Was ist ein Strom Wasser? This German phrase, literally translating to “What is a stream of water,” holds a deeper meaning that delves into the fascinating relationship between water and electricity. From the powerful forces of hydroelectric dams to the subtle currents that carry electrical charges, water plays a vital role in our electrical world. This exploration will unveil the various interpretations of this phrase, examining how water fuels our power grids, influences electrical safety, and even aids in water purification processes.
The phrase “Strom Wasser” is a common expression in German, often used to describe the flow of water in rivers, streams, or even the movement of water through pipes. However, the phrase takes on a more technical meaning when considering its connection to electricity. This connection is particularly evident in the realm of hydroelectric power, where the kinetic energy of moving water is harnessed to generate electricity.
This process, while seemingly simple, involves complex engineering and scientific principles that have revolutionized our energy landscape.
Understanding the Concept of “Strom Wasser”: Was Ist Ein Strom Wasser
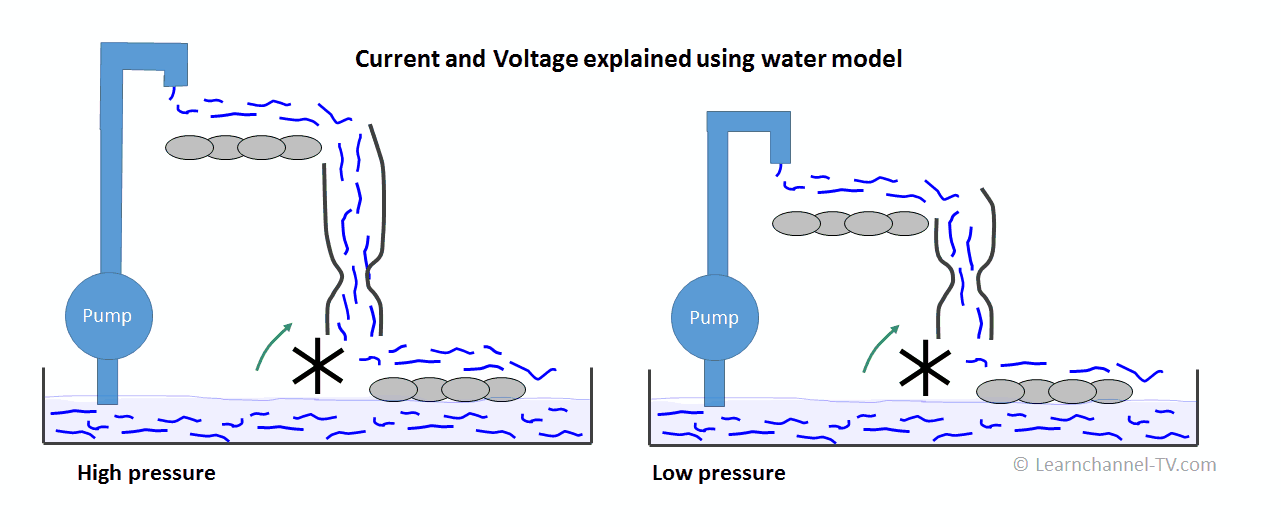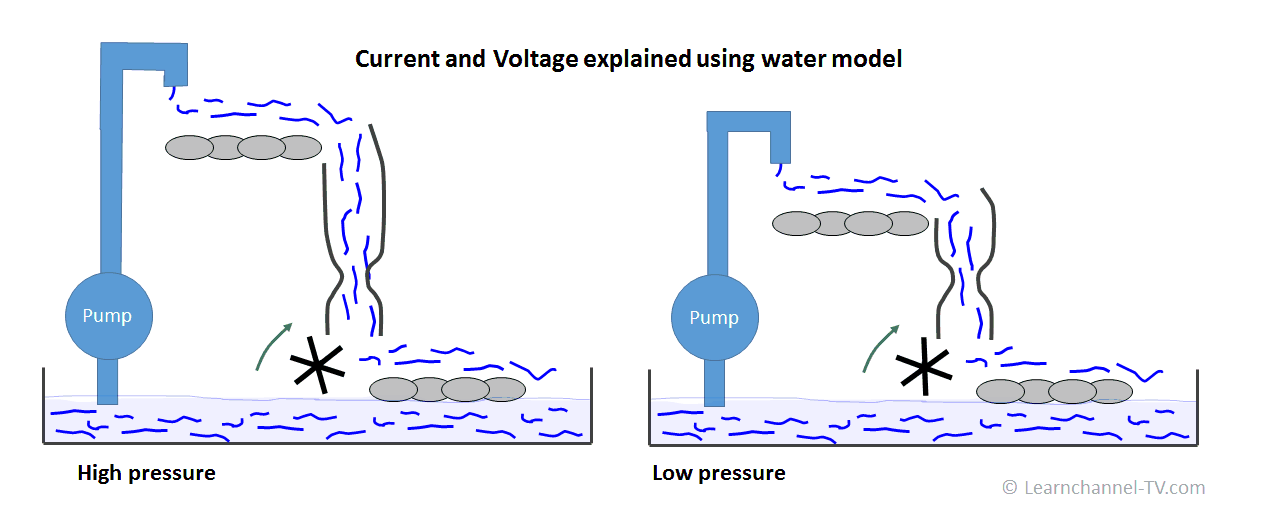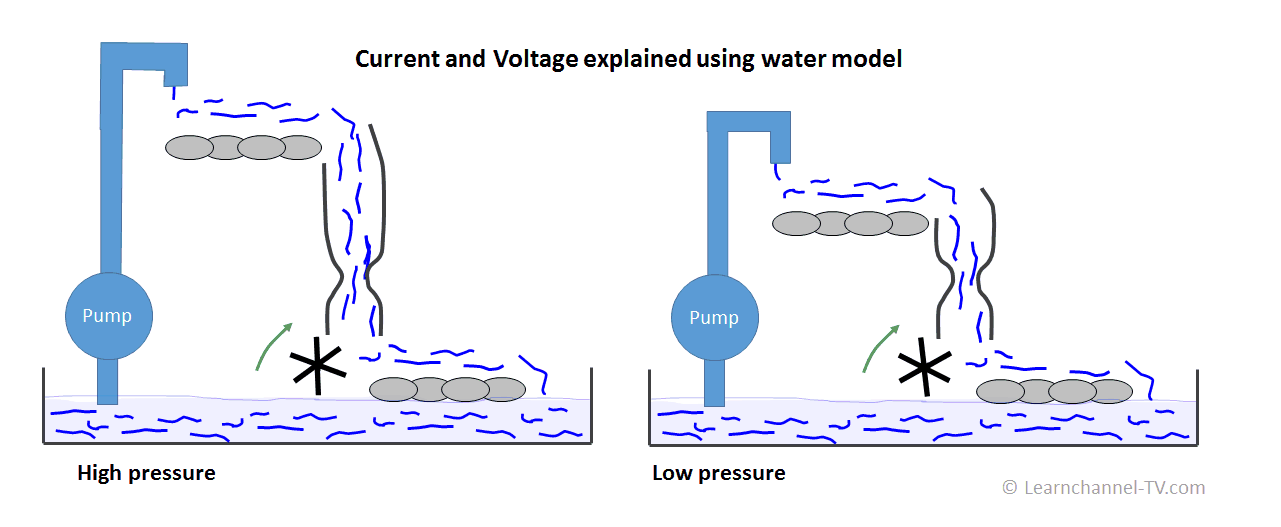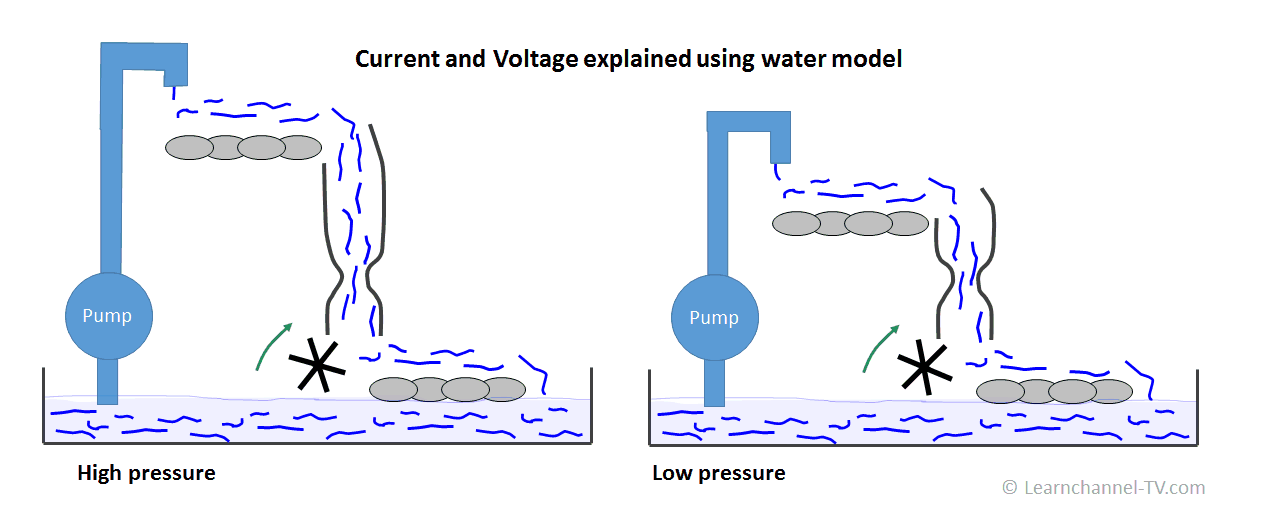
The phrase “Strom Wasser” in German literally translates to “current water.” However, its meaning goes beyond this simple translation, encompassing various interpretations depending on the context.
Interpretations of “Strom Wasser”
The phrase “Strom Wasser” can be interpreted in several ways, each conveying a different meaning:
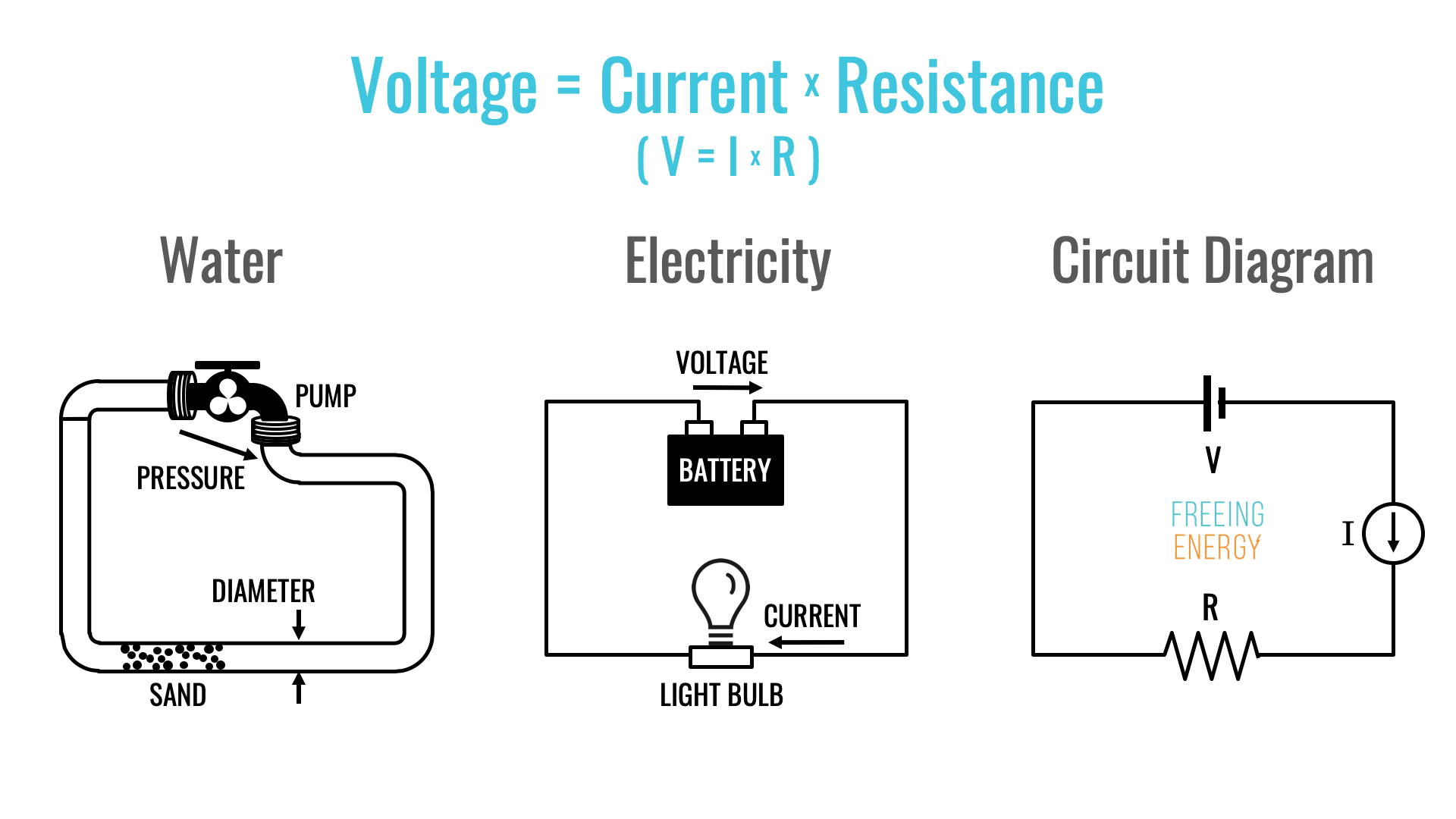
- Electric Current: In the context of electricity, “Strom Wasser” refers to the flow of electric current. This interpretation is used in technical and scientific contexts. For example, “Strom Wasser” could be used to describe the current flowing through a wire or a circuit.
