Was ist MWh bei Strom? This question delves into the heart of understanding how we consume electricity, a fundamental aspect of modern life. MWh, or megawatt-hours, is a unit of energy measurement often used to quantify large-scale electricity consumption, like that of a household, a factory, or even an entire city. Understanding MWh helps us comprehend the scale of our energy usage, the costs associated with it, and the potential for efficiency improvements.
Imagine a world where electricity is a constant, a reliable force that powers our homes, businesses, and transportation. But how do we measure this energy that fuels our lives? Enter the MWh, a unit that quantifies the amount of electricity we use. MWh is essentially a measurement of power over time. Just as a kilowatt-hour (kWh) measures the energy used by a single appliance, MWh measures the energy used by a larger system, like a whole building or even a city.
Understanding MWh in the Context of Electricity
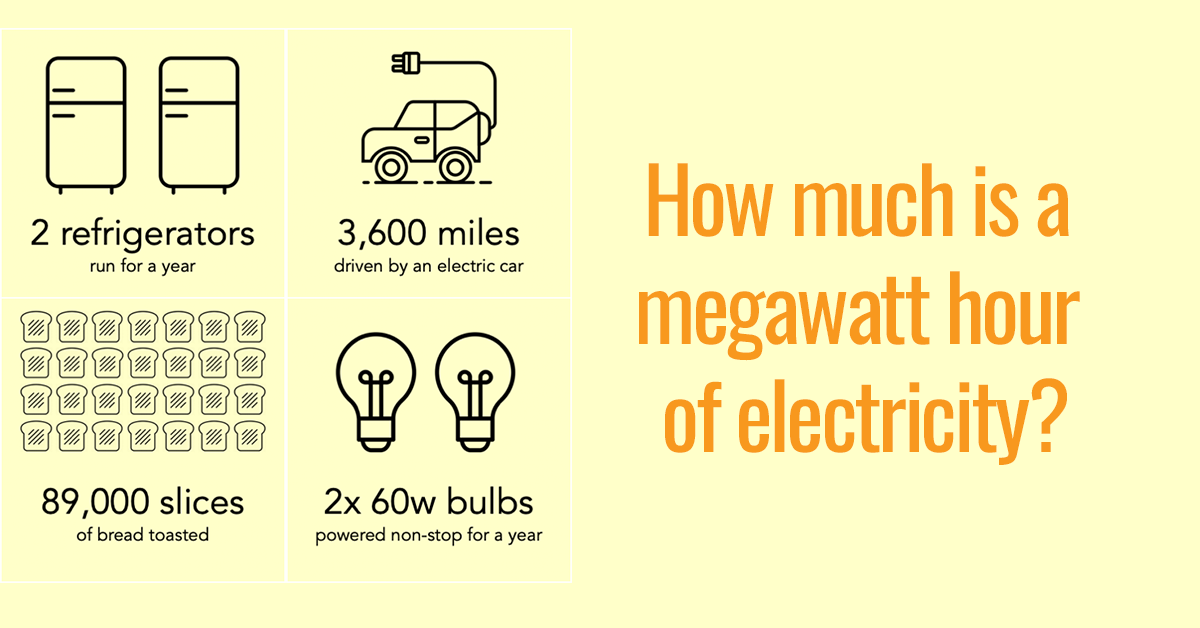
When discussing electricity consumption, you’ll often encounter the unit “MWh.” This stands for megawatt-hour, a measurement of electrical energy. It’s a crucial concept for understanding how much electricity is being used, especially in large-scale applications like power plants and industrial facilities.
The Definition of MWh, Was ist mwh bei strom
A megawatt-hour (MWh) represents the amount of energy consumed by a device or system operating at a power output of one megawatt (MW) for one hour. It’s a unit of energy, similar to kilowatt-hours (kWh), but on a larger scale. To put it simply, 1 MWh is equal to 1,000 kWh.
MWh in Everyday Life
Imagine a household with an average energy consumption of 10 kWh per day. Over a year, this translates to 3,650 kWh, which is equivalent to 3.65 MWh. While this is a small amount compared to industrial usage, it illustrates how MWh is used to measure energy consumption in everyday life.
