Was kostet eine kilowattstunde strom? It’s a question that pops up when you’re trying to figure out how much you’re paying for your electricity bill, especially in a place like Germany where electricity costs can vary depending on the time of day, the season, and even the energy source used. But don’t worry, we’re breaking down the cost of electricity in Germany and how it all works.
Electricity prices in Germany are influenced by a bunch of factors, from government regulations to the increasing use of renewable energy sources. We’ll explore how these factors play a role in shaping your electricity bill and how you can make the most of your energy consumption.
Understanding Electricity Costs

Understanding the cost of electricity is crucial for making informed decisions about energy consumption. To understand electricity costs, it is essential to grasp the concept of kilowatt-hour (kWh) and the various factors influencing the price of electricity.
Kilowatt-Hour (kWh) as a Unit of Energy Consumption, Was kostet eine kilowattstunde strom
The kilowatt-hour (kWh) is the standard unit of measurement for electricity consumption. It represents the amount of energy used when a 1-kilowatt (kW) appliance is operated for one hour. For example, a 100-watt light bulb running for 10 hours consumes 1 kWh of energy (100 watts x 10 hours = 1000 watt-hours = 1 kWh).
Components of Electricity Costs
The cost of electricity is influenced by a combination of factors, including:
- Generation: The cost of producing electricity from various sources, such as coal, natural gas, nuclear power, solar, and wind, varies depending on the fuel source, technology, and environmental regulations.
- Transmission: The cost of transporting electricity from power plants to distribution centers over high-voltage lines.
- Distribution: The cost of delivering electricity to individual consumers through local networks of power lines and transformers.
- Taxes and Fees: State and local governments may impose taxes and fees on electricity consumption, which contribute to the overall cost.
Factors Influencing Electricity Prices
Several factors can influence the price of electricity, including:
- Time of Day: Electricity prices can fluctuate throughout the day, with higher prices during peak demand hours (typically during the afternoon and evening) and lower prices during off-peak hours (typically during the night and early morning). This is often referred to as “time-of-use” pricing.
- Season: Electricity prices may be higher during certain seasons, such as the summer when air conditioning demand is high or the winter when heating demand is high.
- Energy Source: The price of electricity can be affected by the cost of fuel used to generate electricity. For example, if the price of natural gas rises, the cost of electricity generated from natural gas power plants may increase.
- Market Conditions: The price of electricity is also influenced by market conditions, such as supply and demand, and the availability of alternative energy sources. For instance, if there is a shortage of electricity supply, prices may rise due to increased demand.
Factors Affecting Electricity Prices in Germany
Germany’s electricity prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including government regulations, renewable energy integration, and international market dynamics. Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending the current pricing landscape and predicting future trends.
Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies play a significant role in shaping electricity prices in Germany. These regulations encompass a wide range of measures aimed at promoting renewable energy, ensuring grid stability, and ensuring consumer protection. The German government has implemented a series of policies to encourage the development of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. These policies include feed-in tariffs, which guarantee a fixed price for electricity generated from renewable sources, and subsidies for renewable energy projects.
While these policies have contributed to the growth of renewable energy in Germany, they have also increased the cost of electricity for consumers.Furthermore, the government regulates the operation of the electricity market, including the wholesale and retail prices of electricity. This regulation aims to ensure fair competition among electricity providers and protect consumers from price gouging.
The German government’s regulatory framework is designed to balance the competing objectives of promoting renewable energy, ensuring grid stability, and protecting consumers.
Impact of Renewable Energy Sources
The increasing penetration of renewable energy sources in Germany has had a significant impact on electricity costs. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are generally less expensive than fossil fuels in the long term. However, the intermittent nature of these sources, which means they are not always available when needed, presents challenges for grid stability and requires investments in energy storage and backup systems.The integration of renewable energy into the electricity grid has led to fluctuations in electricity prices, particularly during periods of high renewable energy output.
When renewable energy production exceeds demand, electricity prices can fall significantly, even reaching negative values. However, when renewable energy production is low, for example, during calm weather or at night, electricity prices can rise due to increased reliance on fossil fuel-based power plants.
The increasing share of renewable energy in Germany’s electricity mix has led to price volatility, but it has also contributed to a gradual decline in overall electricity costs.
