Was kostet 1 kWh Strom 2018? This question, translated as “How much did 1 kWh of electricity cost in 2018?”, delves into the fascinating world of energy costs in Germany. The year 2018 marked a pivotal point in the country’s energy landscape, with a growing emphasis on renewable sources and a dynamic interplay of factors shaping electricity prices.
Understanding the cost of electricity in 2018 requires a journey through Germany’s energy history. We’ll explore the fluctuations in electricity prices from 2010 to 2018, analyzing the role of government policies, global energy markets, and the rise of renewable energy sources. By comparing German prices to those in other European countries, we’ll gain a broader perspective on the forces driving the energy market.
Understanding “Was kostet 1 kWh Strom 2018”
The phrase “Was kostet 1 kWh Strom 2018” is a German question that translates to “How much does 1 kWh of electricity cost in 2018?” This question is relevant to understanding the cost of energy in Germany during that specific year. It reflects the concerns of individuals and businesses about energy expenses and the potential impact of fluctuating electricity prices.
Interpretations of “Was kostet 1 kWh Strom 2018”
The phrase can be interpreted in various ways, depending on the context and the specific information being sought. * The average cost of 1 kWh of electricity: This interpretation focuses on the general price of electricity for residential or commercial consumers in Germany during 2018. It could refer to an average price calculated across different energy providers and tariffs.
The cost of 1 kWh of electricity from a specific provider
This interpretation considers the price charged by a particular energy provider for 1 kWh of electricity in 2018. It would take into account the specific tariff offered by the provider, which might vary depending on factors such as consumption volume, contract duration, and other services included.
The cost of 1 kWh of electricity for a particular purpose
This interpretation considers the cost of electricity for a specific application, such as heating, lighting, or powering appliances. It might take into account the energy efficiency of the appliances and the time of day when the electricity is used, as some tariffs offer different rates for peak and off-peak hours.
Historical Electricity Prices in Germany: Was Kostet 1 Kwh Strom 2018
Electricity prices in Germany have fluctuated considerably over the past decade, influenced by a complex interplay of factors including energy demand, fuel costs, regulatory policies, and the increasing integration of renewable energy sources. Understanding these historical trends provides valuable insights into the dynamics of the German electricity market and its future trajectory.
Electricity Price Trends from 2010 to 2018
The following timeline provides a detailed overview of electricity prices in Germany from 2010 to 2018:
- 2010: The average electricity price in Germany was €0.19 per kilowatt-hour (kWh). This period was marked by relatively stable prices due to a combination of factors, including moderate energy demand and stable fuel prices.
- 2011: Electricity prices rose to €0.21 per kWh, driven by increased demand and rising fuel costs, particularly for natural gas. The Fukushima disaster in Japan also led to concerns about nuclear power safety, contributing to higher prices.
- 2012: Prices continued to climb, reaching €0.23 per kWh, as Germany’s phase-out of nuclear power and the increasing use of renewable energy sources led to higher grid costs and a reliance on more expensive conventional power plants.
- 2013: Prices stabilized slightly, averaging €0.22 per kWh. However, the trend towards higher prices persisted due to the ongoing transition to renewable energy sources and the increasing costs associated with the integration of intermittent renewables into the grid.
- 2014: Prices experienced a slight decline, falling to €0.21 per kWh, primarily due to lower natural gas prices and increased competition in the electricity market.
- 2015: Prices continued to decline, reaching €0.19 per kWh, as the impact of lower oil prices and the continued growth of renewable energy sources, particularly solar power, put downward pressure on prices.
- 2016: Electricity prices rose slightly to €0.20 per kWh, influenced by a combination of factors including the rising cost of renewable energy subsidies and increased demand for electricity.
- 2017: Prices remained relatively stable at €0.20 per kWh, with the impact of renewable energy sources being offset by the increasing costs associated with grid infrastructure and the phase-out of nuclear power.
- 2018: Electricity prices continued to hover around €0.20 per kWh, reflecting the ongoing balance between the increasing share of renewable energy sources and the rising costs associated with grid infrastructure and the phase-out of nuclear power.
Factors Influencing Electricity Price Fluctuations
Several key factors have influenced electricity price fluctuations in Germany during this period:
- Energy Demand: Fluctuations in energy demand, driven by economic activity, weather patterns, and industrial production, have a significant impact on electricity prices. Higher demand generally leads to higher prices, as power plants need to operate at higher capacity.
