How much is it to send mail? This seemingly simple question opens a world of variables impacting the cost of sending letters and packages. From domestic envelopes to international parcels, the price hinges on a multitude of factors: weight, size, destination, service type, and additional options like insurance or tracking. Understanding these nuances is key to budget-conscious mailing, ensuring your correspondence and packages reach their destinations efficiently and affordably.
This guide will navigate you through the intricacies of postal pricing, empowering you to make informed choices.
We’ll delve into the cost breakdowns for domestic and international mail, exploring the differences between various shipping carriers and services. Discover how factors like package dimensions and the chosen delivery speed significantly influence the final price. We’ll also equip you with practical tips and strategies for minimizing mailing expenses, from optimizing packaging to utilizing online postage calculators. By the end, you’ll possess the knowledge to send mail effectively and economically.
Domestic Mail Costs

Understanding domestic mail costs in the United States requires careful consideration of several factors, primarily weight, size, service type, and additional features. Failing to account for these variables can lead to unexpected expenses. This section provides a clear breakdown to aid in accurate cost estimation.
USPS Postage Costs for Letters and Packages
The United States Postal Service (USPS) offers a tiered pricing structure based on weight and size, differentiating between letters and packages. While precise rates fluctuate, the following table provides a general overview. Note that these are estimates and may not reflect current, exact pricing. Always check the official USPS website for the most up-to-date information.
| Weight | Size | Letter Rate | Package Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 1 ounce | Standard Letter Size | $0.60 (estimate) | N/A |
| 1-3 ounces | Standard Letter Size | $0.80 – $1.00 (estimate) | N/A |
| Over 3 ounces | Standard Letter Size | Variable (estimate) | Variable (estimate) |
| Under 1 pound | Small Package | N/A | $8.00 – $12.00 (estimate) |
| 1-3 pounds | Medium Package | N/A | $15.00 – $25.00 (estimate) |
| Over 3 pounds | Large Package | N/A | Variable (estimate) |
Comparison of USPS Mail Services
First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, and other USPS services offer varying speed and cost. First-Class Mail is the most economical option for letters and small packages, prioritizing delivery speed over absolute cost. Priority Mail offers faster delivery but at a significantly higher price point. Other services, like Media Mail (for books and educational materials) or Parcel Select (for larger packages), cater to specific needs and offer potentially lower rates depending on the item’s characteristics.
Impact of Additional Services on Cost
Adding services like tracking, insurance, or signature confirmation increases the overall cost. Tracking provides updates on the package’s location, insurance protects against loss or damage, and signature confirmation ensures the recipient personally receives the item. These are valuable additions, but their cost should be factored into the budget. For example, adding insurance to a Priority Mail package could easily add $5-$10 or more depending on the declared value of the contents.
USPS vs. Other Carriers
While USPS is a dominant player, FedEx and UPS offer competitive domestic mail services. Their pricing models often depend on factors like weight, distance, and service level. Generally, for standard domestic mail, USPS tends to be more affordable for lighter packages, while FedEx and UPS become more competitive for heavier or expedited shipments. A direct comparison requires real-time quotes from each carrier based on specific package details.
For example, a small, light package might cost $5 with USPS, $10 with FedEx, and $8 with UPS. However, for larger, heavier items, this pricing structure might reverse.
International Mail Costs

Sending mail internationally is significantly more complex and expensive than domestic shipping. Numerous factors contribute to the final cost, making it crucial to understand these variables before shipping to avoid unexpected expenses. Accurate cost estimations require careful consideration of destination, package weight, and the chosen shipping method.
International postage rates are considerably higher than domestic rates due to the increased distance, handling, and customs procedures involved. The added complexity of navigating international regulations and logistical challenges necessitates a more robust pricing structure.
International Shipping Cost Comparison
The cost of international shipping varies dramatically based on the destination country and the weight of the package. Heavier packages naturally incur higher costs due to increased fuel consumption and handling requirements. Geographical distance also plays a significant role; shipping to Australia will generally be more expensive than shipping to Canada.
