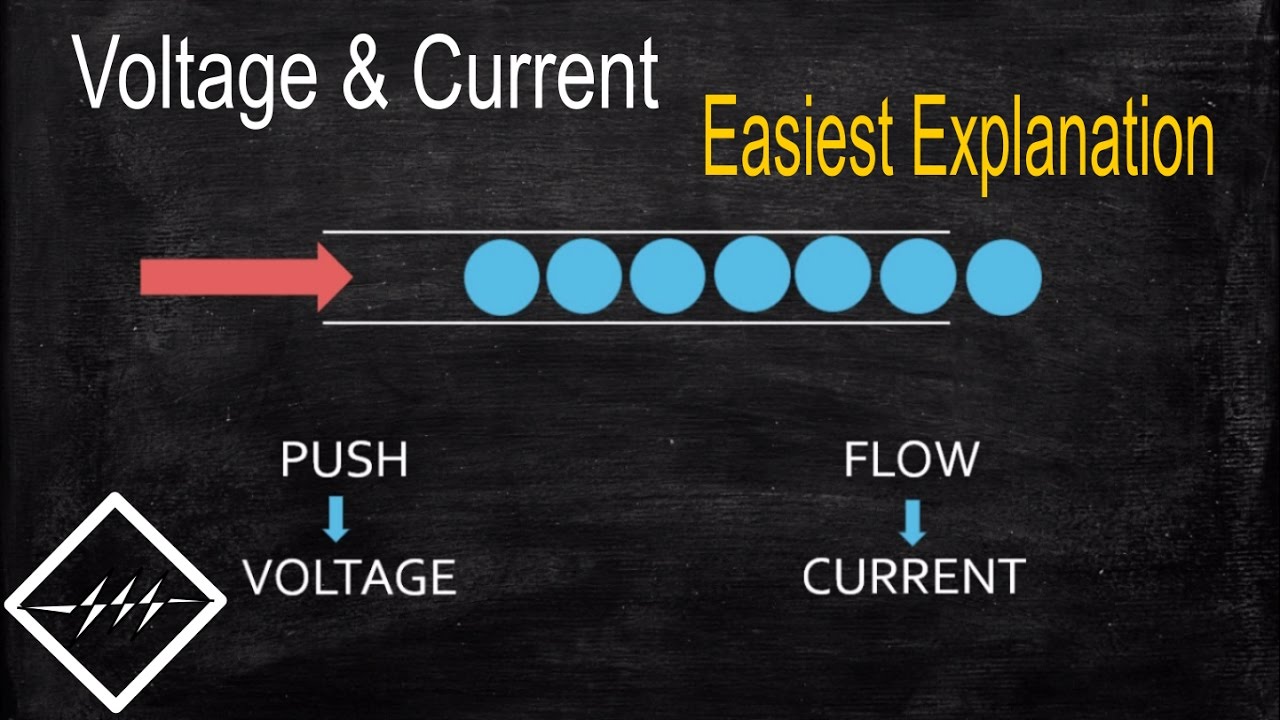
Was ist Spannung Strom? Ever wondered what makes your phone light up, your blender whir, or your fridge stay cool? It’s all about electricity, my friend, and the key players are voltage (Spannung) and current (Strom). Imagine it like this: Voltage is the push, the force that gets the electricity moving. Current is the flow, the actual movement of electrons through wires and circuits.
It’s a dynamic duo that powers our modern world, from the smallest gadgets to the largest power grids.
In this guide, we’ll dive into the heart of electricity, exploring the concepts of voltage and current, their relationship, and how they impact our lives. We’ll uncover the mysteries of Ohm’s Law, discover the power of electrical circuits, and learn how to stay safe around electricity. Ready to get energized? Let’s go!
Understanding “Spannung” (Voltage)
Imagine a water tank. The water at the bottom of the tank has less potential energy than the water at the top. This difference in potential energy is what drives the water to flow out of a hole at the bottom. Similarly, in an electrical circuit, “Spannung” or voltage represents the electrical potential difference between two points. This difference in potential energy is what causes electrons to flow from one point to another, creating an electric current.