- Fuel Costs: The cost of fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, and oil, is a major driver of electricity prices. Fluctuations in global fuel prices, driven by factors such as supply and demand, geopolitical events, and currency exchange rates, directly impact the cost of generating electricity.
- Regulatory Policies: Government policies, such as subsidies for renewable energy sources, taxes on fossil fuels, and regulations on emissions, have a significant impact on electricity prices. These policies can either increase or decrease the cost of generating and distributing electricity.
- Renewable Energy Sources: The increasing integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, has had a complex impact on electricity prices. While these sources can reduce the cost of electricity generation, they also pose challenges for grid stability and require significant investments in grid infrastructure, which can increase costs.
- Nuclear Power Phase-out: Germany’s decision to phase out nuclear power by 2022 has contributed to higher electricity prices. Replacing nuclear power plants with conventional power plants, particularly gas-fired plants, has increased the reliance on more expensive fuels and has also led to higher grid costs.
Impact of Renewable Energy Sources on Electricity Prices in 2018
The increasing share of renewable energy sources in Germany’s electricity mix has had a mixed impact on electricity prices in 2018. While renewable energy sources can reduce the cost of electricity generation, they also pose challenges for grid stability and require significant investments in grid infrastructure, which can increase costs.
“The increasing share of renewable energy sources in Germany’s electricity mix has had a mixed impact on electricity prices in 2018. While renewable energy sources can reduce the cost of electricity generation, they also pose challenges for grid stability and require significant investments in grid infrastructure, which can increase costs.”
In 2018, Germany achieved a record high share of renewable energy in its electricity mix, with wind and solar power contributing significantly to the country’s energy supply. This increased reliance on renewable energy sources has helped to reduce the cost of electricity generation, as these sources are often cheaper than fossil fuels. However, the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources, particularly wind and solar power, poses challenges for grid stability.
When renewable energy sources are not producing electricity, for example, during periods of low wind or sunshine, the grid must rely on more expensive conventional power plants to meet demand. This can lead to higher electricity prices. Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid requires significant investments in infrastructure, such as high-voltage transmission lines and storage facilities.
These investments can increase the cost of electricity for consumers.The impact of renewable energy sources on electricity prices in Germany is a complex issue with no simple answers. While renewable energy sources have the potential to reduce electricity costs, they also pose challenges for grid stability and require significant investments in infrastructure. The overall impact on electricity prices will depend on the balance between these factors.
Key Factors Affecting Electricity Prices in 2018
In 2018, electricity prices in Germany were influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including market dynamics, government policies, and global energy trends. Understanding these factors is crucial for analyzing the price fluctuations and predicting future trends in the German electricity market.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a significant role in shaping electricity prices. The German government has implemented various policies to promote renewable energy sources and reduce carbon emissions, such as the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG). These policies have a direct impact on electricity prices by influencing the cost of renewable energy production and incentivizing investments in renewable energy infrastructure.
- The EEG imposes a surcharge on electricity consumers to fund the development of renewable energy sources. This surcharge contributes to the overall cost of electricity, influencing the final price paid by consumers.
- The German government has also implemented a carbon tax, which adds an additional cost to fossil fuel-based electricity generation. This tax aims to reduce carbon emissions and incentivize the shift towards cleaner energy sources, impacting the competitiveness of fossil fuel-based power plants.
Impact of Global Energy Markets
Germany’s electricity market is closely linked to global energy markets, making it susceptible to fluctuations in global energy prices. Global events and trends, such as geopolitical tensions, economic conditions, and supply and demand dynamics, can significantly impact the price of energy commodities like oil and gas.
- Fluctuations in global oil and gas prices can influence the cost of fossil fuel-based electricity generation in Germany, affecting the overall price of electricity.
- Changes in global energy demand, driven by factors such as economic growth and industrial activity, can also influence electricity prices. For instance, increased demand for natural gas in other regions can lead to higher prices in Germany, impacting the cost of gas-fired power plants.
