Was ist strom für kinder erklärt – ‘Was ist Strom für Kinder erklärt’
– a question that sparks curiosity in young minds. Electricity, a force that powers our world, is often a mysterious concept. Imagine a river of tiny particles called electrons flowing through invisible pathways, carrying energy to light our homes, run our appliances, and connect us to the world. This invisible force is the foundation of our modern lives, and understanding it is key to unlocking a world of possibilities.
From the simple act of flipping a light switch to the complex workings of computers and smartphones, electricity is everywhere. It’s a fundamental force that drives our society, and learning about it can be both exciting and empowering. This guide will explore the fascinating world of electricity, breaking down complex concepts into simple terms that even the youngest learners can grasp.
What is Electricity?
Imagine a tiny, invisible world where tiny particles called electrons are constantly moving around. Electricity is like a flow of these electrons through wires and other materials. It’s like a river flowing through pipes, carrying energy from one place to another.
Electricity in Everyday Life
Electricity powers many things we use every day.
- Lights: Electricity flows through wires to light bulbs, making them glow.
- Computers and Phones: Electricity powers the circuits inside these devices, allowing us to use them.
- Refrigerators: Electricity keeps our food cold by powering a motor that circulates a special liquid.
- Televisions: Electricity allows us to watch our favorite shows by powering the screen and speakers.
Sources of Electricity: Was Ist Strom Für Kinder Erklärt
Electricity is a powerful force that powers our homes, schools, and even our toys! But where does this electricity come from? There are many different ways to generate electricity, and we’ll explore some of the most common methods.
Power Plants
Power plants are large facilities that generate electricity on a large scale. They use different sources of energy to produce electricity, but the basic principle is the same: they use energy to turn a turbine, which spins a generator to produce electricity.
- Coal-fired power plants burn coal to heat water, creating steam that spins a turbine.
- Natural gas power plants burn natural gas to heat water and create steam.
- Nuclear power plants use nuclear fission to generate heat, which is then used to create steam.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources are those that are naturally replenished, such as solar, wind, and hydro power. They are becoming increasingly popular because they are sustainable and don’t produce harmful emissions.
- Solar power uses solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity. Sunlight is a clean and renewable energy source.
- Wind power uses wind turbines to capture the kinetic energy of wind and convert it into electricity. Wind is a clean and renewable energy source.
- Hydro power uses dams to generate electricity from the flow of water. Water is a clean and renewable energy source.
Size Comparison of Power Plants
Imagine a power plant as a giant machine that generates electricity. The size of a power plant depends on how much electricity it needs to produce.
Coal-fired power plants are often the largest, followed by nuclear power plants. Wind farms can be very large, but each individual turbine is smaller than a power plant. Solar farms can also be quite large, but they are made up of many individual solar panels.
How Electricity Travels
Electricity doesn’t just magically appear in our homes and businesses. It takes a journey from power plants to our outlets, and it’s a fascinating process. Imagine electricity as a river flowing through a network of pipes, carrying energy to where it’s needed.The journey begins at power plants, where electricity is generated using various sources like coal, natural gas, nuclear power, or renewable sources like solar and wind energy.
Once generated, the electricity is sent through a complex network of wires and cables, much like a highway system for electricity.
Wires and Cables: The Highways of Electricity
Electricity travels through wires, which act like pathways for the flow of electrons. These wires are made of conductive materials, typically copper or aluminum, which allow electrons to move easily through them. Wires are bundled together to form cables, which are designed to carry large amounts of electricity safely. The choice of wire type depends on the voltage and current being carried, as well as the environment where the cable is installed.
Transformers: Stepping Up and Stepping Down Voltage
Transformers play a crucial role in transmitting electricity efficiently over long distances. They are devices that change the voltage of electricity. Power plants generate electricity at high voltages, typically thousands of volts, which is necessary for efficient transmission over long distances. However, high voltages are dangerous and impractical for use in homes and businesses. Transformers “step down” the voltage to a safer level, usually around 120 volts, for household use.