The Concept of Voltage
Voltage is a measure of the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. It is the force that pushes electrons through a conductor, similar to how a water pump pushes water through a pipe. The higher the voltage, the greater the force pushing the electrons, resulting in a stronger current.
Analogy of Voltage
Imagine a hill with a water slide. The height of the hill represents the voltage. The higher the hill, the greater the potential energy of the water at the top. As the water slides down, it gains kinetic energy, just like electrons flowing through a conductor. The steeper the slide, the faster the water flows, representing a higher current.
Units of Measurement for Voltage
Voltage is measured in Volts (V). One Volt is defined as the potential difference required to move one Coulomb of charge through a conductor, doing one Joule of work.
1 Volt = 1 Joule / 1 Coulomb
The significance of the Volt unit lies in its ability to quantify the electrical potential difference. This measurement is crucial for understanding and controlling the flow of electricity in various applications, from everyday appliances to complex electronic circuits.
Understanding “Strom” (Current)
In the realm of electricity, “Strom” refers to the flow of electric charge. It’s like the movement of water through a pipe, carrying energy from one point to another. Understanding “Strom” is crucial for comprehending how electrical circuits work and how devices utilize electrical energy.
The Relationship Between Current and Electron Flow
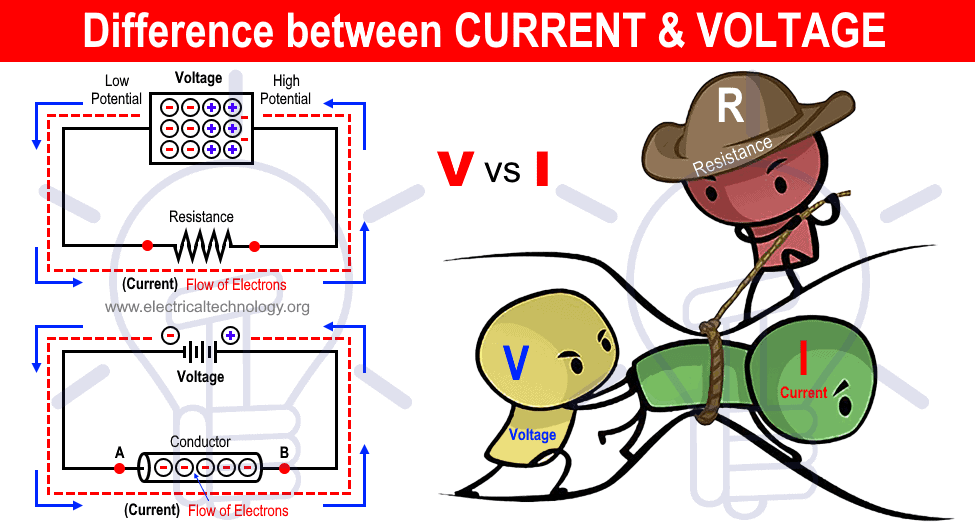
Electric current is the movement of electrically charged particles, primarily electrons, through a conductor. When a voltage is applied across a conductor, an electric field is created. This electric field exerts a force on the free electrons within the conductor, causing them to move in a specific direction. The collective movement of these electrons constitutes the electric current.
Analogy: Water Flowing Through a Pipe
To visualize the concept of current, consider the analogy of water flowing through a pipe. The water pressure in the pipe is analogous to the voltage in an electrical circuit. The rate at which water flows through the pipe is analogous to the electric current. Just as water pressure drives the flow of water, voltage drives the flow of electrons.
Units of Measurement for Current
The standard unit of measurement for electric current is the Ampere (A). One Ampere represents the flow of one Coulomb of electric charge per second.
The higher the Ampere value, the greater the amount of charge flowing per unit of time.
Amps are a crucial measure in electrical systems. They determine the amount of electrical energy being transferred and the capacity of wires and components to handle the flow of electricity.
Relationship between Voltage and Current
Voltage and current are inextricably linked in an electrical circuit. Imagine them as partners, each playing a crucial role in the flow of electrical energy. Understanding their relationship is fundamental to grasping the workings of any electrical system.