Comparison of Electricity Prices in 2018
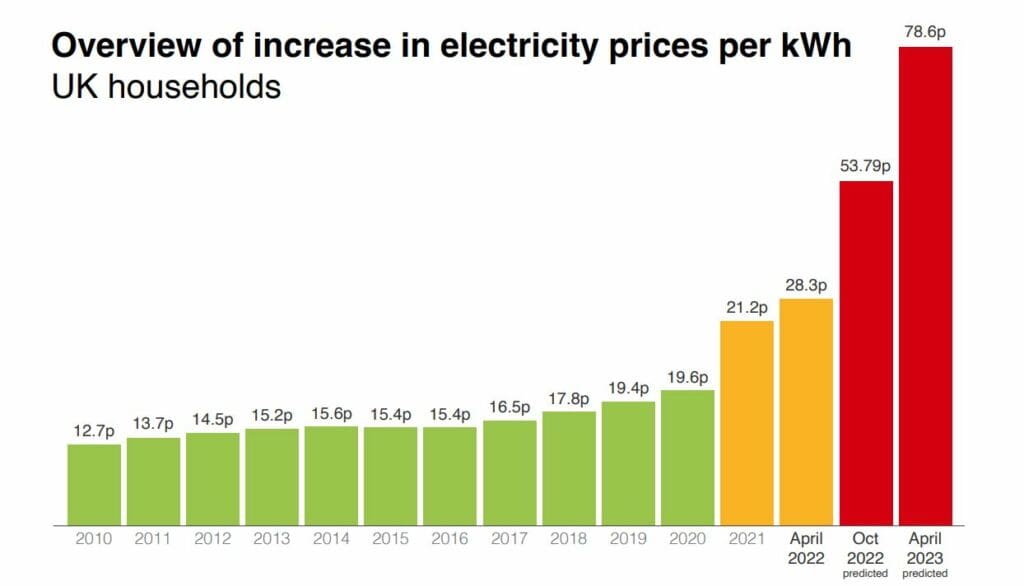
In 2018, Germany’s electricity prices were comparable to those of other European countries, with some variations based on factors such as energy mix, regulatory policies, and market dynamics. Understanding these price differences is crucial for comprehending the broader energy landscape in Europe.
Electricity Price Comparison Across European Countries
A comparative analysis of electricity prices across European countries in 2018 reveals a range of factors contributing to these differences.
- Germany’s average electricity price in 2018 was €0.29 per kilowatt-hour (kWh), according to Eurostat data. This placed Germany in the middle range of electricity prices among European countries.
- Countries like Denmark and Sweden, with a high reliance on renewable energy sources, experienced lower electricity prices than Germany, averaging around €0.23 per kWh.
- Conversely, countries like Belgium and Italy, with a higher reliance on fossil fuels, had higher electricity prices, averaging around €0.32 per kWh.
Factors Influencing Electricity Price Differences
Several factors contribute to the variations in electricity prices across European countries.
- Energy Mix: The composition of an electricity generation mix significantly impacts prices. Countries heavily reliant on renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, tend to have lower electricity prices due to the relatively low cost of these sources. Conversely, countries with a higher reliance on fossil fuels, such as coal and natural gas, face higher electricity prices due to the fluctuating costs of these fuels.
- Regulatory Policies: Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping electricity prices. For example, subsidies for renewable energy, carbon taxes, and feed-in tariffs can influence the cost of electricity generation and, consequently, the final price for consumers.
- Market Structure: The structure of the electricity market, including the presence of competition and regulation, can affect electricity prices. Countries with more competitive electricity markets tend to have lower prices due to greater market forces driving down costs.
Impact of Energy Mix on Electricity Prices
The energy mix employed by different European countries significantly impacts electricity prices.
- Countries with a high proportion of renewable energy sources in their energy mix generally have lower electricity prices. For example, Denmark and Sweden, with a high reliance on wind and hydropower, have relatively low electricity prices. This is because renewable energy sources, once installed, have low operating costs.
- Conversely, countries with a higher reliance on fossil fuels, such as coal and natural gas, often face higher electricity prices. These fuels are subject to price fluctuations, which can significantly impact the cost of electricity generation.
Impact of Electricity Prices on Consumers and Businesses

Electricity prices have a significant impact on both consumers and businesses in Germany. Fluctuations in electricity prices can affect household budgets, business profitability, and the overall economic landscape. This section will delve into the impact of electricity prices on consumers and businesses in Germany during 2018.
