“Was kostet 1 kWh Strom in den USA?” is a question that many people ask, especially those considering relocating or simply curious about energy costs in the United States. The cost of electricity in the US varies significantly depending on location, energy sources, and local regulations. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about energy consumption and saving money on your energy bills.
Electricity costs in the US are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including the type of energy source used to generate power, the cost of transporting electricity, and the regulations imposed by state and local governments. For instance, states with abundant renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, often have lower electricity prices compared to states heavily reliant on fossil fuels.
Transmission costs also play a significant role, as electricity needs to be transported from power plants to homes and businesses, adding to the overall cost. Additionally, local regulations, such as taxes and fees, can influence the final price consumers pay for electricity.
Understanding Electricity Costs in the USA: Was Kostet 1 Kwh Strom In Den Usa
Electricity is an essential part of modern life, powering our homes, businesses, and communities. Understanding how electricity costs are determined and what factors influence them is crucial for making informed decisions about energy consumption and saving money.
Average Electricity Cost
The average cost of electricity in the USA is approximately 13.2 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh) as of 2023, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). However, this average can vary significantly across different regions and states.
Factors Influencing Electricity Prices
Several factors contribute to the variations in electricity prices across the USA. These include:
- Energy Sources: The type of fuel used to generate electricity, such as coal, natural gas, nuclear power, or renewable sources like solar and wind, can impact the cost of production. For instance, states with a high reliance on natural gas may experience fluctuations in electricity prices based on natural gas market prices.
- Transmission Costs: The cost of transmitting electricity from power plants to consumers can vary depending on the distance and infrastructure required. States with extensive transmission networks may have lower transmission costs compared to those with limited infrastructure.
- Local Regulations: State and local regulations can influence electricity prices by imposing taxes, fees, and other charges on utilities. These regulations can vary widely across the country, leading to differences in electricity costs.