Comparison with Other European Countries
Germany’s electricity prices are relatively high compared to those in other European countries. This is partly due to the country’s high renewable energy targets and the associated costs of integrating these sources into the grid. However, it is important to note that electricity prices vary significantly across Europe, influenced by factors such as energy mix, regulatory frameworks, and market competition.In 2022, the average electricity price for households in Germany was €0.34 per kilowatt-hour (kWh), according to Eurostat.
This is higher than the average price in the European Union, which was €0.24 per kWh. However, Germany’s prices are lower than those in Denmark (€0.43 per kWh) and Sweden (€0.42 per kWh), which have also made significant investments in renewable energy.
Germany’s electricity prices are relatively high compared to the European average, but they are lower than those in some other countries with high renewable energy penetration.
Typical Electricity Costs for Households in Germany

Understanding the typical electricity costs for households in Germany is crucial for budgeting and making informed decisions about energy consumption. The average cost of electricity varies depending on factors such as household size, energy consumption levels, and the specific electricity tariff chosen.
Average Electricity Costs per kWh
The average electricity cost per kWh in Germany can vary significantly depending on factors such as household size and energy consumption levels. The following table provides a general overview of average electricity costs for different household sizes and energy consumption levels:
| Household Size | Energy Consumption (kWh/year) | Average Electricity Cost per kWh (€) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Person | 2,000 | 0.30 |
| 2 Persons | 3,500 | 0.28 |
| 3 Persons | 5,000 | 0.26 |
| 4 Persons | 6,500 | 0.25 |
It is important to note that these are just average figures, and actual costs may vary depending on individual circumstances.
Comparison of Electricity Costs with Other Household Utilities
A visual representation comparing the cost of electricity in Germany to the cost of other household utilities can provide a better understanding of the relative expense of electricity. For example, a bar graph could be used to compare the average annual cost of electricity, water, and gas for a typical household.The bar graph would show that electricity costs are typically higher than water costs but lower than gas costs.
This comparison helps to highlight the significance of electricity costs in the overall household budget and emphasizes the importance of energy efficiency measures to reduce electricity consumption.
Common Household Appliances and Their Estimated Energy Consumption
Understanding the energy consumption of common household appliances can help identify areas where energy savings can be made. Here are some examples of common household appliances and their estimated energy consumption in kWh:
| Appliance | Estimated Energy Consumption (kWh/year) |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 250-400 |
| Washing Machine | 200-300 |
| Dishwasher | 150-250 |
| Oven | 100-200 |
| Television | 50-100 |
| Computer | 50-100 |
By understanding the energy consumption of these appliances, households can make informed decisions about their usage and potentially reduce their electricity costs. For example, choosing energy-efficient appliances, using appliances only when necessary, and taking advantage of energy-saving features can all contribute to lower electricity bills.
Strategies for Reducing Electricity Costs: Was Kostet Eine Kilowattstunde Strom
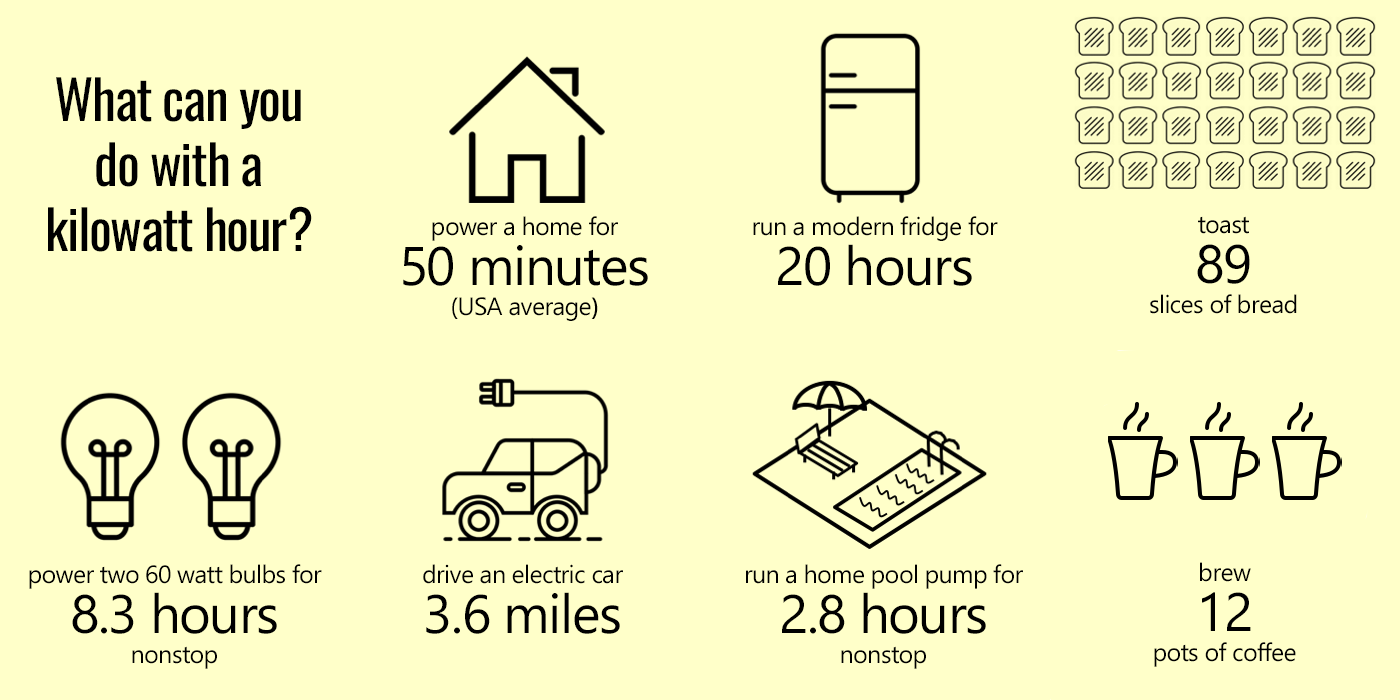