Impact on Consumers
Consumers in Germany are directly affected by changes in electricity prices. Higher electricity prices can lead to increased household expenses, particularly for energy-intensive appliances and activities.
- Increased Household Expenses: Higher electricity prices translate into higher energy bills, reducing disposable income and potentially impacting other household expenses.
- Reduced Consumer Spending: Rising energy costs can force consumers to cut back on other spending, impacting the overall economy.
- Energy Poverty: For low-income households, high electricity prices can lead to energy poverty, where individuals struggle to afford basic energy needs, potentially impacting health and well-being.
Impact on Businesses, Was kostet 1 kwh strom 2018
Businesses are also significantly impacted by electricity price fluctuations. Unpredictable price changes can lead to challenges in cost management, financial planning, and competitiveness.
- Cost Management: Businesses face the challenge of managing energy costs effectively, as fluctuating electricity prices can impact profitability and competitiveness.
- Financial Planning: Unpredictable price changes make it difficult for businesses to accurately forecast future energy expenses, impacting financial planning and investment decisions.
- Competitiveness: Businesses that rely heavily on electricity may face a competitive disadvantage if energy costs rise, particularly in industries with high energy consumption.
Strategies for Mitigating the Impact of High Electricity Prices
To mitigate the impact of high electricity prices, consumers and businesses can adopt various strategies:
- Energy Efficiency: Investing in energy-efficient appliances, insulation, and lighting can significantly reduce electricity consumption and lower energy bills.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Switching to renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, can help businesses and consumers reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and potentially lower energy costs in the long term.
- Demand Response: Participating in demand response programs allows consumers and businesses to adjust their electricity consumption based on real-time pricing signals, potentially reducing costs during peak demand periods.
- Energy Storage: Investing in energy storage systems, such as batteries, can help businesses and consumers manage their electricity consumption and reduce their reliance on the grid, potentially lowering energy costs.
- Government Support: Government policies, such as subsidies for renewable energy or energy efficiency upgrades, can help mitigate the impact of high electricity prices on consumers and businesses.
Future Trends in Electricity Prices
Predicting future electricity prices in Germany is a complex task, influenced by various factors, including technological advancements, energy efficiency measures, and government policies. However, based on current trends and projections, certain patterns can be observed.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in renewable energy sources, energy storage, and smart grids are expected to have a significant impact on electricity prices in the years following 2018.
- The increasing affordability and efficiency of renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, are likely to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, leading to lower electricity prices.
- Advancements in energy storage technologies, such as battery storage, will enable greater integration of renewable energy sources into the grid, reducing the need for traditional power plants and potentially lowering electricity prices.
- Smart grid technologies, which enable real-time monitoring and control of energy consumption, can optimize grid efficiency and reduce electricity waste, potentially leading to lower prices.
Role of Energy Efficiency Measures
Energy efficiency measures play a crucial role in shaping future electricity prices.
- Improved energy efficiency in buildings, appliances, and industrial processes can reduce overall electricity demand, potentially lowering prices.
- Government incentives and regulations promoting energy efficiency can encourage consumers and businesses to adopt energy-saving technologies and practices, contributing to lower electricity consumption and potentially lower prices.
The cost of 1 kWh of electricity in 2018 reflects a complex web of factors, highlighting the delicate balance between energy security, affordability, and environmental sustainability. As Germany continues its transition to a renewable energy future, understanding the forces that shaped electricity prices in 2018 provides valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities ahead. By analyzing past trends and considering the impact of technology, government policies, and global energy markets, we can gain a clearer picture of the future of electricity prices in Germany and beyond.
Common Queries
What are the main factors influencing electricity prices in Germany?
Electricity prices in Germany are influenced by a variety of factors, including the cost of fuel, the availability of renewable energy sources, government policies, and the overall state of the global energy market.
How do electricity prices in Germany compare to other European countries?
Electricity prices in Germany are generally higher than in some other European countries, but lower than in others. The specific price differences are influenced by a range of factors, including energy mix, regulatory policies, and market structure.
What are the potential strategies for mitigating the impact of high electricity prices?
Strategies for mitigating the impact of high electricity prices include investing in energy efficiency measures, diversifying energy sources, and exploring alternative energy technologies.






