What is the income limit for food stamps in Hawaii? That’s a right proper question, innit? Navigating the SNAP (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program) system in the Aloha State can feel like trying to crack a pineapple without a proper knife – tricky, but doable with the right info. This ain’t your nan’s benefits system; we’re talking about gross vs.
net income, household size, and a whole load of other factors that can swing the eligibility scales. Get clued up and find out if you’re in the running for a bit of extra help putting grub on the table.
This guide breaks down the nitty-gritty of Hawaii’s SNAP program, from understanding income limits based on household size to the various deductions that can impact your eligibility. We’ll cover everything from the application process to comparing Hawaii’s benefits with other states, giving you the lowdown on what you need to know to get the support you deserve. Think of us as your personal, street-smart guide to the SNAP system in Hawaii.
Hawaii Food Stamp Program Overview
Navigating the complexities of food insecurity can be challenging, but in Hawaii, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), often referred to as food stamps, provides a vital lifeline for many residents. This program aims to combat hunger and improve the nutritional well-being of eligible individuals and families across the islands. Understanding its purpose, eligibility requirements, and application process is crucial for those seeking assistance.The purpose of SNAP in Hawaii is to supplement the food budget of low-income households, enabling them to purchase nutritious groceries.
Eligibility is determined by a number of factors, primarily household income and size. Income limits are adjusted periodically and are based on federal poverty guidelines, modified to reflect the higher cost of living in Hawaii. Other factors considered include household resources (like savings and assets) and expenses. The program isn’t just about providing food; it’s about improving overall health and well-being by ensuring access to essential nutrients.
SNAP Assistance Offered in Hawaii
SNAP in Hawaii offers a straightforward form of assistance: a monthly electronic benefit transfer (EBT) card. This card functions like a debit card, allowing recipients to purchase eligible food items at participating grocery stores and farmers’ markets throughout the state. The amount of benefits received varies based on household size, income, and other factors. Importantly, SNAP benefits are not limited to just canned goods or staples; they can be used for a wide range of fresh produce, meats, dairy, and other nutritious foods, promoting a balanced diet.
There are some restrictions, however; alcohol, tobacco, and hot foods prepared for immediate consumption are typically ineligible.
Applying for SNAP Benefits in Hawaii
The application process for SNAP benefits in Hawaii involves several steps. Individuals can apply online through the state’s Department of Human Services website, or they can apply in person at a local DHS office. The application requires detailed information about household income, assets, and expenses. Applicants are typically required to provide documentation to support their claims, such as proof of income, identification, and proof of residency.
Once the application is submitted, it undergoes a thorough review process to determine eligibility. This process may involve interviews and verification of the information provided. After a decision is made, applicants are notified of their eligibility status and the amount of benefits they will receive, if approved. The entire process can take several weeks, depending on the volume of applications and the need for additional information.
Continued eligibility is reviewed periodically, typically annually, to ensure ongoing needs are met.