In Germany, where electricity prices are relatively high compared to other European countries, finding ways to reduce energy consumption and lower electricity bills is essential. There are various strategies that households can implement to optimize energy usage and save money on their electricity costs.
Optimizing Energy Consumption at Home
Adopting energy-efficient practices at home can significantly impact electricity consumption and reduce overall costs. This involves making conscious choices regarding appliance usage, lighting, and heating systems.
- Using Energy-Efficient Appliances: Investing in appliances with high energy efficiency ratings, such as those with an A+++ rating, can lead to substantial savings in the long run. Energy-efficient appliances consume less electricity to perform the same tasks, resulting in lower energy bills.
- Adjusting Thermostat Settings: By lowering the thermostat temperature by just a few degrees, you can significantly reduce heating costs. Consider using a programmable thermostat to automatically adjust temperatures based on your daily routines, further optimizing energy consumption.
- Switching to LED Lighting: LED lights are significantly more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. Replacing all incandescent bulbs with LEDs can result in substantial savings on electricity costs, as LEDs consume significantly less power for the same level of brightness.
- Unplugging Devices When Not in Use: Many electronic devices, such as TVs, computers, and chargers, continue to draw power even when they are turned off. Unplugging these devices when not in use can help reduce phantom load and save energy.
- Using Energy-Saving Modes: Many appliances and devices have energy-saving modes that can reduce their power consumption. Utilizing these modes can help reduce electricity usage without compromising functionality.
- Washing Clothes in Cold Water: Washing clothes in cold water significantly reduces energy consumption, as heating water for washing accounts for a significant portion of the energy used by washing machines.
- Air-Drying Clothes: Air-drying clothes instead of using a tumble dryer can save a considerable amount of energy. This practice is particularly effective during warmer months when natural air drying is feasible.
Comparing Electricity Tariffs
Choosing the right electricity tariff can have a significant impact on electricity costs. Different tariffs offer varying pricing structures, with each having its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Fixed Tariffs: Fixed tariffs provide a set price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) for a specific period, usually a year or longer. This predictability is beneficial for budgeting, as you know exactly how much you will be paying for electricity. However, fixed tariffs can be more expensive than variable tariffs if electricity prices decrease during the contract period.
- Variable Tariffs: Variable tariffs fluctuate based on market prices for electricity. This means that your electricity bill can change from month to month, depending on the prevailing market conditions. Variable tariffs can be cheaper than fixed tariffs if electricity prices decrease, but they can also be more expensive if prices rise.
- Time-of-Use Tariffs: Time-of-use tariffs charge different rates for electricity depending on the time of day or day of the week. Typically, electricity is more expensive during peak hours (e.g., evenings and weekends) and cheaper during off-peak hours (e.g., early mornings and late nights). This tariff structure encourages consumers to shift their energy consumption to off-peak hours to save money. However, it requires more careful planning and monitoring of energy usage.