- Demand: The demand for electricity can also affect prices. During peak demand periods, such as hot summer days or cold winter nights, utilities may need to generate more electricity, potentially leading to higher prices.
Typical Electricity Bills
The cost of an electricity bill can vary widely based on factors such as household size, energy consumption habits, and local electricity rates. Here are some examples of typical electricity bills for different household sizes and energy consumption levels:
- Small Household (1-2 people): A small household with moderate energy consumption might have an average monthly bill of $50-$100.
- Medium Household (3-4 people): A medium-sized household with typical energy usage might have an average monthly bill of $100-$200.
- Large Household (5+ people): A large household with high energy consumption, such as a family with multiple appliances and electronic devices, might have an average monthly bill of $200-$300 or more.
It’s important to note that these are just estimates, and actual electricity bills can vary significantly based on individual circumstances.
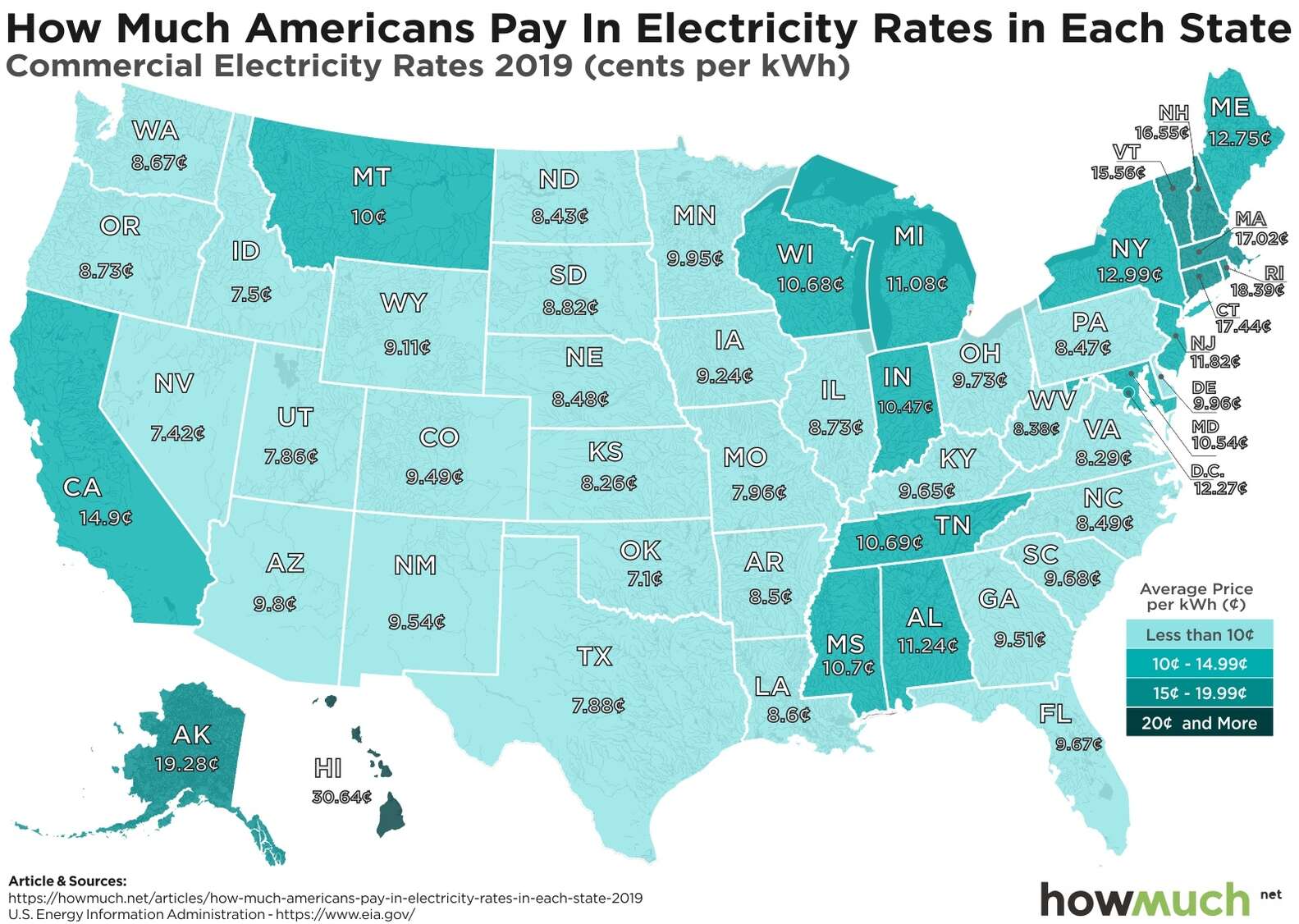
Comparing Electricity Costs Across States

The cost of electricity can vary significantly across the United States, influenced by factors such as energy source, regulatory policies, and local demand. Understanding these variations can help consumers make informed decisions about energy consumption and potentially save money on their electricity bills.
Average Electricity Costs Across States
The average cost of electricity per kilowatt-hour (kWh) in the United States varies significantly across states. This variation is due to several factors, including the energy source used to generate electricity, the regulatory environment, and the local demand for electricity.
| State | Average kWh Cost (cents) | Energy Source | Notable Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hawaii | 36.1 | Mostly oil and renewable sources | High reliance on imported fossil fuels, limited land for renewable energy development |
| Connecticut | 24.5 | Nuclear, natural gas, and renewables | High population density, competitive energy market |
| Texas | 11.8 | Mostly natural gas and coal | Large-scale energy production, deregulated energy market |
| Idaho | 9.5 | Hydroelectric and coal | Abundant hydroelectric resources, low population density |
The average cost of electricity per kWh in the United States is 13.3 cents.
Factors Contributing to Electricity Price Variations
The price of electricity is influenced by several factors, including:
- Energy Source: The cost of generating electricity varies depending on the energy source used. For example, electricity generated from renewable sources like solar and wind is typically cheaper than electricity generated from fossil fuels like coal and natural gas.
