Was kostet strom im monat? It’s a question we all ask ourselves, especially when the bills start rolling in. The truth is, understanding your electricity costs can feel like deciphering a foreign language. But fear not, fellow energy warriors! We’re here to break down the complexities of German electricity bills and empower you to conquer those pesky charges.
From deciphering the different components of your bill to understanding the factors that influence your monthly costs, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your energy consumption. We’ll dive into the fascinating world of tariffs, peak and off-peak hours, and even explore the impact of renewable energy on your wallet. Get ready to become a power-saving pro!
Understanding Electricity Costs in Germany: Was Kostet Strom Im Monat
Navigating the complexities of electricity costs in Germany can be daunting, especially for newcomers. This guide will break down the key factors that determine your monthly electricity bill and provide insights into the different tariff options available.
Electricity Cost Calculation Methods
Electricity costs in Germany are primarily calculated based on your consumption and the applicable tariff. Here’s a breakdown of the common methods:
- kWh-based Billing: This is the most prevalent method, where you pay a fixed price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity consumed. This price can vary based on the tariff you choose.
- Two-Part Tariff: This method combines a fixed monthly fee with a per-kWh charge. The fixed fee covers the costs of network infrastructure and other fixed expenses, while the per-kWh charge reflects the actual energy consumption.
- Dynamic Pricing: This relatively newer approach adjusts the electricity price based on real-time market fluctuations. You may pay lower prices during periods of low demand and higher prices during peak demand.
Components of an Electricity Bill
Your electricity bill will typically include the following components:
- Energy Costs: This represents the largest portion of your bill and reflects the cost of the electricity you consumed.
- Network Charges: These charges cover the costs of maintaining the electricity grid, including transmission and distribution infrastructure.
- Taxes and Levies: Various taxes and levies, such as the renewable energy surcharge (EEG-Umlage), are included in your bill to support renewable energy initiatives and other public policies.
- Metering Costs: These charges cover the costs of reading and maintaining your electricity meter.
- Other Fees: Depending on your provider, you may also see charges for services like customer support or billing.
Electricity Tariffs
Electricity providers in Germany offer a variety of tariffs to cater to different consumption patterns and preferences. Here are some common examples:
- Basic Tariff: This is a simple, straightforward tariff with a fixed price per kWh. It’s suitable for consumers with consistent energy consumption.
- Discount Tariff: These tariffs offer a lower price per kWh for a specific period, often during off-peak hours or for a limited time.
- Variable Tariff: These tariffs allow the price per kWh to fluctuate based on market conditions. They can offer lower prices during periods of low demand, but the risk of higher prices during peak demand exists.
- Green Tariff: These tariffs focus on sourcing electricity from renewable sources like solar or wind power. They may come with a higher price per kWh but support sustainable energy practices.
Factors Influencing Monthly Electricity Costs
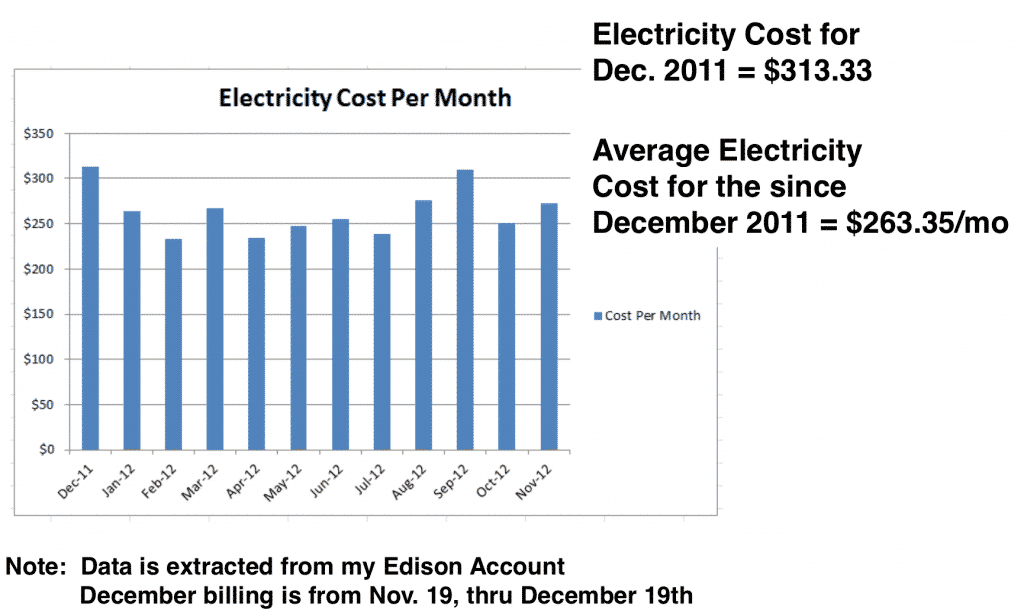
Your monthly electricity bill is not a fixed amount. Several factors influence how much you pay, making it essential to understand these variables to manage your energy consumption effectively. This knowledge empowers you to make informed choices that can significantly impact your electricity costs.