- A 1-pound package to the UK might cost around $20-$30, while the same package to Australia could cost $30-$40 or more.
- A 5-pound package to a nearby country like Mexico might cost around $40-$60, whereas shipping the same package to Japan could cost $80-$120 or more.
- Shipping a 10-pound package to a European country might range from $100-$150, depending on the specific country and service selected. Shipping the same package to a country in South America could easily exceed $150.
Factors Influencing International Postage Rates
Several key factors influence the final cost of international postage. Understanding these factors is essential for accurate budgeting and efficient shipping.
- Weight and Dimensions: Larger and heavier packages inherently cost more to ship due to increased volume and handling needs.
- Destination Country: Shipping to distant countries involves greater fuel consumption and logistical complexity, leading to higher costs. Customs regulations and infrastructure in the destination country also impact pricing.
- Shipping Speed: Faster shipping options, such as express mail, are significantly more expensive than slower, economy services. The trade-off between speed and cost is a critical consideration.
- Customs Fees and Duties: Import duties, taxes, and customs brokerage fees are levied by the destination country and are the responsibility of the recipient. These fees can add substantially to the overall cost and are often unpredictable.
- Insurance: Adding insurance to protect against loss or damage during transit will increase the shipping cost.
International Shipping Options
Various shipping options exist for international mail, each offering a different balance between speed, cost, and tracking capabilities. Choosing the appropriate service depends on the urgency and value of the shipment.
- USPS: Offers a range of international services, including First-Class Package International Service, Priority Mail Express International, and Priority Mail International. Each service provides varying levels of speed and tracking.
- UPS and FedEx: These private carriers provide a wider array of international shipping options, often with more advanced tracking and faster delivery times, but at a higher cost.
- DHL: Another major international carrier offering various services with a focus on speed and reliability.
Average International Shipping Costs for a 1lb Package
The following table provides estimated average costs for sending a 1-pound package internationally to various regions. These are estimates and can vary based on the specific carrier, service level, and destination country within the region. Always check with the carrier for the most up-to-date pricing.
| Region | Average Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Europe | $25 – $40 |
| Asia | $30 – $50 |
| South America | $40 – $60 |
| Australia | $45 – $70 |
| Africa | $50 – $80 |
Factors Affecting Mail Costs
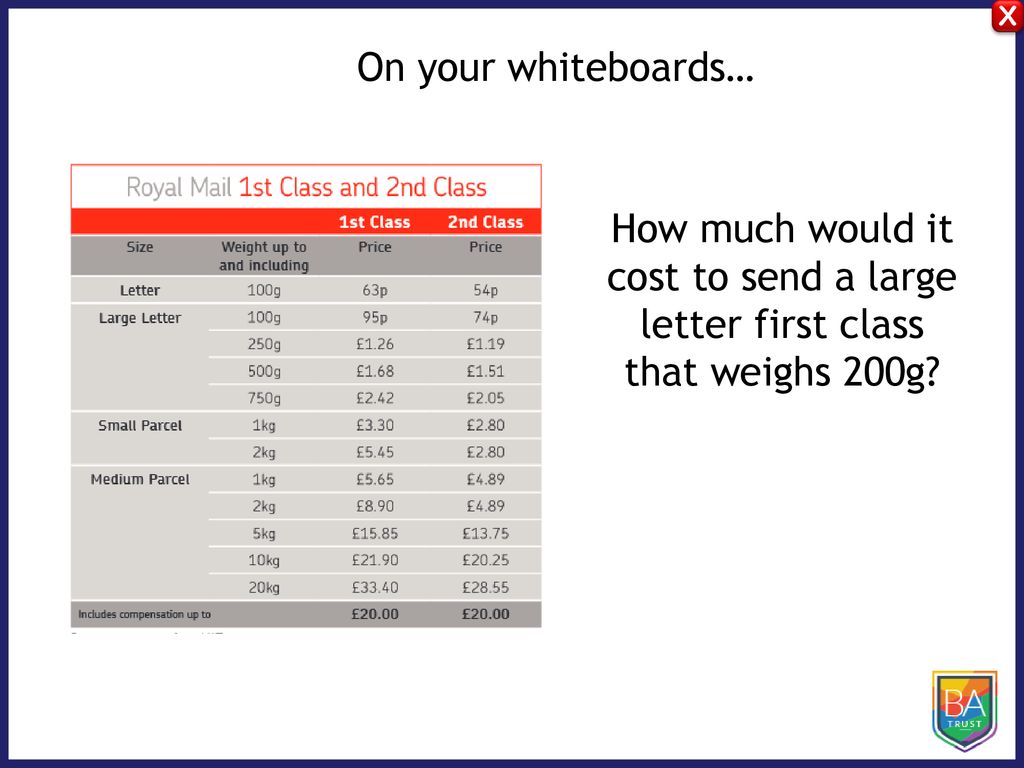
The price of sending mail is not solely determined by weight and distance. Several other crucial factors significantly impact the final cost, often leading to unexpected expenses if not carefully considered. Understanding these factors allows for better budgeting and more efficient shipping practices. This section will detail these key influences on mailing costs.
Packaging Materials Influence on Shipping Costs
