What is focal stroma invasion – What is focal stromal invasion? Imagine a group of cells, like tiny soldiers, breaking free from their designated territory. This is what happens in focal stromal invasion, a crucial concept in understanding cancer’s progression. In this scenario, the soldiers, now cancer cells, begin to invade the surrounding tissue, potentially setting the stage for further spread. This invasion is a critical turning point in the journey of cancer, often influencing the effectiveness of treatment and the overall prognosis.
Focal stromal invasion is a complex process that involves multiple factors. It’s important to understand the different types of focal stromal invasion, how they are diagnosed, and the potential impact they have on cancer progression. By delving deeper into this topic, we can gain valuable insights into the intricate nature of cancer and its potential pathways of spread.
What is Focal Stromal Invasion?: What Is Focal Stroma Invasion
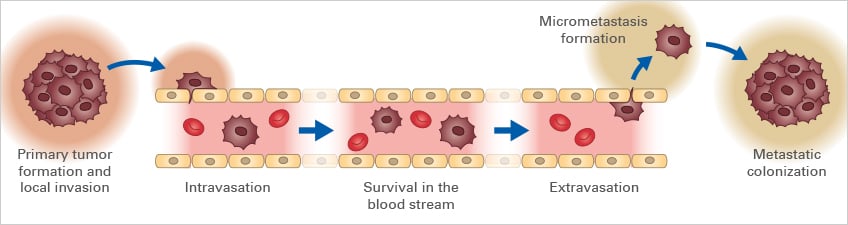
Focal stromal invasion (FSI) is a term used in pathology to describe a specific type of cancer growth pattern. In simple terms, it means that cancer cells have spread from their original location, the tumor, into the surrounding tissue, but only in a few isolated areas. FSI is significant because it is often associated with a higher risk of cancer recurrence and spread to other parts of the body (metastasis).
It is a crucial factor considered by pathologists when determining the stage and grade of a cancer, which in turn influences treatment options and prognosis.
Types of Focal Stromal Invasion
The specific characteristics of FSI can vary depending on the type of cancer. Here are some common types of FSI:
- Single-cell invasion: This is the least aggressive type of FSI, where only a few individual cancer cells have spread into the surrounding tissue.
- Small nests of cells: In this type of FSI, small groups of cancer cells have invaded the surrounding tissue.
- Larger invasive clusters: This is a more aggressive type of FSI, where larger groups of cancer cells have invaded the surrounding tissue.