Income Limits for SNAP in Hawaii
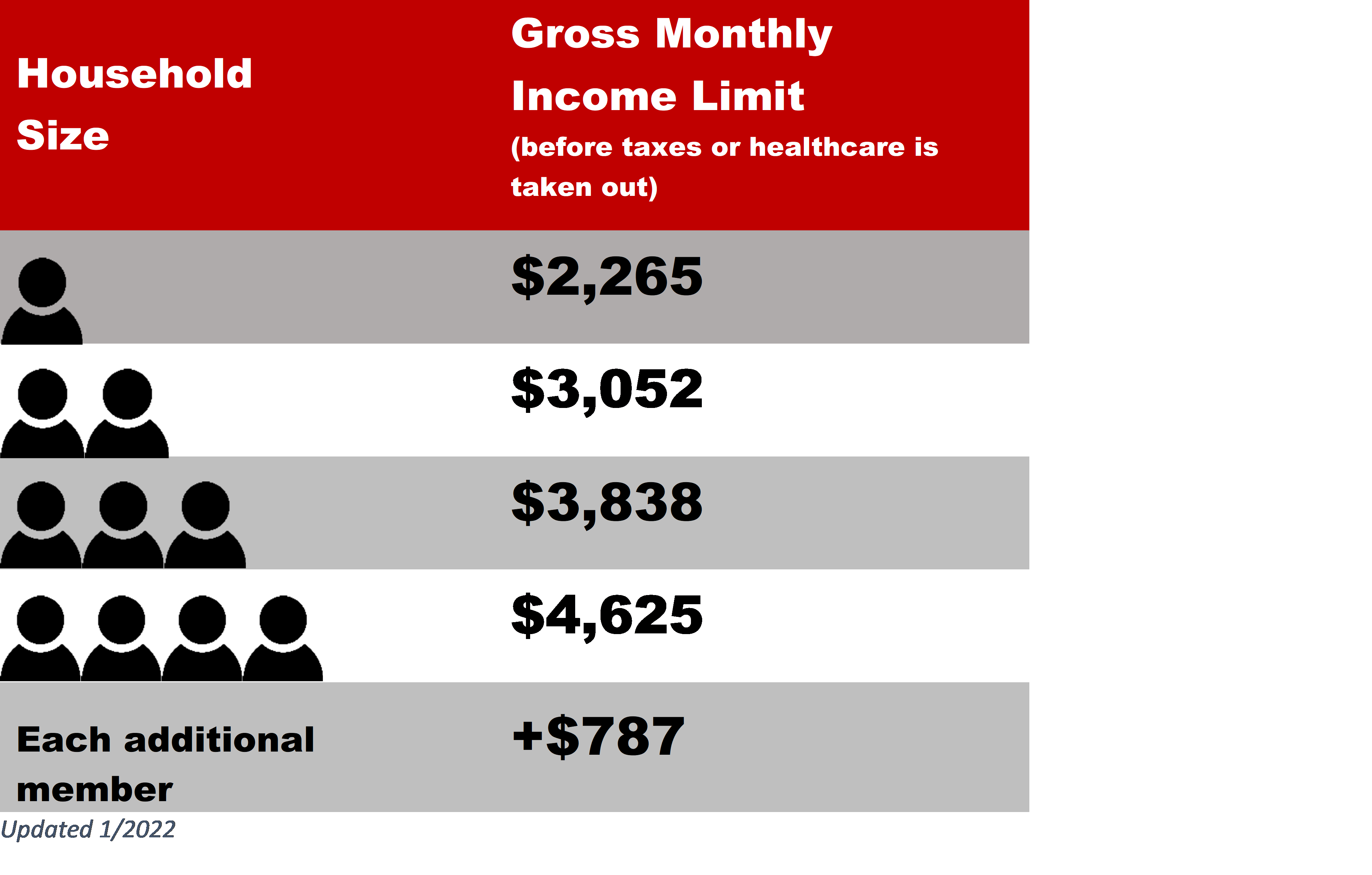
Navigating the world of food stamps, officially known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), in Hawaii can feel a bit like deciphering a treasure map. Understanding the income limits is crucial to determining eligibility, and it’s important to differentiate between gross and net income. This section will clarify the process and help you understand how your income is assessed.
Gross vs. Net Income for SNAP Eligibility
The key to understanding SNAP eligibility in Hawaii lies in the distinction between gross and net income. Gross income represents your total income before taxes and deductions. Net income, on the other hand, is your income after taxes and allowable deductions are subtracted. Both are crucial in determining eligibility, as Hawaii uses both figures to assess your application.
The higher of the two is used for the eligibility determination, ensuring a fair and comprehensive evaluation of your financial situation.
Income Sources Considered for SNAP Eligibility
Determining your eligibility involves a thorough examination of various income sources. This isn’t just your paycheck; it encompasses a broader picture of your financial resources. The Department of Human Services (DHS) in Hawaii considers a wide range of income, including wages, salaries, self-employment income, unemployment benefits, Social Security benefits, pensions, alimony, child support, and interest from savings accounts.
Understanding which income streams are included is critical for an accurate application.
Examples of Included and Excluded Income Sources
Let’s illustrate this with some examples. Wages from your job are definitively included. So are unemployment benefits if you’re temporarily out of work. However, certain income sources are excluded. For instance, certain types of government assistance, such as most housing subsidies and some veterans’ benefits, are typically excluded from the calculation.