The Significance of MWh for Electricity Bills

Understanding how MWh impacts your electricity bill is crucial for managing your energy consumption and costs effectively. The amount of electricity you consume, measured in MWh, is directly linked to the amount you pay on your bill.
The Relationship Between MWh Consumption and Electricity Bills
Your electricity bill is determined by the total amount of energy you consume, expressed in MWh, multiplied by the price per MWh set by your electricity provider. Several factors influence the cost of electricity, including:
- Energy tariffs: Different electricity providers offer varying tariffs based on your consumption levels, time of day, and other factors. For example, some tariffs offer lower rates during off-peak hours (e.g., overnight) and higher rates during peak hours (e.g., afternoon).
- Energy consumption: The more electricity you consume, the higher your bill will be. This is directly proportional to the amount of MWh you use.
- Government taxes and levies: These charges, such as the carbon tax or renewable energy levy, are added to your bill and can vary depending on your location and the electricity provider.
- Network charges: These charges cover the costs of maintaining the electricity network, including transmission and distribution lines, and are typically based on your connection capacity.
How MWh Consumption Translates into Financial Costs
The cost of electricity is usually expressed in cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh) or dollars per megawatt-hour (MWh). To understand how MWh consumption translates into financial costs, consider this:
One MWh is equivalent to 1,000 kWh.
Therefore, if your electricity provider charges 20 cents per kWh, the cost of 1 MWh would be:
- cents/kWh
- 1,000 kWh/MWh = $200/MWh.
Comparing Electricity Costs Based on MWh Consumption
Let’s illustrate how electricity costs vary based on different MWh consumption levels. Imagine two households with different energy consumption patterns:
| Household | MWh Consumption | Electricity Price (cents/kWh) | Total Bill ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Household A | 10 MWh | 20 | 2,000 |
| Household B | 20 MWh | 20 | 4,000 |
As you can see, Household B, which consumes twice as much electricity as Household A, pays twice as much for their electricity bill.
MWh and Energy Efficiency: Was Ist Mwh Bei Strom
Reducing your MWh consumption is not only good for your wallet but also for the environment. By using energy more efficiently, you can lower your electricity bills and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Energy-Saving Strategies and Technologies
There are many ways to reduce your MWh consumption and improve energy efficiency.
- Upgrade your appliances: Replacing older, less efficient appliances with newer, energy-efficient models can significantly reduce your energy consumption. For example, a new refrigerator can save you hundreds of dollars in electricity costs over its lifetime.
- Use energy-efficient lighting: LED lights are much more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. They use less energy and last much longer, saving you money in the long run.
- Insulate your home: Proper insulation helps keep your home cool in the summer and warm in the winter, reducing the amount of energy needed to heat and cool your home. This can have a significant impact on your MWh consumption.
- Install a programmable thermostat: A programmable thermostat can automatically adjust your home’s temperature when you are away or asleep, reducing your energy consumption.
- Use energy-efficient windows: Double- or triple-paned windows can help reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, making your home more energy-efficient.
- Unplug electronics when not in use: Even when turned off, many electronics continue to draw power, known as “phantom load.” Unplugging these devices when not in use can save you money on your electricity bill.
- Use natural light: Maximize the use of natural light during the day by opening curtains and blinds. This can reduce your reliance on artificial lighting.
- Install solar panels: Solar panels can generate electricity from sunlight, reducing your reliance on the grid and your MWh consumption.
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Energy Star-rated appliances are designed to use less energy than standard models, reducing your MWh consumption.
Benefits of Reducing MWh Consumption
Reducing your MWh consumption offers many benefits for both individuals and the environment:
- Lower electricity bills: By using less energy, you can save money on your electricity bills.
- Reduced environmental impact: Generating electricity often involves burning fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Reducing your MWh consumption helps reduce these emissions and combat climate change.
- Increased energy independence: By using less energy, you become less reliant on the power grid and can potentially even generate your own electricity through renewable sources.
“Energy efficiency is the most cost-effective and readily available energy resource. By using energy more wisely, we can save money, protect the environment, and improve our quality of life.”U.S. Department of Energy
MWh in the Energy Sector

The megawatt-hour (MWh) plays a crucial role in the energy sector, serving as the standard unit for measuring electricity generation, consumption, and trading. Its significance extends to both traditional power plants and renewable energy sources, providing a common language for understanding energy production and distribution.
