What type of dam is the Strom Thurmond Dam? This question sets the stage for an exploration of a remarkable engineering feat, a testament to human ingenuity and a force shaping the landscape and lives of those who call this region home. Nestled amidst the scenic beauty of the Savannah River, the Strom Thurmond Dam stands as a colossal structure, its presence a constant reminder of the power of nature and the ambition of humankind.
Built in the mid-20th century, the dam has played a pivotal role in the development of the region, serving multiple purposes that have impacted both the environment and the lives of those who live nearby.
The Strom Thurmond Dam, formerly known as the Clark Hill Dam, is a concrete gravity dam located on the Savannah River, forming the boundary between South Carolina and Georgia. Construction began in 1948 and was completed in 1954, a testament to the dedication and skill of the engineers and workers involved. The dam’s construction marked a significant milestone in the region’s history, impacting the local economy, environment, and way of life.
It stands as a symbol of human ingenuity, a feat of engineering that continues to serve its purpose decades after its completion.
Strom Thurmond Dam: A Monument to Engineering and Controversy: What Type Of Dam Is The Strom Thurmond Dam

The Strom Thurmond Dam, also known as the “Clark Hill Dam,” stands as a testament to human ingenuity and ambition, a concrete giant that reshaped the landscape of the Savannah River. Its construction, spanning a decade from 1948 to 1954, marked a pivotal moment in the region’s history, leaving an enduring legacy that continues to shape the lives of communities in the surrounding area.
Historical Significance and Construction Timeline
The decision to construct the dam was driven by a confluence of factors. Following World War II, the United States embarked on a massive infrastructure development program, aimed at bolstering the nation’s economy and defense capabilities. The Savannah River, with its abundant water resources, presented a prime location for a hydroelectric dam. The project was also intended to provide flood control, enhance navigation, and generate electricity for a growing population.
Construction of the dam was a monumental undertaking, requiring the mobilization of thousands of workers and the utilization of cutting-edge technology. The dam’s massive concrete structure, measuring 1.3 miles in length and 218 feet in height, was built using a complex system of forms and cranes. The dam’s reservoir, Lake Thurmond, inundated over 70,000 acres of land, displacing residents and transforming the local ecosystem.
Dam Type and Design

The Strom Thurmond Dam, also known as the “Clark Hill Dam,” is a testament to engineering ingenuity. It stands as a colossal structure, designed to harness the power of the Savannah River and provide a multitude of benefits to the surrounding region. Understanding the dam’s type and design is crucial to appreciating its engineering feat and its impact on the environment and society.
Dam Type
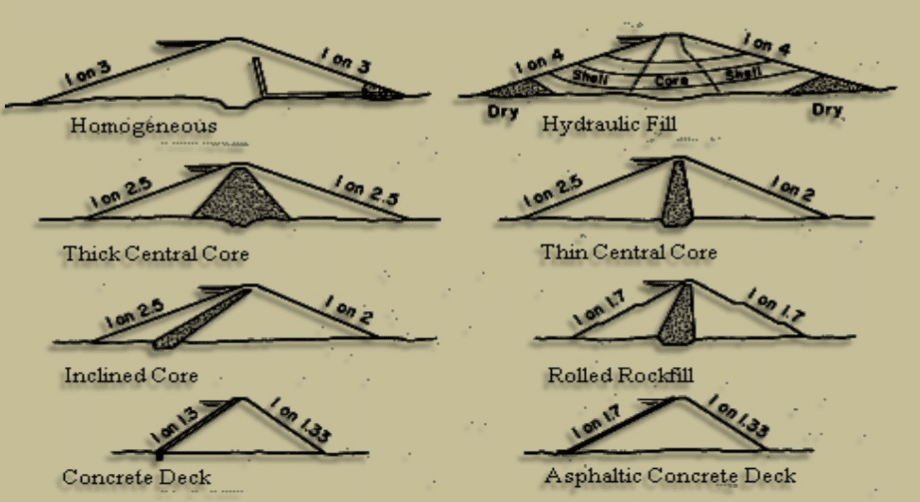
The Strom Thurmond Dam is classified as an embankment dam, a type of dam that is constructed primarily of earthfill materials. These dams are typically characterized by their massive size and their reliance on the weight of the earthfill material to resist the water pressure from the reservoir behind them. Embankment dams are often chosen for their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability to various terrain conditions.
Design Features and Materials
The Strom Thurmond Dam’s design is a marvel of engineering, incorporating several key features to ensure its stability and longevity.