Types of Wires Used in Electrical Systems
Different types of wires are used in electrical systems, each with specific properties and applications. Here’s a table comparing some common types:| Wire Type | Description | Application ||—|—|—|| Solid Wire | Single, solid conductor | General wiring, often used for smaller applications || Stranded Wire | Multiple strands of wire twisted together | More flexible than solid wire, commonly used in applications requiring movement or bending || Coaxial Cable | Consists of a central conductor surrounded by insulation, a braided shield, and an outer jacket | Used for transmitting high-frequency signals, such as cable television and internet connections || Fiber Optic Cable | Transmits data as light pulses through thin strands of glass | Used for high-speed data transmission, including internet and telecommunications |
Using Electricity Safely
Electricity is a powerful force that can be very useful, but it can also be dangerous if not handled properly. It’s important to learn how to use electricity safely to avoid accidents and injuries.
Safety Around Electrical Outlets and Appliances
Electrical outlets and appliances are common sources of electrical hazards. It’s crucial to understand the potential dangers and follow safety precautions.
- Never touch electrical outlets with wet hands. Water conducts electricity, so if your hands are wet, you could get a shock.
- Never put anything metal into an electrical outlet. Metal objects can conduct electricity, and putting them into an outlet can cause a short circuit or even a fire.
- Always unplug appliances before cleaning them. This prevents the risk of electrocution while cleaning.
- Avoid using damaged or frayed electrical cords. Damaged cords can expose live wires, increasing the risk of electric shock or fire.
- Never overload electrical outlets. Overloading an outlet can cause it to overheat and potentially start a fire.
Dangers of Touching Electrical Wires
Electrical wires carry electricity, and touching them can be extremely dangerous.
- Never touch electrical wires that are exposed or dangling. Exposed wires can carry a live electrical current, which can cause a severe shock or even death.
- Never touch a downed power line. Downed power lines are extremely dangerous, and you should stay at least 30 feet away from them.
- If you see a downed power line, call the power company immediately.
Safety Rules for Children
It’s important to teach children about electrical safety to prevent accidents. Here are some safety rules for children to follow:
- Never touch electrical outlets or appliances.
- Never put objects into electrical outlets.
- Never play with electrical cords or wires.
- Always ask an adult for help with electrical appliances.
- Never use electrical appliances in the bathtub or shower.
- Keep electrical cords away from water.
- Be careful when using electrical appliances.
Fun Facts About Electricity
