Ever wondered what it cost to power your German toaster in 2019? “Was kostet 1 kWh Strom 2019” is the question on everyone’s lips, especially if they’re trying to avoid a hefty electricity bill. Let’s break down this German energy puzzle and find out what’s behind the price tag.
It’s like trying to figure out the price of a slice of cake in a bakery full of delicious possibilities! You’ve got your basic ingredients (generation, transmission, distribution), but then there’s the frosting (renewable energy) and the sprinkle of government policies. It all adds up, folks!
Understanding the Query
The phrase “was kostet 1 kwh strom 2019” is a German question that translates to “what did 1 kilowatt-hour of electricity cost in 2019?”. This query reflects a common concern for individuals and businesses alike: understanding the cost of electricity and its potential impact on their budgets.
Context of the Query
This query could stem from various scenarios and motivations. * Personal Finance: Individuals might be interested in the cost of electricity to compare energy bills, understand the financial implications of using specific appliances, or assess the potential savings from switching energy providers.
Business Operations
Businesses might be concerned about the cost of electricity as a major operating expense, particularly in energy-intensive industries. Understanding historical electricity prices can help them forecast future costs, make informed decisions about energy efficiency, and potentially negotiate better rates with energy suppliers.
Historical Analysis
Researchers or analysts might be interested in the historical cost of electricity to understand trends, identify potential factors influencing price fluctuations, and draw insights for future predictions.
Breakdown of Key Elements
Let’s break down the key elements of the query:* “was kostet” (what does it cost): This indicates a request for information about the price or cost of something.
“1 kwh” (kilowatt-hour)
This is the unit of measurement for electricity consumption. One kilowatt-hour represents the amount of energy used by a 1000-watt appliance running for one hour.
“strom” (electricity)
This refers to the energy that is generated and delivered to power our homes and businesses.
“2019” (year)
This specifies the timeframe for the query, focusing on the cost of electricity in a particular year.
Electricity Pricing in Germany
In 2019, Germany had an average electricity price of 30.5 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh). This price reflects a complex interplay of factors, including energy sources, government policies, and market dynamics.
Factors Influencing Electricity Prices
Electricity prices in Germany are influenced by a combination of factors. These include:
- Energy Sources: Germany’s reliance on renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can impact electricity prices. The intermittent nature of these sources can lead to fluctuations in supply and demand, potentially affecting pricing.
- Government Policies: Germany has implemented various policies to promote renewable energy, including subsidies and feed-in tariffs. These policies can influence electricity prices by impacting the cost of generating renewable energy.
- Market Dynamics: The electricity market in Germany is characterized by competition among various energy providers. Market dynamics, such as supply and demand, as well as the pricing strategies of energy providers, can influence electricity prices.
Comparison with Other European Countries
Germany’s electricity prices are relatively high compared to other European countries. In 2019, the average electricity price in the European Union was 21.7 cents per kWh. This difference can be attributed to several factors, including Germany’s higher reliance on renewable energy, which can be more expensive to generate, and its higher taxes on electricity.
Factors Affecting Electricity Costs: Was Kostet 1 Kwh Strom 2019
The price of electricity is influenced by various factors, including the cost of generating, transmitting, and distributing electricity. The cost of generation is the largest component of the electricity price, but transmission and distribution also play a significant role. Additionally, the type of energy source used to generate electricity can impact the price.
Impact of Renewable Energy Sources on Electricity Prices
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, have the potential to lower electricity prices in the long term. This is because these sources are generally cheaper to operate than traditional fossil fuel power plants. However, the initial investment costs for renewable energy projects can be high. This can lead to higher electricity prices in the short term, as utilities try to recoup their investment.