The extent of FSI, as well as the type of cancer and other factors, can influence the prognosis for the patient.
How is Focal Stromal Invasion Diagnosed?
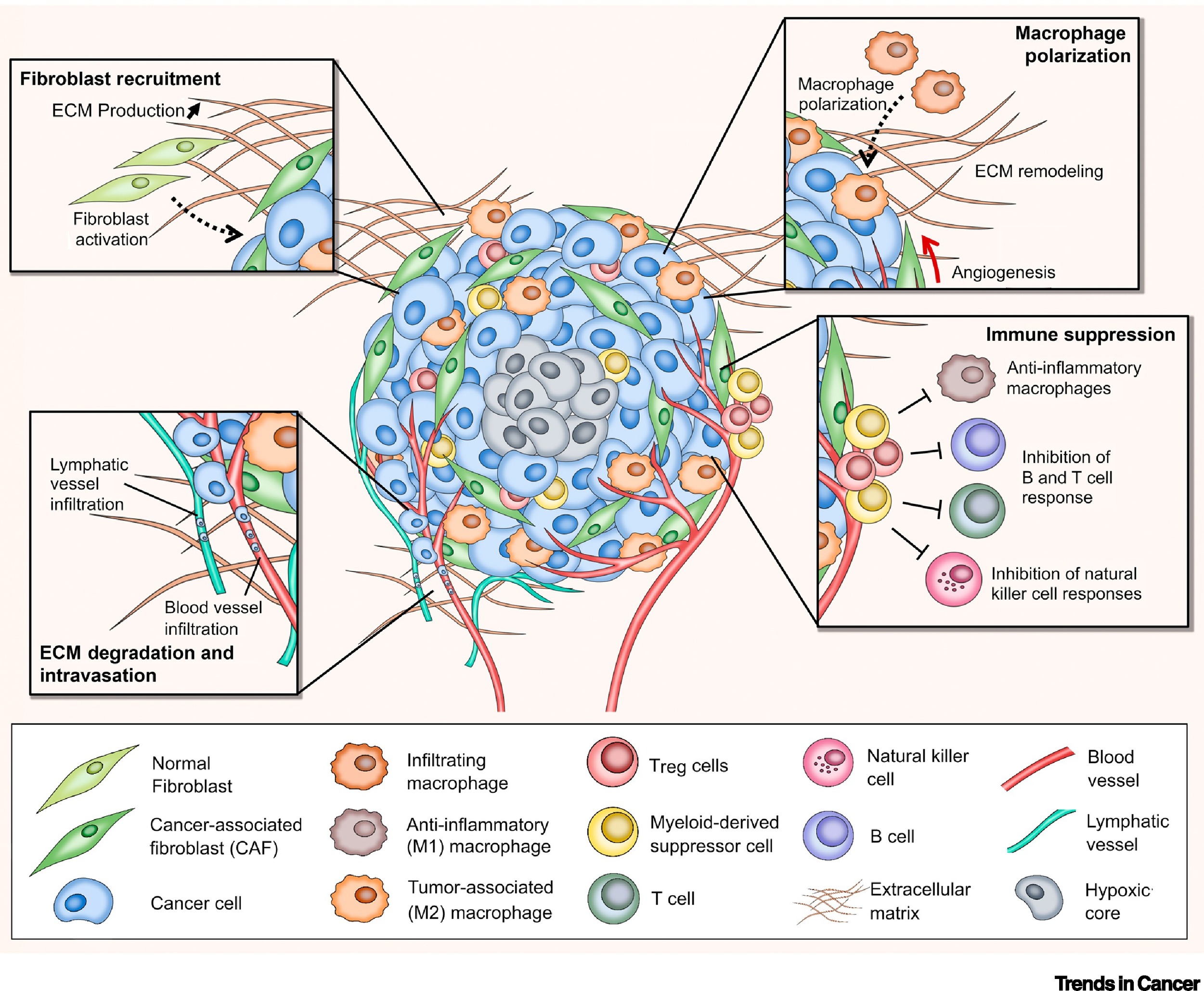
Diagnosing focal stromal invasion (FSI) involves a careful examination of tissue samples obtained from the breast. This process relies on a combination of visual inspection under a microscope and specialized techniques that help identify the characteristic features of FSI.
Pathological Examination
Pathological examination is the cornerstone of diagnosing FSI. It involves a trained pathologist meticulously analyzing tissue samples obtained through a biopsy or surgical procedure. The pathologist examines the tissue under a microscope, looking for specific features that indicate FSI.
Histological Features of Focal Stromal Invasion
- Presence of tumor cells in the stroma: The most defining feature of FSI is the presence of tumor cells within the stromal tissue, which is the connective tissue surrounding the breast ducts and lobules.
- Invasion depth: The depth of invasion is an important factor in determining the extent of FSI. In FSI, the tumor cells invade the stroma to a limited depth, typically less than 1 mm.
- Tumor cell morphology: The appearance of tumor cells can also provide clues about the presence of FSI. In FSI, tumor cells often exhibit features similar to those seen in the ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) from which they originated.
- Presence of a desmoplastic reaction: FSI is often accompanied by a desmoplastic reaction, which is a dense, fibrous tissue response to the presence of tumor cells. This reaction can make it more challenging to identify the tumor cells themselves.
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a technique that uses antibodies to detect specific proteins within tissue samples. In the context of FSI, IHC can be used to:
- Confirm the presence of tumor cells: IHC can help identify tumor cells within the stroma, especially when the cells are small or difficult to distinguish from surrounding tissue.
