Was verbraucht am meisten Strom? This question delves into the heart of Germany’s energy landscape, exploring the sectors and activities that consume the most electricity. Understanding these consumption patterns is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike, as it provides insights into the country’s energy dependence, environmental impact, and potential for sustainability.
Germany, a nation renowned for its technological advancements and industrial prowess, faces the challenge of balancing economic growth with responsible energy use. The country’s energy consumption profile is shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including population growth, industrial activity, climate, and technological innovation. This analysis examines the major energy consumers in Germany, the factors influencing their consumption, and the ongoing efforts to promote sustainable energy practices.
Understanding Energy Consumption in Germany
Germany, a powerhouse of European industry and a leader in renewable energy, faces a critical challenge in managing its energy consumption. The question of “was verbraucht am meisten strom” (what consumes the most electricity) is central to this challenge, as understanding energy consumption patterns is crucial for developing sustainable and efficient energy policies.
Overall Energy Consumption in Germany
Germany’s energy consumption is significant, reflecting its robust industrial base and developed economy. The country’s total energy consumption in 2022 was approximately 1,200 terawatt-hours (TWh), according to the Federal Statistical Office of Germany. This energy consumption is primarily driven by the following sectors:
- Industry: Industry remains a major consumer of energy, accounting for about 30% of Germany’s total energy consumption. Manufacturing, chemical production, and metal processing are particularly energy-intensive.
- Households: Residential buildings contribute significantly to energy consumption, accounting for around 25% of the total. Heating, hot water, and electricity for appliances are the main energy uses in households.
- Transportation: The transportation sector, including road transport, air travel, and rail, accounts for approximately 20% of Germany’s energy consumption. Germany is heavily reliant on road transport, leading to a significant share of energy consumption from gasoline and diesel fuels.
- Other Sectors: Other sectors, including agriculture, services, and public administration, account for the remaining portion of energy consumption. These sectors consume energy for a variety of purposes, including heating, lighting, and powering equipment.
Major Energy Consumers in Germany
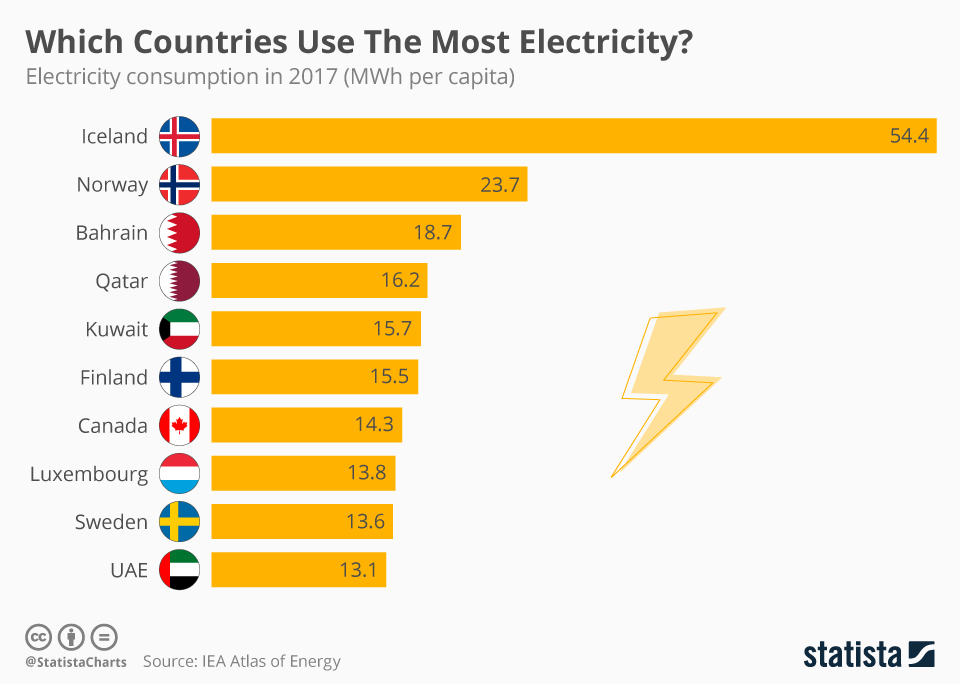
Germany, a powerhouse of industry and innovation, relies heavily on energy to fuel its economy. Understanding the major energy consumers within the country is crucial for developing sustainable energy policies and achieving energy independence.
