Was ist eine mwh strom – What is MWh Strom? This question delves into the heart of how we measure and understand electricity consumption. MWh, or megawatt-hour, is a unit of energy that plays a crucial role in our daily lives, powering homes, businesses, and entire industries. It’s a fundamental concept that helps us grasp the scale of energy usage and the importance of efficient energy management.
MWh Strom is a unit of energy used to measure the amount of electricity consumed over a specific period. One MWh represents the energy consumed by a device with a power output of 1 megawatt (MW) running for one hour. For instance, a 100-watt light bulb left on for 10,000 hours would consume 1 MWh of energy. This unit of measurement is essential for understanding electricity bills, comparing energy consumption across different devices and appliances, and making informed decisions about energy efficiency.
Applications of MWh Strom
The MWh (megawatt-hour) is a fundamental unit for measuring electricity consumption, playing a crucial role in understanding energy usage across various contexts. Its application extends beyond simple metering, influencing billing practices and providing valuable insights for diverse industries.
Electricity Consumption Measurement, Was ist eine mwh strom
MWh is widely used to quantify electricity consumption in various settings, offering a comprehensive view of energy usage.
- Residential: For households, electricity consumption is often measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), with 1 MWh equaling 1,000 kWh. A typical household might consume around 500-1,000 kWh per month, translating to 6-12 MWh annually. This data helps individuals understand their energy usage patterns and potentially implement energy-saving measures.
- Commercial: Businesses, particularly those with significant energy demands, rely on MWh to track their electricity consumption. For instance, a large retail store might consume several thousand MWh per year, depending on factors like store size, operating hours, and energy-efficient practices. This information assists businesses in managing energy costs and optimizing operations.
- Industrial: Industries with high energy requirements, such as manufacturing, mining, and chemical processing, heavily utilize MWh to monitor their electricity consumption. These industries often have complex energy needs, and MWh provides a standardized unit for comparing energy usage across different processes and facilities.
Electricity Billing
MWh serves as the primary unit for billing electricity usage, ensuring fair and transparent pricing for consumers.
- Residential and Commercial Billing: Electricity companies often bill their customers based on the MWh consumed. The billing process typically involves reading the meter, calculating the total MWh used, and applying the applicable tariff rates. This approach provides a clear and quantifiable basis for electricity charges.
- Industrial Billing: For industrial consumers, electricity billing often involves more complex pricing structures, with varying rates depending on factors like time of day, demand, and energy usage patterns. MWh remains the fundamental unit for calculating electricity costs, enabling efficient cost allocation and energy management.
Industries and Sectors
MWh is a crucial unit of measurement in numerous industries and sectors, where it plays a critical role in energy management, efficiency, and cost optimization.
- Power Generation: Power plants measure their electricity output in MWh, providing insights into their energy production capabilities and efficiency. This information is essential for optimizing power generation processes and ensuring reliable energy supply.
- Renewable Energy: The renewable energy sector extensively utilizes MWh to track the energy generated from sources like solar, wind, and hydropower. This data is vital for evaluating the performance of renewable energy installations and assessing their contribution to the energy mix.
- Energy Efficiency: MWh is a key metric for evaluating energy efficiency initiatives and programs. By comparing energy consumption before and after implementing efficiency measures, organizations can quantify the benefits and track progress towards sustainability goals.
- Electric Vehicle Industry: As the electric vehicle industry grows, MWh is increasingly used to measure the energy capacity of batteries and the energy consumption of electric vehicles. This information is crucial for understanding the range, performance, and charging requirements of electric vehicles.
MWh Strom and Renewable Energy

The MWh (megawatt-hour) is a standard unit of energy measurement widely used in the electricity sector. It represents the amount of energy consumed or produced over a specific period. When discussing renewable energy sources, MWh plays a crucial role in quantifying the energy output and evaluating the performance of these sustainable technologies.
MWh Strom in Renewable Energy Production
MWh is essential for measuring the energy output of renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power. This measurement allows for a standardized comparison of different renewable energy technologies and their contributions to the overall energy mix.
- Solar Power: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, and the amount of energy generated is measured in MWh. The output depends on factors like solar irradiance, panel efficiency, and the size of the solar farm. For instance, a 1-megawatt solar farm could produce approximately 4,000 MWh of electricity annually in a sunny region.
- Wind Power: Wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity, and the energy produced is measured in MWh. The output varies based on wind speed, turbine size, and efficiency. A typical 2-megawatt wind turbine can generate around 5,000 MWh of electricity annually in a windy location.