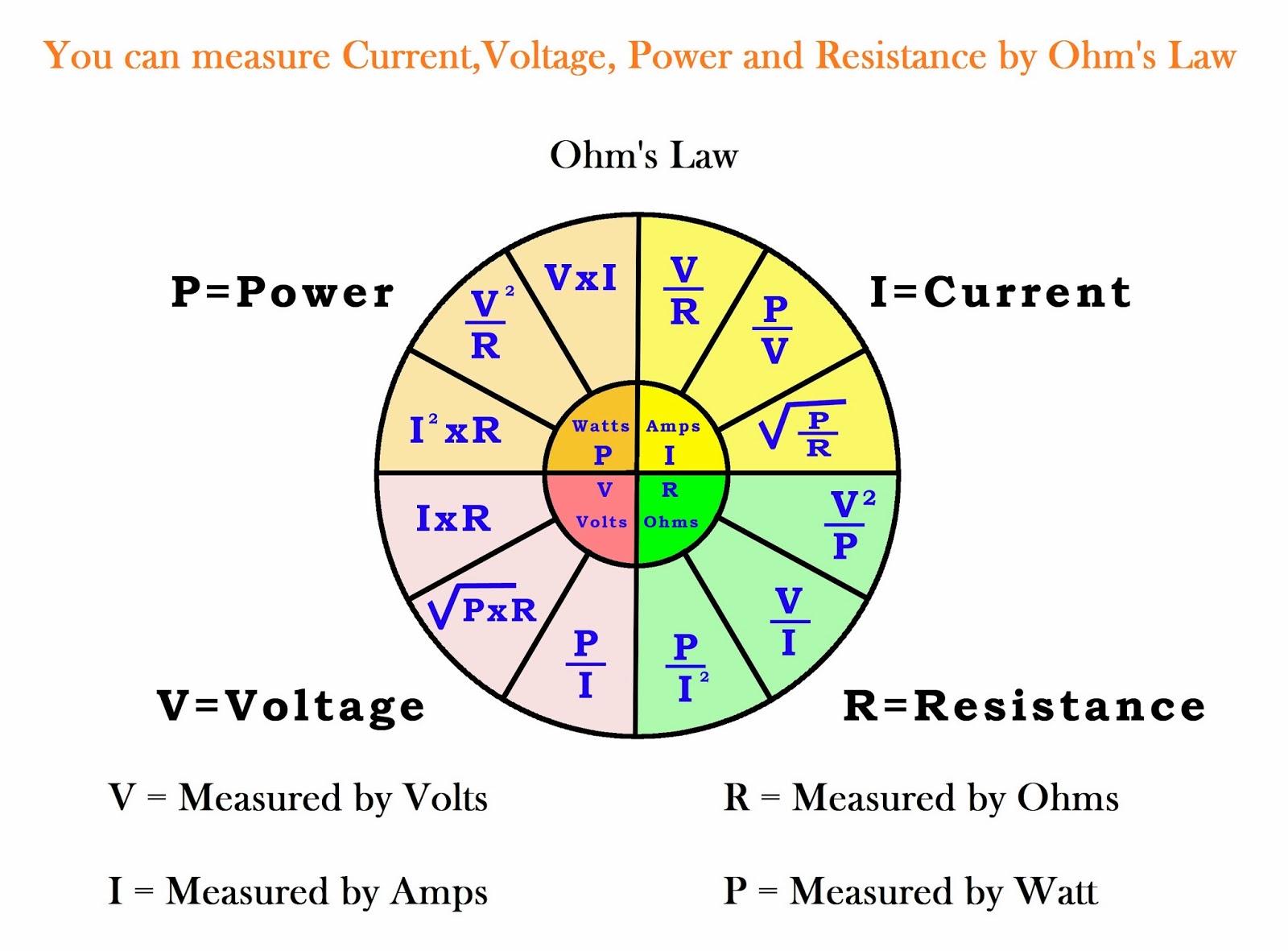
Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. It states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across its ends and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor.
I = V / R
Where:* I represents the current in amperes (A)
- V represents the voltage in volts (V)
- R represents the resistance in ohms (Ω)
This formula highlights the interconnectedness of these three variables. Increasing the voltage will increase the current, while increasing the resistance will decrease the current.
