Which of the following is a part of security audits? This question delves into the heart of cybersecurity, where proactive measures are taken to identify and mitigate potential risks. Security audits are crucial for any organization, from small businesses to large enterprises, as they provide a comprehensive evaluation of security controls and practices. This evaluation helps identify vulnerabilities, assess compliance with industry standards, and ultimately strengthen the overall security posture.
Imagine a security audit as a thorough health checkup for your digital assets. It involves a systematic process of examining systems, networks, applications, and data to identify weaknesses and potential threats. This process is essential for maintaining data integrity, ensuring user privacy, and safeguarding against malicious attacks.
Types of Security Audits: Which Of The Following Is A Part Of Security Audits

Security audits are essential for any organization that wants to protect its data and systems from cyber threats. They help identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. Security audits can be conducted internally by the organization’s own security team or externally by a third-party security firm.
Types of Security Audits, Which of the following is a part of security audits
Security audits can be classified into different types, each with a specific focus and scope.
- Internal Security Audits: These audits are conducted by the organization’s own security team. They are typically focused on identifying vulnerabilities and risks within the organization’s internal systems and networks. Internal audits can help organizations to identify and address security issues before they are exploited by external attackers.
- External Security Audits: These audits are conducted by third-party security firms. They provide an independent and objective assessment of an organization’s security posture.
External audits can help organizations to identify vulnerabilities and risks that may have been missed by internal audits.
- Penetration Testing: This type of audit involves simulating a real-world attack on an organization’s systems and networks. Penetration testing can help organizations to identify and assess the effectiveness of their security controls.
Vulnerability Assessments
Vulnerability assessments are designed to identify and evaluate potential weaknesses in an organization’s systems and networks. This type of audit is typically conducted using automated scanning tools to identify known vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability assessments are a crucial part of any comprehensive security audit.
Vulnerability assessments help organizations to prioritize security issues and allocate resources to address the most critical vulnerabilities.
Compliance Audits
Compliance audits are conducted to ensure that an organization is meeting the requirements of relevant industry standards and regulations. These audits are typically conducted by third-party security firms and often involve reviewing an organization’s security policies, procedures, and controls.
Examples of compliance audits include PCI DSS audits for organizations that process credit card payments and HIPAA audits for healthcare organizations.
Compliance audits help organizations to demonstrate that they are taking appropriate steps to protect sensitive data.
Risk Assessments
Risk assessments are used to identify and evaluate the potential risks to an organization’s systems and networks. These assessments involve identifying potential threats, vulnerabilities, and the likelihood and impact of each risk.