- Regulatory Environment: State regulations can impact the price of electricity. For example, states with deregulated energy markets tend to have lower electricity prices than states with heavily regulated markets.
- Local Demand: The demand for electricity in a particular area can also affect prices. For example, areas with high population density and industrial activity tend to have higher electricity prices than areas with low population density and limited industrial activity.
Impact of Electricity Price Variations on Consumers
The variation in electricity prices across states can have a significant impact on consumers. For example, consumers living in states with high electricity prices may face higher energy bills, which can strain their budgets. This can lead to a greater need for energy conservation efforts to reduce energy consumption and save money.
Understanding Residential Electricity Usage
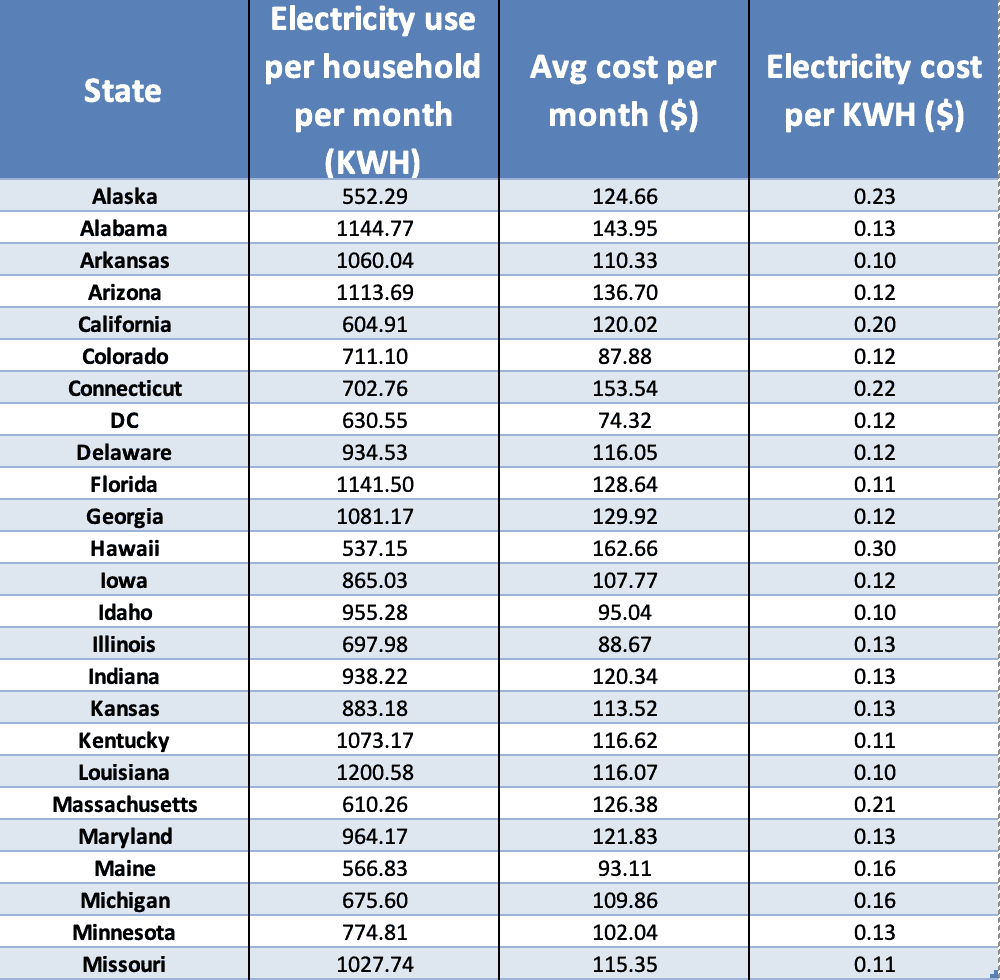
Understanding how much electricity a household uses is essential for managing energy consumption and reducing costs. A typical American household’s electricity usage varies based on factors like location, size, occupancy, and energy efficiency of appliances.