- Hydropower: Hydroelectric dams utilize the potential energy of water stored at a higher elevation to generate electricity. The amount of energy produced is measured in MWh and depends on the water flow rate, dam height, and turbine efficiency. A large hydroelectric dam can produce millions of MWh of electricity annually.
- Geothermal Power: Geothermal power plants utilize the heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity. The energy produced is measured in MWh and depends on the geothermal resource’s temperature and flow rate. A geothermal power plant can produce a significant amount of electricity, contributing to a stable and reliable energy supply.
MWh Strom for Renewable Energy Sources vs. Fossil Fuels
The use of MWh to measure energy output differs significantly between renewable energy sources and fossil fuels. While both are measured in MWh, the underlying processes and implications differ.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Renewable energy sources are inherently sustainable and do not produce greenhouse gases or contribute to climate change. They offer a clean and reliable alternative to fossil fuels. The MWh produced from renewable sources represent a shift towards a more sustainable energy future.
- Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels, like coal, oil, and natural gas, are non-renewable resources that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. While the energy output is also measured in MWh, the environmental impact is significant. The transition to renewable energy sources, measured in MWh, signifies a move away from fossil fuels and their detrimental effects.
Energy Output of Different Renewable Energy Sources in MWh
The table below compares the energy output of various renewable energy sources in MWh, highlighting their potential contributions to a sustainable energy future.
| Renewable Energy Source | Average Annual Energy Output (MWh) |
|---|---|
| Solar Power (1 MW Farm) | 4,000 |
| Wind Power (2 MW Turbine) | 5,000 |
| Hydropower (Large Dam) | Millions |
| Geothermal Power (Typical Plant) | Thousands to Millions |
MWh Strom and Energy Efficiency
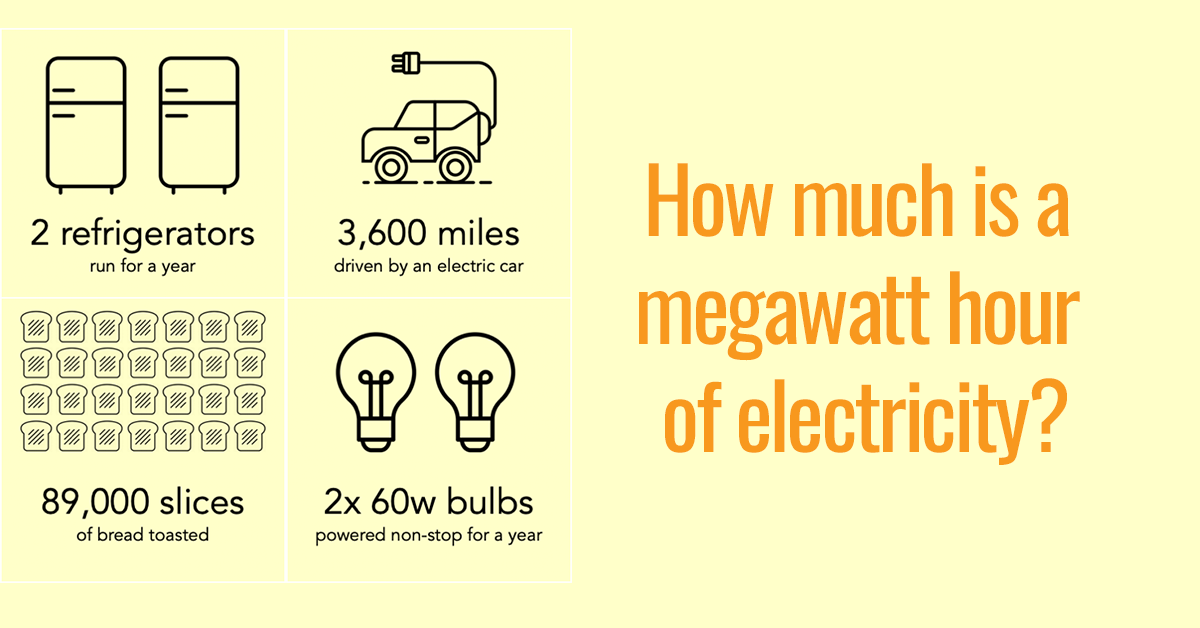
MWh Strom, a measure of electricity consumption, is closely intertwined with energy efficiency measures. By understanding the connection between MWh and energy efficiency, we can optimize energy usage and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Energy Efficiency and MWh Consumption
Energy efficiency is the process of using less energy to achieve the same level of output. When we improve energy efficiency, we reduce the amount of MWh Strom needed to power our homes, businesses, and industries. This reduction in MWh consumption has a direct impact on energy conservation, lowering our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating environmental impact.