Household Size and Energy Consumption Habits
The number of people living in a household directly impacts energy consumption and, consequently, electricity bills. Larger families generally use more electricity due to increased appliance usage, lighting requirements, and heating or cooling needs. Energy consumption habits also play a crucial role. For example, leaving lights on in unoccupied rooms, running appliances unnecessarily, or using high-energy devices frequently contribute to higher electricity bills.
Conversely, adopting energy-saving practices like turning off lights when leaving a room, using energy-efficient appliances, and minimizing the use of high-energy devices can lead to significant cost reductions.
Appliance Efficiency and Usage Patterns
Appliance efficiency plays a critical role in determining electricity costs. Modern appliances, particularly those with energy-efficient labels, consume less electricity than older models. This difference in energy consumption translates directly to lower electricity bills. The frequency and duration of appliance usage also impact costs. For example, running a washing machine or dishwasher only when fully loaded minimizes energy consumption.
Similarly, using energy-efficient light bulbs and opting for shorter showers can lead to substantial savings.
Peak and Off-Peak Electricity Rates
Many electricity providers offer different rates for electricity consumption during peak and off-peak hours. Peak hours typically correspond to periods of high demand, usually during the day, while off-peak hours are typically during the night or early morning.
Electricity costs are generally higher during peak hours due to the increased demand on the power grid.
Taking advantage of off-peak rates by shifting energy-intensive activities like laundry or dishwashing to these hours can result in significant cost savings.
Estimating Monthly Electricity Costs
Accurately estimating your monthly electricity bill is crucial for budgeting and understanding your energy consumption habits. This section will provide you with tools and methods to calculate your estimated electricity bill and gain insights into your energy usage.
Calculating Your Estimated Electricity Bill
Estimating your electricity bill involves a simple calculation that considers your average daily electricity consumption and the current electricity price per kilowatt-hour (kWh). The formula is as follows:
Estimated Monthly Electricity Bill = (Average Daily Consumption in kWh) x (Electricity Price per kWh) x (Number of Days in a Month)
To utilize this formula effectively, you’ll need to know your average daily electricity consumption and the current electricity price per kWh. You can obtain the electricity price from your energy provider’s bill or website.
Average Electricity Consumption for Common Appliances
Understanding the average electricity consumption of common appliances can help you estimate your overall energy usage. The following table Artikels average consumption values for various devices:
| Appliance | Average Power Consumption (Watts) | Average Daily Usage (Hours) | Average Daily Consumption (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 100 | 24 | 2.4 |
| Washing Machine | 1,000 | 1 | 1 |
| Dishwasher | 1,500 | 1 | 1.5 |
| Oven | 2,000 | 1 | 2 |
| Television | 100 | 4 | 0.4 |
| Computer | 100 | 8 | 0.8 |
For example, a refrigerator consuming 100 watts for 24 hours a day would consume 2.4 kWh daily.
Tracking and Analyzing Personal Electricity Usage, Was kostet strom im monat
To gain a comprehensive understanding of your electricity usage, tracking your consumption is essential. This involves monitoring your electricity meter readings and analyzing the data to identify areas for potential savings.
- Record Meter Readings Regularly: Take note of your electricity meter readings at least once a week or even daily. This will allow you to track your consumption over time.
- Analyze Consumption Patterns: Compare your meter readings from different days and weeks to identify any noticeable trends or spikes in consumption. For instance, you might notice higher consumption on weekdays due to increased appliance usage.
- Identify High-Consumption Appliances: By analyzing your consumption data, you can identify appliances that contribute significantly to your overall electricity bill. This information can help you make informed decisions about energy-saving measures.
- Use Energy Monitoring Devices: Smart plugs and energy monitoring devices can provide real-time data on your appliance usage. This can offer valuable insights into the energy consumption of specific devices and help you identify areas for improvement.
