Was ist elektrischer Strom Grundschule? It’s a question that pops up in many kids’ minds. It’s like a super power that makes everything work, from your phone to the lights in your room. Think of it like water flowing through a pipe, but instead of water, it’s tiny, invisible particles called electrons. These electrons move around and create electricity, powering our world.
But how does electricity work? What makes it flow? That’s where the fun begins! We’ll break down the basics of electricity, exploring how it works, its different types, and how it keeps our world running smoothly. Get ready to be amazed by the power of electricity!
What is Electricity?

Imagine a tiny, invisible force that can light up your room, make your toys move, and even cook your food! That force is called electricity. It’s like a special kind of energy that can flow from one place to another.
Electricity is Like Water
Think about water flowing through a pipe. The water represents electricity, and the pipe represents the wires that carry it. Just like water needs a pipe to flow, electricity needs wires to travel from one place to another.
Uses of Electricity
Electricity is used in many ways in our daily lives. Here are some examples:
- Lighting: Electricity powers light bulbs, making our homes and streets bright at night.
- Appliances: From refrigerators and washing machines to televisions and computers, many appliances use electricity to work.
- Transportation: Electric cars and trains use electricity to move.
- Communication: Phones, internet, and radio signals all rely on electricity.
The Building Blocks of Electricity: Was Ist Elektrischer Strom Grundschule
Electricity is all around us, powering our homes, schools, and even our toys! But how does electricity work? To understand electricity, we need to know about its building blocks. Think of electricity like a river flowing through a landscape. Just as a river needs a path to flow, electricity needs a circuit to travel.
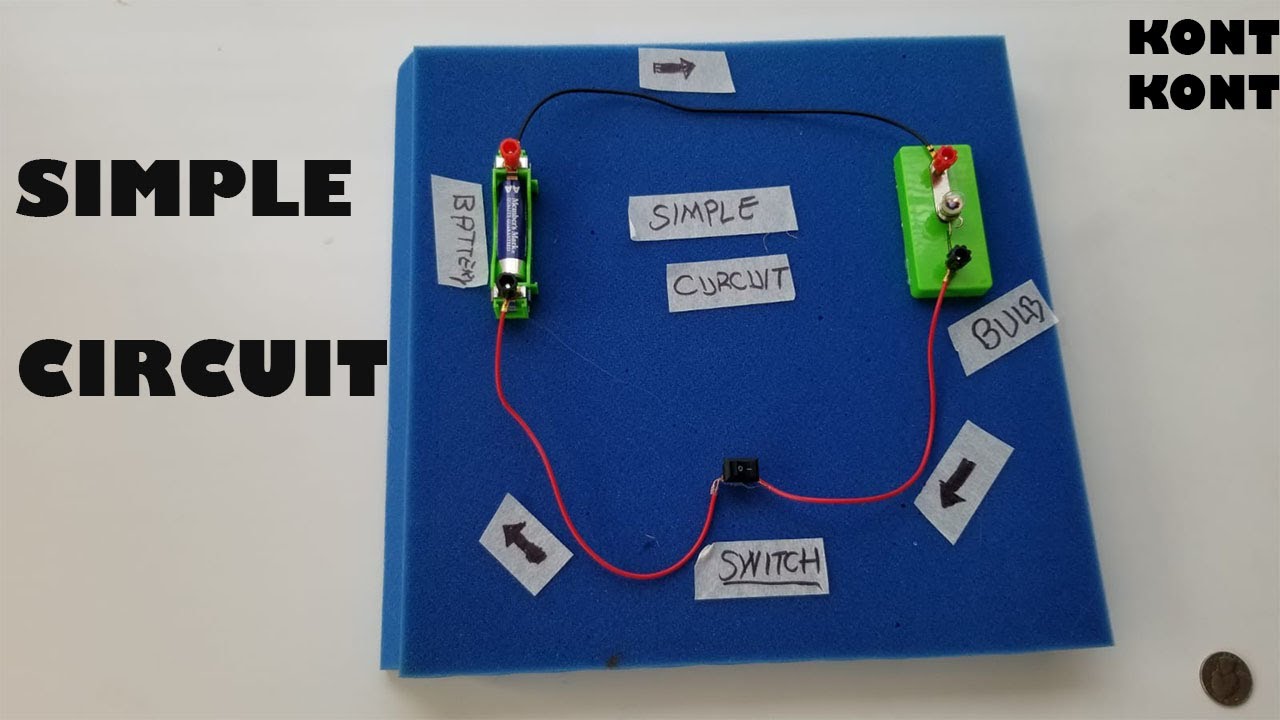
The Components of a Simple Circuit
A simple electric circuit is like a small river, with specific parts that work together to let electricity flow. Here are the key components:
- Battery: The battery is like the source of the river. It provides the energy that pushes the electricity through the circuit. Imagine the battery as a pump that keeps the water flowing in the river.
