value.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
Data breaches involving sensitive email communications can trigger legal and regulatory actions. Organizations may face fines and penalties for failing to comply with data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Additionally, affected individuals may pursue legal action for damages resulting from the breach.
Real-World Examples
Several high-profile IMAP security breaches have highlighted the potential impact on organizations. In 2017, a massive data breach at Equifax, a credit reporting agency, exposed the personal information of millions of individuals, including their email addresses and Social Security numbers. The breach resulted in significant financial losses, regulatory fines, and reputational damage for Equifax. Similarly, in 2018, a data breach at Marriott International exposed the personal information of millions of hotel guests, including their email addresses and passport details.
The breach led to significant financial losses for Marriott and raised concerns about the security of personal data in the hospitality industry.
IMAP security is a serious issue that businesses need to take seriously. By understanding the risks and implementing appropriate security measures, companies can protect themselves from IMAP attacks and ensure that their email communications remain secure. Think of it like a security guard for your email system – a little extra vigilance goes a long way in keeping your company safe.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are some common IMAP attack vectors?
Attackers use various methods to compromise IMAP servers. These include password brute-forcing, phishing attacks, and man-in-the-middle attacks. They often exploit weak or stolen credentials to gain access.
How can I protect my company from IMAP attacks?
Implement strong authentication mechanisms like two-factor authentication, conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments, and stay up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates.
What are the consequences of a successful IMAP security breach?
A successful IMAP security breach can lead to significant financial and reputational damage. It can also result in legal and regulatory consequences, especially if sensitive data is compromised.
What are some real-world examples of IMAP security breaches?
Several high-profile IMAP security breaches have occurred, highlighting the importance of robust security measures. For example, in 2017, a major email provider experienced a data breach affecting millions of users. This breach exposed sensitive data, including email content and user credentials.