Saving Electricity and Reducing Costs
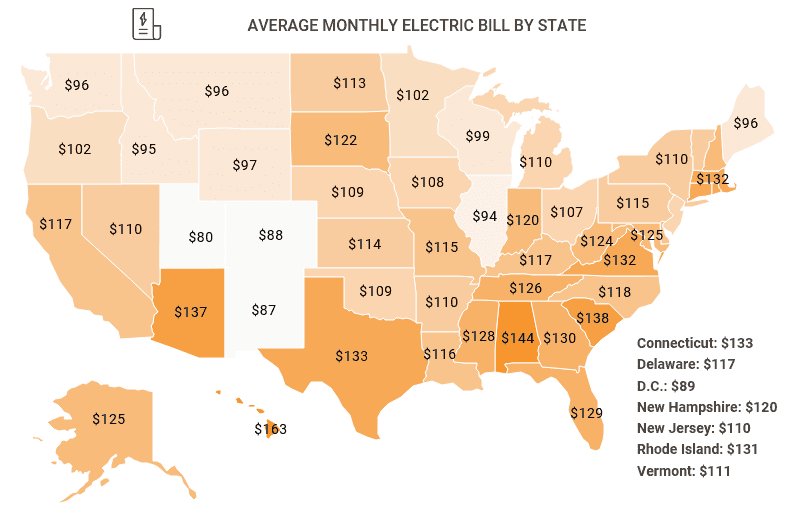
Reducing your electricity consumption in Germany is not only good for the environment but also for your wallet. By adopting energy-saving habits and making informed choices, you can significantly lower your monthly electricity bill.
Energy-Saving Tips for Households
There are many simple yet effective ways to save energy in your home. Implementing these tips can lead to substantial reductions in your electricity consumption:
- Turn off lights when leaving a room: This might seem obvious, but it’s a simple and effective way to reduce your electricity usage. Make sure to use timers or motion sensors for outdoor lights to avoid leaving them on unnecessarily.
- Unplug devices when not in use: Many electronic devices continue to draw power even when turned off, known as “phantom load.” Unplugging chargers, TVs, and other appliances when not in use can help reduce this energy waste.
- Wash clothes in cold water and air-dry them: Washing clothes in cold water instead of hot water can save a significant amount of energy. Air-drying clothes instead of using a dryer is another effective way to reduce your electricity consumption.
- Take shorter showers: Showers account for a significant portion of household water and energy consumption. Taking shorter showers can help reduce your electricity bill and conserve water.
- Insulate your home properly: Proper insulation can help prevent heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling. This can lead to substantial savings on your electricity bill.
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Choosing energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce your electricity consumption. Look for appliances with the Energy Star label, which indicates they meet certain energy efficiency standards.
- Optimize your refrigerator and freezer: Keep your refrigerator and freezer at the recommended temperature and ensure they are properly sealed. Avoid opening the doors frequently and defrost them regularly to prevent energy waste.
- Use natural light: Utilize natural light during the day to reduce your reliance on artificial lighting. Open blinds and curtains to allow sunlight to enter your home.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Appliances and Light Bulbs
Investing in energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs can be a wise decision for both the environment and your wallet. Here are some key benefits:
- Lower electricity bills: Energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs consume less electricity, leading to lower energy bills. This can result in significant cost savings over time.
- Reduced carbon footprint: By using less electricity, you contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, helping to protect the environment.
- Longer lifespan: Energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs often have a longer lifespan than their traditional counterparts, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Improved performance: Some energy-efficient appliances offer improved performance features, such as faster cooking times or quieter operation.
Government Subsidies and Programs for Energy Efficiency Upgrades
The German government offers various subsidies and programs to encourage energy efficiency upgrades in households. These programs can help you finance the purchase of energy-efficient appliances, insulation materials, and other energy-saving measures.
- BAFA (Federal Office of Economics and Export Control): BAFA provides subsidies for various energy efficiency measures, including the installation of solar panels, heat pumps, and energy-efficient windows.
- KFW (KfW Bankengruppe): KFW offers low-interest loans and grants for energy efficiency upgrades, such as insulation, renewable energy systems, and energy-efficient heating systems.
- Energy Saving Program (Energie-Spar-Programm): This program provides financial support for various energy efficiency measures, including insulation, ventilation, and renewable energy systems.