Typical Electricity Consumption Patterns
The average American household uses approximately 10,972 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity annually, which translates to about 914 kWh per month. This average consumption can fluctuate depending on the season and the household’s lifestyle. For example, during the summer months, air conditioning usage increases significantly, leading to higher energy consumption. Conversely, heating systems contribute to increased energy usage during the winter.
Major Appliances and Devices
Several appliances and devices contribute significantly to a home’s electricity consumption. Understanding these energy consumers can help you identify areas where you can save energy and money.
- Heating and Cooling: These systems are the biggest energy consumers in most homes. Air conditioners, furnaces, and heat pumps account for a significant portion of a household’s electricity bill, particularly during extreme weather conditions.
- Water Heating: Electric water heaters consume a substantial amount of energy, especially in homes with large families or frequent hot water usage.
- Refrigerator and Freezer: These appliances operate continuously, making them major electricity consumers. Modern refrigerators are more energy-efficient than older models, but they still contribute significantly to overall consumption.
- Lighting: While individual light bulbs may not consume much energy, the cumulative effect of multiple lights throughout a home can be substantial. Switching to energy-efficient LED bulbs can significantly reduce lighting-related energy consumption.
- Electronics: Televisions, computers, gaming consoles, and other electronic devices contribute to electricity consumption, especially when left on standby mode.
- Other Appliances: Appliances like ovens, washing machines, dryers, dishwashers, and microwaves also contribute to energy consumption, depending on their usage frequency and efficiency.
Typical Household Electricity Bill Breakdown
A typical household electricity bill reflects the breakdown of energy consumption across various appliances and devices. Here is a sample breakdown of a typical household electricity bill:
| Appliance/Device | Percentage of Consumption |
|---|---|
| Heating and Cooling | 30-45% |
| Water Heating | 15-20% |
| Refrigerator and Freezer | 10-15% |
| Lighting | 5-10% |
| Electronics | 5-10% |
| Other Appliances | 10-15% |
It’s important to note that these percentages are approximate and can vary depending on individual usage patterns and appliance efficiency.
Exploring Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
In the United States, residential electricity consumption accounts for a significant portion of household energy bills. By implementing energy efficiency measures, homeowners can significantly reduce their electricity consumption, leading to lower energy costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
Energy-Efficient Appliances and Technologies, Was kostet 1 kwh strom in den usa
Energy-efficient appliances and technologies play a crucial role in reducing electricity consumption in homes.
- LED Lighting: LED lights are significantly more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, consuming up to 80% less energy while lasting significantly longer.
- Energy Star Appliances: The Energy Star program certifies appliances that meet specific energy efficiency standards, helping consumers identify models that consume less energy and save money.
- Smart Thermostats: Smart thermostats learn your heating and cooling preferences and automatically adjust temperatures to optimize energy usage, reducing energy consumption by up to 15%.
- High-Efficiency Windows: Double- or triple-paned windows with low-emissivity coatings reduce heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, lowering energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Identifying and Addressing Energy Waste
Identifying and addressing energy waste in homes can significantly reduce electricity consumption and lower energy bills.
- Phantom Loads: Many electronic devices continue to consume electricity even when turned off. Unplugging these devices or using power strips with on/off switches can reduce phantom loads.
- Air Leaks: Air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings can lead to significant energy loss. Sealing these leaks with weather stripping, caulk, or foam insulation can improve energy efficiency.
- Inefficient Insulation: Insufficient insulation in attics, walls, and crawl spaces can result in heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Adding insulation can significantly improve energy efficiency.
- Water Heating: Water heating accounts for a significant portion of household energy consumption. Installing a tankless water heater or upgrading to a more energy-efficient model can reduce energy use.
