Was ist eigentlich strom grundschule – Was Ist Eigentlich Strom? sets the stage for a journey into the world of electricity, exploring its fundamental nature and its vital role in our lives. This guide, designed for young learners, unravels the mysteries of electricity, making it understandable and engaging.
Imagine electricity as a river of tiny, invisible particles called electrons, flowing through wires. Just like a river carries water, these electrons carry energy that powers our homes, schools, and everything in between. From the light bulb in your room to the phone in your hand, electricity is the unseen force that makes our modern world possible.
What is Electricity?
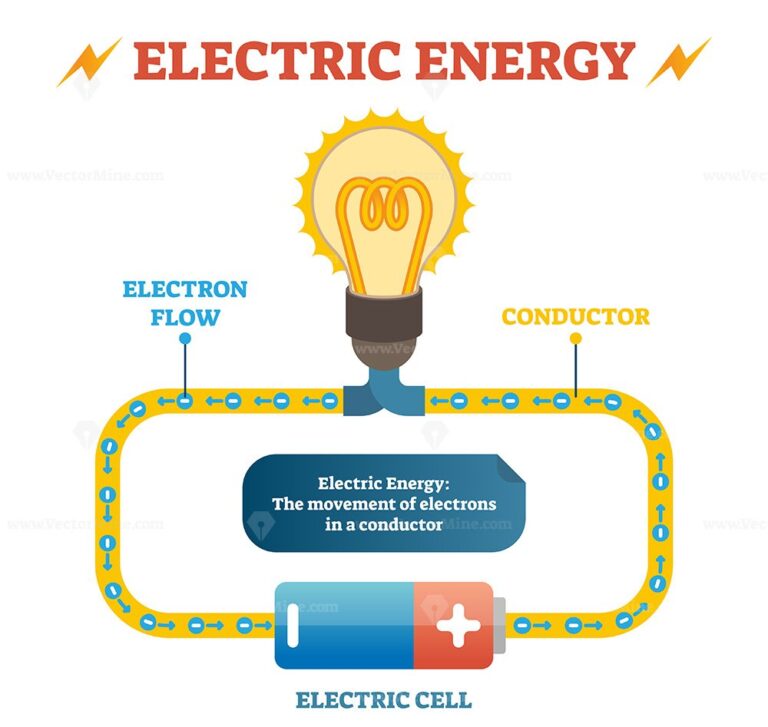
Electricity is a powerful force that we use every day, but what exactly is it? Imagine a tiny, invisible particle called an electron. These electrons are constantly moving around in everything, but they can also move from one place to another in a special way, creating what we call electricity.
How Electricity Flows
Think of electricity like water flowing through a pipe. The electrons are like the water molecules, and the wires are like the pipes. When we turn on a light switch, we create a path for the electrons to flow from a power source, like a battery or a power plant, to the light bulb. The flow of these electrons is what makes the light bulb glow.
Uses of Electricity in Everyday Life
Electricity powers many things we use every day. Here are a few examples:
- Lighting: Light bulbs use electricity to produce light.
- Heating and Cooling: Electric heaters and air conditioners use electricity to heat or cool our homes.
- Communication: Our phones, computers, and televisions all rely on electricity to work.
- Transportation: Electric cars and trains use electricity to move.
- Cooking: Electric ovens, stoves, and microwaves use electricity to cook our food.
Sources of Electricity: Was Ist Eigentlich Strom Grundschule
Electricity is a powerful force that we use every day, from powering our homes to running our factories. But where does this electricity come from? The answer lies in the different sources of electricity, which can be broadly categorized as renewable and non-renewable sources.
Renewable Sources of Electricity
Renewable sources of electricity are those that can be replenished naturally over a relatively short period of time. They are considered sustainable because they do not deplete finite resources and have a minimal impact on the environment.
- Solar Energy: Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This technology is becoming increasingly affordable and efficient, making it a popular choice for residential and commercial applications.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity. Wind farms are often located in areas with consistent and strong winds, such as coastal regions and open plains.
- Hydropower: Hydroelectric power plants use the force of moving water to generate electricity. Dams are constructed across rivers to create reservoirs, and the water is released through turbines to generate electricity.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal power plants utilize the heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity. This heat is used to boil water, creating steam that drives turbines.
- Biomass Energy: Biomass energy is derived from organic matter, such as wood, crops, and waste. It is burned to produce heat, which is then used to generate electricity.
Non-Renewable Sources of Electricity
Non-renewable sources of electricity are those that are finite and cannot be replenished at a rate comparable to their consumption. These sources have a significant environmental impact, contributing to pollution and climate change.
- Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, are the most common sources of electricity worldwide. They are burned to generate heat, which is used to produce steam that drives turbines.
- Nuclear Energy: Nuclear power plants generate electricity through nuclear fission, a process that releases energy from the atom’s nucleus. Nuclear power is a low-carbon source of electricity, but it also poses risks related to radioactive waste and the potential for accidents.