- Determine the type of tumor: IHC can help determine the type of breast cancer present, which is crucial for guiding treatment decisions.
- Assess the expression of certain proteins: Some proteins, such as estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR), can be used to predict the likelihood of tumor recurrence and response to hormonal therapy.
Molecular Testing
Molecular testing can provide additional information about the genetic makeup of the tumor, which can help predict the likelihood of recurrence and guide treatment decisions.
The Impact of Focal Stromal Invasion on Cancer Progression
Focal stromal invasion (FSI) is a significant factor that can influence the progression of cancer. Its presence indicates that cancer cells have begun to break through the basement membrane, the barrier that normally separates the tumor from the surrounding tissues. This invasion allows cancer cells to spread to other parts of the body, leading to metastasis and a more aggressive disease course.
The Relationship Between Focal Stromal Invasion and Cancer Progression
FSI is a crucial indicator of the potential for cancer to spread. When cancer cells are confined to the original tumor site, they are generally considered less aggressive. However, once FSI occurs, the risk of cancer progression increases significantly. The invasion of surrounding tissues allows cancer cells to access blood vessels and lymphatic channels, facilitating their spread to distant organs.
This process of metastasis can lead to the development of secondary tumors, making the disease much more challenging to treat.
The Influence of Focal Stromal Invasion on Cancer Spread
FSI can influence cancer spread in several ways:
- Increased Mobility: FSI allows cancer cells to break free from the confines of the primary tumor and move into surrounding tissues. This increased mobility provides more opportunities for the cells to access blood vessels and lymphatic channels, facilitating metastasis.
- Enhanced Survival: The surrounding stroma, which includes connective tissues and blood vessels, can provide cancer cells with a more favorable environment for survival and growth. This can contribute to the formation of secondary tumors in distant organs.
- Immune Evasion: FSI can allow cancer cells to evade the immune system, which normally recognizes and destroys abnormal cells. The stromal environment can provide a sanctuary for cancer cells, protecting them from immune surveillance.
The Impact of Focal Stromal Invasion on Treatment Options
FSI can have a significant impact on treatment options for cancer. The presence of FSI often indicates a more aggressive disease, requiring more intensive treatment strategies. Some examples include:
- More Aggressive Surgery: Surgery may need to be more extensive to remove all of the tumor and surrounding invaded tissues. This may involve removing lymph nodes or other nearby structures to ensure that all cancerous cells are eliminated.
- Adjuvant Therapies: Patients with FSI may require additional therapies, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, to target any remaining cancer cells after surgery. These therapies can help to reduce the risk of recurrence and improve overall survival.
- Targeted Therapies: In some cases, targeted therapies that specifically target the molecular pathways involved in FSI may be used to inhibit cancer cell growth and spread.
Treatment Options for Cancer with Focal Stromal Invasion

Focal stromal invasion (FSI) is a significant factor in determining the treatment strategy for various cancers, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, and colorectal cancer. The treatment approach depends on the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, and the patient’s overall health.
Treatment Options for Cancer with Focal Stromal Invasion
The choice of treatment for cancer with FSI is determined by several factors, including the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, and the patient’s overall health. The goal of treatment is to remove or destroy the cancerous cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
- Surgery: Surgery is often the first-line treatment for cancer with FSI. The aim of surgery is to remove the tumor and a margin of surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that all cancerous cells are removed. The extent of the surgery will depend on the size and location of the tumor.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It may be used before surgery to shrink the tumor or after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Radiation therapy can also be used as the primary treatment for some cancers with FSI, especially if surgery is not an option.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It is often used to treat cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. Chemotherapy can be administered intravenously (through a vein), orally (by mouth), or topically (applied to the skin).
- Hormone therapy: Hormone therapy is used to block the effects of hormones that can stimulate cancer growth. It is often used to treat cancers such as breast cancer and prostate cancer.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells. These drugs can interfere with the growth and spread of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps the body’s immune system fight cancer. It works by boosting the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Effectiveness of Treatment Modalities
The effectiveness of treatment for cancer with FSI varies depending on the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, and the patient’s overall health.