- Earthfill Core: The dam’s core, the central portion that bears the brunt of the water pressure, is made of impervious materials like clay. This core acts as a barrier, preventing water from seeping through the dam. The impervious core is surrounded by layers of less permeable materials, such as sand and gravel, which act as drainage layers. This drainage system helps to prevent water pressure from building up within the dam’s embankment.
- Riprap: To protect the dam’s slopes from erosion, a layer of riprap, which consists of large, durable rocks, is placed on the upstream and downstream faces. This layer acts as a shield, preventing the erosion of the dam’s embankment by the force of water.
- Spillway: The dam features a large spillway, a controlled channel that allows excess water to flow over the dam during periods of high rainfall or snowmelt. The spillway helps to prevent the reservoir from overflowing and protects the dam from damage due to excessive water pressure.
- Powerhouse: Integrated into the dam’s design is a powerhouse, which houses turbines and generators that convert the energy of flowing water into electricity. The powerhouse is strategically located to maximize the use of the water’s potential energy.
Comparison with Other Dams
While the Strom Thurmond Dam is an embankment dam, it shares some similarities with other types of dams, such as arch dams and gravity dams.
- Arch Dams: Arch dams, like the Hoover Dam, are curved structures that transfer the water pressure to the surrounding rock formations. They are typically built in narrow canyons where the rock is strong and stable. The Strom Thurmond Dam, being an embankment dam, relies on the weight of its earthfill materials for stability, unlike arch dams, which rely on the strength of the surrounding rock.
- Gravity Dams: Gravity dams, such as the Grand Coulee Dam, are massive, straight structures that rely on their weight to resist the water pressure. They are typically built in wider valleys where the rock is less stable. While the Strom Thurmond Dam also uses its weight for stability, it is an embankment dam, meaning it is constructed primarily of earthfill materials, unlike gravity dams, which are built of concrete.
Purpose and Functions
The Strom Thurmond Dam, towering over the Savannah River, serves as a multifaceted infrastructure project, designed to meet a variety of critical needs for the surrounding region. Its primary functions encompass power generation, flood control, and water supply, each playing a vital role in the economic and social well-being of the area.The dam’s design and operation have had a profound impact on the surrounding environment and ecosystems.
Understanding these impacts is crucial to evaluating the overall effectiveness and sustainability of the project.
Power Generation
The Strom Thurmond Dam is a major source of hydroelectric power for the southeastern United States. The dam’s turbines harness the energy of the flowing water, converting it into electricity that powers homes, businesses, and industries. The dam’s power generation capacity is significant, contributing a substantial amount to the region’s energy supply.
Flood Control
The dam’s reservoir, Lake Thurmond, acts as a giant sponge, absorbing excess water during periods of heavy rainfall and preventing downstream flooding. The dam’s flood control function is crucial for protecting communities and infrastructure along the Savannah River from the devastating effects of floods. The dam’s ability to regulate water flow has significantly reduced the risk of flooding in the region.
Water Supply
The dam’s reservoir also serves as a vital source of water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use. The water stored in Lake Thurmond provides a reliable and consistent water supply for millions of people and businesses in the region. The dam’s water supply function is essential for sustaining the region’s economic and social activities.
Environmental Impacts, What type of dam is the strom thurmond dam
The construction and operation of the Strom Thurmond Dam have had significant environmental impacts. The dam’s construction led to the flooding of a vast area of land, displacing numerous plant and animal species. The dam’s presence has also altered the natural flow of the Savannah River, impacting fish populations and aquatic ecosystems. The dam’s reservoir, while providing numerous benefits, has also led to changes in water temperature and chemistry, affecting the diversity and abundance of aquatic life.
The dam’s presence has also altered the sediment transport patterns of the river, impacting downstream ecosystems.
Economic and Social Benefits
The Strom Thurmond Dam has brought numerous economic and social benefits to the surrounding region. The dam’s power generation capacity has stimulated economic development, creating jobs and boosting local economies. The dam’s flood control function has protected communities and infrastructure, reducing economic losses due to flooding. The dam’s water supply function has supported agriculture, industry, and residential development, contributing to the overall growth and prosperity of the region.The dam has also played a significant role in promoting tourism and recreation.
Lake Thurmond is a popular destination for boating, fishing, and other recreational activities, attracting visitors and generating revenue for local businesses. The dam’s presence has also enhanced the quality of life for residents of the region, providing access to clean water and recreational opportunities.