Risk assessments help organizations to prioritize security issues and allocate resources to mitigate the most significant risks.
Risk assessments can help organizations to develop effective security strategies that are tailored to their specific needs and risks.
Key Components of Security Audits

A security audit is a systematic examination of an organization’s security posture to identify vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and compliance gaps. It’s a crucial process for any organization that wants to protect its data, systems, and reputation.
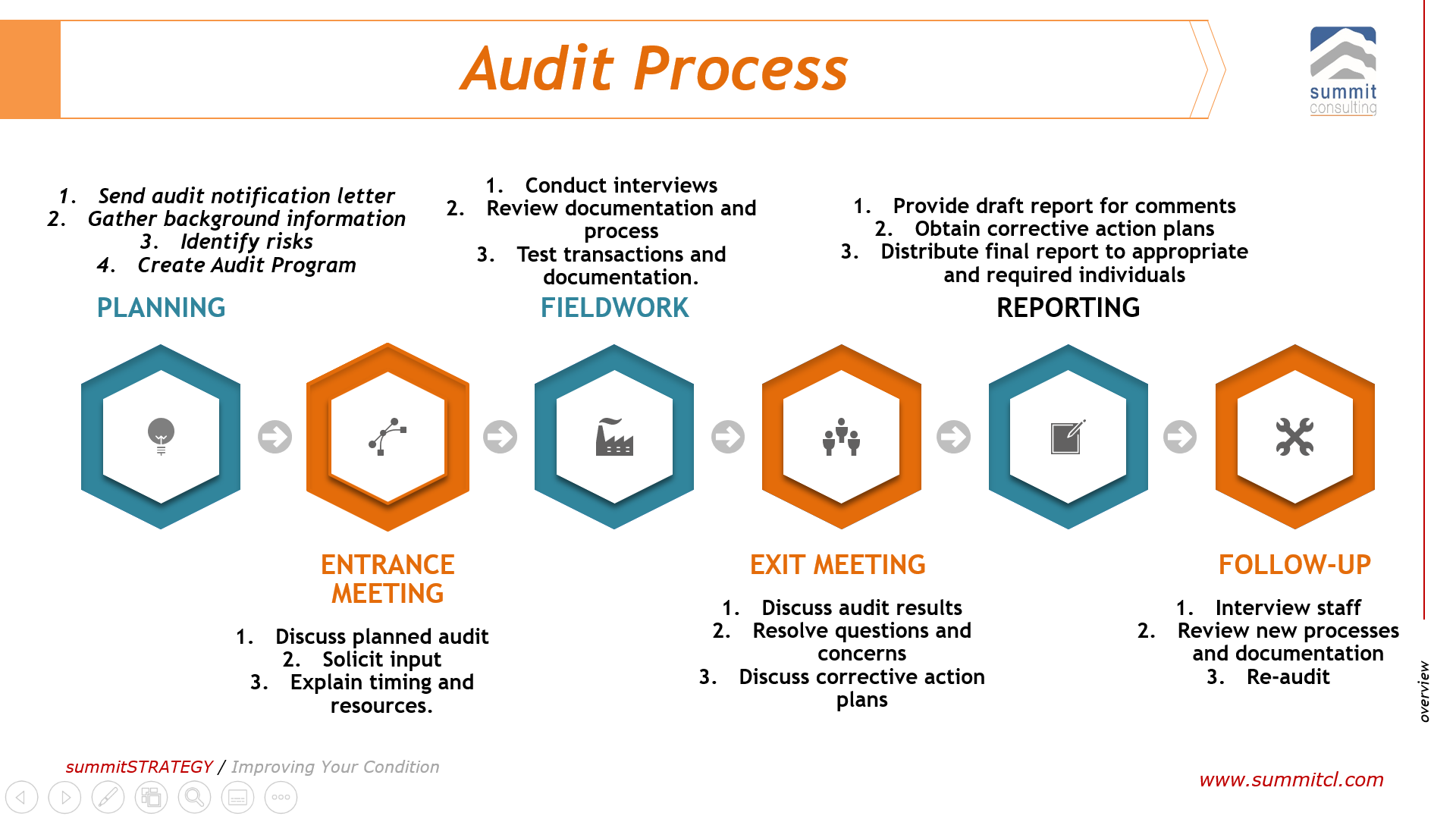
Phases of a Security Audit
The security audit process is typically divided into distinct phases, each contributing to a comprehensive assessment.
- Planning: The initial phase involves defining the audit scope, objectives, methodology, and timeline. This includes identifying the systems, applications, and data to be audited, as well as the specific security standards or regulations to be assessed.
- Information Gathering: This phase involves collecting data about the organization’s security controls, policies, procedures, and infrastructure. This data can be gathered through interviews, document reviews, network scans, and vulnerability assessments.
- Analysis: The collected data is then analyzed to identify vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and non-compliance issues. This analysis involves comparing the organization’s security practices against industry best practices, security standards, and regulatory requirements.
- Reporting: The findings of the security audit are documented in a comprehensive report that Artikels the identified vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and non-compliance issues. The report also includes recommendations for remediation and improvement.
- Remediation: This phase involves implementing the recommendations Artikeld in the security audit report to address the identified vulnerabilities and weaknesses. This may involve updating security policies, implementing new security controls, or patching vulnerabilities.
Roles and Responsibilities
The success of a security audit depends on the clear roles and responsibilities of both the audit team and the organization being audited.
- Audit Team: The audit team is responsible for conducting the audit, collecting data, analyzing findings, and reporting the results. They should possess expertise in security assessment methodologies, industry best practices, and relevant security standards.
- Organization Being Audited: The organization being audited is responsible for providing the audit team with access to relevant information, systems, and personnel. They should also actively participate in the audit process by providing feedback and answering questions.
Methodologies and Tools
Security audits utilize a range of methodologies and tools to conduct a thorough assessment.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Automated tools are used to scan systems and networks for known vulnerabilities. These tools can identify common security flaws, such as outdated software, weak passwords, and open ports.
- Penetration Testing: This involves simulating real-world attacks to assess the effectiveness of security controls. Penetration testers use a variety of techniques, such as social engineering, brute force attacks, and exploit kits, to try to gain unauthorized access to systems and data.