Similarly, one-time payments like inheritances or lottery winnings are generally not factored into the ongoing eligibility determination. It’s always best to consult the official DHS guidelines for a comprehensive list of included and excluded income sources. This ensures accuracy and prevents delays or denials due to misunderstandings.
Hawaii SNAP Income Limits by Household Size
The following table provides a simplified representation of the income limits. These are subject to change, so always refer to the official DHS website for the most up-to-date information. Remember, this is a general guideline, and individual circumstances may vary.
| Household Size | Gross Income Limit | Net Income Limit | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $1,071 | $857 | These are approximate figures. Deductions such as childcare expenses and medical expenses may affect the net income limit. |
| 2 | $1,442 | $1,154 | Deductions can significantly lower the net income limit for larger households. |
| 3 | $1,813 | $1,450 | Always consult the official DHS website for precise figures. |
| 4 | $2,184 | $1,746 | Eligibility is also affected by other factors besides income, such as assets. |
Factors Affecting Income Limits
Navigating the Hawaii SNAP (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program), often called food stamps, involves more than just looking at your gross income. Eligibility hinges on a complex interplay of factors, extending beyond the simple number on your paycheck. Understanding these nuances is crucial for successfully applying and receiving benefits.It’s not just about how much you earn; it’s about how much you have left after essential expenses are considered.
Household size, age, disability status, and allowable deductions all play significant roles in determining your net income and, consequently, your eligibility for SNAP benefits.
Household Size, What is the income limit for food stamps in hawaii
The number of people in your household directly impacts your eligibility. Larger households have higher income limits than smaller ones. This reflects the increased cost of food for a larger family. For instance, a household of four will have a significantly higher allowable income than a single-person household. The Hawaii Department of Human Services (DHS) provides specific income guidelines based on household size, which are updated periodically.
These guidelines are available on their website and at local DHS offices.
Disability and Age
Individuals with disabilities or those aged 60 and older may qualify for higher income limits. This recognition acknowledges the increased challenges and often higher costs associated with these circumstances. For example, a senior citizen with a disability might have higher medical expenses, impacting their net income and thus their eligibility. Documentation of disability or age is required during the application process.
Deductions: Childcare and Medical Expenses
The calculation of your net income for SNAP eligibility doesn’t stop at your gross income. Several essential expenses are deducted to arrive at your net income, which is the crucial factor determining eligibility. Two significant deductions are childcare costs and medical expenses.Childcare costs are a substantial expense for many families, especially those with young children. These costs, including daycare, preschool, and after-school programs, are deducted from your gross income to arrive at your net income.
Similarly, substantial medical expenses, exceeding a certain percentage of your income, can also be deducted. This accounts for the reality that unexpected or significant health issues can drastically reduce disposable income.
Documenting Deductions
Providing proper documentation is essential for successfully claiming these deductions. For childcare expenses, you will generally need proof of payment, such as receipts or statements from the childcare provider. For medical expenses, documentation might include doctor’s bills, hospital statements, and insurance explanation of benefits (EOB). It’s crucial to keep accurate records of all expenses, as the DHS may request verification.
Failing to provide adequate documentation can delay or even deny your application. It’s advisable to contact your local DHS office for specific guidance on acceptable documentation for your situation. They can provide detailed information on the types of documents required and ensure your application is complete and accurate.
Resources and Assistance for SNAP Applicants in Hawaii
Navigating the SNAP application process can feel overwhelming, but thankfully, Hawaii offers various resources to guide applicants through each step. These resources provide crucial support, ensuring individuals and families have access to the assistance they need. From application assistance to financial literacy programs, a network of support is available to help you successfully obtain SNAP benefits.
Several state agencies and community organizations offer comprehensive support for SNAP applicants in Hawaii. This support ranges from helping with the application process itself to providing valuable financial literacy resources to improve long-term financial stability. Knowing where to turn for help can significantly reduce stress and increase the likelihood of a successful application.