Energy Consumption by Sector
The energy consumption in Germany is divided into various sectors, each playing a significant role in the country’s overall energy demand. The industrial sector, with its vast manufacturing activities, consumes the largest share of energy, followed by the residential sector, which includes homes and apartments. The commercial sector, encompassing businesses and services, also contributes significantly to the energy consumption landscape.
- Industrial Sector: This sector is the biggest energy consumer in Germany, accounting for approximately 38% of the total energy consumption. The industrial sector comprises various industries, including manufacturing, mining, and construction.
- Manufacturing: Industries like automotive, chemical, and metal production are energy-intensive, relying heavily on electricity and heat for their operations.
- Mining: Extracting raw materials, such as coal and natural gas, requires substantial energy for processing and transportation.
- Construction: Building and infrastructure projects consume energy for equipment, materials, and heating or cooling.
- Residential Sector: The residential sector, encompassing homes and apartments, consumes approximately 25% of Germany’s total energy.
- Heating: Heating homes during the colder months accounts for a large portion of residential energy consumption, with natural gas and district heating being primary sources.
- Hot Water: Heating water for showers, cooking, and cleaning also contributes significantly to energy use.
- Electricity: Appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and lighting consume a considerable amount of electricity.
- Commercial Sector: The commercial sector, encompassing businesses and services, accounts for approximately 20% of Germany’s total energy consumption.
- Office Buildings: Heating, cooling, and lighting office spaces are major energy consumers.
- Retail Stores: Refrigeration, lighting, and heating systems in supermarkets and department stores contribute to energy consumption.
- Hospitality: Hotels and restaurants require significant energy for heating, cooling, and cooking.
Transportation Energy Consumption
Transportation plays a vital role in Germany’s energy consumption, accounting for approximately 27% of the total energy demand.
- Road Transportation: Cars, trucks, and buses are the primary mode of transportation in Germany, relying heavily on gasoline and diesel fuel.
- Air Transportation: Air travel contributes significantly to energy consumption, with airplanes relying on jet fuel.
- Rail Transportation: Trains are a relatively energy-efficient mode of transportation, relying primarily on electricity.
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption: Was Verbraucht Am Meisten Strom
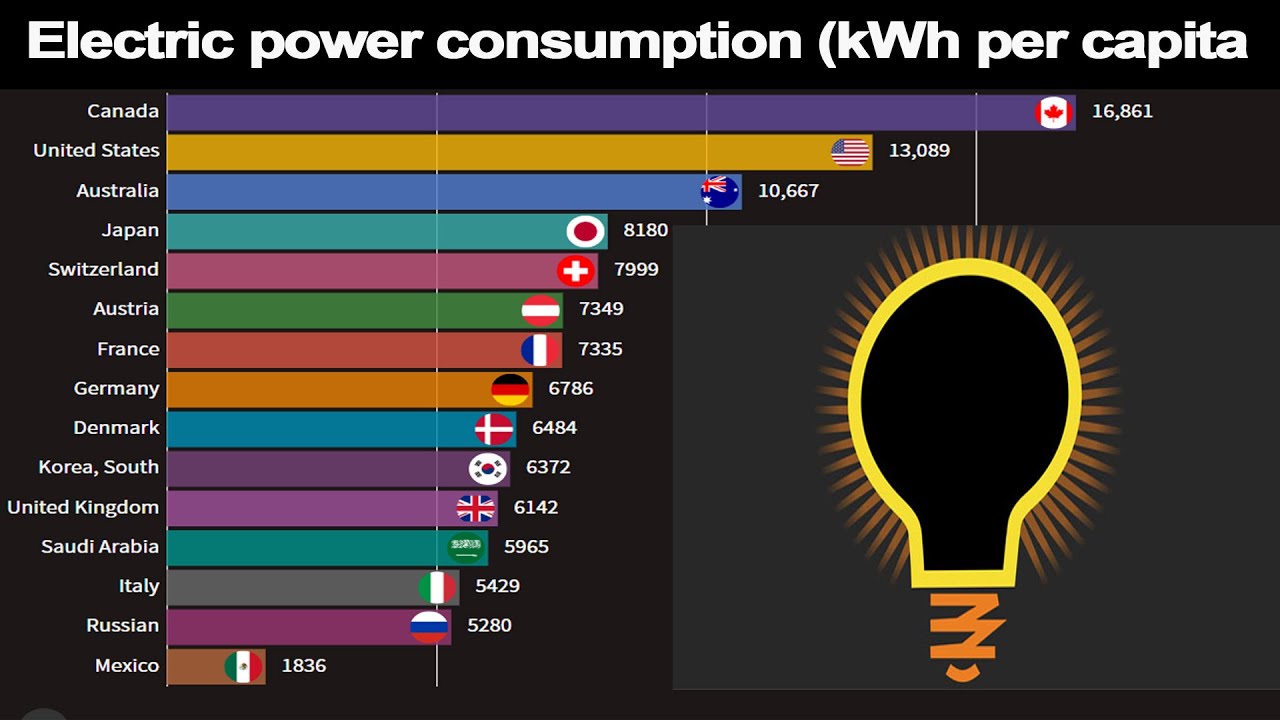
Energy consumption in Germany is a complex interplay of various factors, each contributing to the overall energy demand. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective energy policies and promoting sustainable practices.