Measuring Power Plant Output
MWh is used to quantify the total amount of electricity generated by power plants. For instance, a coal-fired power plant operating at a capacity of 1,000 megawatts (MW) for 24 hours would generate 24,000 MWh of electricity. This measurement helps in assessing the plant’s efficiency, comparing its performance with other power plants, and determining the cost of electricity production.
Measuring Renewable Energy Production
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, also use MWh to measure their output. A solar farm with a capacity of 100 MW, operating for 6 hours of peak sunlight, would generate 600 MWh of electricity. This measurement is essential for understanding the potential of renewable energy sources, planning grid integration, and evaluating their contribution to the overall energy mix.
Comparison of Energy Sources
| Energy Source | MWh Production Capabilities | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Coal-fired Power Plant | High (depending on plant size and operating hours) | Large-scale power generation, but significant carbon emissions. |
| Natural Gas Power Plant | Moderate (depending on plant size and operating hours) | Lower emissions than coal, but still a fossil fuel. |
| Nuclear Power Plant | High (depending on plant size and operating hours) | Low carbon emissions, but safety concerns and radioactive waste. |
| Solar Power Plant | Variable (dependent on sunlight intensity and duration) | Clean energy source, but intermittent production. |
| Wind Power Plant | Variable (dependent on wind speed and duration) | Clean energy source, but intermittent production. |
MWh and Climate Change
The consumption of MWh (megawatt-hours) is directly linked to greenhouse gas emissions, a major contributor to climate change. Understanding this connection is crucial for mitigating our environmental impact and transitioning to a sustainable future.
The Relationship Between MWh Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The production of electricity from fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The more MWh generated from these sources, the greater the emissions.
For example, burning one ton of coal to generate electricity produces approximately 2.5 tons of CO2.
Therefore, reducing our MWh consumption from fossil fuel-based sources is essential for lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
The Environmental Impact of Different Energy Sources
The environmental impact of different energy sources varies significantly based on their MWh output and associated emissions.
- Fossil Fuels (Coal, Oil, Natural Gas): These sources are the primary contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily CO2. Coal is the most polluting, followed by oil and natural gas.
- Renewable Energy (Solar, Wind, Hydro): These sources are considered clean and sustainable as they produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions.
- Nuclear Power: Nuclear power plants generate electricity without producing greenhouse gases, but they pose risks related to radioactive waste and potential accidents.
Visual Representation of MWh and Carbon Footprint
A simple bar chart can illustrate the connection between MWh consumption and carbon footprint. The X-axis represents different energy sources, and the Y-axis represents MWh consumed and corresponding CO2 emissions. The bars representing fossil fuels would be significantly taller than those representing renewable sources, highlighting the significant difference in their environmental impact.
Understanding MWh is crucial for navigating the complexities of energy consumption, costs, and environmental impact. By grasping the significance of MWh, we can make informed decisions about our energy use, contributing to a more sustainable future. As we delve deeper into the world of electricity, we realize that every watt, every kilowatt-hour, and every megawatt-hour plays a vital role in shaping our energy landscape.
Question Bank
How is MWh related to kWh?
MWh stands for megawatt-hours, which is equivalent to 1,000 kilowatt-hours (kWh). Think of it like this: 1 MWh is a larger unit used for measuring larger amounts of electricity consumption, while kWh is a smaller unit used for measuring smaller amounts of electricity consumption.
What are some practical examples of how MWh is used in everyday life?
Imagine a typical household’s monthly electricity bill. It might state that you used 500 kWh of electricity. This could be expressed as 0.5 MWh. Similarly, a large factory might consume 10,000 MWh of electricity per month to power its machinery and operations.
What are some common energy-saving strategies that impact MWh usage?
Simple changes like using energy-efficient appliances, switching off lights when leaving a room, and utilizing natural light can significantly reduce MWh consumption. Additionally, investing in renewable energy sources like solar panels can further decrease your dependence on traditional energy sources and lower your MWh usage.
What is the relationship between MWh consumption and greenhouse gas emissions?
The more MWh we consume, the greater our reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation, which leads to higher greenhouse gas emissions. Transitioning to renewable energy sources and adopting energy-efficient practices can help mitigate these emissions and reduce our carbon footprint.