Comparing Electricity Providers and Tariffs
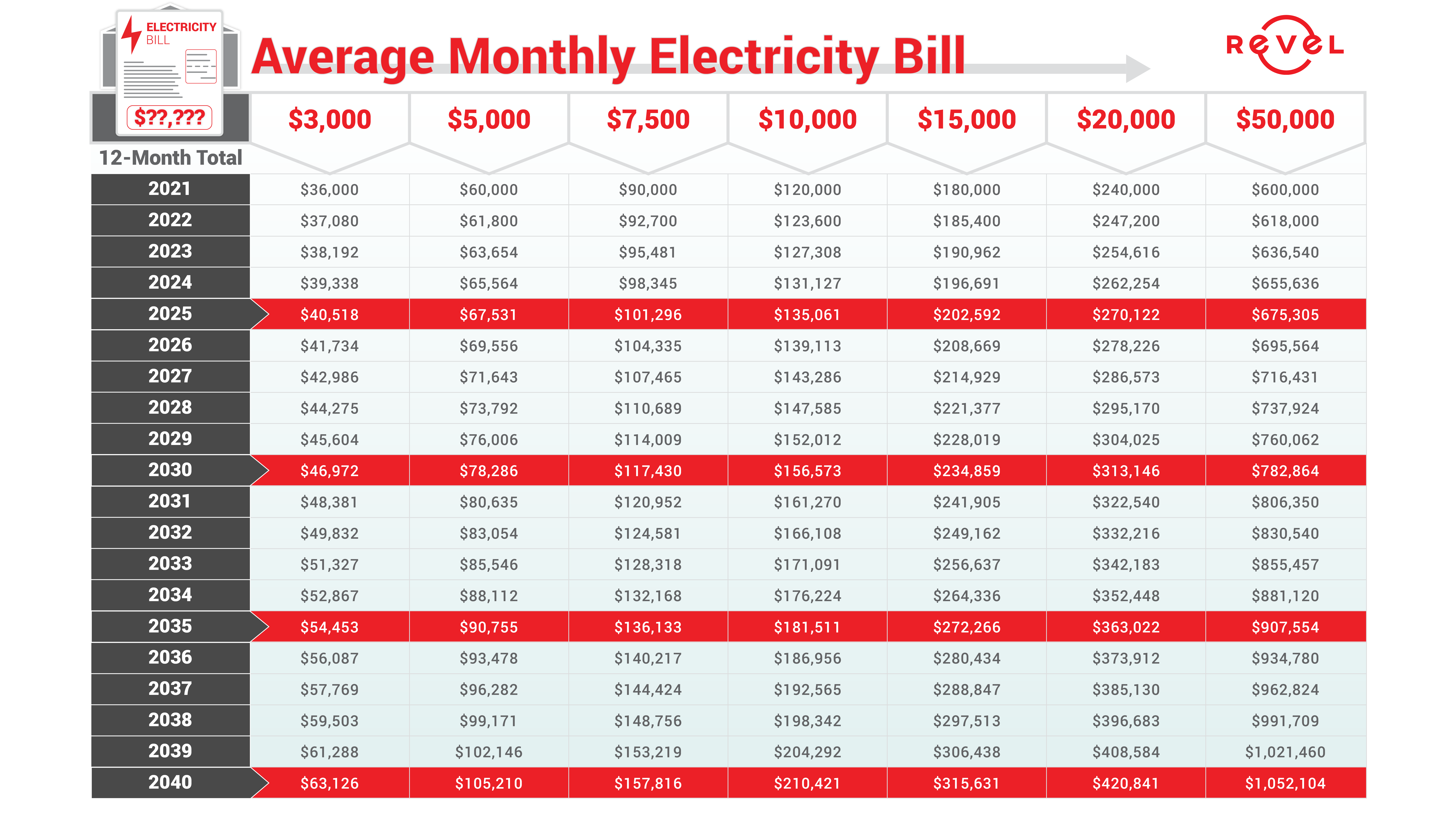
Finding the most cost-effective electricity provider in Germany can be a daunting task, given the numerous options available. To make an informed decision, comparing the prices and features of different providers is crucial. This involves understanding the different tariff types, their pros and cons, and the process of switching providers.
Comparing Electricity Providers and Tariffs
A comparison table can help you quickly assess the different options available in the German electricity market. Here’s an example, though specific prices and features may vary:| Provider | Tariff Type | Price per kWh (incl. VAT) | Contract Duration | Other Features ||—|—|—|—|—|| Anbieter A | Fixed | 0.30 € | 12 months | Green energy, 100% renewable || Anbieter B | Variable | 0.28 € | 12 months | Discount for online payment || Anbieter C | Fixed | 0.32 € | 24 months | Free electricity meter, 100% regional energy |It’s important to note that this is just a sample table and actual prices and features may differ depending on the provider and your specific energy consumption.
It’s always recommended to compare offers from multiple providers and use online comparison tools to find the best deal for your needs.
