What does decidualized stroma mean? Imagine a hidden world within the female body, a realm where cells transform and dance to the rhythm of life’s greatest symphony: pregnancy. Decidualized stroma, a specialized tissue in the uterine lining, plays a pivotal role in this symphony, orchestrating the intricate processes that enable a tiny embryo to find its home and grow.
This remarkable tissue undergoes a profound metamorphosis, morphing from ordinary endometrial stroma into a nurturing haven for a developing fetus. It’s a fascinating story of cellular transformation, hormonal influences, and the delicate balance required for a successful pregnancy.
Decidualized Stroma: What Does Decidualized Stroma Mean
Imagine a cozy little nest for a growing baby. That’s what decidualized stroma is all about! It’s a special kind of tissue that forms in the lining of the uterus during pregnancy. This tissue is like a super-powered version of the usual uterine lining, with a whole bunch of extra cells and blood vessels to support the developing fetus.
Decidualized Stroma: Location and Function
Decidualized stroma, also known as the decidua, is found in the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. It’s like a special layer of cells that forms during pregnancy. This layer is super important because it provides a safe and comfy environment for the fertilized egg to implant and grow. Think of it as a soft, cushioned bed for the baby to snuggle in.
The decidua also helps with blood supply to the growing fetus, making sure it gets all the nutrients it needs. It’s like a little delivery system for the baby, bringing all the good stuff it needs to thrive.
Decidualized Stroma: Characteristics, What does decidualized stroma mean
Decidualized stroma is a unique tissue with some special features. It’s made up of different types of cells, including:
- Decidual cells: These are the main players in the decidua. They’re like little helpers, creating a cozy environment for the baby. They’re packed with nutrients and have a special ability to produce hormones that help support pregnancy.
- Endothelial cells: These cells line the blood vessels in the decidua, ensuring a smooth flow of blood to the developing fetus.
- Immune cells: These cells are like the bodyguards of the pregnancy. They protect the baby from any unwanted invaders, keeping it safe and healthy.
The decidua also has a special structure, with lots of blood vessels and a rich network of connective tissue. This structure is essential for providing the necessary nutrients and oxygen to the growing fetus.
Physiological Significance of Decidualized Stroma
The decidua plays a crucial role in pregnancy. It’s like the hero of the story, supporting the fetus and ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Here’s how:
- Implantation: The decidua provides a welcoming environment for the fertilized egg to implant and start growing.
- Placentation: The decidua helps in the formation of the placenta, the vital organ that connects the mother and fetus, allowing for nutrient and oxygen exchange.
- Immune tolerance: The decidua helps to suppress the mother’s immune system, preventing it from attacking the fetus, which is essentially half-foreign to the mother’s body.
- Hormone production: The decidua produces various hormones that are crucial for maintaining pregnancy, including progesterone, which helps prepare the uterus for the baby and keeps the pregnancy going.
Formation and Development of Decidualized Stroma

Okay, let’s get down to the nitty-gritty of how this whole decidualization thing works. Imagine the endometrial stroma as a blank canvas, and decidualization is the process of transforming this canvas into a beautiful, functional masterpiece!
Hormonal Influences and Signaling Pathways
The whole process of decidualization is orchestrated by a complex interplay of hormones and signaling pathways. It’s like a well-rehearsed dance where each player has a crucial role to play. The star of the show is progesterone, a hormone that’s produced by the ovaries. Progesterone acts as the conductor, guiding the transformation of stromal cells into decidual cells. It does this by binding to progesterone receptors, triggering a cascade of molecular events.
- Progesterone receptor signaling: Progesterone binds to its receptor, triggering a cascade of downstream signaling events that lead to the activation of specific genes involved in decidualization.
- Growth factors and cytokines: Other important players include growth factors and cytokines like insulin-like growth factor (IGF), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). These molecules further enhance the decidualization process by promoting cell growth, differentiation, and survival.
Cellular and Molecular Changes
Now, let’s dive into the fascinating world of cellular and molecular changes that occur during decidualization. It’s like watching a time-lapse video of a caterpillar transforming into a butterfly!The transformation of stromal cells into decidual cells is a remarkable feat of cellular differentiation. These stromal cells, which were once quiescent and undifferentiated, undergo a dramatic makeover.
- Increased cell size and volume: Stromal cells become plump and rounded, increasing their size and volume significantly. It’s like they’re getting ready to host a grand party!