Hawaii Department of Human Services (DHS)
The Hawaii Department of Human Services is the primary agency responsible for administering the SNAP program in the state. Their website and phone lines are invaluable resources for accessing information and assistance.
The DHS website provides detailed information about eligibility requirements, application procedures, and frequently asked questions. They also offer a wealth of resources explaining the program and answering common questions. Their dedicated phone lines allow direct communication with trained staff who can answer questions and provide guidance.
- Website: [Insert DHS Website Address Here – replace with actual address]
- Phone Number: [Insert DHS Phone Number Here – replace with actual number]
- Type of Assistance: Application assistance, information on eligibility, benefit calculation explanations, and general program information.
Local Community Action Agencies
Across Hawaii, numerous community action agencies provide vital support to low-income individuals and families. These agencies often have staff dedicated to assisting with SNAP applications and related financial matters.
These agencies frequently offer one-on-one assistance with completing applications, ensuring all necessary documentation is submitted correctly, and following up on application status. Many also provide additional services, such as financial literacy workshops and budgeting assistance, to empower individuals to manage their finances effectively.
- Example Agency (replace with actual agency and contact information): [Insert Name of Local Community Action Agency Here]
– [Insert Website Address/Phone Number Here] - Type of Assistance: Application assistance, financial literacy workshops, budgeting assistance, and referrals to other relevant services.
Non-profit Organizations
Numerous non-profit organizations throughout Hawaii offer assistance to individuals applying for SNAP benefits. These organizations often work closely with vulnerable populations, providing comprehensive support beyond just application help.
These organizations can provide a range of services, including assistance with completing applications, navigating bureaucratic processes, and advocating for applicants’ rights. Some may also offer additional support services such as food banks or other social services to address broader needs.
- Example Organization (replace with actual organization and contact information): [Insert Name of Relevant Non-profit Organization Here]
-[Insert Website Address/Phone Number Here] - Type of Assistance: Application assistance, advocacy, referrals to other social services, and potentially food bank access.
SNAP Application Process Infographic
The infographic would visually depict the steps involved in applying for SNAP benefits in Hawaii. It would use simple icons and clear text to guide users through the process.
Step 1: Gather necessary documents (proof of income, residency, household size, etc.). Step 2: Complete the application online or via paper application. Step 3: Submit the application to the DHS. Step 4: Attend an interview (if required). Step 5: Receive notification of approval or denial.
Step 6: Receive benefits (if approved). The infographic would clearly display the contact information for the DHS and other relevant agencies for assistance at each step.
Comparison with Other States

Navigating the complexities of the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), often known as food stamps, reveals significant variations across states. While the federal government sets the overall framework for SNAP, individual states possess considerable leeway in determining eligibility criteria, including income limits. This leads to a patchwork of benefits, impacting food security differently across the nation. Let’s compare Hawaii’s SNAP income limits with those of two other states to illustrate this point.Understanding the disparities in SNAP income limits requires examining several key factors.
Cost of living differences are paramount; a household needing $2,000 per month to meet basic needs in Manhattan might only require $1,500 in a rural area. State economies also play a crucial role; states with robust economies might set higher income limits, reflecting a greater capacity to support their residents. Furthermore, state budgetary priorities and political climates influence the level of social safety net programs, directly impacting SNAP eligibility thresholds.
Income Limit Differences: Hawaii, California, and Mississippi
Hawaii, California, and Mississippi offer a compelling comparison. Hawaii, with its high cost of living, generally has higher SNAP income limits than many other states. California, another high cost-of-living state, also tends to have relatively generous SNAP benefits. In contrast, Mississippi, a state with a lower cost of living and a different economic structure, often displays lower income limits for SNAP eligibility.
While precise figures fluctuate annually based on federal updates and state adjustments, a consistent pattern emerges showing a significant difference between the highest (Hawaii and California) and lowest (Mississippi) limits. For example, a family of four might qualify for SNAP in Hawaii at an income significantly higher than the same family’s eligibility threshold in Mississippi. This disparity highlights the significant impact of state-level policy decisions on access to crucial food assistance.
