“Was kostet 3000 kWh Strom?” This common question in Germany reflects a growing concern about energy costs. Understanding how much electricity costs is essential for managing household budgets and making informed decisions about energy consumption. This article breaks down the factors that influence electricity prices, provides a step-by-step guide for calculating your own costs, and offers practical tips for saving money on your energy bills.
Electricity prices in Germany are influenced by various factors, including energy tariffs, energy providers, and government regulations. Different tariffs, such as fixed or variable rates, can significantly impact the cost of electricity. Understanding the pricing structures of energy providers and their associated fees is crucial for making informed choices about your energy supply.
Understanding “Was kostet 3000 kWh Strom?”
The German phrase “Was kostet 3000 kWh Strom?” translates to “How much does 3000 kWh of electricity cost?” in English. This question is fundamental to understanding the cost of energy consumption, particularly in households and businesses.
Breaking Down the Components, Was kostet 3000 kwh strom
The question “Was kostet 3000 kWh Strom?” is composed of four key components:
- Was: This is the interrogative pronoun in German, meaning “what” in English. It signifies the question being asked about the cost of electricity.
- kostet: This is the verb “to cost” in the present tense, indicating the price or expense associated with the energy consumption.
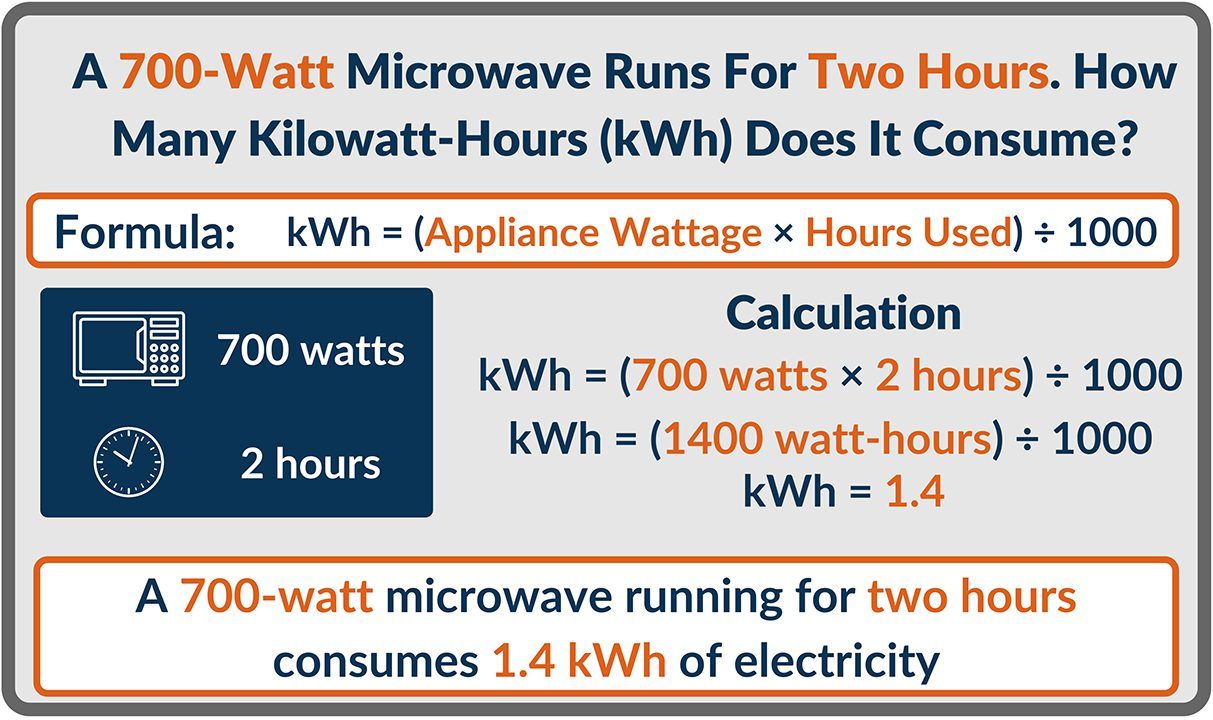
- 3000 kWh: This represents the amount of electricity being considered, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). One kilowatt-hour is the amount of energy used by a 1000-watt appliance operating for one hour.