Components of Electricity Costs, Was kostet 1 kwh strom 2019
The cost of electricity is made up of several components, each contributing to the final price. These components can be broken down as follows:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Price |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | The cost of producing electricity from different energy sources, such as coal, natural gas, nuclear, or renewable sources. | The most significant factor in electricity pricing. Different energy sources have varying costs, with renewable sources generally having lower operating costs but potentially higher initial investment costs. |
| Transmission | The cost of transporting electricity from power plants to consumers through high-voltage power lines. | This cost is generally lower than generation but can vary depending on the distance and infrastructure required. |
| Distribution | The cost of delivering electricity to individual consumers through local networks. | This cost can vary depending on the density of the population and the length of the distribution network. |
| Regulation and Taxes | Government regulations and taxes imposed on electricity production and consumption. | These costs can vary depending on the specific regulations and taxes in place. |
| Market Factors | Factors such as supply and demand, fuel prices, and competition in the electricity market. | These factors can influence the overall price of electricity in a particular region or country. |
Electricity Consumption in Germany
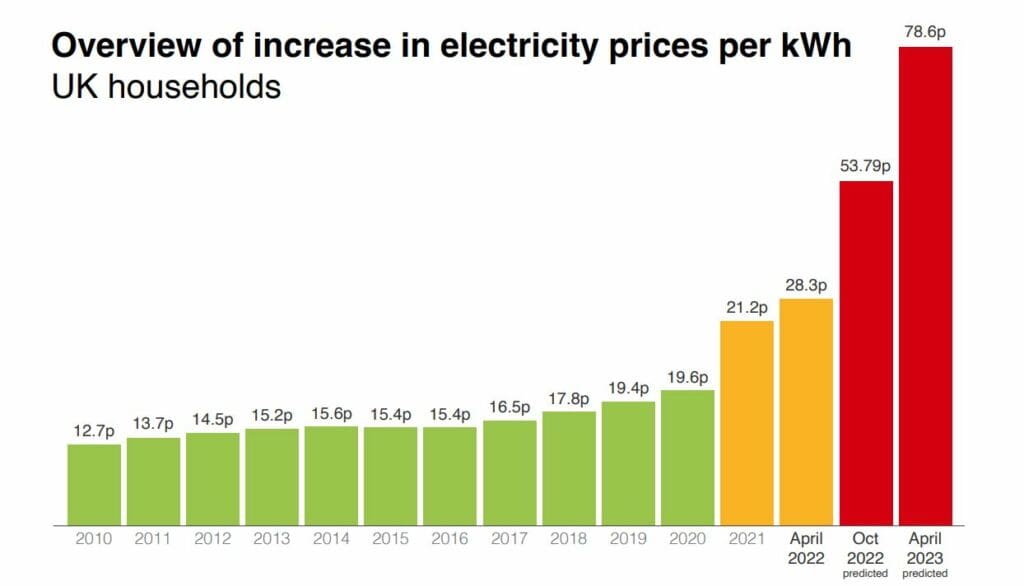
Germany is a significant consumer of electricity, with its energy consumption heavily reliant on this resource. Understanding the trends and patterns in electricity consumption is crucial for evaluating energy policies, planning future energy needs, and assessing the impact of these policies on the environment.
Electricity Consumption in Germany in 2019
Germany’s electricity consumption in 2019 was approximately 500 terawatt-hours (TWh). This represents a slight decrease from previous years, highlighting a trend of declining electricity consumption in Germany. The decrease in electricity consumption can be attributed to several factors, including increased energy efficiency measures, a shift towards renewable energy sources, and economic factors.
Trends in Electricity Consumption over Time
- Decreasing Trend: Over the past few decades, Germany has witnessed a gradual decline in electricity consumption. This trend is largely attributed to improvements in energy efficiency, technological advancements, and economic factors.
- Impact of Renewable Energy: The increasing share of renewable energy sources in Germany’s energy mix has also contributed to the decrease in electricity consumption. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are generally more efficient and less energy-intensive compared to fossil fuels.
- Economic Factors: Economic fluctuations and changes in industrial activity can also influence electricity consumption. Periods of economic growth often correspond to increased electricity demand, while recessions or slowdowns can lead to a decrease in consumption.
Visual Representation of Electricity Consumption Trends
Line Graph: A line graph depicting electricity consumption in Germany over the past few decades would clearly illustrate the decreasing trend. The graph’s x-axis would represent time (years), while the y-axis would represent electricity consumption in terawatt-hours (TWh). The line would show a gradual downward slope, indicating a consistent decrease in electricity consumption. Bar Chart: A bar chart could also effectively visualize electricity consumption trends.
Each bar would represent a specific year, and its height would correspond to the electricity consumption in that year. The bar chart would visually highlight the fluctuations in electricity consumption over time, making it easy to compare consumption levels between different years.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
In Germany, where electricity costs are a significant household expense, reducing energy consumption is crucial for both financial well-being and environmental sustainability. By adopting energy-efficient practices, individuals and businesses can significantly lower their electricity bills and contribute to a greener future.