- Flow of Water: In a more general sense, “Strom Wasser” can refer to the flow of water in a river, stream, or other water body. This interpretation is used in everyday language and in descriptions of natural phenomena. For instance, “Strom Wasser” could be used to describe the current in a river or the flow of water from a tap.
- Water Power: In the context of renewable energy, “Strom Wasser” can refer to hydropower, which is the generation of electricity from the flow of water. This interpretation is used in discussions about sustainable energy sources and environmental issues. For example, “Strom Wasser” could be used to describe a hydroelectric dam or a water turbine.
Examples of “Strom Wasser” in Everyday German
The phrase “Strom Wasser” is commonly used in everyday German language in various situations:
- “Der Strom Wasser ist zu schwach.” (The water current is too weak.)
-This statement could be used to describe a slow-moving river or a low water pressure in a tap. - “Die Strom Wasserkraftwerke produzieren viel Energie.” (The hydroelectric power plants produce a lot of energy.)
-This statement highlights the role of hydropower in generating electricity. - “Wir müssen den Strom Wasser schützen.” (We must protect the water current.)
-This statement emphasizes the importance of preserving water resources and the environment.
Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power, also known as hydropower, is a renewable energy source that harnesses the power of flowing water to generate electricity. It’s a crucial component of the global energy landscape, providing a significant portion of the world’s electricity.
How Hydroelectric Power Plants Work
Hydroelectric power plants utilize the potential energy of water stored at higher elevations to generate electricity. The process involves capturing the water’s kinetic energy as it flows downhill, converting it into mechanical energy, and finally transforming it into electrical energy. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Water Collection: Water is collected in a reservoir, often created by a dam. The reservoir acts as a storage facility, accumulating water over time.