How Power Plants Generate Electricity
Power plants, regardless of the source of energy, follow a similar process to generate electricity.
- Energy Source: The primary energy source, such as coal, natural gas, or solar energy, is used to heat water.
- Steam Production: The heated water turns into steam, which is then directed to a turbine.
- Turbine Rotation: The steam rotates the turbine, which is connected to a generator.
- Electricity Generation: The generator converts mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy.
- Transmission and Distribution: The electricity is then transmitted through power lines to distribution networks, where it is delivered to homes and businesses.
Environmental Impact of Electricity Sources
Different sources of electricity have varying environmental impacts.
- Renewable Sources: Renewable sources of electricity, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, have minimal environmental impact. They do not produce greenhouse gases or air pollution. However, some renewable sources, like hydropower, can have impacts on ecosystems and water flow.
- Non-Renewable Sources: Non-renewable sources, such as fossil fuels and nuclear energy, have significant environmental impacts. Fossil fuel combustion releases greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. Nuclear energy poses risks related to radioactive waste and the potential for accidents.
Electricity in the Home

Electricity is a vital part of our daily lives, powering everything from lights and appliances to computers and entertainment systems. Understanding how electricity gets to our homes and how to use it safely is essential.
The journey of electricity begins at a power plant, where energy sources like coal, natural gas, nuclear power, or renewable sources like solar and wind are used to generate electricity. This electricity is then transmitted through high-voltage power lines to substations, where the voltage is reduced to a safer level for distribution to homes and businesses. From the substations, electricity travels through underground or overhead cables to individual homes.
Components of a Household Electrical System
A household electrical system consists of various components that work together to deliver and manage electricity safely and efficiently.
The electrical system in a home typically includes the following components:
- Meter: The meter measures the amount of electricity used by a household and sends this information to the utility company.
- Main Breaker Panel: The main breaker panel contains a series of switches, or breakers, that control the flow of electricity to different parts of the house. Each breaker protects a specific circuit from overloads and short circuits.
- Wiring: Electrical wires, typically made of copper or aluminum, carry electricity throughout the house. They are installed in walls, ceilings, and floors.
- Outlets and Switches: Outlets provide points where electrical devices can be plugged in, while switches control the flow of electricity to lights and other appliances.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): GFCIs are safety devices that detect ground faults and interrupt the flow of electricity to prevent electric shocks. They are commonly found in bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas.
Electrical Safety
Electricity can be dangerous if not handled properly. It’s important to follow safety precautions to prevent electrical accidents.
Here are some important electrical safety tips:
- Never touch electrical wires or equipment with wet hands. Water conducts electricity, increasing the risk of shock.
- Avoid using damaged or frayed electrical cords. Replace them immediately.
- Unplug appliances and electronics before cleaning or repairing them.
- Never overload electrical outlets. Too many appliances plugged into one outlet can cause overheating and fire.
- Keep electrical cords away from heat sources and sharp objects.
- Use caution when working around electrical equipment. Always disconnect the power source before working on it.
- Teach children about electrical safety. Explain the dangers of electricity and how to avoid accidents.
It’s essential to be aware of the potential hazards associated with electricity and to follow safety precautions to protect yourself and your family. By understanding the components of a household electrical system and practicing safe electrical habits, you can ensure a safe and reliable electrical environment in your home.
Electricity and Magnetism

Electricity and magnetism are two fundamental forces of nature that are closely intertwined. They are not separate entities, but rather two sides of the same coin. This relationship is known as electromagnetism.
The Relationship Between Electricity and Magnetism
Electricity and magnetism are inseparable. A moving electric charge creates a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field creates an electric current. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction.
- Electric currents create magnetic fields: When electrons flow through a wire, they create a magnetic field around the wire. The strength of the magnetic field is directly proportional to the current flowing through the wire. This principle is used in electromagnets, which are temporary magnets created by passing an electric current through a coil of wire.
- Changing magnetic fields induce electric currents: When a magnetic field changes, it can induce an electric current in a nearby conductor. This principle is used in generators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Generators use rotating magnets to create a changing magnetic field, which induces an electric current in a coil of wire.
Examples of Magnetism in Electrical Devices
Magnetism plays a crucial role in many electrical devices. Here are a few examples:
- Electric motors: Electric motors use the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents to produce rotational motion. They consist of a rotating armature that is surrounded by a magnetic field. When an electric current flows through the armature, it interacts with the magnetic field, causing the armature to rotate.
- Speakers: Speakers use electromagnetism to convert electrical signals into sound waves. They consist of a coil of wire attached to a cone. When an electrical signal passes through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with a permanent magnet, causing the cone to vibrate and produce sound.
- Hard drives: Hard drives store data magnetically. They use a magnetic head to write data onto a spinning magnetic disk. The magnetic head creates a magnetic field that aligns the magnetic domains on the disk, representing data bits. When reading data, the magnetic head senses the magnetic fields on the disk and converts them into electrical signals.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses strong magnetic fields to create detailed images of the inside of the body. It works by aligning the protons in water molecules in the body. When a radio wave pulse is applied, the protons temporarily align themselves with the magnetic field, creating a signal that can be detected and used to create an image.