The type and quality of packaging materials directly affect shipping costs. Heavier packaging, such as rigid boxes or excessive amounts of padding, increase the overall weight, leading to higher postage fees. Conversely, using lightweight yet protective materials, such as bubble mailers or appropriately sized boxes filled with minimal packing peanuts, can significantly reduce costs. Furthermore, the durability of the packaging influences the risk of damage during transit.
Damage necessitates claims processing and potentially replacement shipments, adding further expenses. Choosing robust packaging that adequately protects the contents is a cost-effective strategy in the long run, even if the initial material cost is slightly higher.
Package Dimensions and Cost
Package dimensions, alongside weight, are critical in determining shipping costs. Dimensional weight, often calculated as a function of length, width, and height, is frequently used by carriers to determine the price. A large, lightweight package might have a higher dimensional weight than its actual weight, resulting in a higher shipping cost. For example, a large, empty cardboard box will be charged based on its dimensional weight, even though its actual weight is negligible.
Optimizing package size to minimize wasted space is essential for cost-effectiveness. Choosing the smallest appropriately sized box for the contents directly reduces shipping costs by lowering the dimensional weight.
Cost-Effectiveness of Different Packaging Options
The most cost-effective packaging option depends heavily on the type of mail and the item being shipped. For example, sending a single, lightweight letter requires only an envelope, making it the most economical choice. However, shipping fragile items necessitates sturdy boxes with ample cushioning. Bubble mailers are cost-effective for smaller, non-fragile items, offering good protection at a lower cost than rigid boxes.
For heavier or larger items, selecting the right size box to minimize wasted space is paramount. Choosing reusable packaging, when possible, can also offer long-term cost savings, though this is often not practical for businesses that deal with high volumes of varying-sized shipments. Careful consideration of these factors ensures that the chosen packaging is both protective and cost-effective.
Finding the Cheapest Mailing Options
Minimizing mailing costs is crucial for both personal and business budgets. Strategic planning and utilizing available resources can significantly reduce expenditure without compromising delivery reliability. This section details methods for identifying the most economical shipping options and implementing cost-saving strategies.Finding the absolute cheapest mailing option requires a multi-faceted approach. It’s not simply about choosing the cheapest service offered; it’s about optimizing every aspect of the mailing process.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Most Affordable Shipping Option, How much is it to send mail
To pinpoint the cheapest shipping option, follow these steps: First, accurately determine the package’s dimensions and weight. Next, specify the destination address, including ZIP codes for domestic mail and country codes for international shipments. Then, compare prices across various carriers using online postage calculators. Finally, consider factors like delivery speed and insurance needs to balance cost with expediency and risk mitigation.
Ignoring any of these steps could lead to unexpectedly high shipping costs.