Population Growth and Economic Activity
Population growth and economic activity exert significant influence on energy demand. As the population expands, so does the need for housing, transportation, and other services, all of which consume energy. Economic growth, particularly in industrial sectors, leads to increased production, requiring more energy for manufacturing and operations.
“Germany’s population is projected to decline slightly in the coming decades, but the country’s economic activity is expected to remain robust, potentially leading to increased energy demand.”
Climate and Weather Patterns
Climate and weather patterns play a crucial role in energy consumption. Cold winters, for instance, drive up demand for heating, while hot summers increase the need for air conditioning. Germany’s temperate climate generally results in moderate energy consumption for heating and cooling, but extreme weather events, such as heatwaves or cold snaps, can significantly impact energy demand.
“The increasing frequency and intensity of heatwaves in recent years have led to a surge in energy consumption for cooling in Germany.”
Technological Advancements and Energy Efficiency Measures
Technological advancements and energy efficiency measures can significantly impact energy consumption. The development of energy-efficient appliances, lighting, and building materials reduces energy demand. Similarly, advancements in renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, provide alternative energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
“Germany has been a leader in promoting energy efficiency measures and renewable energy technologies, resulting in a decline in energy consumption per unit of GDP.”
Energy Sources and Consumption
Germany’s energy consumption story is a tale of transformation, with a focus on transitioning away from fossil fuels towards a cleaner energy future. This section dives into the primary energy sources fueling Germany’s economy and explores how consumption patterns have evolved over time.
Energy Sources in Germany
Germany relies on a diverse mix of energy sources to meet its energy demands.
- Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels, including coal, natural gas, and oil, have historically played a significant role in Germany’s energy mix. While their dominance has decreased in recent years, they still contribute considerably to the country’s energy supply.
- Renewable Energy: Germany has made substantial progress in developing renewable energy sources, particularly wind and solar power. These sources are becoming increasingly important in meeting the country’s energy needs, contributing significantly to its goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Nuclear Power: Nuclear power has been a significant contributor to Germany’s energy supply for decades. However, the country has made a policy decision to phase out nuclear power by 2022, leading to a gradual reduction in its reliance on this source.
Energy Consumption Trends
Germany’s energy consumption patterns have undergone significant changes over time, reflecting the country’s efforts to shift towards a more sustainable energy mix.
- Declining Fossil Fuel Consumption: Germany’s consumption of fossil fuels has been steadily declining in recent years, driven by policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting renewable energy sources. The country’s commitment to phasing out coal power is a prime example of this trend.
- Growing Renewable Energy Consumption: The share of renewable energy in Germany’s energy mix has been steadily increasing. The country has witnessed a remarkable growth in wind and solar power installations, leading to a significant increase in renewable energy consumption. This trend is expected to continue as Germany strives to achieve its ambitious renewable energy targets.
- Nuclear Power Phase-Out: Germany’s decision to phase out nuclear power by 2022 has led to a gradual reduction in nuclear power consumption. This decision has been driven by concerns about nuclear safety and waste disposal, as well as a desire to transition to a more sustainable energy system.