- Water Flow: The water is then released from the reservoir through a system of pipes or channels called penstocks. The controlled flow of water creates pressure, driving turbines.
- Turbine Rotation: The high-pressure water strikes the blades of a turbine, causing it to rotate. This mechanical energy is the result of the water’s kinetic energy being transferred to the turbine.
- Generator Operation: The rotating turbine shaft is connected to a generator. The generator, using electromagnetic principles, converts the mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy.
- Electricity Transmission: The generated electricity is then transmitted through power lines to homes, businesses, and industries.
Types of Hydroelectric Power Plants
There are several types of hydroelectric power plants, each with its unique characteristics and applications:
- Dam Power Plants: These plants utilize large dams to create reservoirs and control the flow of water. They are typically large-scale projects, capable of generating substantial amounts of electricity. The Hoover Dam in the United States is a prime example.
- Run-of-River Power Plants: These plants are smaller in scale and do not require the construction of large dams. They utilize the natural flow of a river to generate electricity. Run-of-river plants have minimal impact on the environment, as they don’t significantly alter the river’s flow.
- Pumped Storage Hydroelectric Plants: These plants operate on the principle of storing excess electricity during periods of low demand and releasing it during peak demand. They use pumps to move water uphill to a reservoir during low demand periods. When electricity is needed, the water is released downhill through turbines, generating electricity.
Benefits of Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power offers numerous benefits, making it a valuable source of energy:
- Renewable Energy Source: Water is a renewable resource, ensuring a continuous supply for power generation. Unlike fossil fuels, it is not depleted by use.
- Clean Energy Source: Hydroelectric power plants do not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants during operation, making it a clean energy source.
- Reliable Energy Source: Hydroelectric power is generally reliable, as water flow can be controlled and predicted. This makes it a stable source of electricity, particularly in areas with consistent rainfall.
- Economic Benefits: Hydroelectric power plants create jobs during construction and operation, contributing to local economies. They also reduce dependence on fossil fuels, saving money on fuel costs.
Drawbacks of Hydroelectric Power, Was ist ein strom wasser
While hydroelectric power offers significant advantages, it also comes with certain drawbacks:
- Environmental Impact: Dam construction can disrupt ecosystems, displace wildlife, and alter water flow patterns. This can impact aquatic life and surrounding habitats.
- High Initial Investment: Hydroelectric power plants require significant upfront investment, making them expensive to build. This can be a barrier to development, especially in developing countries.
- Limited Geographic Suitability: Not all locations are suitable for hydroelectric power generation. The availability of water, topography, and environmental factors play crucial roles in determining feasibility.
The phrase “Was ist ein Strom Wasser” serves as a gateway to understanding the multifaceted relationship between water and electricity. From the colossal scale of hydroelectric dams to the microscopic level of water molecules carrying electrical charges, water plays an indispensable role in our electrical world. Understanding this connection is crucial for appreciating the importance of water in modern society, from powering our homes and businesses to ensuring the safety of our electrical systems.
As we continue to explore the potential of renewable energy sources, the relationship between water and electricity will only grow in significance, shaping our future energy landscape.
FAQ Guide
What are some examples of electrical hazards related to water?
Common electrical hazards related to water include faulty wiring in wet areas, using electrical appliances near water sources, and contact with exposed electrical wires in wet environments. It’s crucial to exercise caution and follow safety guidelines to prevent accidents.
How does electricity contribute to water purification?
Electricity plays a key role in water purification through processes like electrolysis and electrocoagulation. These methods use electrical currents to remove impurities, bacteria, and other contaminants from water, resulting in cleaner and safer drinking water.
Are there any specific safety precautions to take when working with water and electricity?
Always ensure that electrical equipment is properly insulated and grounded. Avoid using electrical appliances with wet hands or in wet environments. Never touch exposed electrical wires, especially near water. It’s also important to have a clear understanding of electrical safety guidelines and to seek professional help when necessary.