Comparison of Online Postage Calculators
Several online postage calculators offer competitive features. Pitney Bowes, Stamps.com, and the USPS website are popular choices. Pitney Bowes and Stamps.com often integrate with various shipping carriers, providing a broader range of options and potentially better rates. The USPS website offers a straightforward calculator specific to their services. However, each calculator’s interface and features vary; some may be more user-friendly than others, and the specific features offered may influence your choice of which calculator to use.
For instance, some may offer better visualization tools to help estimate package size and weight more accurately, leading to a more precise cost estimate.
Strategies for Reducing Mailing Costs
Using lighter packaging is a significant cost-saver. Opt for lightweight yet durable materials like corrugated cardboard instead of heavier alternatives. Consolidating shipments is another effective strategy; sending multiple items in one package reduces the per-item shipping cost significantly. For example, a business sending multiple small packages to the same customer will find substantial savings by combining them into one larger box.
This strategy is especially effective for businesses with a high volume of mail.
Tips for Saving Money on Postage
Reducing mailing costs involves a combination of strategic choices and practical steps.
- Choose the right shipping carrier: Compare prices from different carriers like USPS, FedEx, and UPS. USPS often offers lower rates for domestic mail, while FedEx and UPS may be more competitive for international or expedited shipping.
- Negotiate rates with carriers: Businesses with high mailing volumes can often negotiate discounted rates with carriers. This requires a commitment to high volume usage and a consistent shipping pattern.
- Use free packaging: Some carriers provide free packaging materials, eliminating the cost of purchasing boxes and envelopes. This should be factored into the total cost analysis.
- Print your own postage: Online postage services often offer lower rates than purchasing stamps at the post office. This method also often provides tracking information.
- Ship during off-peak seasons: Shipping rates can fluctuate based on demand. Sending packages during less busy periods might yield lower costs. The holiday season, for example, usually sees increased shipping costs due to higher demand.
Mail Service Options and Their Costs
Understanding the various mail service options available is crucial for efficient and cost-effective mailing. The United States Postal Service (USPS) offers a range of services, each designed for specific needs and priorities, impacting both speed and price. Choosing the right service can significantly affect the overall cost and delivery time of your mail. Failure to do so can result in unnecessary expenses or delayed delivery.Choosing the correct mail service requires careful consideration of factors such as delivery speed, tracking needs, and the nature of the item being sent.
The following sections detail the key differences and associated costs for various USPS options.
USPS Mail Classes and Their Costs
The USPS offers several mail classes, each with varying speeds, features, and prices. The cost depends on factors such as weight, size, and destination. While prices fluctuate, the general cost structure remains consistent. It is advisable to check the USPS website for the most up-to-date pricing information.
| Mail Class | Description | Speed | Tracking | Cost (Approximate) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Class Mail | Letters, postcards, large envelopes, and small packages. | 1-5 business days | No (unless add-on services are purchased) | $0.60 – $5+ (depending on weight and size) | Standard letters, postcards, and small packages. |
| Priority Mail | Packages up to 70 lbs. | 1-3 business days | Yes (included) | $8 – $150+ (depending on weight and zone) | Time-sensitive packages that require tracking. |
| Priority Mail Express | Packages up to 70 lbs. | Overnight or 1-2 business days | Yes (included) | $25 – $200+ (depending on weight and zone) | Extremely time-sensitive packages requiring guaranteed delivery. |
| First-Class Package Service | Packages up to 15.99 oz. | 1-3 business days | No (unless add-on services are purchased) | $4 – $10+ (depending on weight and size) | Small packages requiring relatively quick delivery without tracking. |
| Media Mail | Books, manuscripts, sound recordings, and other educational materials. | 2-8 business days | No | Lower than First-Class Mail (depending on weight and size) | Sending books and educational materials. |
Certified Mail and Other Add-on Services
Beyond the basic mail classes, the USPS offers several add-on services that enhance security and provide proof of delivery. These services increase the overall cost but offer significant benefits in specific situations.Certified Mail provides proof of mailing and delivery, adding a layer of security for important documents. Return Receipt Requested adds confirmation of delivery and recipient signature. Insurance protects against loss or damage, providing compensation up to a specified amount.