- Wires: The wires are like the riverbed, providing a path for the electricity to flow. They are made of metal, which allows electricity to pass through easily. Imagine the wires as the channels that guide the water in the river.
- Light Bulb: The light bulb is like a waterfall, where the energy from the electricity is used to create light and heat. The light bulb is connected to the circuit so that the electricity can flow through it. Imagine the light bulb as a place where the water falls and generates energy.
How Electricity Flows in a Circuit
Imagine a simple circuit with a battery, wires, and a light bulb. When the circuit is complete, the battery pushes electricity through the wires to the light bulb. This flow of electricity creates light and heat in the light bulb. The electricity then flows back to the battery, completing the circuit.
Electricity flows in a continuous loop, from the battery, through the wires, to the light bulb, and back to the battery.
Think of it like a game of tag! The electricity starts at the battery, runs through the wires, “tags” the light bulb, and then runs back to the battery. The game continues as long as the circuit is complete and the battery has energy.
Types of Electrical Charge
Electricity is made up of tiny particles called charges. These charges can be either positive or negative. Think of it like a magnet with two poles, a north and a south pole. Just like magnets, these charges also have an attraction and repulsion relationship.
Types of Electrical Charges
The two types of electrical charges are positive and negative.
- Positive Charge: A positive charge is represented by a plus sign (+). It is carried by particles called protons, which are found in the nucleus of an atom.
- Negative Charge: A negative charge is represented by a minus sign (-). It is carried by particles called electrons, which orbit the nucleus of an atom.
Attraction and Repulsion, Was ist elektrischer strom grundschule
Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract each other. This is similar to how two magnets with the same poles will push away from each other, while two magnets with opposite poles will pull towards each other.
Like charges repel. Opposite charges attract.
Properties of Positive and Negative Charges
Here is a table comparing the properties of positive and negative charges:
| Property | Positive Charge | Negative Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | + | – |
| Carried by | Protons | Electrons |
| Location in atom | Nucleus | Orbiting the nucleus |
| Interaction with other charges | Repels other positive charges, attracts negative charges | Repels other negative charges, attracts positive charges |
The Power of Electricity

Electricity is not just a mysterious force; it’s a powerful tool that makes our lives easier and more comfortable. Imagine a world without lights, computers, or even refrigerators. Electricity is the unseen force that powers these devices and countless others.
Electrical Current: The Flow of Charge
Electrical current is the movement of electric charges through a conductor. Think of it like water flowing through a pipe. The electric charges, like electrons, are the water molecules, and the conductor, like a wire, is the pipe. The rate at which these charges flow is measured in amperes (A). A higher current means more charges are flowing per second.
The Relationship Between Voltage and Current
Voltage is the electrical “pressure” that drives the current. Imagine a water tower; the higher the water level in the tower, the more pressure is exerted on the water in the pipes below. Similarly, a higher voltage means more pressure on the electric charges, causing them to flow faster. The relationship between voltage and current is described by Ohm’s Law:
Voltage (V) = Current (I) x Resistance (R)
Resistance is a property of the material that opposes the flow of current. A higher resistance means less current will flow for a given voltage.