- Strom: This is the German word for “electricity”, indicating the type of energy being discussed.
Significance of the Question
The question “Was kostet 3000 kWh Strom?” holds significant importance in understanding energy consumption and cost. It directly addresses the financial implications of using electricity, a crucial factor in budgeting and managing household or business expenses.
- Household budgeting: Understanding the cost of electricity consumption helps households plan their budgets effectively. By knowing the cost of 3000 kWh, individuals can estimate their monthly energy bills and adjust their usage accordingly.
- Business operations: For businesses, the cost of electricity is a significant operational expense. Determining the cost of 3000 kWh helps businesses understand their energy consumption patterns and identify areas for potential cost savings through energy efficiency measures.
- Energy policy and sustainability: The cost of electricity is directly linked to energy policy and sustainability initiatives. Understanding the cost of 3000 kWh provides insights into the economic implications of different energy sources and their impact on consumer costs.
Factors Influencing Electricity Costs

The cost of electricity in Germany is influenced by various factors, including energy sources, market dynamics, and government regulations. Understanding these factors is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions about their electricity consumption and to navigate the complexities of the energy market.
Electricity Tariffs and Their Associated Costs
Electricity tariffs are the pricing structures used by energy providers to charge their customers for electricity consumption. These tariffs can vary significantly based on factors such as the type of energy source used, the time of day, and the amount of electricity consumed.
- Basic Tariff: This is the most common tariff type, where customers pay a fixed price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) regardless of their consumption. This type of tariff is typically suitable for households with consistent electricity consumption patterns.
- Variable Tariff: Under this tariff, the price per kWh fluctuates based on market prices for electricity. This can be advantageous for customers who can adjust their consumption patterns to take advantage of lower prices during off-peak hours. However, it also carries the risk of higher costs during periods of high demand.
- Time-of-Use Tariff: This tariff charges different prices for electricity consumed at different times of the day. For example, electricity may be cheaper during off-peak hours (e.g., overnight) and more expensive during peak hours (e.g., midday). This tariff encourages customers to shift their energy consumption to off-peak hours, thereby reducing overall costs.
Role of Energy Providers and Their Pricing Structures
Energy providers play a crucial role in determining the cost of electricity for consumers. They source electricity from various sources, including renewable and non-renewable energy, and then sell it to consumers through different tariffs.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Energy providers using renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, often have higher upfront costs but can offer lower electricity prices in the long term due to the absence of fuel costs. For example, a solar panel installation might require a significant initial investment, but it can provide free electricity for years to come, reducing overall costs.
- Non-Renewable Energy Sources: Energy providers using non-renewable energy sources, such as coal and natural gas, face fluctuating fuel costs that can impact their electricity prices. These costs are often passed on to consumers, leading to price volatility in electricity tariffs.
- Market Competition: The competitive landscape of the energy market can also influence pricing structures. In a highly competitive market, energy providers may offer lower prices to attract customers. However, in a less competitive market, providers may have more leverage to set higher prices.
By understanding the factors that influence electricity costs, you can make informed decisions about your energy consumption and potentially save money on your bills. From exploring different tariffs to implementing energy-saving strategies, there are various ways to manage your energy usage and optimize your household budget. By embracing a proactive approach to energy consumption, you can contribute to a more sustainable future while ensuring affordable energy for your home.
Clarifying Questions: Was Kostet 3000 Kwh Strom
What is the average electricity cost in Germany?
The average electricity cost in Germany varies depending on factors like location, energy provider, and consumption level. However, it’s generally around 30-35 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh).
How can I find out my electricity tariff?
You can find your current electricity tariff on your energy bill or by contacting your energy provider directly.
What are some common energy-saving tips?
Common tips include using energy-efficient appliances, reducing your heating and cooling needs, and switching off lights when you leave a room.
What are the benefits of renewable energy sources?
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are environmentally friendly, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and can help lower electricity costs in the long run.