- Accumulation of glycogen and lipids: Decidual cells store large amounts of glycogen and lipids, which serve as energy reserves for the developing embryo. They’re basically stocking up for the big event!
- Production of decidual proteins: Decidual cells start producing a unique set of proteins, including prolactin, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 (IGFBP1), and tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI). These proteins are crucial for maintaining the pregnancy and supporting the embryo’s growth.
- Changes in extracellular matrix: The extracellular matrix surrounding the decidual cells also undergoes significant changes, becoming more organized and supportive. This is like building a sturdy foundation for the embryo to thrive.
Role of Decidualized Stroma in Pregnancy
Think of the decidualized stroma as the VIP lounge of the uterus, where the embryo gets the royal treatment it needs to thrive. It’s not just a comfy couch for the embryo to hang out on, but a bustling hub of activity, ensuring everything goes smoothly for a successful pregnancy.
Supporting Implantation and Early Pregnancy
The decidualized stroma is like a welcoming committee for the embryo, creating a cozy and nourishing environment for it to settle in. It plays a vital role in the initial stages of pregnancy, making sure the embryo gets the best possible start.
- Provides a Vascularized Bed: The decidualized stroma undergoes significant vascular remodeling, creating a rich network of blood vessels. This vascularization is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the growing embryo.
- Secretes Growth Factors: The decidual cells are busy bees, churning out a variety of growth factors like IGF-1 and VEGF. These growth factors promote the development of the embryo and the placenta, ensuring a healthy pregnancy.
- Provides a Barrier: The decidualized stroma acts as a protective barrier, shielding the embryo from the mother’s immune system. This is crucial because the embryo has different genetic material from the mother, and the immune system could mistakenly attack it.
Contribution to Placental Formation and Fetomaternal Communication
The decidualized stroma doesn’t just support the embryo; it actively participates in the formation of the placenta, the vital organ that connects the mother and the fetus.
- Forms the Decidua Basalis: The decidualized stroma at the implantation site forms the decidua basalis, which is the maternal part of the placenta. The decidua basalis is essential for anchoring the placenta to the uterine wall.
- Facilitates Fetomaternal Communication: The decidualized stroma facilitates communication between the mother and the fetus. It does this by secreting hormones and other signaling molecules that influence the development of both the mother and the fetus.
- Regulates Nutrient Exchange: The decidualized stroma plays a crucial role in regulating the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products between the mother and the fetus. This exchange is vital for the healthy growth and development of the fetus.
Regulation of Immune Tolerance, Vascular Remodeling, and Hormone Production
The decidualized stroma is a multi-tasker, juggling a range of important functions during pregnancy.
- Immune Tolerance: The decidualized stroma helps to suppress the mother’s immune response to the embryo. This is crucial because the embryo is essentially a foreign body, and the immune system could attack it. The decidual cells secrete immune-modulating molecules like cytokines and chemokines, creating an environment where the embryo is tolerated.
- Vascular Remodeling: As we mentioned earlier, the decidualized stroma undergoes significant vascular remodeling. This is essential for establishing a healthy blood supply to the placenta and for allowing for the exchange of nutrients and gases between the mother and the fetus.
- Hormone Production: The decidualized stroma produces a variety of hormones that are essential for maintaining pregnancy. These hormones include progesterone, estrogen, and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Progesterone is crucial for maintaining the lining of the uterus, while estrogen plays a role in the growth and development of the placenta. hCG is the hormone that is detected in pregnancy tests.
Decidualized Stroma and Reproductive Disorders

Okay, so we’ve talked about how awesome decidualized stroma is during pregnancy, right? But what happens when things go a little off-kilter? Well, just like any good party, sometimes the guest list gets messed up, and that’s where problems can arise. Let’s dive into how decidualization can go awry and impact reproductive health.
Decidualization Defects and Infertility
Imagine a party where the decorations are all wonky, and the food is… well, let’s just say not appetizing. That’s kind of what happens when decidualization goes wrong. Defects in decidualization can make it difficult for an embryo to implant and thrive, leading to infertility. Here’s the lowdown:
- Insufficient Decidualization: If the endometrium doesn’t “dress up” properly with enough decidualized stroma, it might not be a welcoming place for an embryo. It’s like having a party with no snacks – who wants to stay?