Electricity is a fascinating and powerful force that plays a crucial role in our daily lives. It powers our homes, schools, and businesses, and it’s responsible for many of the technologies we rely on. But did you know that electricity can also be quite surprising and even a little bit magical? Let’s explore some fun facts about electricity.
The Speed of Electricity
Electricity travels incredibly fast. In fact, it can travel at the speed of light, which is about 186,000 miles per second! That’s fast enough to travel around the world seven times in one second. This incredible speed is why we can turn on a light switch and see the light almost instantly.
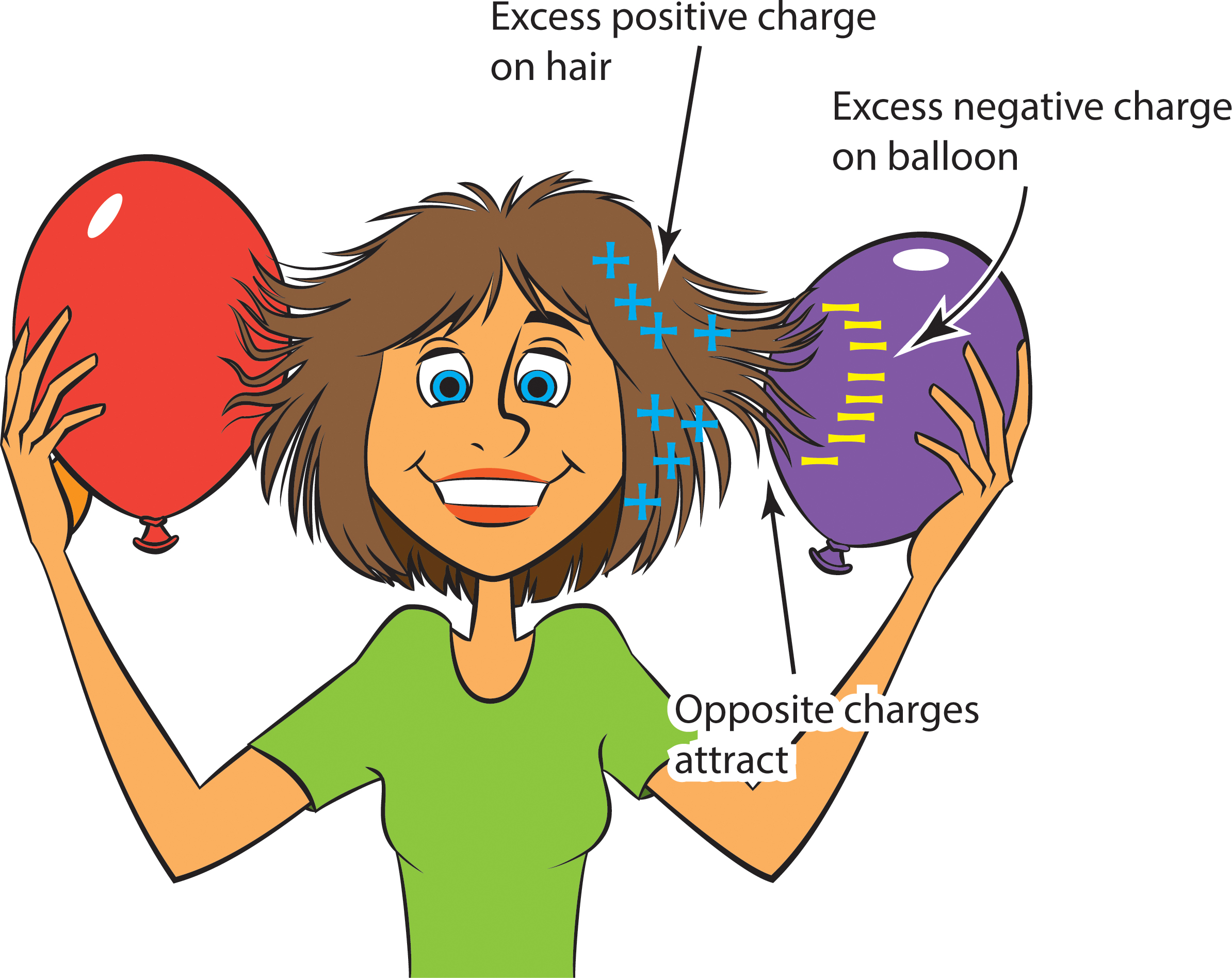
Static Electricity
Static electricity is a type of electricity that builds up on the surface of objects. You can experience static electricity when you rub a balloon on your hair and then hold it near a wall. The balloon will stick to the wall because the friction between the balloon and your hair causes a buildup of static electricity.
Static electricity is caused by an imbalance of electric charges on the surface of an object.
Here’s a simple experiment you can try to demonstrate static electricity:
- Rub a balloon on your hair. This will cause a buildup of static electricity on the balloon.
- Hold the balloon near a wall. The balloon will stick to the wall because of the static electricity.
- Touch the balloon to the wall. The static electricity will discharge, and the balloon will fall off the wall.
Electricity’s Power, Was ist strom für kinder erklärt
Electricity is a powerful force that can be used to create light, heat, and motion. It can also be used to power many other things, such as computers, phones, and appliances.
Electricity is a form of energy that can be converted into other forms of energy, such as light, heat, and motion.
Electricity is more powerful than other forms of energy, such as wind and water. This is because electricity can be easily transported and stored, making it a very versatile form of energy.For example, a single hydroelectric dam can generate enough electricity to power a large city, while a wind turbine can only generate enough electricity to power a few homes.
Understanding electricity is not just about memorizing facts; it’s about appreciating the power of this invisible force and using it safely and responsibly. By exploring its origins, its journey, and its applications, we can unlock a deeper understanding of the world around us. So, the next time you flip a light switch or charge your phone, remember the fascinating story of electricity, a force that continues to shape our lives in countless ways.
Q&A
What are some examples of how electricity is used in everyday life?
Electricity powers everything from lights and appliances in our homes to cars, trains, and even the internet.
How does electricity travel from power plants to our homes?
Electricity travels through a network of wires and cables, carried by transformers that adjust the voltage for safe use in homes and businesses.
Why is it important to be safe around electricity?
Electricity can be dangerous if not handled properly. It’s crucial to follow safety rules to prevent shocks and fires.