Energy-Efficient Appliances and Technologies
Investing in energy-efficient appliances and technologies can lead to substantial cost savings over time. These appliances are designed to consume less energy while maintaining performance, leading to lower electricity bills.
- Energy-Efficient Lighting: Replacing traditional incandescent bulbs with LED or CFL bulbs can reduce energy consumption by up to 80%, leading to significant cost savings on lighting bills.
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Look for appliances with energy efficiency labels, such as the EU Energy Label, which indicates their energy consumption and efficiency. Choosing appliances with higher energy efficiency ratings can lead to significant savings on electricity bills over their lifetime.
- Smart Home Technologies: Smart thermostats, smart plugs, and other smart home technologies can help optimize energy usage and reduce electricity consumption. These devices can automate tasks like adjusting thermostats based on occupancy or scheduling appliance usage during off-peak hours, resulting in significant cost savings.
Practical Steps for Lowering Electricity Bills
Beyond investing in energy-efficient appliances, there are numerous practical steps that individuals and businesses can take to reduce their electricity consumption and lower their bills.
- Unplug Devices When Not in Use: Even when turned off, many electronic devices continue to draw power, known as “phantom load.” Unplugging devices when not in use can significantly reduce electricity consumption.
- Wash Clothes in Cold Water: Washing clothes in cold water instead of hot water can significantly reduce energy consumption, as heating water accounts for a large portion of the energy used by washing machines.
- Air-Dry Clothes: Line-drying clothes instead of using a dryer can save a considerable amount of energy.
- Use Natural Light: Maximize natural light during the day by opening curtains and blinds, reducing the need for artificial lighting.
- Insulate Your Home: Proper insulation can significantly reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling, and ultimately lowering electricity consumption.
- Seal Air Leaks: Seal any air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings to prevent drafts and reduce energy loss.
Future Trends in Electricity Pricing
Predicting future electricity prices in Germany is a complex task, influenced by a multitude of factors, including policy changes, technological advancements, and global market dynamics. However, several trends and developments are likely to shape the future of electricity pricing in the coming years.
Impact of Climate Change and Renewable Energy
The transition to a more sustainable energy system, driven by the need to combat climate change, is expected to have a significant impact on electricity prices. Germany has set ambitious targets for renewable energy generation, aiming to significantly reduce its reliance on fossil fuels. This shift towards renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is likely to influence electricity prices in several ways:
- Increased Renewable Energy Penetration: As renewable energy sources become more prevalent, they will likely displace fossil fuels in the electricity generation mix. This could lead to a decrease in wholesale electricity prices, as renewable energy sources generally have lower operating costs than traditional power plants.
- Intermittency and Storage: The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind power, presents challenges for grid stability and energy storage. To address these challenges, investments in energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro, are likely to increase. These investments may initially lead to higher electricity prices, but in the long term, they could contribute to a more reliable and affordable energy system.
- Carbon Pricing: To encourage the shift towards cleaner energy sources, the German government has implemented a carbon pricing mechanism, known as the Emissions Trading System (ETS). This system places a price on carbon dioxide emissions, making fossil fuels more expensive. As the price of carbon increases, it is expected to incentivize further investments in renewable energy, potentially leading to higher electricity prices in the short term but ultimately contributing to a lower-carbon electricity grid.
So, there you have it – the cost of electricity in Germany in 2019, demystified. While it might seem like a complex equation, remember, you’re not alone in trying to understand the energy game. With a little knowledge and some smart strategies, you can keep your lights on and your wallet happy. And who knows, maybe you’ll even discover a hidden energy-saving secret that’ll make you the envy of your neighbors!
FAQ
What’s the biggest factor influencing electricity prices in Germany?
The biggest factor is the cost of generating electricity, which is influenced by things like fuel prices, the type of power plants used, and the availability of renewable energy sources.
Is electricity cheaper in Germany than other European countries?
It depends! Germany’s prices are generally higher than some other European countries, but lower than others. It’s a fluctuating market!
Can I really save money on my electricity bill by switching to energy-efficient appliances?
Absolutely! Investing in energy-efficient appliances and technologies can significantly reduce your electricity consumption and save you money in the long run. Think of it as a wise investment in your future.