- Security Auditing Frameworks: Standardized frameworks, such as ISO 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and PCI DSS, provide a structured approach to security audits. These frameworks define specific security controls and requirements that organizations should implement.
Commonly Audited Areas
Security audits are comprehensive assessments that evaluate an organization’s security posture, identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses. They focus on various aspects of the organization’s security infrastructure, systems, and practices. This section delves into commonly audited areas, highlighting the importance of each area and the security controls typically assessed.
Network Security
Network security is a crucial aspect of any organization’s security posture. It encompasses the protection of an organization’s network infrastructure, including devices, data, and applications. Audits in this area typically focus on:
- Firewall configuration: Firewalls act as a barrier between an organization’s network and the external world, controlling network traffic. Audits assess the firewall’s rules, configuration, and effectiveness in blocking unauthorized access.
- Network segmentation: Segmenting a network into smaller, isolated zones can limit the impact of a security breach. Audits examine the network segmentation strategy and its implementation.
- Wireless security: Wireless networks are often a target for attackers. Audits evaluate the security protocols used for wireless networks, including encryption and authentication mechanisms.
- Vulnerability scanning: Vulnerability scanning identifies security flaws in network devices and applications. Audits assess the frequency and effectiveness of vulnerability scans.
A robust network security posture is essential for protecting sensitive data, maintaining business operations, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Application Security
Applications are increasingly becoming the primary targets of cyberattacks. Auditing application security focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in software applications that could be exploited by attackers. Key areas assessed include:
- Code review: Code review involves examining application code for security flaws, such as buffer overflows, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Input validation: Input validation ensures that user inputs are sanitized and validated before being processed by the application. Audits examine the input validation mechanisms and their effectiveness in preventing attacks.
- Authentication and authorization: Authentication verifies the identity of users, while authorization controls access to resources. Audits assess the authentication and authorization mechanisms used in applications.
- Security testing: Security testing involves simulating attacks to identify vulnerabilities. Audits assess the types of security testing performed and their effectiveness in uncovering weaknesses.
Secure applications are critical for protecting sensitive data, maintaining user trust, and ensuring business continuity.
Data Security
Data is a valuable asset for any organization. Data security audits assess the measures taken to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
| Area | Security Controls | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Encrypting data at rest and in transit | Protects sensitive data from unauthorized access even if the systems are compromised. |
| Access Control | Restricting access to data based on user roles and permissions | Ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Monitoring and blocking the transfer of sensitive data outside the organization | Prevents data breaches and leaks. |
| Data Backup and Recovery | Regularly backing up data and having a disaster recovery plan | Enables the restoration of data in case of a data loss event. |
Effective data security measures are essential for protecting privacy, complying with regulations, and maintaining business operations.
Physical Security
Physical security refers to the measures taken to protect physical assets, such as data centers, servers, and devices. Audits in this area typically focus on:
- Access control: Access control measures, such as security guards, surveillance systems, and key card systems, restrict unauthorized access to physical facilities.
- Environmental controls: Environmental controls, such as fire suppression systems, temperature and humidity controls, and power backup systems, protect equipment from damage.
- Data center security: Audits examine the security measures implemented in data centers, including access control, surveillance, and environmental controls.
- Device security: Audits assess the security measures implemented for devices, such as laptops, mobile phones, and tablets, including encryption, password policies, and access controls.
Strong physical security measures are essential for protecting equipment, data, and personnel from physical threats.
Understanding the components of a security audit is critical for any organization seeking to protect its digital assets. By implementing a robust security audit program, organizations can proactively identify and address vulnerabilities, minimizing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. As technology evolves and threats become more sophisticated, the importance of security audits only grows. Organizations must remain vigilant and adapt their security practices to stay ahead of the curve.
Expert Answers
What are the benefits of conducting security audits?
Security audits offer numerous benefits, including identifying vulnerabilities, improving security posture, demonstrating compliance, reducing risk, and enhancing overall security awareness within an organization.
Who should conduct a security audit?
Security audits can be conducted by internal security teams, external security consultants, or a combination of both. The choice depends on the organization’s size, resources, and specific needs.
How often should security audits be conducted?
The frequency of security audits depends on factors such as the organization’s industry, size, and risk profile. However, it’s generally recommended to conduct audits at least annually or more frequently if significant changes occur within the organization’s IT infrastructure or security environment.