- Abnormal Decidualization: Sometimes the decidualization process gets a bit confused, leading to an uneven or disorganized structure. This can disrupt the implantation process and make it harder for the embryo to get comfortable. It’s like having a party with mismatched furniture – awkward, right?
Decidualization and Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
Now, let’s say an embryo does manage to get past the “party entrance” but things still go wrong. Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) is a heartbreaking experience, and decidualization can play a role.
- Compromised Decidualization: If the decidualized stroma isn’t robust enough, it might not provide adequate support for the growing embryo. Think of it like a flimsy party tent – not ideal for a long stay! This can lead to miscarriages, especially in the first trimester.
- Premature Decidualization: Sometimes the decidualization process starts too early, before an embryo even arrives. This can disrupt the normal uterine environment and make it difficult for implantation. It’s like setting up the party decorations before the guests arrive – the fun might be over before it even starts!
Decidualized Stroma in Endometriosis
Alright, let’s talk about endometriosis – a condition where endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus. It’s like having a party in the wrong place! Decidualized stroma can play a role in this condition:
- Ectopic Decidualization: In endometriosis, decidualization can occur in ectopic endometrial tissue, contributing to inflammation and pain. It’s like having a party in the living room, but the decorations are all over the place – not exactly a pleasant experience!
- Abnormal Decidualization: Decidualized stroma in ectopic endometrial tissue can also be abnormally structured, further contributing to the development and progression of endometriosis. It’s like having a party with decorations that are all out of place – it just doesn’t feel right.
Decidualized Stroma in Uterine Fibroids
Now, let’s move on to uterine fibroids, noncancerous growths in the uterus. Decidualized stroma can be involved here too:
- Fibroid Decidualization: Fibroids can undergo decidualization, which can contribute to their growth and symptoms. It’s like having a party where the decorations are growing out of control – not a good look!
- Hormonal Influences: Hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy, can influence decidualization in fibroids, potentially leading to complications like bleeding or pain. It’s like having a party where the music is too loud and the guests are getting out of hand – time to call it a night!
Therapeutic Targets and Strategies
Okay, so we’ve seen how decidualization can go wrong. But what can we do about it? Scientists are working on ways to harness the power of decidualization for reproductive health:
- Modulating Decidualization: Researchers are exploring ways to modulate decidualization to improve implantation and reduce the risk of pregnancy loss. It’s like fine-tuning the party decorations to create the perfect atmosphere.