How Electricity Powers Devices
Electricity powers devices by converting electrical energy into other forms of energy. Here are some examples:
- Light Bulbs: Electricity flows through a filament in a light bulb, causing it to heat up and emit light. This is an example of converting electrical energy into heat and light energy.
- Electric Motors: Electricity creates a magnetic field that interacts with a rotating coil, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Computers: Electricity powers circuits that process information, converting electrical energy into computational power.
- Refrigerators: Electricity powers a compressor that circulates a refrigerant, converting electrical energy into cooling power.
Electricity and Safety
Electricity is a powerful force that can be very useful, but it can also be dangerous if not handled properly. Just like a sharp knife, electricity can cause serious harm if used carelessly. Therefore, it is important to learn about electrical safety and follow these precautions to avoid accidents.
Electrical Hazards
Electricity can be dangerous because it can cause electric shocks, fires, and even death. It is crucial to be aware of the potential hazards associated with electricity and take necessary precautions to prevent accidents.
- Electric Shock: When an electric current passes through the body, it can cause severe burns, muscle spasms, and even cardiac arrest. This can happen when someone comes into contact with a live wire or faulty electrical equipment.
- Electrical Fires: Overloaded circuits, faulty wiring, and exposed wires can lead to electrical fires. These fires can spread quickly and cause significant damage to property and even result in injuries or fatalities.
- Electrocution: This is a fatal electric shock that can occur when a person comes into contact with a high voltage source. Electrocution is a serious hazard and can happen quickly and unexpectedly.
Safety Tips for Handling Electricity
It is essential to practice electrical safety at all times to protect yourself and others from potential hazards. Here are some important tips to keep in mind:
- Never touch electrical wires or equipment with wet hands: Water conducts electricity, increasing the risk of electric shock.
- Never overload electrical outlets: Overloading circuits can cause overheating and lead to fires.
- Use caution when working around electrical equipment: Always unplug electrical appliances before working on them.
- Keep electrical cords away from heat sources: Heat can damage cords and increase the risk of fire.
- Inspect electrical cords regularly for damage: Damaged cords should be replaced immediately.
- Never use electrical appliances in wet areas: This includes bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas during rainy weather.
- Teach children about electrical safety: Explain the dangers of electricity and how to handle it safely.
- Call a qualified electrician for any electrical repairs: Attempting to fix electrical problems yourself can be dangerous and should be left to professionals.
Electrical Safety Poster
To further emphasize the importance of electrical safety, consider creating a poster with the following safety tips:
“Electricity is powerful and can be dangerous. Be careful and follow these safety tips.”
- Never touch electrical wires or equipment with wet hands.
- Never overload electrical outlets.
- Use caution when working around electrical equipment.
- Keep electrical cords away from heat sources.
- Inspect electrical cords regularly for damage.
- Never use electrical appliances in wet areas.
- Teach children about electrical safety.
- Call a qualified electrician for any electrical repairs.
So, there you have it! Electricity is a super cool force that’s everywhere, powering our lives. From the light bulbs in our homes to the phones in our pockets, electricity is a vital part of our world. Remember, it’s important to be safe around electricity, so always ask a grown-up if you have any questions. Keep exploring, keep learning, and keep the power of electricity flowing!
Questions and Answers
Can electricity be dangerous?
Yes, electricity can be dangerous if not handled properly. It’s important to always follow safety rules and never touch electrical wires or outlets without an adult’s supervision.
How do I make a simple circuit?
You can make a simple circuit using a battery, wires, and a light bulb. Connect the wires to the battery and the light bulb, and watch the light bulb light up! It’s a fun and easy way to learn about how circuits work.
What are some examples of how electricity is used in everyday life?
Electricity powers everything from your TV and computer to your refrigerator and washing machine. It’s also used to power cars, trains, and airplanes.