A Simple Experiment Demonstrating the Relationship Between Electricity and Magnetism, Was ist eigentlich strom grundschule
- Materials:
- A battery
- A coil of wire (around 100 turns)
- A compass
- Some insulated wire
- Procedure:
- Connect the ends of the coil of wire to the positive and negative terminals of the battery. This creates a circuit, allowing electricity to flow through the coil.
- Place the compass near the coil of wire. Observe the compass needle.
- When the current flows through the coil, the compass needle will deflect, indicating the presence of a magnetic field around the coil.
- Explanation:
- The electric current flowing through the coil creates a magnetic field around the coil.
- The compass needle aligns itself with the magnetic field, indicating the direction of the magnetic field.
- This experiment demonstrates that electricity and magnetism are interconnected.
The Future of Electricity
The future of electricity is intertwined with the need to transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy system. This transition necessitates a significant shift towards renewable energy sources, which are abundant and have minimal environmental impact.
Renewable Energy Sources in the Future of Electricity
Renewable energy sources are crucial for meeting the world’s growing energy demands while minimizing our reliance on fossil fuels. These sources offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy production methods.
- Solar Energy: Harnessing the sun’s energy through photovoltaic panels, solar energy is a clean and abundant source. It has become increasingly cost-effective, making it a viable option for both residential and commercial applications. For example, Germany, a leader in solar energy adoption, generated over 40% of its electricity from solar power on a sunny day in 2022.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity. Wind energy is a mature technology, and advancements in turbine design have increased efficiency and reduced costs. Denmark, for instance, generates over 50% of its electricity from wind power.
- Hydropower: Utilizing the flow of water to generate electricity, hydropower is a reliable and efficient source. Large hydroelectric dams are capable of producing significant amounts of electricity, while smaller-scale hydropower systems can be used in rural areas. China, the world’s largest producer of hydropower, relies heavily on this source for electricity generation.
- Geothermal Energy: Harnessing the heat from the Earth’s core, geothermal energy provides a consistent and reliable source of power. Geothermal power plants are typically located in areas with high geothermal activity, such as Iceland, which derives almost 100% of its electricity from geothermal sources.
- Bioenergy: Derived from organic matter, such as wood and agricultural waste, bioenergy is a renewable source that can be used to generate electricity. While bioenergy has the potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, it’s essential to ensure sustainable practices in biomass harvesting and processing.
Challenges and Opportunities of Electricity in the Future
The future of electricity presents both challenges and opportunities. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring a sustainable and reliable energy system.
- Intermittency of Renewable Energy Sources: Solar and wind energy are intermittent, meaning their availability fluctuates depending on weather conditions. Developing energy storage solutions, such as batteries and pumped hydro, is crucial for addressing this challenge.
- Grid Modernization: Integrating large-scale renewable energy sources into existing power grids requires significant upgrades and advancements in grid management technologies. Smart grids, which utilize digital technologies for real-time monitoring and control, are essential for optimizing energy flow and enhancing grid reliability.
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption through improved efficiency is critical for achieving sustainability. This can be achieved through advancements in appliance design, building insulation, and promoting energy-saving practices.
- Electrification of Transportation: The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly gaining momentum. Expanding charging infrastructure and developing advanced battery technologies are key to supporting the widespread adoption of EVs.
- Access to Electricity: Ensuring access to electricity for all populations, particularly in developing countries, is a significant challenge. Expanding rural electrification through off-grid renewable energy solutions and promoting microgrids can address this issue.
Benefits of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources offer numerous benefits, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
| Renewable Energy Source | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Solar Energy | Clean, abundant, cost-effective, low maintenance, reduces greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Wind Energy | Clean, abundant, cost-effective, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, can be located in remote areas. |
| Hydropower | Reliable, efficient, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, can provide flood control and irrigation benefits. |
| Geothermal Energy | Clean, reliable, consistent, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, can be used for heating and cooling. |
| Bioenergy | Renewable, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, can be used for heating, cooling, and electricity generation. |
Understanding electricity is like unlocking a secret code that powers our world. From the sources that generate it to the devices that use it, electricity is a fascinating subject that connects us all. By exploring its basic principles and appreciating its significance, we can become more conscious of its impact on our lives and make informed decisions about its use.
FAQs
How does electricity travel?
Electricity travels through wires like a river flowing through a channel. Electrons, the tiny particles that carry electricity, move along the wire, carrying energy from one point to another.
Why is electricity important?
Electricity is essential for modern life. It powers our homes, schools, hospitals, and industries. It allows us to use computers, phones, appliances, and many other devices that make our lives easier and more comfortable.
What are some ways to save electricity?
We can save electricity by turning off lights when we leave a room, using energy-efficient appliances, and avoiding unnecessary use of electronic devices. Small changes can make a big difference in conserving energy.