Examples of Energy-Efficient Practices
Numerous energy-efficient practices can significantly reduce MWh consumption, contributing to energy conservation. These practices span various aspects of our lives, from home appliances to industrial processes.
- Using Energy-Efficient Appliances: Replacing older, less efficient appliances with newer, energy-star certified models can significantly reduce energy consumption. For example, a modern refrigerator can use up to 50% less energy than an older model, leading to a noticeable decrease in MWh Strom usage.
- Optimizing Building Insulation: Adequate insulation in buildings helps prevent heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, reducing the reliance on heating and cooling systems. This, in turn, lowers the overall MWh Strom consumption for temperature regulation.
- Implementing Smart Lighting Solutions: Utilizing LED lighting, which consumes significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, can dramatically reduce MWh Strom usage. Additionally, incorporating smart lighting systems that automatically adjust brightness based on occupancy and daylight levels further enhances energy efficiency.
- Adopting Renewable Energy Sources: Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power reduces reliance on fossil fuels, leading to a significant decrease in MWh Strom consumption derived from non-renewable sources. This transition not only conserves energy but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
MWh Strom and the Future of Energy

The transition to a sustainable energy system is a critical global endeavor. In this context, MWh (megawatt-hour) plays a significant role as a unit of measurement for electricity consumption and generation. Understanding the importance of MWh and its future implications is essential for navigating this energy transition effectively.
The Future Role of MWh in a Sustainable Energy System
As we move towards a more sustainable energy future, the importance of MWh as a unit of measurement will only grow. This is due to the increasing emphasis on:
- Energy Efficiency: MWh will be crucial for tracking and improving energy efficiency across various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial. By measuring energy consumption in MWh, we can identify areas for optimization and implement strategies to reduce energy waste.
- Renewable Energy Integration: MWh will be vital for managing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. By accurately measuring MWh generated from these sources, we can optimize grid stability and ensure a reliable energy supply.
- Decentralized Energy Systems: With the rise of distributed generation and microgrids, MWh will be essential for monitoring and managing energy flows within local communities. This will empower consumers to become more active participants in the energy system.
- Smart Grid Technologies: MWh will play a crucial role in the development and implementation of smart grid technologies. These technologies rely on real-time data, including MWh measurements, to optimize energy distribution, manage demand, and enhance grid resilience.
Challenges and Opportunities Related to MWh in the Future
The future of MWh in the energy sector presents both challenges and opportunities.
| Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Data Accuracy and Interoperability: Ensuring accurate and consistent MWh data across diverse energy systems is essential for effective decision-making. This requires standardized measurement protocols and interoperable data platforms. | Data Analytics and Optimization: The availability of accurate MWh data opens up new possibilities for data analytics and optimization. This can lead to improved energy efficiency, reduced costs, and better grid management. |
| Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about the significance of MWh and its role in the energy transition is crucial for engaging citizens and fostering a more sustainable energy future. | New Business Models and Innovation: The shift towards a more sustainable energy system driven by MWh measurements can foster new business models and innovation. This includes the development of new energy technologies, services, and markets. |
| Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Developing robust policy and regulatory frameworks that support the use of MWh as a key metric for energy management and sustainability is essential for guiding the energy transition. | Increased Energy Security and Resilience: By leveraging MWh data and promoting renewable energy integration, we can enhance energy security and resilience, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change. |
MWh Strom is a crucial concept in understanding energy consumption, particularly in the context of renewable energy and energy efficiency. As we transition towards a more sustainable energy future, understanding the significance of MWh and its role in measuring and managing energy consumption becomes increasingly vital. By embracing energy-efficient practices and exploring renewable energy sources, we can strive for a future where MWh Strom is used responsibly to power our world.
Question & Answer Hub: Was Ist Eine Mwh Strom
What is the difference between MWh and kWh?
MWh stands for megawatt-hour, while kWh stands for kilowatt-hour. Both are units of energy, but MWh is a larger unit equal to 1000 kWh.
How is MWh used in electricity billing?
Electricity bills typically list the amount of energy consumed in kilowatt-hours (kWh). To convert kWh to MWh, divide the kWh value by 1000.
What are some examples of industries that use MWh as a unit of measurement?
Industries that heavily rely on electricity, such as manufacturing, mining, and data centers, use MWh to track and manage their energy consumption.