- Surgery: Surgery is generally effective in removing localized cancer with FSI, especially when performed at early stages.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy is effective in controlling cancer growth and reducing tumor size, but it may have side effects, such as fatigue and skin irritation.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is effective in treating cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, but it can have significant side effects, such as nausea, hair loss, and fatigue.
- Hormone therapy: Hormone therapy is effective in treating cancers that are sensitive to hormones, such as breast cancer and prostate cancer.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy is effective in treating certain types of cancer with FSI, but it may not be effective for all patients.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a relatively new treatment option for cancer with FSI, and its effectiveness is still being studied.
Treatment Plans Tailored to Different Stages of Focal Stromal Invasion, What is focal stroma invasion
The treatment plan for cancer with FSI is tailored to the specific stage of the disease.
- Early-stage cancer: For early-stage cancer with FSI, surgery is often the primary treatment. Radiation therapy may be used after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Locally advanced cancer: For locally advanced cancer with FSI, a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy may be used.
- Metastatic cancer: For metastatic cancer with FSI, treatment options may include chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy.
Prognosis and Future Research
The prognosis for patients diagnosed with focal stromal invasion varies depending on the type of cancer, its stage, and other individual factors. While focal stromal invasion generally indicates a more aggressive tumor compared to those without invasion, it’s crucial to understand that the impact on prognosis is complex and not always straightforward.
Prognosis for Patients with Focal Stromal Invasion
The prognosis for patients with focal stromal invasion is generally better than for those with extensive stromal invasion. However, it’s important to remember that this is a complex issue and that the prognosis can vary widely depending on the type of cancer, its stage, and other individual factors. For example, a patient with early-stage breast cancer and focal stromal invasion may have a good prognosis, while a patient with advanced-stage lung cancer and focal stromal invasion may have a poorer prognosis.
Areas of Ongoing Research
Research into focal stromal invasion is ongoing, with several key areas of focus:
- Identifying biomarkers for focal stromal invasion: Researchers are working to identify specific markers that can help to predict which tumors are more likely to invade the surrounding stroma. This could help to identify patients who may benefit from more aggressive treatment.
- Understanding the mechanisms of focal stromal invasion: Scientists are studying the biological processes that underlie focal stromal invasion to better understand how tumors invade the surrounding stroma. This knowledge could lead to the development of new therapies that target these processes.
- Developing new treatments for cancer with focal stromal invasion: Researchers are working to develop new treatments that are specifically effective against cancers with focal stromal invasion. These treatments may target the tumor cells directly or they may target the surrounding stroma to prevent further invasion.
Potential Impact of Future Research
Future research on focal stromal invasion has the potential to significantly impact the understanding and treatment of this condition. For example, the identification of new biomarkers could lead to earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment. Additionally, the development of new therapies that target the mechanisms of focal stromal invasion could lead to more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Focal stromal invasion, a key concept in cancer biology, underscores the importance of early detection and personalized treatment approaches. By understanding the nuances of this phenomenon, we can better predict the behavior of cancer and devise strategies to effectively combat its spread. Ongoing research continues to shed light on the intricate mechanisms of focal stromal invasion, paving the way for innovative therapies and improved patient outcomes.
User Queries
What are the implications of focal stromal invasion on the treatment of cancer?
Focal stromal invasion often necessitates more aggressive treatment strategies, such as surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The specific treatment plan will depend on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the extent of the invasion.
Is focal stromal invasion always a sign of aggressive cancer?
While focal stromal invasion can indicate a more aggressive cancer, it’s not always the case. Some cancers with focal stromal invasion may have a favorable prognosis, especially if detected early and treated appropriately.
What are the chances of survival for patients with focal stromal invasion?
The prognosis for patients with focal stromal invasion varies significantly depending on the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, and the effectiveness of treatment. It’s important to consult with a medical professional for a personalized assessment and prognosis.