- Targeting Decidualization in Endometriosis: Drugs that target decidualization in ectopic endometrial tissue could potentially help manage endometriosis symptoms. It’s like finding a way to turn down the volume on the music at a party that’s getting out of hand.
- Fibroid Treatment: Understanding the role of decidualization in fibroid growth could lead to new therapies for fibroids. It’s like finding a way to stop the decorations from growing out of control at a party.
Research and Future Directions
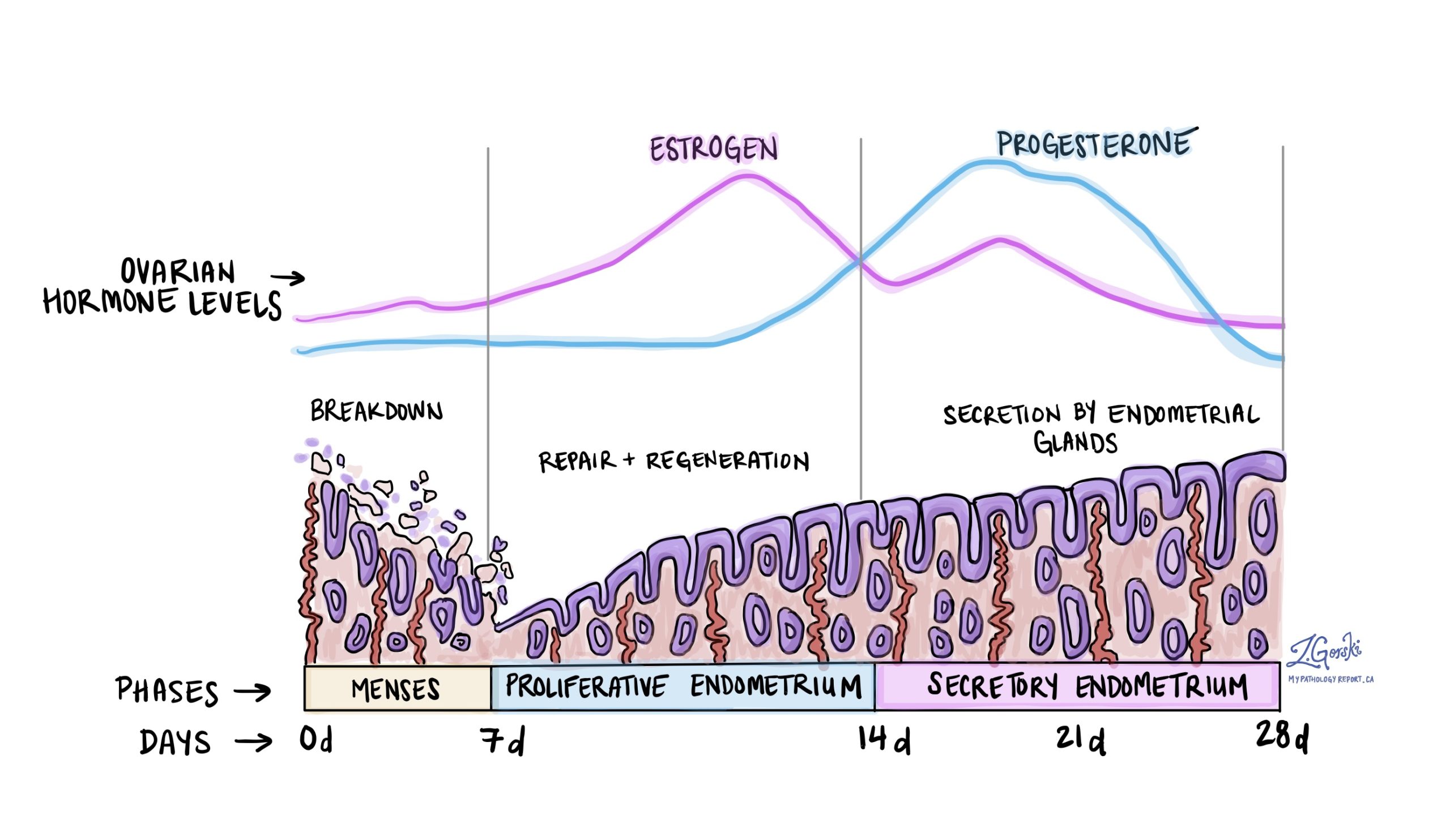
The intricate dance of decidualization, the transformation of the uterine lining during pregnancy, holds immense promise for unraveling the mysteries of reproductive health and disease. Scientists are delving deep into the molecular mechanisms that orchestrate this process, seeking to unlock its potential for clinical applications and therapeutic interventions.
Deciphering the Molecular Mechanisms of Decidualization
Understanding the intricate molecular mechanisms that drive decidualization is crucial for developing targeted therapies and diagnostic tools. Researchers are focusing on:
- Identifying and characterizing key signaling pathways: This involves pinpointing the specific molecules and pathways that govern the differentiation of endometrial stromal cells into decidual cells.
- Investigating the role of epigenetics: Epigenetics, the study of heritable changes in gene expression without altering the DNA sequence, plays a crucial role in decidualization. Researchers are exploring how epigenetic modifications influence decidual cell function and how they might be modulated for therapeutic purposes.
- Exploring the interplay between decidual cells and other cell types: Decidual cells interact with a diverse cast of characters, including immune cells, vascular cells, and the developing embryo. Understanding these interactions is vital for deciphering the complex signaling networks that govern pregnancy.
Decidualized stroma, a testament to the body’s remarkable ability to adapt and create, is a vital player in the grand drama of pregnancy. From its humble beginnings as endometrial stroma to its crucial role in implantation, development, and immune regulation, this tissue stands as a beacon of life’s resilience and the intricate interplay between biology and destiny.
Question Bank
What are some common conditions related to decidualized stroma?
Abnormalities in decidualization can contribute to conditions like infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, endometriosis, and uterine fibroids.
Is decidualization a normal process?
Yes, decidualization is a normal physiological process that occurs in the uterus during the menstrual cycle and, more significantly, during pregnancy.
How does decidualization differ from normal endometrial stroma?
Decidualized stroma is characterized by distinct cellular changes, including the differentiation of stromal cells into decidual cells, which have unique functions and morphology.
What are the key hormones involved in decidualization?
Estrogen, progesterone, and other signaling molecules play crucial roles in regulating the process of decidualization.