Resources for Comparing Electricity Providers and Tariffs
Several resources and tools are available to consumers in Germany to help them compare electricity providers and tariffs. These resources can provide valuable information to make informed decisions and potentially save money on electricity bills.
- Verbraucherzentrale: The Verbraucherzentrale is a consumer protection organization that offers free and independent advice on various topics, including energy. Their website provides information on electricity tariffs, energy-saving tips, and resources for comparing providers.
- Check24: Check24 is a popular comparison website that allows consumers to compare electricity tariffs from different providers. The website provides a comprehensive overview of tariffs, including their pricing structures, contract terms, and customer reviews.
- Verivox: Verivox is another comparison website that provides detailed information on electricity tariffs. They offer a wide range of filters and sorting options to help consumers find the best tariff for their needs.
- Energy Saving Calculator: Several online energy saving calculators are available that allow consumers to estimate their potential savings by switching to a different tariff or implementing energy-saving measures.
Future Trends in Electricity Prices
Predicting future electricity prices is a complex task, influenced by various factors such as technological advancements, environmental policies, and evolving consumer behavior. Understanding these trends is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, as it allows for informed decision-making regarding energy consumption and investments.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a significant role in shaping future electricity prices. The integration of smart grids, energy storage solutions, and renewable energy technologies is expected to transform the energy landscape, leading to both cost reductions and increased efficiency.
- Smart grids enable real-time monitoring and control of electricity distribution, optimizing energy flow and reducing losses. This can lead to lower transmission costs and potentially lower electricity prices for consumers.
- Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro, allow for the storage of excess renewable energy generated during periods of high production. This helps balance supply and demand, reducing the need for expensive peak-load power plants and potentially lowering overall electricity costs.
- Advancements in renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, have led to significant cost reductions in recent years. As these technologies continue to improve and become more affordable, they are expected to play a larger role in the energy mix, potentially driving down electricity prices.
Climate Change and Sustainability Initiatives
The increasing focus on climate change and sustainability is driving the transition to a low-carbon energy system, which will significantly impact electricity prices. Governments and regulatory bodies are implementing policies to promote renewable energy and reduce carbon emissions, influencing the cost of electricity generation.
- Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or emissions trading schemes, incentivize the use of low-carbon energy sources. This can lead to higher electricity prices for fossil fuel-based power plants, but also create opportunities for renewable energy to become more competitive.
- Renewable energy subsidies and feed-in tariffs are government programs designed to encourage the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies. These subsidies can reduce the cost of renewable energy generation, potentially leading to lower electricity prices for consumers.
- Energy efficiency standards are regulations that promote the use of energy-efficient appliances and building materials. By reducing energy consumption, these standards can help lower overall electricity demand, potentially contributing to lower electricity prices.
Emerging Trends in Energy Consumption Patterns
Consumer behavior and energy consumption patterns are evolving rapidly, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing lifestyles, and growing awareness of environmental issues. These trends have significant implications for electricity pricing.
- The rise of electric vehicles is expected to increase electricity demand, potentially putting pressure on electricity prices. However, the development of smart charging technologies, which can optimize charging times to coincide with periods of low electricity demand, can mitigate this impact.
- The increasing adoption of smart home technologies, such as automated lighting and temperature control systems, can lead to more efficient energy consumption. This can help reduce overall electricity demand and potentially lower electricity prices.
- The growing popularity of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar panels and home battery storage systems, is empowering consumers to generate their own electricity. This can lead to a shift away from traditional centralized power generation, potentially impacting electricity pricing models.
So, there you have it! Understanding the factors that affect electricity costs in Germany can help you make informed decisions about your energy usage and potentially save some dough. From choosing energy-efficient appliances to exploring different tariffs, there are plenty of ways to optimize your electricity consumption and keep your wallet happy. Remember, being aware of your energy usage is the first step to taking control of your electricity costs.
Essential Questionnaire
What are some tips for saving money on my electricity bill in Germany?
Switch to energy-efficient appliances, use LED lighting, adjust your thermostat settings, and consider switching to a cheaper electricity tariff.
How do I compare electricity providers and tariffs in Germany?
Check out online comparison websites and use tools provided by consumer protection organizations to find the best deals.
What is the average electricity cost per kWh in Germany?
The average electricity cost per kWh in Germany varies, but it’s generally around 30 cents per kWh.
How does renewable energy impact electricity costs in Germany?
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power can help reduce electricity costs in the long run, but they can also lead to fluctuations in pricing due to factors like weather conditions.