Fixed and Variable Electricity Tariffs
Fixed and variable tariffs are the two main types of electricity tariffs available in Germany. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages:
Fixed Tariffs
- Pros:
- Provides price stability and predictability, protecting you from rising energy prices.
- Offers peace of mind by knowing your electricity costs for the duration of the contract.
- Cons:
- May be more expensive than variable tariffs, especially if energy prices fall.
- May not reflect actual energy consumption, leading to overpayment if your usage is lower than expected.
Variable Tariffs
- Pros:
- Typically cheaper than fixed tariffs, especially if energy prices are low.
- Can benefit from falling energy prices, leading to lower electricity bills.
- Cons:
- Price fluctuations can make it difficult to budget for electricity costs.
- May become more expensive if energy prices rise significantly.
The choice between a fixed or variable tariff depends on your individual circumstances and risk tolerance. If you value price stability and predictability, a fixed tariff may be a better option. However, if you are willing to accept some price fluctuations and potentially benefit from lower prices, a variable tariff might be more suitable.
Switching Electricity Providers
Switching electricity providers in Germany is a relatively straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Compare offers: Use online comparison tools or contact multiple providers directly to compare prices, tariffs, and features.
- Choose a provider: Select the provider that best suits your needs and budget.
- Terminate your existing contract: Contact your current provider and inform them of your decision to switch. You’ll need to provide your contract details and the date you wish to terminate the contract.
- Sign a new contract: Once you’ve chosen a new provider, sign the contract and provide them with the necessary information, including your meter reading and bank details.
- Wait for the switch: The new provider will take care of the necessary administrative procedures and ensure a smooth transition. The switch usually takes a few weeks to complete.
Switching electricity providers can save you money and potentially access better services. It’s a good idea to review your options regularly and consider switching if you find a better deal.
Renewable Energy and its Impact on Costs
Germany has been a pioneer in the transition to renewable energy sources, significantly reducing its reliance on fossil fuels. This shift has had a notable impact on electricity costs, influencing both the price of electricity and the overall cost of living for German citizens.
Costs of Renewable vs. Non-Renewable Energy
The cost of electricity generated from renewable sources has been steadily decreasing in recent years. This decline is primarily attributed to technological advancements and economies of scale in the renewable energy sector. In contrast, the cost of electricity generated from non-renewable sources, such as coal and natural gas, has been more volatile, influenced by factors like global fuel prices and environmental regulations.
- Solar Power: The cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) technology has plummeted over the past decade, making it one of the most cost-effective renewable energy sources. In 2022, the average cost of electricity generated from solar PV in Germany was estimated to be around €0.05 per kilowatt-hour (kWh), significantly lower than the cost of electricity from fossil fuels.
- Wind Power: Onshore wind energy has also become increasingly cost-competitive, with the average cost of electricity generated from wind turbines in Germany estimated to be around €0.04 per kWh in 2022. The cost of offshore wind energy is higher, but it is still expected to become more affordable in the future.
- Fossil Fuels: The cost of electricity generated from fossil fuels varies depending on the specific fuel source and the prevailing market conditions. In 2022, the average cost of electricity generated from coal in Germany was estimated to be around €0.08 per kWh, while the cost of electricity generated from natural gas was around €0.10 per kWh.
Future Impact of Renewable Energy on Electricity Prices
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources is expected to have a significant impact on electricity prices in the future. While the cost of renewable energy is already competitive with fossil fuels in many cases, further technological advancements and economies of scale are expected to drive down the cost of renewable energy even further. This could lead to a decrease in overall electricity prices, benefiting consumers and businesses alike.
“The transition to renewable energy is a key driver of sustainable economic growth and job creation. It also offers the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.”
German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action
So, there you have it! Armed with this knowledge, you can navigate the world of electricity costs with confidence. Remember, every watt counts, and even small changes in your energy habits can make a big difference. Embrace energy efficiency, explore renewable options, and say goodbye to those sky-high electricity bills! It’s time to take control of your energy destiny and become a master of your monthly electricity costs.
Essential FAQs
What are the most common ways to save money on my electricity bill?
There are many ways to save money on your electricity bill. Start by using energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs, turning off lights when you leave a room, and unplugging devices when not in use. Consider taking advantage of government subsidies for energy efficiency upgrades, and look into renewable energy options for your home.
Can I switch electricity providers to get a better deal?
Absolutely! Switching electricity providers is a great way to find a better deal. Compare prices and features from different providers to find the best fit for your needs. Remember to consider the type of tariff, whether fixed or variable, and any additional services offered.