Operational Aspects
The Strom Thurmond Dam is a complex and vital piece of infrastructure that requires careful management and maintenance to ensure its continued operation and safety. Its operation involves a sophisticated system of monitoring, control, and procedures that aim to balance the needs of power generation, flood control, and recreation.
Water Flow Management
The dam’s primary function is to regulate water flow in the Savannah River. This involves managing the volume of water released downstream, which is crucial for a variety of purposes, including:
- Power Generation: The dam’s hydroelectric power plant generates electricity by using the force of water flowing through its turbines. The amount of water released is adjusted to meet changing energy demands.
- Flood Control: During periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt, the dam can store excess water in its reservoir, preventing flooding downstream. This is crucial for protecting communities and infrastructure along the river.
- Navigation: The dam’s operation also influences water levels downstream, which is important for navigation and recreational activities.
- Water Quality: The dam’s operation can affect water quality by influencing the flow of nutrients and pollutants downstream.
Maintenance and Safety
To ensure the dam’s long-term stability and operational efficiency, regular maintenance and inspections are essential. These activities include:
- Structural Inspections: The dam’s concrete structure is inspected for signs of cracks, erosion, or other damage.
- Spillway Inspections: The spillway, which is used to release excess water during high flows, is inspected for any blockages or damage.
- Turbine Maintenance: The hydroelectric turbines are regularly inspected and maintained to ensure their efficiency and reliability.
- Emergency Preparedness: The dam operators have a comprehensive emergency plan in place to address potential risks such as earthquakes, floods, or structural failures.
Safety Concerns
While the Strom Thurmond Dam is designed to be safe, there are potential risks associated with its operation. These include:
- Dam Failure: While highly unlikely, the possibility of dam failure exists. This could be caused by factors such as earthquakes, floods, or structural weaknesses.
- Spillway Overtopping: If water levels in the reservoir rise too high, the spillway could be overtopped, potentially leading to damage to the dam or downstream infrastructure.
- Erosion: Erosion of the dam’s foundation or surrounding areas could compromise the dam’s stability.
- Security Threats: The dam is a critical piece of infrastructure, and there is a potential for security threats, such as acts of sabotage or terrorism.
Dam Monitoring and Control
The dam’s operation is monitored and controlled by a sophisticated system that includes:
- Sensors: Sensors are used to monitor water levels, flow rates, and other parameters in the reservoir and downstream.
- Control Systems: Control systems are used to adjust the dam’s gates and turbines to manage water flow and power generation.
- Remote Monitoring: The dam’s operation is monitored remotely by engineers and operators, allowing for quick response to any problems.
Environmental Impact
The construction and operation of the Strom Thurmond Dam have had significant environmental impacts on the Savannah River and its surrounding ecosystems. While the dam has provided numerous benefits, it has also altered the natural flow of the river, impacting fish migration, water quality, and biodiversity.
Fish Migration
The dam’s presence creates a physical barrier, preventing the free movement of fish species that rely on the river for spawning and feeding grounds.
- Upstream Migration: Anadromous fish, such as American shad and striped bass, which migrate upstream to spawn, are unable to reach their traditional spawning grounds above the dam. The dam has significantly reduced the populations of these species in the Savannah River.
- Downstream Migration: Catadromous fish, such as American eel, which migrate downstream to the ocean, are also affected. Young eels migrating downstream to the ocean may be trapped in the reservoir, hindering their journey.
To mitigate these impacts, fish ladders and fish passage structures have been implemented to allow some fish to bypass the dam. However, the effectiveness of these structures is limited, and the overall impact on fish migration remains significant.
The Strom Thurmond Dam, a remarkable engineering feat, stands as a testament to human ingenuity and a force shaping the landscape and lives of those who call this region home. Its construction, a testament to human ambition and skill, has left an indelible mark on the environment and the lives of those who live nearby. The dam’s legacy, a complex tapestry of benefits and challenges, continues to be debated and analyzed, reminding us of the profound impact that human endeavors can have on the world around us.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the height of the Strom Thurmond Dam?
The Strom Thurmond Dam is approximately 210 feet (64 meters) high.
What is the purpose of the Strom Thurmond Dam?
The primary purposes of the Strom Thurmond Dam include hydroelectric power generation, flood control, and water supply.
Who is the Strom Thurmond Dam named after?
The dam was renamed in honor of Strom Thurmond, a prominent US Senator from South Carolina, in 1989.
What are the environmental impacts of the Strom Thurmond Dam?
The dam has had significant impacts on the surrounding ecosystem, including altering fish migration patterns, impacting water quality, and influencing biodiversity.