Understanding Alternative Energy Sources
The United States is increasingly turning to renewable energy sources to meet its energy needs and reduce its reliance on fossil fuels. These sources offer a cleaner and more sustainable way to power homes and businesses.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources are derived from natural resources that are replenished over time, making them sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels. The most common types of renewable energy sources in the USA include:
- Solar Power: Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun through photovoltaic cells, converting sunlight directly into electricity. Solar panels are installed on rooftops, in solar farms, or even integrated into building materials. The USA has seen significant growth in solar power installations, particularly in sunny states like California, Arizona, and Nevada.
- Wind Power: Wind turbines capture the kinetic energy of wind and convert it into electricity. Wind farms are often located in areas with consistent wind speeds, such as coastal regions and open plains. Wind energy is a rapidly growing sector in the USA, with major wind farms operating in states like Texas, Iowa, and Oklahoma.
- Hydroelectric Power: Hydroelectric power utilizes the force of flowing water to generate electricity. Dams are built on rivers to create reservoirs, and the water is released through turbines to generate electricity. Hydroelectric power is a mature technology and provides a significant portion of the USA’s electricity generation, particularly in the Pacific Northwest.
- Geothermal Power: Geothermal energy taps into the heat beneath the Earth’s surface to generate electricity. Geothermal power plants are typically located in areas with volcanic activity or high geothermal gradients. The USA has several geothermal power plants operating in states like California, Nevada, and Utah.
- Biomass Energy: Biomass energy utilizes organic matter, such as wood, crops, and waste, to produce energy. Biomass can be burned directly to generate heat or converted into biofuels like ethanol. The USA has a significant biomass energy sector, particularly in states with abundant forest resources.
Costs and Benefits of Renewable Energy
The costs and benefits of renewable energy sources vary depending on the specific technology and location.
- Cost: The initial investment costs for renewable energy projects can be higher than traditional fossil fuel power plants. However, the operating costs of renewable energy sources are generally lower, as they do not require fuel.
- Benefits: Renewable energy sources offer several benefits, including:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Renewable energy sources do not emit greenhouse gases, contributing to mitigating climate change.
- Energy Security: Renewable energy sources reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security.
- Economic Development: Renewable energy projects create jobs and stimulate local economies.
Examples of Successful Renewable Energy Projects
The USA has numerous successful renewable energy projects demonstrating the viability and benefits of these technologies.
- California: California has a thriving solar energy industry, with numerous rooftop solar installations and large-scale solar farms. The state has ambitious goals for renewable energy development, aiming to achieve 100% clean energy by 2045.
- Texas: Texas is a leading state in wind energy, with vast wind farms generating electricity for homes and businesses. The state’s wind energy capacity has grown significantly in recent years, making it a major contributor to the USA’s renewable energy portfolio.
- Washington State: Washington State has a long history of hydroelectric power generation, with dams on the Columbia River providing a significant source of clean energy. The state is also exploring other renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power.
Understanding the factors that influence electricity costs in the USA is essential for both individuals and businesses. By making informed decisions about energy consumption and exploring energy efficiency measures, you can reduce your electricity bills and contribute to a more sustainable future. As the demand for energy continues to grow, it’s crucial to explore alternative energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to meet the energy needs of the nation while reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
Essential FAQs
What are some ways to save money on my electricity bill?
There are several ways to reduce your electricity consumption and save money on your bill, including using energy-efficient appliances, turning off lights when you leave a room, and using natural light whenever possible. You can also consider installing a programmable thermostat to optimize heating and cooling, and ensure your home is well-insulated to prevent heat loss.
How can I find out the average electricity cost in my state?
You can find the average electricity cost in your state by visiting the website of your local utility company or the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). The EIA provides detailed data on electricity prices across the country, including average costs by state and region.
What are the benefits of using renewable energy sources?
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, offer numerous benefits, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, creating jobs, and enhancing energy security. By relying less on fossil fuels, we can mitigate the negative impacts of climate change and promote a cleaner, more sustainable future.