Impact of Energy Policy and Regulations, Was verbraucht am meisten strom
Energy policy and regulations play a crucial role in shaping Germany’s energy consumption patterns.
- Renewable Energy Targets: Germany has set ambitious renewable energy targets, aiming to achieve a significant share of renewable energy in its energy mix. These targets have spurred investments in renewable energy technologies and infrastructure, driving the growth of renewable energy consumption.
- Carbon Pricing: Germany has implemented carbon pricing mechanisms, such as the Emissions Trading System (ETS), to incentivize businesses to reduce their carbon emissions. This has led to a decrease in fossil fuel consumption and a shift towards cleaner energy sources.
- Energy Efficiency Measures: Germany has implemented various energy efficiency measures to reduce energy consumption in buildings, industry, and transportation. These measures have contributed to a decline in overall energy consumption and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Sustainable Energy Practices in Germany
Germany is a global leader in sustainable energy, demonstrating a strong commitment to transitioning towards a greener future. The country has implemented a wide range of policies and initiatives to promote energy efficiency and renewable energy adoption, making significant progress in reducing its carbon footprint.
Initiatives and Policies
Germany’s commitment to sustainable energy is evident in its ambitious policies and initiatives. The country’s “Energiewende” (energy transition) program, launched in 2000, aims to phase out nuclear power and significantly increase the share of renewable energy in its energy mix.
- The Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), enacted in 2000, provides financial incentives for renewable energy producers, leading to a rapid increase in solar, wind, and biomass power generation.
- The German government has set ambitious targets for renewable energy, aiming to achieve 65% of electricity from renewable sources by 2030 and 100% by 2045.
- Energy efficiency measures are also a key component of the Energiewende, with programs to improve building insulation, promote energy-efficient appliances, and encourage sustainable transportation options.
Examples of Successful Energy Conservation Programs and Technologies
Germany has a rich history of successful energy conservation programs and technologies.
- The “KfW-Effizienzhaus” program provides financial incentives for homeowners to renovate their homes to improve energy efficiency, leading to significant reductions in energy consumption.
- Germany is a pioneer in the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies, particularly in solar and wind power. The country has a vast network of wind farms and solar installations, contributing significantly to its renewable energy production.
- Smart grids, which use advanced technology to optimize energy distribution and consumption, are being implemented in Germany to enhance energy efficiency and integrate renewable energy sources into the grid.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its progress, Germany faces challenges in achieving its sustainable energy goals.
- The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, poses challenges for grid stability and requires advanced energy storage solutions.
- Balancing the economic and environmental costs of energy transition is another challenge, as the transition requires significant investments and may impact certain industries.
- Public acceptance and support for renewable energy projects, particularly large-scale wind farms, can be a challenge in some regions.
Germany’s sustainable energy journey presents significant opportunities for innovation and economic growth.
- The country’s strong commitment to renewable energy has fostered a vibrant green technology industry, creating jobs and driving economic growth.
- Germany’s experience and expertise in sustainable energy can serve as a model for other countries seeking to transition towards a greener future.
- Continued investment in research and development of renewable energy technologies and energy storage solutions will be crucial for achieving Germany’s sustainable energy goals.
Germany’s journey towards a more sustainable energy future is marked by both progress and challenges. The country has made significant strides in promoting renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures. However, continued efforts are needed to reduce dependence on fossil fuels, address the complexities of energy storage and grid integration, and ensure equitable access to affordable energy for all citizens.
By understanding the dynamics of energy consumption and embracing innovative solutions, Germany can pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable energy future.
FAQ Explained
What are the main energy sources used in Germany?
Germany relies on a mix of energy sources, including fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil), renewable energy (wind, solar, biomass), and nuclear power. The specific mix has evolved over time, with a growing emphasis on renewables.
How does Germany compare to other countries in terms of energy consumption per capita?
Germany’s energy consumption per capita is relatively high compared to some other developed countries. However, it has been steadily decreasing in recent years due to energy efficiency measures and the shift towards renewable energy.
What are the major challenges facing Germany’s energy transition?
Challenges include ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply as nuclear power plants are phased out, managing the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources into the grid, and addressing the cost of transitioning to a low-carbon economy.