Impact on Food Security
The variations in SNAP income limits directly affect food security across different regions. In states with higher income limits, like Hawaii and California, a larger percentage of low-income households can access SNAP benefits, potentially mitigating food insecurity within those populations. Conversely, in states with lower income limits, like Mississippi, a greater number of families may fall below the eligibility threshold, leaving them vulnerable to food insecurity.
This results in uneven access to essential nutrition support, leading to disparities in health outcomes and overall well-being across different states. This uneven distribution underscores the need for a more comprehensive, nationally consistent approach to addressing food insecurity, while acknowledging the unique economic and social contexts of individual states.
Impact of Changes in Income Limits
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), often called food stamps, plays a vital role in ensuring food security for many low-income families in Hawaii. Changes to the program’s income eligibility limits, however, can have profound and far-reaching consequences, impacting not only the individuals directly affected but also the broader economic landscape of the state. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for policymakers and advocates alike.Changes in Hawaii’s SNAP income limits directly affect the number of individuals and families eligible for assistance.
An increase in the limit would expand the program’s reach, potentially reducing food insecurity among a larger population. Conversely, a decrease would shrink the program’s reach, leaving more individuals and families struggling to afford adequate food. This ripple effect extends beyond individual households, influencing local economies through changes in consumer spending and the overall demand for food products.
Consequences of Increased Income Limits
Raising the income limits for SNAP in Hawaii would undeniably lead to a greater number of eligible recipients. This increased participation could stimulate local economies. More people would have greater purchasing power, leading to increased demand for groceries and other essential goods, benefiting local farmers, supermarkets, and related businesses. However, this expansion might also place a greater strain on the program’s budget, necessitating increased funding from the state and federal governments.
The potential increase in administrative costs associated with processing a larger number of applications should also be considered. For example, a similar increase in California led to a temporary surge in application processing times, highlighting the need for adequate resource allocation.
Consequences of Decreased Income Limits
Lowering the income limits would have the opposite effect, resulting in fewer individuals qualifying for SNAP benefits. This would directly impact food security for many low-income families, potentially leading to increased rates of hunger and malnutrition. The reduction in consumer spending within the food sector could also negatively impact local businesses, particularly smaller grocery stores and farmers markets that rely heavily on SNAP recipients as customers.
Families forced to reduce their food budget might also be compelled to forgo other essential expenses, such as healthcare or childcare, further exacerbating economic hardship. For instance, a study in a similar situation in Mississippi showed a noticeable decrease in children’s access to regular healthcare visits following a reduction in SNAP benefits.
Strategies for Mitigating Negative Consequences
Implementing strategies to mitigate the negative consequences of income limit changes is essential. For example, if income limits are decreased, policymakers could explore supplemental programs that offer targeted assistance to those newly excluded from SNAP. These might include temporary food banks or increased funding for community food initiatives. Simultaneously, increased investment in job training and workforce development programs could help individuals gain the skills and employment opportunities necessary to increase their income and move beyond reliance on SNAP benefits.
Another approach involves improving public awareness of available resources and streamlining the application process to make it easier for eligible individuals to access assistance. Such strategies aim to provide a safety net for those most vulnerable to the impacts of income limit adjustments.
So, there you have it, bruv. Getting a handle on Hawaii’s food stamp income limits isn’t rocket science, but it does require understanding the ins and outs of the system. Remember, knowing your rights and how to access support is key. Don’t be shy about seeking help – there are resources out there to guide you through the process.
Get yourself sorted and make sure you’re getting what you’re entitled to. Peace out.
Popular Questions: What Is The Income Limit For Food Stamps In Hawaii
What happens if my income fluctuates throughout the year?
You’ll need to report any significant changes in your income to the relevant authorities. They’ll reassess your eligibility based on your current circumstances.
Can I still qualify for SNAP if I have savings?
Generally, savings aren’t directly factored into SNAP eligibility calculations, but extremely high savings could affect your case. It’s best to check with the authorities.
What if I’m self-employed?
Your income will be calculated based on your net profit after business expenses. You’ll need to provide accurate financial records.
Are there penalties for providing false information?
Yes, providing false information on your application can result in serious consequences, including loss of benefits and potential legal action.