These services are particularly valuable when sending sensitive or high-value items. The cost of these add-ons varies depending on the level of coverage required.For example, a Certified Mail letter might cost an additional $4-5, while insurance on a Priority Mail package could cost several dollars depending on the declared value. These additional costs are justified when the security and peace of mind they offer are paramount.
Sending Large or Unusual Items: How Much Is It To Send Mail
Shipping oversized or irregularly shaped packages presents unique challenges and often incurs higher costs than standard mail. These increased expenses stem from the need for specialized handling, larger packaging materials, and potentially different transportation methods. Understanding these complexities is crucial for ensuring your items arrive safely and within a reasonable budget.Oversized or irregularly shaped packages require careful consideration of dimensions and weight.
Shipping services typically impose size and weight limits, and exceeding these limits will result in surcharges. Items exceeding the standard dimensions may require additional packaging to protect them during transit, further increasing the cost. For example, a large piece of artwork might require a custom-built crate, adding significantly to the overall expense. Similarly, an unusually long or oddly shaped item might necessitate special handling and possibly more expensive shipping options to prevent damage.
Dimensional Weight Charges
Shipping companies often calculate costs based on dimensional weight rather than actual weight, particularly for bulky, lightweight items. Dimensional weight is a calculation based on the package’s dimensions (length x width x height) and considers the space the package occupies in the carrier’s vehicle. A large, lightweight package might have a lower actual weight but a higher dimensional weight, resulting in a higher shipping cost.
For instance, a large, empty cardboard box will likely be charged based on its dimensional weight, even though it weighs very little. This is because it takes up considerable space during transport.
Shipping Hazardous Materials
The shipment of hazardous materials is strictly regulated and requires specialized handling and documentation. These materials, including flammable liquids, corrosive substances, and toxic materials, pose safety risks during transit and require specific packaging and labeling to meet stringent safety regulations. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and delays, or even the rejection of the shipment.
For example, sending aerosol cans requires specific packaging and labeling, including UN numbers and hazard classifications. The costs associated with shipping hazardous materials are significantly higher than standard shipping due to the added safety precautions and handling requirements. This includes specialized packaging, additional documentation, and potentially higher insurance premiums.
Insuring Valuable or Fragile Items
For valuable or fragile items, purchasing insurance is highly recommended. Insurance protects against loss or damage during transit, providing financial compensation in case of unforeseen circumstances. The cost of insurance is typically a percentage of the item’s declared value, with higher-value items incurring higher insurance premiums. For example, insuring a valuable antique or a piece of delicate electronics will cost more than insuring a less expensive or less fragile item.
Choosing the appropriate insurance coverage is crucial; underinsurance may not fully cover the replacement cost in case of loss or damage. Proper documentation, including detailed descriptions and photographs of the item, is essential when filing an insurance claim.
Sending mail, whether across town or across continents, requires a careful consideration of costs. This guide has illuminated the key factors influencing postage prices, from weight and distance to service type and packaging choices. By understanding these variables and employing the strategies Artikeld, you can effectively manage your mailing budget while ensuring reliable and timely delivery. Remember to compare rates from different carriers and utilize online tools to find the most economical option for your specific needs.
Efficient mailing isn’t just about saving money; it’s about smart planning and informed decision-making.
FAQ Section
What is the cheapest way to send a letter domestically?
Generally, First-Class Mail is the most affordable option for domestic letters.
Can I insure a package sent via First-Class Mail?
Yes, but insurance options and costs vary; check with your chosen carrier.
How do customs fees affect international shipping costs?
Customs fees are levied by the recipient’s country and depend on the item’s value and type; they’re added to the shipping cost.
What are the consequences of using improper packaging?
Improper packaging can lead to damage, delays, and increased costs due to potential replacements or claims.