Effects of Changing Voltage or Resistance
- Changing Voltage: Imagine a simple circuit with a battery and a light bulb. If you increase the voltage of the battery, the current flowing through the circuit and the light bulb will also increase, causing the bulb to shine brighter. Conversely, decreasing the voltage will dim the light bulb.
- Changing Resistance: Now, consider the same circuit but with a variable resistor. Increasing the resistance of the resistor will decrease the current flowing through the circuit, resulting in a dimmer light bulb. Decreasing the resistance will increase the current, making the bulb shine brighter.
Electrical Power
Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred or used. It is measured in watts (W) and is calculated by multiplying the voltage by the current.
P = V – I
Where:* P represents the power in watts (W)
- V represents the voltage in volts (V)
- I represents the current in amperes (A)
For example, a light bulb rated at 100 watts operating on a 120-volt circuit draws a current of 0.83 amperes (100 W / 120 V = 0.83 A). This relationship underscores the importance of understanding voltage and current in determining the power consumption of electrical devices.
Practical Applications of Voltage and Current
Voltage and current are fundamental concepts in electricity, playing crucial roles in powering our modern world. They are the driving forces behind a wide range of applications, from everyday household appliances to complex electronic devices and vast power grids. Understanding how voltage and current interact is essential for comprehending the workings of electrical systems and ensuring their safe and efficient operation.
Household Appliances
Voltage and current are essential for powering household appliances. Each appliance has specific voltage and current requirements, which are typically indicated on its label.
- Voltage: Determines the electrical potential difference that drives the flow of current. Household appliances in most countries operate on standard voltages, such as 120 volts (V) in the United States and 230 V in Europe.
- Current: Represents the rate of flow of electrical charge. Higher current ratings indicate a greater amount of electrical energy flowing through the appliance. For example, a microwave oven requires a higher current than a simple lamp due to its higher power consumption.
Electronic Devices
Electronic devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and televisions, rely heavily on voltage and current.
- Voltage: Determines the operating voltage of the device’s internal components, such as the processor, memory, and display. These components are designed to operate within a specific voltage range, ensuring their proper functioning.
- Current: Represents the amount of electrical charge flowing through the device’s circuitry. Higher current ratings are often required for devices with more powerful processors or larger displays.
Power Grids, Was ist spannung strom
Power grids are vast networks that distribute electricity from power plants to consumers.
- Voltage: Power plants generate electricity at high voltages, typically thousands of volts, for efficient transmission over long distances. Transformers are used to step up and step down the voltage along the grid, ensuring safe and efficient delivery to consumers.
- Current: The current flowing through the power grid varies depending on the load, or the amount of electricity being used by consumers. Higher current flow occurs during peak demand periods, such as evenings and weekends, when more appliances and devices are in use.
Safety Precautions
Electricity can be dangerous if not handled properly. High voltage and current can cause severe burns, electrocution, and even death.
- High Voltage: Contact with high-voltage lines or equipment can be fatal. Always maintain a safe distance from these sources and never attempt to repair or modify them without proper training and safety equipment.
- High Current: Even low-voltage circuits can carry dangerous currents. Always use caution when working with electrical wires and appliances, and unplug devices before working on them. Never touch electrical wires or appliances with wet hands, as water can conduct electricity and increase the risk of electrocution.
So, there you have it! Voltage and current, two fundamental forces that shape our world. From the simple act of turning on a light switch to the complex workings of a computer, these electric concepts are everywhere. Understanding them helps us appreciate the power of electricity and use it safely and effectively. Keep exploring, keep learning, and remember, the world is full of electrifying possibilities!
FAQ Compilation: Was Ist Spannung Strom
What is the difference between AC and DC current?
AC (Alternating Current) changes direction periodically, while DC (Direct Current) flows in one direction. AC is used in most household outlets, while DC powers devices like phones and laptops.
What is the danger of high voltage?
High voltage can cause electric shock, which can be fatal. Always be cautious around high-voltage equipment and follow safety guidelines.
How do I calculate the power used by a device?
Power is calculated by multiplying voltage and current (P = V x I). The unit of power is the watt (W).






